
Cover
(10MB)
Summary: this page describes software and procedures for producing paper maps from OSM data.
download & index

Cover |
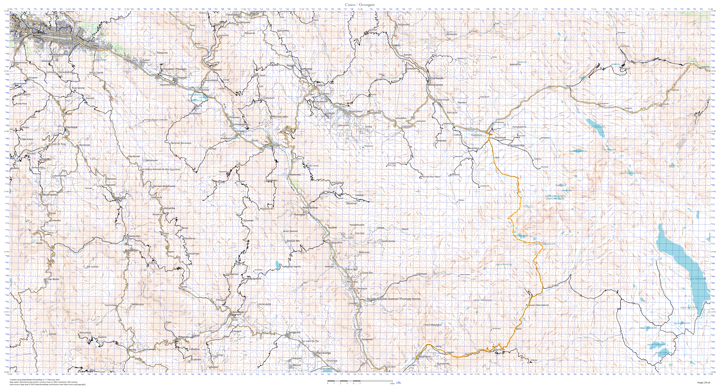
Click to see the full map (56MB) |
MyOSMatic is a front end to OCitysMap, which generates an initial map using Mapnik, which in turn pulls data from OSM and the SRTM altitude database.
If you are able to attach a cover to the map (as illustrated), a program described below can be used to generate it.
The first step is to get an initial map from OCitysMap passing parameters from the printmap web interface. You simply click on the printmap link to launch it. The parameters you pass are the lats and longs of the bounding box, the desired scale, and desired overlays. You do not want a title (this will be added later).
It is impossible to force OCitysMap to use the exact bounding box or scale you supply. The parameters it accepts are bounding box and page size. The bounding box may be adjusted in order that its aspect ratio will be compatible with the paper size, and the scale is implied by the result. printmap tries to supply a page size which gives the right scale, but is unable to do so exactly.
If you want your final map to have a 1:100k scale, then you should not enter 1:100k in printmap. You will request some scale s0 in printmap; you will actually get some other scale s1; and by adjusting the dpi you get a final scale of s2, which is the scale you care about so it doesn’t matter if s0 and s1 are somewhat different.
In fact it is desirable that they should be so. This is because Mapnik changes the level of detail as you cross a series of thresholds corresponding to the natural map scales: 1:25k, 1:50k, etc., so you want to have control of which side of the relevant threshold you lie on. Moreover, since the scale you request will be adjusted by a sequence of unpredictable small changes, you want to be comfortably on the right side. My own practice, when I want a scale of 1:100k, is to request an initial scale of 1:90909. Correcting the dpi from 300 to 330 (or something close) will then give the desired final scale.
This process relies on reframe being able to adjust from the input scale to a specified output scale by setting the dpi appropriately. But how does it know the input scale? It won’t be exactly what you’ve asked for, nor does OCitysMap report it. What reframe does is to look at the bounding box, as reported by OCitysMap, and measure its pixel size in the png, assuming 300 dpi. But any inexactitude in the bounding box will be reflected in the result; moreover I rely on the map margins as printed by OCitysMap. These are 1-pixel wide black lines, but they do not always lie on pixel boundaries in the image, so I have to look at the darkness of the final pixel to get an estimate of the logical position. All of this is ugly but not, I hope, fatally inexact; after all, errors no greater than 1 pixel can’t detract from usability.
OCitysMap can add numerous overlays, many of which are of very specialised interest.
OCitysMap offers a large selection of style sheets, but few of them are usable for large format maps. Some are pale, others are obliterated by hill shading, some lack place names, some serve highly specialised purposes. ‘Veloroad’ seems to me the most nearly acceptable, but it doesn’t show enough detail and it makes poor use of colour. I wish I was able to supply my own style sheet, but I can see reasons why this might be a bad idea.
printmap should be self-explanatory. It asks only for those parameters which are used to produce maps in the way I describe. But it is clunky. If it’s worth keeping I’ll make it pleasanter to use.
The one thing to note is that you do not want a title. printmap doesn’t ask for one, so you might think you’re safe, but you aren’t. Mapnik will construct a title if it can find a means to do so. In particular, if you try to plot a GPS track on the map, a waypoint name may be adopted as title. My procedure is to remove all ‘<name>...</name>’s from the GPS track manually.
When you hit the [submit] button, printmap will hand over parameters to OCitysMap, and when this has finished you will be shown a list of files created. Of these I use only the png, which you should download. If you then select the option to make another map, you will be sent not to printmap but to MyOSMatic, which collects a different set of parameters and allows less control. If you really want another map, you have to find your way back to printmap by your own devices.
OSM has a list of web tools producing images suitable for printing. I eventually plumped for OCitysMap without being certain it was the best choice. Each one was painful and time-consuming to evaluate, so my investigation was no more than cursory.
OCitysMap, as its name suggests, is intended for town plans. No doubt it’s excellent for its purpose, but it certainly falls short of the ideal for large format topo maps. If anyone knows of a better alternative, I hope they will let me know. I care more about inescapable limitations than about those which can be bypassed by means of front ends and postprocessors.
I have been surprised that there isn’t an officially adopted and properly maintained tool. We get more than we have a right to expect from informal efforts. I’m also a little surprised that I didn’t find any useful guidance to choosing between the alternatives.
In fact it seems to me now that OCitysMap does more than I need, and that it is the extra capabilities which get in the way. All I really need is Mapnik: if I could submit a bounding box, a scale, and a style sheet, and get a png back, then I would have the perfect tool. In principle I could do this if I could install Mapnik on my own computer and run it locally; but installing it is a heroic task and it’s insufficiently documented for casual use. I tried; I gave in.
It is the difficulty of installing Mapnik which creates the need for it to be a web service; but web services put the cost on the service provider rather than the user, and you’re dependent on someone else’s generosity. It so happens that town plans have a generous provider, but no one can complain that the generosity doesn’t extend further.
Style sheets are another problem. I have never been in a position to make a map under a style sheet of my own. maputnik is supposed to provide a tool for developing style sheets, but I haven’t found it easy to use. I have no idea where it gets icons from or how to specify a source.
I’ve concentrated on the Veloroad style sheet. Its worst fault (shared with several others) is that mountains aren’t marked. Selecting the right mountains to display is not an easy task; in practice you should probably use a region-dependent altitude threshold.
There are issues pages for both MapOSMatic and OCitysMap on Github.
Please email me with any questions: colin·champion&routemaster·app, substituting full stops for the dots and an ampersat for the ampersand.
reframe is a C/C++ program which you run on your own computer. It takes as input the png file you have downloaded, and produces a new png image from it containing some extra elements. Specifically:
These are all purely cosmetic additions; if you don’t care for them, you have no need for reframe.
reframe takes its parameters from a text file whose format should be self-explanatory. An example (‘reframe.parms’) is this:
@nwes -13.5 -72 -71 -14
@scale 100000
@title "Cusco / Ocongate"
@sheet "Hojas 28-s/t"
@fonts "Academy Engraved LET Fonts.ttf"
LiberationSerif-Regular.ttf
LiberationSans-Regular.ttf
@utm 1
@deg 1
The calling sequence is
reframe parmfile infile outfile
where parmfile is the parameter file and the other two arguments are the png files taken as input and written as output.
The map shown at the top of this page is representative output. If you want to see the corresponding input, it’s here (51MB).
This keyword introduces the lats and longs of the bounding box. I don’t know if there’s a conventional order for such sets of values; CSS goes NESW (I think) but is hard to remember. Mapnik implicitly goes NWSE. My own ordering corresponds to how boxes are presented in a web form, and the keyword name acts as a mnemonic. In the example given, the bounds are -13.5°N, -72°W, -71°E and -14°S.
This is the scale you want for the finished map. reframe will work out the scale of its input and adjust it for output so that the desired scale is obtained. Do not write ‘1:100k’; you need the number in decimals.
This will be written (usually in a decorative font) at the top of the map. It may include Unicode characters.
This is an arbitrary text string which will be written at the bottom right of the output. (Hojas is Spanish for ‘sheets’.) It is optional, and can say anything you want. Again Unicode is permitted.
This should be followed by 3 character strings, each the name of a font stored in ttf format. (.otf may well work; I haven’t tried it.) Quote them as shown if their names include special characters (eg. space). You can use the same font more than once, but it will be loaded separately each time.
The first is the display font to use for the title; ‘Academy Engraved’ comes free on my Mac for non-commercial use, and is a good match to the style of Peruvian 1:100k maps which are my model.
The second font will be used solely for a few numbers: the labels of the lat/long tick marks and the numbers on the scale bar. Liberation fonts are open source.
The third font will be used for the labels of the UTM grid and for the sheet number. The labels for the graticule and the grid differ in colour, size, and font to help the eye keep them separate.
These two parameters are optional and affect the intervals used for the grid and graticule. reframe has a default (which is scale-dependent); a value of 1 for this parameter tells it to increase the density by one notch whereas -1 tells it to decrease it; values of 2, 3, etc. tell it to make larger changes; but since only a small set of intervals is accepted, values beyond a certain range have no further effect.
Bounds (NWES): -13.500 -72.000 -71.000 -14.000 Horiz/vert scale = 7.695977/7.700756 m/pixel (geom. mean=7.698366) Printing at 329.94 dpi (=12990 dpm) to achieve the desired scale Resulting print size: 1112mm (width)x600mm (height) To print as Welsh Landranger, run magick calca.png -resize 14611x11559 -background white -gravity north -extent 14611x11559 calcapad.pdf Graticule separation = 10' UTM grid separation = 2000m
reframe prints some diagnostic output to the screen. The horizontal and vertical scales are those deduced by pixel scraping: you should worry if they’re discrepant. (The geometric mean is the scale assumed; the scale of the larger dimension might be a better choice.) The resolution is expressed in dots per metre as well as dpi because these are png’s intrinsic units (as an integer, alas). The magick command converts to pdf at a recognised OS size (if no size is identified, you don’t get this command).
reframe is a desktop program which does everything at a fairly low level. You don’t usually expect to have to deal with the nitty-gritty of font rendering. Could I have written it as a web app? I doubt it, but I don’t know enough to be sure. Could I have written it at a higher level, eg. generating an SVG file rather than a png? Who knows? I made my choice and ran with it.
The labels for the UTM grid and the lat/long graticule fall in the same region outside the map. I do my best to avoid collisions; the graticule, being sparser, gets priority.
The positioning is inexact for the reasons I’ve given. You can check against OCitysMap’s own grid to make sure that the errors aren’t significant.
In one respect my calculation is more accurate than OCitysMap’s: I do not assume that grid lines are straight. Instead, using a quadratic interpolation, I allow correctly for the earth’s curvature. I measured the error in a linear fit at a certain point for one of my maps and found it to be 56m, which is enough to be worth correcting.
The grid is drawn for a single UTM zone, namely the one appropriate to the map centre. Its number is given next to the scale bar. A location can be given coordinates corresponding to zones other than the one it naturally belongs to (up to the point at which they become negative or too large), so the grid should be usable even for maps which span zones. I’m not sure what’s the best thing to do when maps span zones; I think cartographers generally avoid creating the problem, and that’s why the UK national grid is better than UTM for London.
In one respect my labelling is unsatisfactory. Professional maps will repeat the grid labels inside the map, ideally once per double fold. This requires a lot of care to avoid collisions with map detail (especially text). OS do it, but I suspect they invest more effort in their software than I can (and the results are far from perfect).
All my calculations assume that the map I’m given uses the plate carrée projection (i.e. that latitude is a linear function of vertical position). I haven’t seen this fact documented, but can’t imagine what would induce Mapnik to adopt an alternative projection (sc. transverse Mercator).
Beware that reframe was written for one-off use; it isn’t bombproof. If you use parameters unlike those I’m expecting, you may get unsatisfactory results. I’m happy to fix problems as they arise.
mapcover is a C/C++ program to generate a map cover. Only if you have access to a specialist map printing company will it be of use to you. Its mode of use is similar to that of reframe.
Here is an example parameter file (‘cover.parms’)
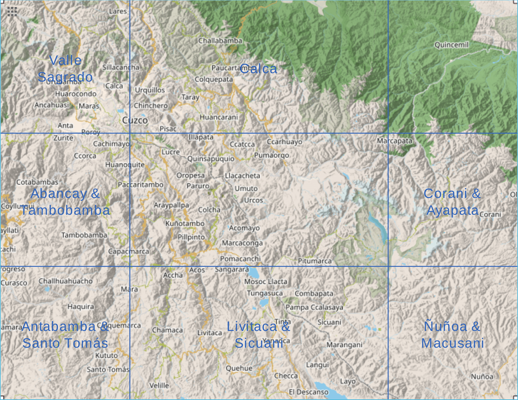
@width 134 @height 227 @spine 7 @bleed 3 @background 55bbdd d3d3d3 @foreground ffffff 0 225599 @font LiberationSans-Regular.ttf @fontsize 0 2.5 3 @title "Cusco &" Ocongate @subtitle Perú @image ausangate.jpg @caption "Cover photo: Ausangate with its head in cloud, 2002. © Colin Champion." @scale 100000 @summary ausangatelocator.png @logo osmlogo.png @vfrac 0.3333333333 0.6666666666 @hfrac 0.25 0.75 @mapnw Valle Sagrado @mapn Calca @mapw "Abancay &" Tambobamba @mape "Corani &" Ayapata @mapsw "Antabamba &" "Santo Tomás" @maps "Livitaca &" Sicuani @mapse "Ñuñoa &" Macusani
The calling sequence is
mapcover parmfile outfile
These are dimensions in mm of the folded map cover. The total printed area will be cut down to the given width and to a height of 2×height+spine; but in order to allow for slippage, an extra bleed mm need to be allowed on all 4 sides.

|
This keyword should be followed by 2 rgb values in hex. The first is the colour used where you see blue in the diagram; the second is used where you see grey. Don’t write ‘background #55bbdd’: the ‘#’ will be interpreted as a comment character. If you like to see the ‘#’s write ‘background "#55bbdd"’. HTML colour names (such as ‘red’) are not accepted.
This keyword, by contrast, should be followed by 3 rgb values, representing the colours of text written over the various backgrounds. The first two correspond to the two plain backgrounds; the last is the colour which will be used to label the summary map.
This keyword is again followed by 3 values, the first of which is not used. They are the sizes (in mm) of the text written in the various places. The sizes written on the main background (blue in the example) are determined by the software.
This should give the name of a font file, as for reframe.
This should be followed by one or two character strings (Unicode is allowed); they will need to be quoted if they include spaces or other special characters. If one string is given the title will be written on one line; if two are given it will be split between two lines.
This should be followed by a single character string (Unicode is allowed). It will be written after the title on a separate line in a somewhat smaller font.
mapcover tries to align the title vertically in a visually acceptable position, but it doesn’t try very hard and the results are not ideal. If you supply a position as titlepos, it specifies how many millimetres the title should be positioned below its default position (hence negative values move upwards). Eg.
@titlepos -2.5
This keyword is optional. If it is omitted, the main title will be converted to capitals and written as a single string on the spine. The drawback to letting this happen is that case conversion of non-Ascii characters is not fully determinate, so providing your own version is a safe alternative.
This should be the name of a file containing a photo, in non-progressive jpg, to be shown on the map cover.
mapcover’s default is to run the image from the far left of the output (i.e. starting in the bleed region) to the far right. If you have an image in portrait aspect, you may want to reduce its size. You may supply an amount of padding which is applied on both sides: it specifies how far the image will be placed inside the nominal page boundary. Therefore if you supply -x as the padding, where x is the bleed, you get back to default behaviour. This is the minimum accepted padding. If you supply “10” then the image will be positioned 10mm inside the nominal page boundary, which may be 13mm inside the image if your bleed is 3mm. Write:
@imagepad 10
This is a description of the photo to be written on the back cover. It should fit into one line.
The scale of the map will be written onto the front cover.
|
|
mapcover crops your summary in this way to make it easier for you to obtain the map from a screen shot whose edges may extend beyond the region you want to keep.
This is a png image to use as the map logo. I expect it to be the OSM logo; 480×480 is fine. There’s a copy here.
These keywords should each take 2 floating point numbers. The vfrac values specify vertical divisions of the summary map, eg. ⅓ and ⅔ the way down, while the hfrac values determine horizontal divisions. The divisions are marked by lines drawn across the map.
These parameters (which are optional) specify the names of maps to be written on the regions specified by vfrac/hfrac (the centre is assumed to be the current map). The names may be 1 or 2 character strings, depending on whether you want to split them over 2 lines.
My method of making the initial map was as follows. It needs a computer with a large screen.
This procedure is satisfactory for map series laid out as a simple grid, as is the case with the Peruvian 1:100k series; but series for general use generally aim for geographically meaningful boundaries, leading to overlapping maps in a higgledy-piggledy arrangement. How should you produce a summary map and label adjoining maps in this case?
My answer is that you (i.e. someone) should write a web app which collects bounding boxes in the same way as printmap and the openstreetmap export dialogue, but should simply draw and label the boxes on the map shown, leaving you to take a screen shot for your map cover. This wouldn’t be too hard, especially for someone familiar with OSM programming.
mapcover prints a certain amount of diagnostic output, but I may cut it back.
Making cover for Cusco & Ocongate downsampling jpg by 1.00x png=3000x1900 png bounding box = 47 607 2789 1734 (nwes) downsampling png by 0.96x
It tells you how it has cropped the png summary you supplied and the downscaling factors it has applied to both the photo and the summary. A value less than 1 implies upscaling which is not particularly desirable, but since its output is to high resolution (500dpi) you have a little leeway.
The pngs output by reframe and mapcover are perfectly suitable for printing, but for best results you would like to use a specialist map printer’s. In the UK Dennis Maps who print for Ordnance Survey are the natural choice. Unfortunately they expect to receive digital maps as pdfs, and – at least if they are to be printed with a cover – require them to come in a standard size. However if the paper size you use is significantly larger than is needed for the map, they will probably be willing to cut the page down for you.
Their faqs page (under the question “What are my map/chart size options?” lists the paper sizes they can print: I’ve been using the Welsh Landranger format.
pdf doesn’t work well as an image format on my Mac. Programs for viewing pdfs often give the impression that artefacts have been introduced when they haven’t; they display artistic 3-D effects rather than showing the true edges of the image.
I use image magick to convert from png to pdf. The command
magick cover.png cover.pdf
converts the cover from png to pdf.
The map itself is trickier. If you need to expand it to fill a given page size, then you may use a command such as the following
magick ausangate.png -resize 14614x11561 -background white -gravity north -extent 14614x11561 ausangatepad.pdf
The tricky thing here is to determine the desired page size. reframe prints out the resolution of its output image. If you multiply the dots per metre by the desired page size in metres you get the pixel size you need. reframe will print a magick command in its output if it recognises a suitable OS format.
Unfortunately I find that image magick can choke trying to pad large files, so reframe also prints a double command in which ffmpeg pads the file and image magick converts it to pdf. This runs much faster. (I think ffmpeg also compresses png more effectively.)
Do not pad an image after converting it to pdf. pdfs do not have an intrinsic resolution, and image magick is likely to degrade it to 72dpi.
I’m not at all knowledgeable about the Unix procedures for handling software libraries, which I heartily dislike (as with all Unix trickery). I’m happier when I build a program from scratch, as I do with my own software.
For convenience I have made this page self-contained. It houses all the software libraries (with compilation instructions) you need to build reframe and mapcover, leading to a certain amount of bloat. If you have difficulties, or want to make sure you have up-to-date versions, you should refer to the definitive repositories. These are:
As you may guess, I have a preference for manageably small pieces of software. zlib crept in which I wasn’t looking.
To download and compile these programs, first click on the download link at the foot of this page. This should get you a tarfile ‘mapping.tar’. Put it in the directory in which you wish to work, and execute
tar -xvf mapping.tar
This gives you all the software to compile both reframe and mapcover together with sample parameter files.
Then compile the library routines, starting with munchparms, my personal parameter file reader:
g++ -O -g -c -w munchparms.c
Notice that I turn off all warnings of deprecated notations. These are a pain in the neck. In fact in real life I alias g++='g++ -g -w' in my .bash_profile script.
Some of the compilations use gcc, others use g++.
The next step is to compile schrift, the font renderer.
gcc -O -g -c -w schrift.c
Now you will need the zlib library invoked by spng. One of the header files – crc32.h – is software-generated, so you need to produce it:
g++ -w -o gencrc -D MAKECRCH crc32.c ; gencrc ; wc crc32.h
This should show you
9446 37984 591749 crc32.h
confirming that the file has indeed been created.
Move on to zlib itself:
g++ -O -g -c -w adler32.c compress.c crc32.c deflate.c infback.c inffast.c inflate.c inftrees.c trees.c uncompr.c zutil.c
I find that I have to use gcc to compile spng:
gcc -O -g -c -w spng.c
You are now in a position to compile reframe:
g++ -O -g -w reframe.c -o reframe munchparms.o spng.o schrift.o adler32.o compress.o crc32.o deflate.o infback.o inffast.o inflate.o inftrees.o trees.o uncompr.o zutil.o
For mapcover you need a few more library functions for reading jpgs:
g++ -O -g -c -w nanojpeg.c tinyreadjpg.c rescale.c
and then you compile the main program
g++ -O -g -w mapcover.c -o mapcover munchparms.o spng.o schrift.o rescale.o tinyreadjpg.c nanojpeg.o adler32.o compress.o crc32.o deflate.o infback.o inffast.o inflate.o inftrees.o trees.o uncompr.o zutil.o
Sample parameter files are included in the download, but make sure you have the font files before trying to run any program, and a suitable logo before running mapcover.
• flip • latlong • utm • tick • lims • opacity • drawv • drawh • genglyphs • pixlen • inscribe • revisek • pixprint • strtoint • expandrow • blankrow • main • UTMLetterDesignator • utmify • haversine
#include "memory.h" #include <stddef.h> #include <math.h> #include "quadinterp.h" #include "munchparms.h" #include "spng.h" #include "schrift.h" #define uchar unsigned char genvector(uchar,ucharvector) ; static xy flip(xy a) { return xy(a.y,a.x) ; } struct utm ; struct latlong { double lat,lon ; latlong() { lat = lon = 0 ; } latlong(double x,double y) { lat = x ; lon = y ; } latlong(utm u) ; } ; struct utm { double northing,easting ; char zone[4] ; utm() { zone[0] = easting = northing = 0 ; } utm(double x,double y,char *z) { northing = x ; easting = y ; strncpy(zone,z,3) ; zone[3] = 0 ; } utm(latlong x) ; utm(latlong x,char *z) ; } ; struct canvas { int toffs,loffs ; double roffs,boffs ; } ; struct tick { double offs ; int minutes,labstart,labend ; tick(double x,int y) { offs = x ; minutes = y ; labstart = labend = 0 ; } void lims(int x,int y) { labstart = x ; labend = y ; } } ; genvector(tick,tickvector) ; double haversine(latlong x,latlong y) ; /* --------------------------------- drawing -------------------------------- */ // in real space the pen lies between qlo and qhi, but in discrete space we // have a pixel from i to i+1, so if the pixel lies wholly under the pen we // simply render it, whereas if it lies partly under the pen we render it with a // certain opacity in order that the background pixel should be partially seen. double opacity(int i,double qlo,double qhi) { if(i<qlo) { if(i+1<=qlo) return 0 ; else if(i+1<=qhi) return (i+1)-qlo ; else return qhi-qlo ; } else if(i>=qhi) return 0 ; else if(i+1<=qhi) return 1 ; else return qhi-i ; } // a point is defined as (pix E of SW corner,pix N of SW corner) int drawv(xy x1,settable xm,xy x2,uchar **r,canvas c,uchar *rgb,double pen) { int rowno,ind,k,i ; double x,alpha ; for(rowno=(int)x2.y;rowno>x1.y;rowno--) // x1.y should be an integer if(rowno>=0&&rowno<c.boffs-c.toffs) { if(!xm.set) x = lininterp(rowno,flip(x1),flip(x2)) ; else x = quadinterp(2*(rowno-x1.y)/(x2.y-x1.y)-1,x1.x,xm,x2.x) ; for(i=(int)(x-pen/2);i<(int)(x+pen/2+1);i++) { if(i<0||i>c.roffs-c.loffs) continue ; alpha = opacity(i,x-pen/2,x+pen/2) ; ind = 3 * (c.loffs+i) ; if(alpha==1) for(k=0;k<3;k++) r[((int)c.boffs)-rowno][ind+k] = rgb[k] ; else for(k=0;k<3;k++) r[((int)c.boffs)-rowno][ind+k] = alpha*rgb[k] + (1-alpha)*r[c.toffs+rowno][ind+k] ; } } return (x1.x>0&&x1.x<c.roffs-c.loffs) + 2*(x2.x>0&&x2.x<c.roffs-c.loffs) ; } int drawh(xy x1,settable ym,xy x2,uchar **r,canvas c,uchar *rgb,double pen) { int colno,ind,k,i ; double y,alpha ; // y vals are distances north of the southern edge for(colno=(int)x1.x+1;colno<x2.x;colno++) // x2.x should be an integer if(colno>=0&&colno<c.roffs-c.loffs) { if(!ym.set) y = c.boffs - lininterp(colno,x1,x2) ; else y = c.boffs - quadinterp(2*(colno-x1.x)/(x2.x-x1.x)-1,x1.y,ym,x2.y) ; for(i=(int)(y-pen/2);i<(int)(y+pen/2+1);i++) { if(i<=c.toffs||i>c.boffs) continue ; alpha = opacity(i,y-pen/2,y+pen/2) ; if(alpha==1) for(k=0;k<3;k++) r[i][3*(colno+c.loffs)+k] = rgb[k] ; else for(k=0;k<3;k++) r[i][3*(colno+c.loffs)+k] = alpha*rgb[k] + (1-alpha)*r[i][3*(colno+c.loffs)+k] ; } } return (x1.y>0&&x1.y<c.boffs-c.toffs) + 2*(x2.y>0&&x2.y<c.boffs-c.toffs) ; } /* --------------------------------- writing -------------------------------- */ void genglyphs(SFT *sft,int *str,int n, SFT_Glyph *glyph,SFT_GMetrics *gm,SFT_Image *gim) { SFT_GMetrics gg ; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { sft_lookup(sft,str[i],glyph+i) ; sft_gmetrics(sft,glyph[i],&gg) ; gm[i] = gg ; gim[i].width = gg.minWidth ; gim[i].height = gg.minHeight ; gim[i].pixels = ucharvector(gg.minWidth*gg.minHeight) ; sft_render(sft,glyph[i],gim[i]) ; } } int pixlen(SFT_GMetrics *g,int n) { int i,len ; if(n<=0) return 0 ; for(len=i=0;i<n-1;i++) len += (int)( 0.5 + g[i].advanceWidth + g[i+1].leftSideBearing ) ; return len + (int) (0.5+g[n-1].minWidth) ; } // (xoffs,yoffs) is position on the page with top left the origin, incr down void inscribe(SFT_GMetrics *g,SFT_Image *im,int n, int xoffs,int yoffs,uchar rgb[3],uchar **r,int maxh) { int i,j,k,cno,ind,w,h ; uchar pix ; for(cno=0;cno<n;cno++) { for(w=g[cno].minWidth,h=g[cno].minHeight,ind=i=0; i<h&&i+yoffs+g[cno].yOffset<maxh; i++) for(j=0;j<w;j++,ind++) for(pix=((uchar *)im[cno].pixels)[ind],k=0;k<3;k++) r[i+yoffs+g[cno].yOffset][3*(j+xoffs)+k] = (int)((pix/255.0)*rgb[k]+0.5) + 255-pix ; if(cno<=n-1) xoffs += (int)( 0.5 + g[cno].advanceWidth + g[cno+1].leftSideBearing ) ; } } int revisek(int k,int w1,int w2,tick *grat,int ngrat,int padpx) { int i,err1,err2 ; // utm label goes from k-w1 to k-w1+w2 for(i=0;i<ngrat;i++) // see if it collides with any graticule label { err1 = (grat[i].labend+padpx)-(k-w1) ; if(err1<=0) continue ; // positive if utm label starts before graticule end err2 = ( k-w1+w2+padpx) - grat[i].labstart ; if(err2<=0) continue ; // positive if utm label ends after graticule start if(err1<err2) // shift the utm label to the right { if(err1<w1) return k + err1 ; else return -1 ; } else { if(err2<w2-w1) return k - err2 ; else return -1 ; } } return k ; } ij pixprint(int k,int mod,SFT_GMetrics *g,SFT_Image *im, SFT_GMetrics *gind,SFT_Image *imind) { char s[20] ; int j,ind,deg ; if(k<mod*60) snprintf(s,10,"%d*%02d\'",(mod*60-k)/60,(mod*60-k)%60) ; else snprintf(s,10,"%d*%02d\'",(k-mod*60)/60,(k-mod*60)%60) ; for(j=0;s[j];j++) { if(s[j]=='*') { ind = 10 ; deg = j ; } else if(s[j]=='\'') ind = 11 ; else ind = s[j] - '0' ; gind[j] = g[ind] ; imind[j] = im[ind] ; } return ij(deg,j) ; } int strtoint(char *s,int *v) { int i,k,n=strlen(s) ; if(n>=200) throw up("s is too long a string",s) ; uchar *u=(uchar *) s ; for(k=i=0;i<n;) if((u[i]&0b11110000)==0b11110000) { v[k++] = ((u[i]&7)<<18) | ((u[i+1]&63)<<12) | ((u[i+2]&63)<<6) | (u[i+3]&63) ; i += 4 ; } else if((u[i]&0b11100000)==0b11100000) { v[k++] = ((u[i]&15)<<18) | ((u[i+1]&63)<<12) | ((u[i+2]&63)<<6) ; i += 3 ; } else if((u[i]&0b11000000)==0b11000000) { v[k++] = ((u[i]&31)<<6) | (u[i+1]&63) ; i += 2 ; } else { v[k++] = u[i] & 127 ; i += 1 ; } return k ; } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ uchar *expandrow(uchar *r,int w,int pad) { uchar *u=ucharvector(3*(w+2*pad)) ; int i ; for(i=0;i<3*pad;i++) u[i] = u[3*(w+pad)+i] = 255 ; for(i=0;i<3*w;i++) u[3*pad+i] = r[i] ; free(r) ; return u ; } uchar *blankrow(int w) { uchar *u=ucharvector(3*w) ; for(int i=0;i<3*w;i++) u[i] = 255 ; return u ; } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ int main(int argc,char **argv) { int i,j,k,l,m,n,space,pos,utmoffs,utmstep,gap1px,titlepx,gap2px ; int labpx,smallpx,degpx,maxw,degoffs,minstep,ngrat[2],dir,tickpx,padpx ; int gap3px,gap4px,gap5px,sum1,sum2,w,h,hdash,wdash,ind[10],fl,iq,w1,w2 ; int bounded,fonted[3]={0,0,0},str[200],pad,px1,px2,len,sheetpx ; int copystart,copyend,copywid,zonepx,sheetlen,zonelen,unicode[256]={0} ; int griddle[] = { 100,200,500 , 1000,2000,5000 , 10000,20000,50000 , 0 } ; int driggle[] = { 1,2,5 , 10,15,30 , 60 , 0 } ; int ossizes[][2] = { {1270,952} , {1000,890} , {1125,890} , {1143,952} , {1016,952} , {0,0} } ; double q,q1,q2,*bounds,W,H,scale,pixscale,dpi,dpcm,utmerr,vscale,hscale ; double x1,x2,y1,y2,qlo,qhi,linewid ; uchar header[9],**rptr,**rdash,*row,blue[3]={0,34,194},blk[3]={0,0,0} ; uchar *px[4] ; char **fonts,s[10],*title,*sheet,*oflname ; char *osnames[] = { "Explorer" , "Landranger" , "Welsh Landranger" , "Alternative Option 1" , "Alternative Option 2" } ; FILE *ifl,*ofl ; settable zilch,xm,ym ; spng_ctx *ctx ; struct spng_ihdr ihdr ; struct spng_phys pixelres ; SFT sft ; SFT_Glyph glyph[200],keep1[14] ; SFT_GMetrics glyphmetrics[200],g[10],gg,keep2[14] ; SFT_Image glyphim[200],im[10],keep3[14] ; utm unw,une,usw,use,uw,uc,ue,un,us ; canvas c ; tick *grat[2] ; ij p ; parmlist *parms ; parmkey *key ; /* --------------------------- parse the arguments ------------------------ */ if(argc<4) { printf("usage: %s parmfile infile outfile\n",argv[0]) ; return 0 ; } parms = munchreadparms(argv[1]) ; if(getparms(bounds,"nwes")!=4) throw up("You need 4 nwes bounds") ; getparm(scale,"scale") ; getparm(title,"title") ; getparm(sheet,"sheet",0) ; if(getparms(fonts,"fonts")!=3) throw up("You need 3 fonts (display/serif/sans)") ; getparm(utmoffs,"utm",0) ; getparm(degoffs,"deg",0) ; key = getparmkey(0) ; if(key) throw up("unused keyword at %s:\n@%s %s\n", munchparmloc(),key->key,key->dat) ; parms->release() ; free(parms) ; printf("Bounds (NWES): %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f\n", bounds[0],bounds[1],bounds[2],bounds[3]) ; /* ------------------------------ read the map ---------------------------- */ ifl = fopenread(argv[2]) ; if(!(ctx=spng_ctx_new(0))) throw up("spng_ctx_new() failed") ; /* Ignore and don't calculate chunk CRC's */ spng_set_crc_action(ctx,SPNG_CRC_USE,SPNG_CRC_USE) ; /* Set source PNG */ spng_set_png_file(ctx,ifl) ; if((i=spng_get_ihdr(ctx,&ihdr))) throw up("spng_get_ihdr() error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; if(ihdr.color_type!=2||ihdr.bit_depth!=8) throw up("colour type %d, bit depth %d",ihdr.color_type,ihdr.bit_depth) ; w = ihdr.width ; h = ihdr.height ; if((i=spng_decode_image(ctx,0,0,SPNG_FMT_PNG,SPNG_DECODE_PROGRESSIVE))) throw up("progressive spng_decode_image error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; rptr = (uchar **) cjcalloc(h,sizeof(uchar *)) ; for(i=0;i<h;i++) { rptr[i] = ucharvector(3*w) ; if(spng_decode_row(ctx,rptr[i],3*w)&&i<h-1) throw up("read failure on row %d",i) ; } spng_ctx_free(ctx) ; fclose(ifl) ; /* -------------------------- find the bounding box ----------------------- */ for(i=0;i<h;i++) { for(j=0;j<3*w&&rptr[i][j]==255&&rptr[i][j+1]==255&&rptr[i][j+2]==255;j+=3) ; if(j<3*w) break ; } if(i==h) throw up("Blank map!") ; c.toffs = i ; c.loffs = j / 3 ; for(j=3*w-3; j>=0&&rptr[i][j]==255&&rptr[i][j+1]==255&&rptr[i][j+2]==255; j-=3) ; c.roffs = j/3 + (1-rptr[i][j]/255.0) ; // j/3 is ind of the last non-wh pixel for(j=3*c.loffs; i<h&&(rptr[i][j]!=255||rptr[i][j+1]!=255||rptr[i][j+2]!=255); i++) ; // i emerges as the index of the first white pixel down the column if(i==h) throw up("Unterminated map!") ; c.boffs = i - rptr[i-1][j]/255.0 ; /* -------------------------- find the copyright box ---------------------- */ for(i=(int)c.boffs+1;i<h;i++) { for(j=3*c.loffs;j<3*w;j++) if(rptr[i][j]!=255) break ; if(j<3*w) break ; } if(i==h) throw up("No copyright box") ; else copystart = i ; for(i=h-1;i>copystart;i--) { for(j=3*c.loffs;j<3*w;j++) if(rptr[i][j]!=255) break ; if(j<3*w) break ; } if(i==copystart) throw up("Faulty copyright box") ; else copyend = i + 1 ; for(copywid=0,i=copystart;i<copyend;i++) { for(j=3*w-1;j>=c.loffs;j--) if(rptr[i][j]!=255) break ; if(j>copywid) copywid = j ; } copywid = j/3 ; /* --------------------------- compute the scaling ------------------------ */ W = haversine(latlong(bounds[0],bounds[1]),latlong(bounds[0],bounds[2])) ; H = haversine(latlong(bounds[0],bounds[1]),latlong(bounds[3],bounds[1])) ; hscale = W / (c.roffs-c.loffs) ; vscale = H / (c.boffs-c.toffs) ; pixscale = sqrt(hscale*vscale) ; printf("Horiz/vert scale = %.6f/%.6f m/pixel (geom. mean=%.6f)\n", hscale,vscale,pixscale) ; if(max(hscale,vscale)/min(hscale,vscale)>1.01) printf("*** WARNING: THE SCALES DO NOT LOOK CORRECT ***\n") ; dpcm = scale / (pixscale*100) ; dpi = .0254 * scale / pixscale ; printf("Printing at %.2f dpi (=%d dpm) to achieve the desired scale\n", dpi,(int)(0.5+100*dpcm)) ; /* ------------------------------- pad the map ---------------------------- */ gap1px = (int) (0.5+1.0*dpcm) ; // gap above title titlepx = (int) (0.5+1.0*dpcm) ; // height of title gap2px = (int) (0.5+0.4*dpcm) ; // gap between title and top labels degpx = (int) (0.5+0.275*dpcm) ; // height of utm labels labpx = (int) (0.5+0.3*dpcm) ; // height of lat/long labels smallpx = (int) (0.5+0.2*dpcm) ; // height of leading digits of utm labels gap3px = (int) (0.5+0.2*dpcm) ; // gap between top labels and map gap4px = gap5px = (int) (0.5+0.1*dpcm) ; // gap above and below bottom labels sheetpx = (int) (0.5+0.35*dpcm) ; // height of sheet no zonepx = (int) (0.5+0.42*dpcm) ; // height of zone no sum1 = gap1px + titlepx + gap2px + labpx + gap3px ; sum2 = gap4px + labpx + gap5px ; px2 = 1 + (int) c.boffs ; hdash = h + sum1 - c.toffs + sum2 ; pad = (int) (0.5+1.5*dpcm) - c.loffs ; // padding on L/R sides if(pad<=0) throw up("padding inconsistency") ; wdash = w + 2*pad ; rdash = (uchar **) cjcalloc(hdash,sizeof(uchar *)) ; for(i=0;i<sum1;i++) rdash[i] = blankrow(wdash) ; for(i=0;i<px2-c.toffs;i++) rdash[sum1+i] = expandrow(rptr[c.toffs+i],w,pad) ; for(i=px2+sum1-c.toffs;i<px2+sum1-c.toffs+sum2;i++) rdash[i] = blankrow(wdash) ; for(i=0;i<h-px2;i++) rdash[px2+sum1+sum2-c.toffs+i] = expandrow(rptr[px2+i],w,pad) ; free(rptr) ; rptr = rdash ; c.boffs += sum1 - c.toffs ; c.toffs = sum1 ; c.loffs += pad ; c.roffs += pad ; copystart += hdash - h ; copyend += hdash - h ; copywid += (wdash-w) / 2 ; h = hdash ; w = wdash ; printf("Resulting print size: %dmm (width)x%dmm (height)\n", (int)(0.5+10*w/dpcm),(int)(0.5+10*h/dpcm)) ; // is there a landscape OS size suitable for my map? for(q=k=i=0;ossizes[i][0];i++) if(ossizes[i][0]>=10*w/dpcm&&ossizes[i][1]>=10*h/dpcm) if(q==0||ossizes[i][0]<q) { q = ossizes[i][0] ; k = i ; } if(q) { wdash = (int) ( 0.5 + ossizes[k][0]*dpcm/10 ) ; hdash = (int) ( 0.5 + ossizes[k][1]*dpcm/10 ) ; for(j=strlen(argv[3])-4,oflname=charvector(j+1),i=0;i<j;i++) oflname[i] = argv[3][i] ; printf("To print as %s, run\nmagick %s -resize %dx%d -background white " "-gravity north -extent %dx%d %s.pdf\nor\n" "ffmpeg -i %s -vf \"pad=%d:%d:%d:%d:white\" -dpm %d %s.pad.png ; " "magick %s.pad.png %s.pdf\n", osnames[k],argv[3],wdash,hdash,wdash,hdash,oflname, argv[3],wdash,hdash,(wdash-w)/2,0,(int)(0.5+100*dpcm), oflname,oflname,oflname) ; } tickpx = (int) (0.5+0.45*dpcm) ; padpx = (int) (0.5+0.2*dpcm) ; // min gap between tick marks linewid = 0.015 * dpcm ; // about a 200th of an inch /* ---------------------------- process the title ------------------------ */ sft.font = sft_loadfile(fonts[0]) ; sft.flags = SFT_DOWNWARD_Y ; sft.xScale = sft.yScale = titlepx ; len = strtoint(title,str) ; genglyphs(&sft,str,len,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; w1 = pixlen(glyphmetrics,len) ; inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,len,(w-w1)/2,gap1px+titlepx,blk,rptr,h) ; for(i=0;i<len;i++) free(glyphim[i].pixels) ; sft_freefont(sft.font) ; /* ------------------------------ find the zone --------------------------- */ uc = utm(latlong((bounds[0]+bounds[3])/2,(bounds[1]+bounds[2])/2)) ; unw = utm(latlong(bounds[0],bounds[1]),uc.zone) ; une = utm(latlong(bounds[0],bounds[2]),uc.zone) ; usw = utm(latlong(bounds[3],bounds[1]),uc.zone) ; use = utm(latlong(bounds[3],bounds[2]),uc.zone) ; un = utm(latlong(bounds[0],(bounds[1]+bounds[2])/2),uc.zone) ; uw = utm(latlong((bounds[0]+bounds[3])/2,bounds[1]),uc.zone) ; ue = utm(latlong((bounds[0]+bounds[3])/2,bounds[2]),uc.zone) ; us = utm(latlong(bounds[3],(bounds[1]+bounds[2])/2),uc.zone) ; /* ---------------------------- process the serif ------------------------- */ for(i=0;i<10;i++) str[i] = i + '0' ; str[10] = 176 ; // ° str[11] = '\'' ; str[12] = 'k' ; str[13] = 'm' ; sft.font = sft_loadfile(fonts[1]) ; sft.xScale = sft.yScale = degpx ; genglyphs(&sft,str,14,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; sft_freefont(sft.font) ; for(i=0;i<14;i++) // it would be better to put the sans serif somewhere else { keep1[i] = glyph[i] ; keep2[i] = glyphmetrics[i] ; keep3[i] = glyphim[i] ; } /* -------------------------- find the graticule sep ---------------------- */ q = ( unw.northing - usw.northing ) / ( 60 * scale * (bounds[0]-bounds[3]) ) ; // metres/minute of latitude on the page for(utmerr=-1,i=0;driggle[i];i++) { q1 = fabs(log((driggle[i]*q)/0.2)) ; if(utmerr<0||q1<utmerr) { utmerr = q1 ; minstep = i ; } } for(;degoffs<0;degoffs++) if(driggle[minstep+1]) minstep += 1 ; for(;degoffs>0;degoffs--) if(minstep>0) minstep -= 1 ; minstep = driggle[minstep] ; printf("Graticule separation = %d\'\n",minstep) ; /* -------------------------- find graticule coords ----------------------- */ for(dir=0;dir<2;dir++) // first lat, then long { if(dir==0) { qlo = bounds[3] ; qhi = bounds[0] ; q = c.boffs-c.toffs ; k = 90 ; } else { qlo = bounds[1] ; qhi = bounds[2] ; q = c.roffs-c.loffs ; k = 180 ; } q1 = (qlo+k) * 60 ; // long of LH edge in min E of date line iq = minstep*(int)(q1/minstep) ; // (or lat of bottom in mi N of south pole) if(iq<q1) iq += minstep ; // q2 = (qhi+k) * 60 ; // long of RH edge n = 1 + (q2-iq) / minstep ; grat[dir] = tickvector(n) ; for(i=0;iq<=q2;iq+=minstep) { if(iq==n) throw up("logic error in graticule calculation %d",dir) ; grat[dir][i++] = tick(q*(iq-q1)/(q2-q1),iq) ; } ngrat[dir] = i ; } /* ----------------------------- draw tick marks -------------------------- */ for(i=0;i<ngrat[0];i++) // latitude { q = grat[0][i].offs ; if( q>tickpx && q<c.boffs-c.toffs-tickpx ) { drawh(xy(0.0,q),zilch,xy(tickpx,q),rptr,c,blk,linewid) ; drawh(xy((int)(c.roffs-c.loffs)-tickpx,q),zilch, xy(c.roffs-c.loffs,q),rptr,c,blk,linewid) ; } // pix print produces glyphs for “12°34'” returning ind of ‘°’ and length p = pixprint(grat[0][i].minutes,90,glyphmetrics,glyphim,g,im) ; w2 = pixlen(g,p.j) ; // this is an arbitrary formula which roughly centres the label: the correct w1 = (int)(c.boffs-q)+degpx/4 ; // formula would be gratefully received inscribe(g,im,p.j,c.loffs-w2-gap4px,w1,blk,rptr,h) ; inscribe(g,im,p.j,(int)c.roffs+gap4px+1,w1,blk,rptr,h) ; grat[0][i].lims((int)c.boffs-w1,(int)c.boffs-w1+glyphmetrics[0].minHeight) ; } px1 = gap1px + titlepx + gap2px ; px2 = 1 + (int) c.boffs + gap4px ; for(i=0;i<ngrat[1];i++) // longitude { q = grat[1][i].offs ; if( q>tickpx && q<c.roffs-c.loffs-tickpx ) { drawv(xy(q,0.0),zilch,xy(q,tickpx),rptr,c,blk,linewid) ; drawv(xy(q,(int)(c.boffs-c.toffs)-tickpx),zilch, xy(q,(int)(c.boffs-c.toffs)),rptr,c,blk,linewid) ; } p = pixprint(grat[1][i].minutes,180,glyphmetrics,glyphim,g,im) ; w1 = ( pixlen(g,p.i) + pixlen(g,p.i+1) ) / 2 ; w2 = pixlen(g,p.j) ; inscribe(g,im,p.j,c.loffs+(int)q-w1,px1+labpx,blk,rptr,h) ; inscribe(g,im,p.j,c.loffs+(int)q-w1,px2+degpx,blk,rptr,h) ; grat[1][i].lims((int)q-w1,(int)q-w1+w2) ; } /* ----------------------------- draw graticule --------------------------- */ for(i=0;i<ngrat[0];i++) // latitude { q1 = grat[0][i].offs ; // how far above bottom edge if(q1>tickpx&&q1<c.boffs-c.toffs-tickpx) for(j=0;j<ngrat[1];j++) // longitude { q2 = grat[1][j].offs ; // how far to the right of LH edge if(q2>tickpx&&q2<c.roffs-c.loffs-tickpx) { drawv(xy(q2,(int)(q1-tickpx+0.5)),zilch, xy(q2,(int)(q1+tickpx+0.5)),rptr,c,blk,linewid) ; drawh(xy((int)(q2-tickpx+0.5),q1),zilch, xy((int)(q2+tickpx+0.5),q1),rptr,c,blk,linewid) ; } } } /* -------------------------- process the sans serif ---------------------- */ sft.font = sft_loadfile(fonts[2]) ; sft.xScale = sft.yScale = labpx ; genglyphs(&sft,str,10,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; sft.xScale = sft.yScale = smallpx ; genglyphs(&sft,str,10,glyph+10,glyphmetrics+10,glyphim+10) ; /* -------------------------- find the utm grid sep ----------------------- */ for(utmerr=-1,i=0;griddle[i];i++) { q1 = fabs(log((griddle[i]/scale)/0.025)) ; if(utmerr<0||q1<utmerr) { utmerr = q1 ; utmstep = i ; } } for(;utmoffs<0;utmoffs++) if(griddle[utmstep+1]) utmstep += 1 ; for(;utmoffs>0;utmoffs--) if(utmstep>0) utmstep -= 1 ; utmstep = griddle[utmstep] ; printf("UTM grid separation = %dm\n",utmstep) ; /* ------------------------------ draw eastings --------------------------- */ if(usw.easting<unw.easting) q = usw.easting ; else q = unw.easting ; iq = utmstep + utmstep*(int)(q/utmstep) ; q = (c.roffs-c.loffs) / 2 ; px1 = gap1px + titlepx + gap2px ; px2 = 1 + (int) c.boffs + gap4px ; for(;;iq+=utmstep) { // x1 is where an easting of iq is obtained on the top edge, x2 on bottom x2 = q * ( 1 + invquadinterp(iq,unw.easting,un.easting,une.easting) ) ; xm = q * ( 1 + invquadinterp(iq,uw.easting,uc.easting,ue.easting) ) ; x1 = q * ( 1 + invquadinterp(iq,usw.easting,us.easting,use.easting) ) ; if(!(fl=drawv(xy(x1,0.0),xm,xy(x2,c.boffs-c.toffs),rptr,c,blue,linewid))) break ; snprintf(s,7,"%06d",iq) ; for(j=0;j<3;j++) { k = s[j] - '0' + (j==0?10:0) ; g[j] = glyphmetrics[k] ; im[j] = glyphim[k] ; } g[0].yOffset -= labpx-smallpx ; w2 = pixlen(g,3) ; w1 = w2 - pixlen(g+1,2) ; // label goes from k-w1 to k-w1+w2 if((fl&1)&&0<=(k=revisek((int)(x2+0.5),w1,w2,grat[1],ngrat[1],padpx))) inscribe(g,im,3,c.loffs+k-w1,px1+labpx,blue,rptr,h) ; if((fl&2)&&0<=(k=revisek((int)(x1+0.5),w1,w2,grat[1],ngrat[1],padpx))) inscribe(g,im,3,c.loffs+k-w1,px2+labpx,blue,rptr,h) ; } /* ------------------------------ draw northings -------------------------- */ if(use.northing<usw.northing) q = use.northing ; else q = usw.northing ; iq = utmstep + utmstep*((int)(q/utmstep)) ; // we will draw northings at iq, iq+utmstep, iq+2*utmstep... q = (c.boffs-c.toffs) / 2 ; for(;;iq+=utmstep) { y1 = q * ( 1 + invquadinterp(iq,usw.northing,uw.northing,unw.northing) ) ; ym = q * ( 1 + invquadinterp(iq,us.northing,uc.northing,un.northing) ) ; y2 = q * ( 1 + invquadinterp(iq,use.northing,ue.northing,une.northing) ) ; if(!(fl=drawh(xy(0.0,y1),ym,xy(c.roffs-c.loffs,y2),rptr,c,blue,linewid))) break ; snprintf(s,8,"%07d",iq) ; for(j=0;j<4;j++) { k = s[j] - '0' + (j<2?10:0) ; g[j] = glyphmetrics[k] ; im[j] = glyphim[k] ; } for(i=0;i<2;i++) g[i].yOffset -= labpx-smallpx ; // the following code was written by trial and error if( (fl&1) && 0<=(k=revisek((int)(y1+0.5),labpx/4,labpx,grat[0],ngrat[0],padpx)) ) inscribe(g,im,4,c.loffs-pixlen(g,4)-gap4px,(int)(c.boffs-k)+labpx/4, blue,rptr,h) ; if( (fl&2) && 0<=(k=revisek((int)(y2+0.5),labpx/4,labpx,grat[0],ngrat[0],padpx/2)) ) inscribe(g,im,4,(int)c.roffs+1+gap4px,(int)(c.boffs-k)+labpx/4, blue,rptr,h) ; } for(i=0;i<20;i++) free(glyphim[i].pixels) ; /* ---------------------------- process the sheet ------------------------ */ if(sheet&&strlen(sheet)) { sft.xScale = sft.yScale = sheetpx ; len = strtoint(sheet,str) ; genglyphs(&sft,str,len,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; sheetlen = pixlen(glyphmetrics,len) ; w2 = (copystart+copyend+sheetpx) / 2 ; inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,len,(int)c.roffs-sheetlen,w2,blk,rptr,h) ; for(i=0;i<len;i++) free(glyphim[i].pixels) ; } else sheetlen = 0 ; /* ---------------------------- get the zone number ----------------------- */ sft.xScale = sft.yScale = zonepx ; for(i=0;i<3;i++) str[i] = uc.zone[i] ; genglyphs(&sft,str,3,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; zonelen = pixlen(glyphmetrics,3) ; w2 = (copystart+copyend+zonepx) / 2 ; // vertical position of zone number /* ---------------------------- draw the scale bar ------------------------ */ // |pad| | | // |(---------)[--]<--------------------->[-----](-----)[--]<--------->| | // | copywid zpx scale bar 3zpx/2 zone zpx sheet |pad| // how many km to display in the bar space = (int) c.roffs - copywid - sheetlen - zonelen - 7*zonepx/2 ; if(scale>70000) n = 10 ; else if(scale>35000) n = 5 ; else if(scale>15000) n = 2 ; else n = 1 ; // find n and the corresponding bar length while(n) { len = (int) ( 0.5 + n * dpcm * 100000 / scale ) ; if(len<space) break ; n /= 2 ; } if(n==0) len = 0 ; // the scale bar will start at horizontal position pos pos = (int)((c.loffs+c.roffs)/2) ; // tentative central position if(pos-len/2<copywid+zonepx) pos = len/2 + copywid + zonepx ; else if(pos+len/2>(int)c.roffs-sheetlen-zonelen-5*zonepx/2) pos = (int)c.roffs-sheetlen-zonelen-5*zonepx/2-len/2 ; pos -= len/2 ; // write the zone number inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,3,len+pos+3*zonepx/2,w2,blue,rptr,h) ; sft_freefont(sft.font) ; for(i=0;i<14;i++) // restore serif font properties { glyph[i] = keep1[i] ; glyphmetrics[i] = keep2[i] ; glyphim[i] = keep3[i] ; } if(n) { px2 = 1 + (int) c.boffs + gap4px ; // value used previously l = (copystart+copyend-(36+labpx)) / 2 ; if(l<px2 + labpx + gap3px) l = px2 + labpx + gap3px ; for(j=l;j<l+3;j++) for(i=3*pos;i<3*(pos+len);i++) rptr[j][i] = rptr[20+j][i] = 0 ; if(n>=5) k = 5 ; else if(n==2) k = 1 ; else k = 0 ; for(m=0;m<=n;m++) if(m<=k||m==n) { for(j=l-2;j<l+39;j++) { w1 = pos + (int) ( 0.5 + m*len/double (n) ) ; for(i=3*w1;i<3*(w1+3);i++) rptr[j][i] = 0 ; } if(m<n) w2 = snprintf(s,6,"%d",m) ; else w2 = snprintf(s,6,"%dkm",m) ; for(j=0;j<w2;j++) { if(s[j]=='k') { i = 12 ; g[j-1].advanceWidth += 2 ; } else if(s[j]=='m') i = 13 ; else i = s[j] - '0' ; g[j] = glyphmetrics[i] ; im[j] = glyphim[i] ; } inscribe(g,im,w2,w1+1-pixlen(g,w2)/2,l+36+labpx,blk,rptr,h) ; } for(m=0;m<k;m+=2) { w1 = pos + (int) ( 0.5 + m*len/double (n) ) ; w2 = pos + (int) ( 0.5 + (m+1)*len/double (n) ) ; for(j=l+8;j<l+15;j++) for(i=3*w1;i<3*w2;i++) rptr[j][i] = 0 ; } } /* ------------------------------ write the map --------------------------- */ ofl = fopenwrite(argv[3]) ; ctx = spng_ctx_new(SPNG_CTX_ENCODER) ; spng_set_png_file(ctx,ofl) ; for(i=0;i<sizeof(spng_ihdr);i++) ((uchar *)(&ihdr))[i] = 0 ; ihdr.width = w ; ihdr.height = h ; ihdr.color_type = 2 ; ihdr.bit_depth = 8 ; spng_set_ihdr(ctx,&ihdr) ; pixelres.ppu_x = pixelres.ppu_y = (int)(0.5+100*dpcm) ; pixelres.unit_specifier = 1 ; // dpm spng_set_phys(ctx,&pixelres) ; if((i=spng_encode_image(ctx,0,0,SPNG_FMT_PNG,SPNG_ENCODE_PROGRESSIVE))) throw up("progressive spng_encode_image error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; for(i=0;i<h;i++) if(spng_encode_row(ctx,rptr[i],3*w)&&i<h-1) throw up("write failure on row %d",i) ; spng_encode_chunks(ctx) ; fclose(ofl) ; } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ /* -*- mode: C++ -*- * * Conversions between Latitude/Longitude and UTM * (Universal Transverse Mercator) coordinates. * * License: Modified BSD Software License Agreement * * $Id$ */ /** @file @brief Universal Transverse Mercator transforms. Functions to convert (spherical) latitude and longitude to and from (Euclidean) UTM coordinates. @author Chuck Gantz- chuck.gantz@globalstar.com */ // Grid granularity for rounding UTM coordinates to generate MapXY. const double grid_size = 100000.0; ///< 100 km grid // WGS84 Parameters #define WGS84_A 6378137.0 ///< major axis #define WGS84_B 6356752.31424518 ///< minor axis #define WGS84_F 0.0033528107 ///< ellipsoid flattening #define WGS84_E 0.0818191908 ///< first eccentricity #define WGS84_EP 0.0820944379 ///< second eccentricity // UTM Parameters #define UTM_K0 0.9996 ///< scale factor #define UTM_FE 500000.0 ///< false easting #define UTM_FN_N 0.0 ///< false northing, northern hemisphere #define UTM_FN_S 10000000.0 ///< false northing, southern hemisphere #define UTM_E2 (WGS84_E*WGS84_E) ///< e^2 #define UTM_E4 (UTM_E2*UTM_E2) ///< e^4 #define UTM_E6 (UTM_E4*UTM_E2) ///< e^6 #define UTM_EP2 (UTM_E2/(1-UTM_E2)) ///< e'^2 static double pi=3.1415926535897932384626433832795029 ; static double DEG_TO_RAD = pi / 180 , RAD_TO_DEG = 180 / pi ; /** * Determine the correct UTM letter designator for the * given latitude * * @returns 'Z' if latitude is outside the UTM limits of 84N to 80S * * Written by Chuck Gantz- chuck.gantz@globalstar.com */ static inline char UTMLetterDesignator(double Lat) { char LetterDesignator; if ((84 >= Lat) && (Lat >= 72)) LetterDesignator = 'X'; else if ((72 > Lat) && (Lat >= 64)) LetterDesignator = 'W'; else if ((64 > Lat) && (Lat >= 56)) LetterDesignator = 'V'; else if ((56 > Lat) && (Lat >= 48)) LetterDesignator = 'U'; else if ((48 > Lat) && (Lat >= 40)) LetterDesignator = 'T'; else if ((40 > Lat) && (Lat >= 32)) LetterDesignator = 'S'; else if ((32 > Lat) && (Lat >= 24)) LetterDesignator = 'R'; else if ((24 > Lat) && (Lat >= 16)) LetterDesignator = 'Q'; else if ((16 > Lat) && (Lat >= 8)) LetterDesignator = 'P'; else if (( 8 > Lat) && (Lat >= 0)) LetterDesignator = 'N'; else if (( 0 > Lat) && (Lat >= -8)) LetterDesignator = 'M'; else if ((-8 > Lat) && (Lat >= -16)) LetterDesignator = 'L'; else if((-16 > Lat) && (Lat >= -24)) LetterDesignator = 'K'; else if((-24 > Lat) && (Lat >= -32)) LetterDesignator = 'J'; else if((-32 > Lat) && (Lat >= -40)) LetterDesignator = 'H'; else if((-40 > Lat) && (Lat >= -48)) LetterDesignator = 'G'; else if((-48 > Lat) && (Lat >= -56)) LetterDesignator = 'F'; else if((-56 > Lat) && (Lat >= -64)) LetterDesignator = 'E'; else if((-64 > Lat) && (Lat >= -72)) LetterDesignator = 'D'; else if((-72 > Lat) && (Lat >= -80)) LetterDesignator = 'C'; // 'Z' is an error flag, the Latitude is outside the UTM limits else LetterDesignator = 'Z'; return LetterDesignator; } /** * Convert lat/long to UTM coords. Equations from USGS Bulletin 1532 * * East Longitudes are positive, West longitudes are negative. * North latitudes are positive, South latitudes are negative * Lat and Long are in fractional degrees * * Written by Chuck Gantz- chuck.gantz@globalstar.com modified by CJC */ utm utmify(latlong x,char *zone) { double Lat = x.lat , Long = x.lon ; double a = WGS84_A; double eccSquared = UTM_E2; double k0 = UTM_K0; double LongOrigin; double eccPrimeSquared; double N, T, C, A, M; //Make sure the longitude is between -180.00 .. 179.9 double LongTemp = (Long+180)-int((Long+180)/360)*360-180; double LatRad = Lat*DEG_TO_RAD; double LongRad = LongTemp*DEG_TO_RAD; double LongOriginRad; int ZoneNumber , ZoneLetter ; utm u ; if(zone) { ZoneNumber = atoi(zone) ; ZoneLetter = zone[2]?zone[2]:zone[1] ; } else { ZoneNumber = int((LongTemp + 180)/6) + 1; if( Lat >= 56.0 && Lat < 64.0 && LongTemp >= 3.0 && LongTemp < 12.0 ) ZoneNumber = 32; // Special zones for Svalbard if( Lat >= 72.0 && Lat < 84.0 ) { if( LongTemp >= 0.0 && LongTemp < 9.0 ) ZoneNumber = 31; else if( LongTemp >= 9.0 && LongTemp < 21.0 ) ZoneNumber = 33; else if( LongTemp >= 21.0 && LongTemp < 33.0 ) ZoneNumber = 35; else if( LongTemp >= 33.0 && LongTemp < 42.0 ) ZoneNumber = 37; } // +3 puts origin in middle of zone ZoneLetter = UTMLetterDesignator(Lat) ; } LongOrigin = (ZoneNumber - 1)*6 - 180 + 3; LongOriginRad = LongOrigin * DEG_TO_RAD; //compute the UTM Zone from the latitude and longitude snprintf(u.zone,4,"%d%c",ZoneNumber,ZoneLetter) ; eccPrimeSquared = (eccSquared)/(1-eccSquared); N = a/sqrt(1-eccSquared*sin(LatRad)*sin(LatRad)); T = tan(LatRad)*tan(LatRad); C = eccPrimeSquared*cos(LatRad)*cos(LatRad); A = cos(LatRad)*(LongRad-LongOriginRad); M = a*((1 - eccSquared/4 - 3*eccSquared*eccSquared/64 - 5*eccSquared*eccSquared*eccSquared/256) * LatRad - (3*eccSquared/8 + 3*eccSquared*eccSquared/32 + 45*eccSquared*eccSquared*eccSquared/1024)*sin(2*LatRad) + (15*eccSquared*eccSquared/256 + 45*eccSquared*eccSquared*eccSquared/1024)*sin(4*LatRad) - (35*eccSquared*eccSquared*eccSquared/3072)*sin(6*LatRad)); u.easting = (double) (k0*N*(A+(1-T+C)*A*A*A/6 + (5-18*T+T*T+72*C-58*eccPrimeSquared)*A*A*A*A*A/120) + 500000.0); u.northing = (double) (k0*(M+N*tan(LatRad) *(A*A/2+(5-T+9*C+4*C*C)*A*A*A*A/24 + (61-58*T+T*T+600*C-330*eccPrimeSquared)*A*A*A*A*A*A/720))); if(Lat < 0) u.northing += 10000000.0; //10000000 meter offset for southern hemisphere return u ; } utm::utm(latlong x) { this[0] = utmify(x,0) ; } utm::utm(latlong x,char *z) { this[0] = utmify(x,z) ; } /** * Converts UTM coords to lat/long. Equations from USGS Bulletin 1532 * * East Longitudes are positive, West longitudes are negative. * North latitudes are positive, South latitudes are negative * Lat and Long are in fractional degrees. * * Written by Chuck Gantz- chuck.gantz@globalstar.com modified by CJC */ latlong::latlong(utm u) { double UTMNorthing = u.northing , UTMEasting = u.easting , Lat , Long ; char *UTMZone = u.zone ; double k0 = UTM_K0; double a = WGS84_A; double eccSquared = UTM_E2; double eccPrimeSquared; double e1 = (1-sqrt(1-eccSquared))/(1+sqrt(1-eccSquared)); double N1, T1, C1, R1, D, M; double LongOrigin; double mu, phi1Rad; double x, y; int ZoneNumber; char* ZoneLetter; x = UTMEasting - 500000.0; //remove 500,000 meter offset for longitude y = UTMNorthing; ZoneNumber = strtoul(UTMZone, &ZoneLetter, 10); if((*ZoneLetter - 'N') < 0) { //remove 10,000,000 meter offset used for southern hemisphere y -= 10000000.0; } //+3 puts origin in middle of zone LongOrigin = (ZoneNumber - 1)*6 - 180 + 3; eccPrimeSquared = (eccSquared)/(1-eccSquared); M = y / k0; mu = M/(a*(1-eccSquared/4-3*eccSquared*eccSquared/64 -5*eccSquared*eccSquared*eccSquared/256)); phi1Rad = mu + ((3*e1/2-27*e1*e1*e1/32)*sin(2*mu) + (21*e1*e1/16-55*e1*e1*e1*e1/32)*sin(4*mu) + (151*e1*e1*e1/96)*sin(6*mu)); N1 = a/sqrt(1-eccSquared*sin(phi1Rad)*sin(phi1Rad)); T1 = tan(phi1Rad)*tan(phi1Rad); C1 = eccPrimeSquared*cos(phi1Rad)*cos(phi1Rad); R1 = a*(1-eccSquared)/pow(1-eccSquared*sin(phi1Rad)*sin(phi1Rad), 1.5); D = x/(N1*k0); Lat = phi1Rad - ((N1*tan(phi1Rad)/R1) *(D*D/2 -(5+3*T1+10*C1-4*C1*C1-9*eccPrimeSquared)*D*D*D*D/24 +(61+90*T1+298*C1+45*T1*T1-252*eccPrimeSquared -3*C1*C1)*D*D*D*D*D*D/720)); lat = Lat * RAD_TO_DEG; Long = ((D-(1+2*T1+C1)*D*D*D/6 +(5-2*C1+28*T1-3*C1*C1+8*eccPrimeSquared+24*T1*T1) *D*D*D*D*D/120) / cos(phi1Rad)); lon = LongOrigin + Long * RAD_TO_DEG; } // distance between two points in metres (CJC after wikipedia) double haversine(latlong x,latlong y) { double dlat,dlon,slat,slon,clon,cbar ; double lat1 = x.lat*pi/180 , lon1 = x.lon*pi/180 ; double lat2 = y.lat*pi/180 , lon2 = y.lon*pi/180 ; slat = sin((lat1-lat2)/2) ; slon = sin((lon1-lon2)/2) ; clon = cos((lon1-lon2)/2) ; cbar = cos((lat1+lat2)/2) ; slat *= clon ; slon *= cbar ; return 2 * 6371000 * asin(sqrt(slat*slat+slon*slon)) ; // radius of earth }
• genglyphs • pixlen • inscribe • erase • blankrow • hexcolour • strtoint • main • jo_write_jpg
/* - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - */ /* "mapcover" program for making OSM map covers (c) Colin Champion 2024/5 */ /* MIT Licence */ /* https://www.routemaster.app/mapping */ /* - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - */ #include "memory.h" #include <stddef.h> #include <math.h> #include "quadinterp.h" #include "spng.h" #include "schrift.h" #include "readjpg.h" #include "munchparms.h" #include <cwctype> #include <time.h> uchar *rescale(uchar *img,int W,int H,int w,int h,int ncol) ; /* --------------------------------- writing -------------------------------- */ void genglyphs(SFT *sft,int *str,int n, SFT_Glyph *glyph,SFT_GMetrics *gm,SFT_Image *gim) { SFT_GMetrics gg ; int i,r ; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(0>sft_lookup(sft,str[i],glyph+i)) sft_lookup(sft,'?',glyph+i) ; r = sft_gmetrics(sft,glyph[i],&gg) ; gm[i] = gg ; gim[i].width = gg.minWidth ; gim[i].height = gg.minHeight ; gim[i].pixels = ucharvector(gg.minWidth*gg.minHeight+200) ; sft_render(sft,glyph[i],gim[i]) ; } } int pixlen(SFT_GMetrics *g,int n) { int i,len ; if(n<=0) return 0 ; for(len=i=0;i<n-1;i++) len += (int)( 0.5 + g[i].advanceWidth + g[i+1].leftSideBearing ) ; return len + (int) (0.5+g[n-1].minWidth) ; } // (xoffs,yoffs) is position on the page with top left the origin, incr down void inscribe(SFT_GMetrics *g,SFT_Image *im,int n,int xoffs,int yoffs, uchar rgb[3],uchar **r,int W,int H,int flip) { int i,j,k,cno,ind,w,h,x,y ; double q ; uchar *p ; for(cno=0;cno<n;cno++) { for(w=g[cno].minWidth,h=g[cno].minHeight,ind=i=0; i<h&&(y=i+yoffs+g[cno].yOffset)<H; i++) for(p=flip?r[H-y]:r[y],j=0;j<w;j++,ind++) { if(flip) x = 3*(W-(xoffs+j))-3 ; else x = 3*(j+xoffs) ; q = ((uchar *)im[cno].pixels)[ind] / 255.0 ; if(x>=0&&x<3*W) for(k=0;k<3;k++) p[x+k] = (uchar) ( 0.5 + q*rgb[k] + (1-q)*p[x+k] ) ; } xoffs += (int)( 0.5 + g[cno].advanceWidth + g[cno+1].leftSideBearing ) ; } } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ void erase(uchar *u,int w,uchar *colour) { for(int i=0;i<3*w;i+=3) { u[i] = colour[0] ; u[i+1] = colour[1] ; u[i+2] = colour[2] ; } } uchar *blankrow(int w,uchar *colour) { uchar *u=ucharvector(3*w) ; erase(u,w,colour) ; return u ; } void hexcolour(char *str,uchar *colour) { int i , k = strtol(str+(str[0]=='#'?1:0),0,16) ; for(i=0;i<3;i++,k>>=8) colour[2-i] = k & 255 ; } int strtoint(char *s,int *v) { int i,k ; uchar *u=(uchar *) s ; for(k=i=0;u[i];) if((u[i]&0b11110000)==0b11110000) { v[k++] = ((u[i]&7)<<18) | ((u[i+1]&63)<<12) | ((u[i+2]&63)<<6) | (u[i+3]&63) ; i += 4 ; } else if((u[i]&0b11100000)==0b11100000) { v[k++] = ((u[i]&15)<<18) | ((u[i+1]&63)<<12) | ((u[i+2]&63)<<6) ; i += 3 ; } else if((u[i]&0b11000000)==0b11000000) { v[k++] = ((u[i]&31)<<6) | (u[i+1]&63) ; i += 2 ; } else { v[k++] = u[i] & 127 ; i += 1 ; } return k ; } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ int main(int argc,char **argv) { int i,j,k,l,w,h,spine,W,H,dpmm=20,bleed,ntitle,nvfrac,nhfrac,fracno,maxh,len ; int l0,l1,l2,h0,h2,h3,h8,h9,bt,bl,br,bb,nmap[9]={0},mapno,t0,t1,x,y ; int fontsize[3],scale,ww,lw,lh,lcol,ind,iter,len2,penpx,max2,istr[1000] ; int imagepad,titlepos ; double q,*vfrac,*hfrac,*qfontsize ; uchar **r,**rptr,*rr,*rp,bg[2][3],fg[3][3]={0} ; char *font,*jpg,*png,**str,**title,**map[9],*spinetitle,*caption[4] = {0} ; char *logo , *subtitle , *mapname[] = { "mapnw","mapn","mapne" , "mapw",0,"mape" , "mapsw","maps","mapse" } ; FILE *ifl,*ofl ; time_t seconds = time(0) ; struct tm *current_time = localtime(&seconds) ; spng_ctx *ctx ; struct spng_ihdr ihdr ; struct spng_phys pixelres ; SFT sft ; SFT_Glyph glyph[1000] ; SFT_GMetrics glyphmetrics[1000] ; SFT_Image glyphim[1000] ; image img,omg ; parmlist *parms ; parmkey *key ; /* --------------------------- parse the arguments ------------------------ */ if(argc<3) { printf("usage: %s parmfile outfile\n",argv[0]) ; return 0 ; } parms = munchreadparms(argv[1]) ; munchsetlist(parms) ; getparm(jpg,"image") ; getparm(png,"summary") ; getparm(w,"width") ; w *= dpmm ; ww = w ; getparm(h,"height") ; h *= dpmm ; getparm(bleed,"bleed",0) ; getparm(imagepad,"imagepad",-bleed) ; if(imagepad<-bleed) imagepad = -bleed ; bleed *= dpmm ; imagepad *= dpmm ; getparm(spine,"spine") ; spine *= dpmm ; getparm(titlepos,"titlepos",0) ; titlepos *= dpmm ; getparm(scale,"scale",0) ; nhfrac = getparms(hfrac,"hfrac") ; if(nhfrac==1) throw up("You need 2 hfrac values") ; nvfrac = getparms(vfrac,"vfrac") ; if(nvfrac==1) throw up("You need 2 vfrac values") ; k = getparms(str,"background") ; if(k!=2) throw up("Two background colours are needed") ; for(i=0;i<2;i++) hexcolour(str[i],bg[i]) ; free(str) ; k = getparms(str,"foreground") ; if(k!=3) throw up("Three foreground colours are needed") ; for(i=0;i<k;i++) hexcolour(str[i],fg[i]) ; free(str) ; k = getparms(qfontsize,"fontsize") ; if(k>0&&k!=3) throw up("Three font sizes should be provided") ; if(k<=0) { qfontsize = vector(3) ; qfontsize[1] = 2.5 ; qfontsize[2] = 3 ; } for(i=1;i<3;i++) fontsize[i] = (int) (0.5+qfontsize[i]*dpmm) ; free(qfontsize) ; getparm(font,"font") ; getparm(subtitle,"subtitle",0) ; getparm(spinetitle,"spinetitle",0) ; getparm(caption[0],"caption",0) ; getparm(logo,"logo",0) ; ntitle = getparms(title,"title") ; if(ntitle!=1&&ntitle!=2) throw up("You need a 1- or 2-string title") ; for(i=0;i<9;i++) if(mapname[i]) nmap[i] = getparms(map[i],mapname[i]) ; key = getparmkey(0) ; if(key) throw up("unused keyword at %s:\n@%s %s\n", munchparmloc(),key->key,key->dat) ; parms->release() ; free(parms) ; printf("Making cover for %s %s\n",title[0],ntitle>1?title[1]:"") ; W = w + 2*bleed ; H = 2*h + 2*bleed + spine ; r = (uchar **) cjcalloc(H,sizeof(uchar *)) ; h9 = H - (bleed+12*dpmm) ; h8 = h9 - dpmm/2 ; h3 = (H-spine)/2 - 8*dpmm ; h2 = h3 - dpmm/2 ; for(i=0;i<h2;i++) r[i] = blankrow(W,bg[1]) ; for(i=h2;i<h3;i++) r[i] = blankrow(W,fg[0]) ; for(i=h3;i<h8;i++) r[i] = blankrow(W,bg[0]) ; for(i=h8;i<h9;i++) r[i] = blankrow(W,fg[0]) ; for(i=h9;i<H;i++) r[i] = blankrow(W,bg[1]) ; /* -------------------------- generate the captions ----------------------- */ caption[1] = charvector("Mapping by www.routemaster.app/mapping.") ; caption[2] = charvector(100) ; snprintf(caption[2],99,"Map data © %d OpenStreetMap contributors. " "See https://osm.org/copyright.",current_time->tm_year+1900) ; /* --------------------------- read the jpg image ------------------------- */ img = readjpg(jpg) ; if(img.ncol!=3) throw up("%s is not a colour image",jpg) ; k = W - 2*(imagepad+bleed) ; // pixel width of displayed image q = k / (double) img.w ; printf("downsampling jpg by %.2fx\n",1/q) ; omg = image(k,(int)(0.5+img.h*q),img.ncol,0) ; omg.u = rescale(img.u,img.w,img.h,omg.w,omg.h,img.ncol) ; // crop vertically to at most 15cm if(omg.h>150*dpmm) { l0 = (omg.h-150*dpmm)/2 ; l1 = omg.h - l0 ; } else { l0 = 0 ; l1 = omg.h ; } h0 = h8 - (l1-l0) ; // top of photo l = 3*(imagepad+bleed) ; for(k=omg.w*3*l0,i=0;i<l1-l0;i++) { for(j=l-3;j>=l-3-3*dpmm/2&&j>=0;j-=3) { r[h0+i][j] = fg[0][0] ; r[h0+i][j+1] = fg[0][1] ; r[h0+i][j+2] = fg[0][2] ; } for(j=0;j<3*omg.w;j++,k++) r[h0+i][l+j] = omg.u[k] ; if(0) for(;j<3*(omg.w+dpmm/2);j+=3) { r[h0+i][l+j] = fg[0][0] ; r[h0+i][l+j+1] = fg[0][1] ; r[h0+i][l+j+2] = fg[0][2] ; } } for(i=h0-dpmm/2;i<h0;i++) erase(r[i],W,fg[0]) ; free(img.u,omg.u) ; /* ---------------------------- process the title ------------------------ */ if(!(sft.font=sft_loadfile(font))) throw up("%s not found",font) ; sft.flags = SFT_DOWNWARD_Y ; if(ntitle==1) l0 = 14 * dpmm ; else l0 = 12 * dpmm ; sft.xScale = sft.yScale = l0 ; len = k = strtoint(title[0],istr) ; istr[k] = ' ' ; if(ntitle==2) len += 1 + strtoint(title[1],istr+k+1) ; genglyphs(&sft,istr,len,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; for(maxh=i=0;i<len;i++) if(glyphmetrics[i].minHeight>maxh) maxh = glyphmetrics[i].minHeight ; if(subtitle) { sft.xScale = sft.yScale = (4*l0) / 5 ; len2 = strtoint(subtitle,istr+len) ; genglyphs(&sft,istr+len,len2,glyph+len,glyphmetrics+len,glyphim+len) ; for(max2=i=0;i<len2;i++) if(glyphmetrics[len+i].minHeight>max2) max2 = glyphmetrics[i].minHeight ; } l2 = l1 = l0 ; // l0, l1, l2 = height of first, first 2, all 3 lines if(ntitle>1) l2 = l1 = 2*l0 + 4*dpmm ; // add in second line if(subtitle) l2 += (4*l0)/5 + (7*dpmm)/2 ; // add in subtitle l = (h0+h+bleed+spine+15*dpmm-l2) / 2 ; // start y val of title if(l+l2-l0+max2>h0) l -= l+l2-l0+max2-h0 ; // don't trample on the photo l += titlepos ; // adjust at your own risk // so put the centre half way between 3cm below the top of the page and // the start of the image inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,k, bleed+10*dpmm,l+maxh,fg[0],r,W,H,0) ; if(ntitle>1) inscribe(glyphmetrics+k+1,glyphim+k+1,len-(k+1), bleed+10*dpmm,l+l1-l0+maxh,fg[0],r,W,H,0) ; if(subtitle) inscribe(glyphmetrics+len,glyphim+len,len2, bleed+10*dpmm,l+l2-l0+max2,fg[0],r,W,H,0) ; for(i=0;i<len+(subtitle?len2:0);i++) free(glyphim[i].pixels) ; /* ----------------------------- write the spine -------------------------- */ sft.xScale = sft.yScale = 0.6 * spine ; if(spinetitle) len = strtoint(spinetitle,istr) ; else for(i=0;i<len;i++) istr[i] = towupper(istr[i]) ; genglyphs(&sft,istr,len,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; k = pixlen(glyphmetrics,len) ; inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,len,(W-k)/2,h+bleed+0.7*spine,fg[0],r,W,H,0) ; for(i=0;i<len;i++) free(glyphim[i].pixels) ; /* ------------------------------ read the logo --------------------------- */ if(logo) { ifl = fopenread(logo) ; if(!(ctx=spng_ctx_new(0))) throw up("spng_ctx_new() failed") ; /* Ignore and don't calculate chunk CRC's */ spng_set_crc_action(ctx,SPNG_CRC_USE,SPNG_CRC_USE) ; /* Set source PNG */ spng_set_png_file(ctx,ifl) ; if((i=spng_get_ihdr(ctx,&ihdr))) throw up("spng_get_ihdr() error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; if((ihdr.color_type!=2&&ihdr.color_type!=6)||ihdr.bit_depth!=8) throw up("colour type %d, bit depth %d",ihdr.color_type,ihdr.bit_depth) ; img = image(ihdr.width,ihdr.height,ihdr.color_type==2?3:4,0) ; if((i=spng_decode_image(ctx,0,0,SPNG_FMT_PNG,SPNG_DECODE_PROGRESSIVE))) throw up("progressive spng_decode_image error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; img.u = ucharvector(img.w*img.h*img.ncol) ; for(k=i=0;i<img.h;i++,k+=img.ncol*img.w) if(spng_decode_row(ctx,img.u+k,img.ncol*img.w)&&i<img.h-1) throw up("read failure on row %d",i) ; spng_ctx_free(ctx) ; fclose(ifl) ; k = 20 * dpmm ; q = k / sqrt(img.w*img.h) ; omg = image((int)(0.5+q*img.w),(int)(0.5+q*img.h),img.ncol,0) ; printf("logo=%dx%d->%dx%d; %d colours\n",img.w,img.h,omg.w,omg.h,img.ncol) ; omg.u = rescale(img.u,img.w,img.h,omg.w,omg.h,img.ncol) ; /* ----------------------------- draw the logo -------------------------- */ x = w + bleed - omg.w - 10*dpmm ; y = h + bleed + spine + 10*dpmm ; for(iter=0;iter<2;iter++) for(ind=i=0;i<omg.h;i++) for(rp=iter?r[(H-1)-i-y-10*dpmm]:r[i+y],j=0;j<omg.w;j++) if(img.ncol==3) { if(iter) l = 3*(W-1-j-x) ; else l = 3*(j+x) ; rp[l] = omg.u[ind++] ; rp[l+1] = omg.u[ind++] ; rp[l+2] = omg.u[ind++] ; } else { k = omg.u[ind+3] ; if(iter) l = 3*(W-1-j-x) ; else l = 3*(j+x) ; if(k==255) { rp[l] = omg.u[ind++] ; rp[l+1] = omg.u[ind++] ; rp[l+2] = omg.u[ind+=2] ; } else if(k==0) { ind += 4 ; continue ; } else { q = k / 255.0 ; rp[l] = (1-q)*rp[l] + q*omg.u[ind++] ; rp[l+1] = (1-q)*rp[l+1] + q*omg.u[ind++] ; rp[l+2] = (1-q)*rp[l+2] + q*omg.u[ind+=2] ; } } } /* ------------------------ read the png overview map --------------------- */ ifl = fopenread(png) ; if(!(ctx=spng_ctx_new(0))) throw up("spng_ctx_new() failed") ; /* Ignore and don't calculate chunk CRC's */ spng_set_crc_action(ctx,SPNG_CRC_USE,SPNG_CRC_USE) ; /* Set source PNG */ spng_set_png_file(ctx,ifl) ; if((i=spng_get_ihdr(ctx,&ihdr))) throw up("spng_get_ihdr() error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; if((ihdr.color_type!=2&&ihdr.color_type!=6)||ihdr.bit_depth!=8) throw up("colour type %d, bit depth %d",ihdr.color_type,ihdr.bit_depth) ; ww = ihdr.width ; h = ihdr.height ; if(ihdr.color_type==2) k = 3 ; else k = 4 ; if((i=spng_decode_image(ctx,0,0,SPNG_FMT_PNG,SPNG_DECODE_PROGRESSIVE))) throw up("progressive spng_decode_image error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; rptr = (uchar **) cjcalloc(h,sizeof(uchar *)) ; if(k==4) { rr = ucharvector(4*ww) ; for(i=0;i<h;i++) { if(spng_decode_row(ctx,rr,4*ww)&&i<h-1) throw up("read failure on row %d",i) ; rptr[i] = ucharvector(3*ww) ; for(j=0;j<ww;j++) { rptr[i][3*j] = rr[4*j] ; rptr[i][3*j+1] = rr[4*j+1] ; rptr[i][3*j+2] = rr[4*j+2] ; } } free(rr) ; } else for(i=0;i<h;i++) { rptr[i] = ucharvector(3*ww) ; if(spng_decode_row(ctx,rptr[i],3*ww)&&i<h-1) throw up("read failure on row %d",i) ; } spng_ctx_free(ctx) ; fclose(ifl) ; printf("png=%dx%d\n",ww,h) ; /* -------------------------- find the bounding box ----------------------- */ k = 3*(ww/2) ; for(i=0;i<h&&(rptr[i][k]<240||rptr[i][k+1]<240||rptr[i][k+2]<240);i++) ; for(;i<h&&rptr[i][k]>=240&&rptr[i][k+1]>=240&&rptr[i][k+2]>=240;i++) ; if(i==h) throw up("Unable to find top of bounding box") ; bt = i ; for(i=h-1;i>=0&&(rptr[i][k]<240||rptr[i][k+1]<240||rptr[i][k+2]<240);i--) ; for(;i>=0&&rptr[i][k]>=240&&rptr[i][k+1]>=240&&rptr[i][k+2]>=240;i--) ; if(i<0) throw up("Unable to find bottom of bounding box") ; bb = 1+i ; i = (bb+bt)/2 ; for(j=0;j<3*ww&&(rptr[i][j]<240||rptr[i][j+1]<240||rptr[i][j+2]<240);j+=3) ; for(;j<3*ww&&rptr[i][j]>=240&&rptr[i][j+1]>=240&&rptr[i][j+2]>=240;j+=3) ; if(j==3*ww) throw up("Unable to find LHS of bounding box") ; bl = j/3 ; for(j=3*ww-3;j>=0&&(rptr[i][j]<240||rptr[i][j+1]<240||rptr[i][j+2]<240);j-=3) ; for(;j>=0&&rptr[i][j]>=240&&rptr[i][j+1]>=240&&rptr[i][j+2]>=240;j-=3) ; if(j<0) throw up("Unable to find RHS of bounding box") ; br = 1+j/3 ; printf("png bounding box = %d %d %d %d (nwes)\n",bt,bl,br,bb) ; /* ----------------------- truncate the bounding box ---------------------- */ img = image(br-bl,bb-bt,3,ucharvector(3*(br-bl)*(bb-bt))) ; for(k=i=0;i<img.h;i++) { for(j=0;j<3*img.w;j++,k++) img.u[k] = rptr[bt+i][3*bl+j] ; free(rptr[bt+i]) ; } free(rptr) ; bl = bleed + 10*dpmm ; omg = image(W-2*bl,(int)(0.5+(img.h*(W-2*bl)/img.w)),3,0) ; omg.u = rescale(img.u,img.w,img.h,omg.w,omg.h,img.ncol) ; printf("downsampling png by %.2fx\n",img.w/(double) omg.w) ; h = (H-spine-2*bleed)/2 ; // this is the original value bt = (h-omg.h) / 2 ; for(k=3*omg.w*omg.h,i=0;i<omg.h;i++) for(j=0;j<3*omg.w;j+=3,k-=3) { r[bt+i][3*bl+j] = omg.u[k-3] ; r[bt+i][3*bl+j+1] = omg.u[k-2] ; r[bt+i][3*bl+j+2] = omg.u[k-1] ; } free(img.u,omg.u) ; // border for(i=0;i<dpmm;i++) for(j=0;j<3*(omg.w+2*dpmm);j+=3) { r[bt-dpmm+i][3*(bl-dpmm)+j] = bg[0][0] ; r[bt-dpmm+i][3*(bl-dpmm)+j+1] = bg[0][1] ; r[bt-dpmm+i][3*(bl-dpmm)+j+2] = bg[0][2] ; } for(i=0;i<dpmm;i++) for(j=0;j<3*(omg.w+2*dpmm);j+=3) { r[bt+omg.h+i][3*(bl-dpmm)+j] = bg[0][0] ; r[bt+omg.h+i][3*(bl-dpmm)+j+1] = bg[0][1] ; r[bt+omg.h+i][3*(bl-dpmm)+j+2] = bg[0][2] ; } for(i=bt-dpmm;i<bt+omg.h+dpmm;i++) for(j=bl-dpmm;j<bl;j++) { r[i][3*j] = bg[0][0] ; r[i][3*j+1] = bg[0][1] ; r[i][3*j+2] = bg[0][2] ; } for(i=bt-dpmm;i<bt+omg.h+dpmm;i++) for(j=bl+omg.w;j<bl+omg.w+dpmm;j++) { r[i][3*j] = bg[0][0] ; r[i][3*j+1] = bg[0][1] ; r[i][3*j+2] = bg[0][2] ; } /* ----------------------------- adjoining maps --------------------------- */ for(fracno=0;fracno<nvfrac;fracno++) if(vfrac[fracno]>0&&vfrac[fracno]<1) { k = (int) ( 0.5 + (1-vfrac[fracno])*omg.h ) ; for(i=bt+k-2;i<bt+k+2;i++) for(j=3*bl;j<3*(bl+omg.w);j+=3) { r[i][j] = fg[2][0] ; r[i][j+1] = fg[2][1] ; r[i][j+2] = fg[2][2] ; } } for(fracno=0;fracno<nhfrac;fracno++) if(hfrac[fracno]>0&&hfrac[fracno]<1) { k = (int) ( 0.5 + (1-hfrac[fracno])*omg.w ) ; for(i=bt;i<bt+omg.h;i++) for(j=3*(bl+k-2);j<3*(bl+k+2);j+=3) { r[i][j] = fg[2][0] ; r[i][j+1] = fg[2][1] ; r[i][j+2] = fg[2][2] ; } } sft.xScale = sft.yScale = fontsize[2] ; if(nhfrac>0&&nvfrac>0) for(t1=mapno=0;mapno<9;mapno++) { if(mapno%3==0) t0 = t1 ; if(mapno/3==0) t1 = (int) (0.5+vfrac[0]*omg.h) ; else if(mapno/3==1) t1 = (int) (0.5+vfrac[1]*omg.h) ; else t1 = omg.h ; if(0==mapno%3) { l0 = 0 ; l1 = (int) (0.5+hfrac[0]*omg.w) ; } else if(1==mapno%3) { l0 = (int) (0.5+hfrac[0]*omg.w) ; l1 = (int) (0.5+hfrac[1]*omg.w) ; } else { l0 = (int) (0.5+hfrac[1]*omg.w) ; l1 = omg.w ; } for(i=0;i<nmap[mapno];i++) { len = strtoint(map[mapno][i],istr) ; genglyphs(&sft,istr,len,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; k = pixlen(glyphmetrics,len) ; y = H - bt - omg.h + (t0+t1)/2 ; if(nmap[mapno]==1) y += fontsize[2]/2 ; else if(i==0) y -= fontsize[2]/8 ; // fontsize[2]/8 line sep else y += fontsize[2] + fontsize[2]/8 ; inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,len,bl+(l0+l1-k)/2,y,fg[2],r,W,H,1) ; for(j=0;j<len;j++) free(glyphim[j].pixels) ; } } /* ------------------------------- small print ---------------------------- */ sft.xScale = sft.yScale = fontsize[1] ; if(scale) { caption[3] = charvector(50) ; snprintf(caption[3],49,"Scale 1:%d",scale) ; } for(i=0;i<4;i++) if(caption[i]&&strlen(caption[i])) { len = strtoint(caption[i],istr) ; genglyphs(&sft,istr,len,glyph,glyphmetrics,glyphim) ; if(i==3&&scale>=10000) glyphmetrics[len-4].advanceWidth += fontsize[1]/6 ; k = pixlen(glyphmetrics,len) ; if(i==3) { y = H - bleed - 5*dpmm ; inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,len,W-bleed-5*dpmm-k,y,fg[1],r,W,H,0) ; } else { y = H - bleed - 5*dpmm - (fontsize[1]+fontsize[1]/4)*(2-i) ; inscribe(glyphmetrics,glyphim,len,W-bleed-5*dpmm-k,y,fg[1],r,W,H,1) ; } for(j=0;j<len;j++) free(glyphim[j].pixels) ; } /* ------------------------------- page guides ---------------------------- */ for(i=0;i<4;i++) { if(i==0) y = bleed ; else if(i==1) y = h + bleed ; else if(i==2) y = h + spine + bleed ; else y = 2*h + spine + bleed ; for(j=0;j<bleed/2;j++) for(k=0;k<3;k++) r[y-1][3*j+k] = r[y][3*j+k] = r[y-1][3*(W-j)-k-1] = r[y][3*(W-j)-k-1] = fg[1][k] ; } for(i=0;i<2;i++) { if(i==0) x = bleed ; else x = w + bleed ; for(j=0;j<bleed/2;j++) for(k=0;k<3;k++) r[j][3*(x-1)+k] = r[j][3*x+k] = r[H-1-j][3*(x-1)+k] = r[H-1-j][3*x+k] = fg[1][k] ; } /* ------------------------------ write the map --------------------------- */ ofl = fopenwrite(argv[2]) ; ctx = spng_ctx_new(SPNG_CTX_ENCODER) ; spng_set_png_file(ctx,ofl) ; for(i=0;i<sizeof(spng_ihdr);i++) ((uchar *)(&ihdr))[i] = 0 ; ihdr.width = W ; ihdr.height = H ; ihdr.color_type = 2 ; ihdr.bit_depth = 8 ; spng_set_ihdr(ctx,&ihdr) ; pixelres.ppu_x = pixelres.ppu_y = 1000*dpmm ; pixelres.unit_specifier = 1 ; // dpm spng_set_phys(ctx,&pixelres) ; if((i=spng_encode_image(ctx,0,0,SPNG_FMT_PNG,SPNG_ENCODE_PROGRESSIVE))) throw up("progressive spng_encode_image error: %s",spng_strerror(i)) ; for(i=0;i<H;i++) if(spng_encode_row(ctx,r[i],3*W)&&i<H-1) throw up("write failure on row %d",i) ; spng_encode_chunks(ctx) ; fclose(ofl) ; } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ void jo_write_jpg(const char *,const void *,int,int,int,int) { ; } // dummy
• max • min • cjcup • cjcuplog • cjcformat • cjcprint2 • cjcprint1 • complex • print • xy • print • xi • ij • settable • unset • double • print • free • cjcupalloc • cjcuprealloc • swap • freename • charvector • xivector • isortup • realsort • realsortdown • xysort • xisort • ijsort • xisortdown • fupopenread • fupopenwrite • freadline • readline
#ifndef MEMORY_H #define MEMORY_H #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdarg.h> static double max(double a,double b) { if(a>b) return a ; else return b ; } static double min(double a,double b) { if(a<b) return a ; else return b ; } static double max(double a,int b) { if(a>b) return a ; else return b ; } static double min(double a,int b) { if(a<b) return a ; else return b ; } static double max(int a,double b) { if(a>b) return a ; else return b ; } static double min(int a,double b) { if(a<b) return a ; else return b ; } static int max(int a,int b) { if(a>b) return a ; else return b ; } static int min(int a,int b) { if(a<b) return a ; else return b ; } #define abnormal(x) (!!((x)-(x))) // x-x forced to boolean /* ---------------------------- define throwing up -------------------------- */ static int cjcupline=-1,cjcperror=0 ; static const char *cjcupfile="",*cjcupfunc="" ; static int cjcup(const char *m,...) { va_list vl ; fprintf(stderr,"*** Error at line %d of %s [function %s]:\n", cjcupline,cjcupfile,cjcupfunc) ; if(cjcperror) perror(0) ; va_start(vl,m) ; vfprintf(stderr,m,vl) ; va_end(vl) ; fprintf(stderr,"\n") ; fflush(0) ; return 0 ; } ; static void cjcuplog(const char *f,int l,const char *ff) { cjcupfile = f ; cjcupline = l ; cjcupfunc = ff ; } #define up (cjcuplog(__FILE__,__LINE__,__PRETTY_FUNCTION__),cjcup) /* -------------------------- simple ordered pairs -------------------------- */ static char cjcbuf[600]={0} ; static int cjcind = 40 , cjcint = 0 ; static void cjcformat(char *fmt) { int i ; if(strlen(fmt)>18) throw up("overlong cjcprint format %s") ; strcpy(cjcbuf,fmt) ; for(i=0;fmt[i]&&fmt[i]!='%';i++) ; for(;fmt[i]&&(fmt[i]=='l'||(fmt[i]<'a'||fmt[i]>'z'));i++) ; cjcint = (fmt[i]=='d') ; } static char *cjcprint2(double x,double y) { if(cjcbuf[0]==0) cjcformat((char *)"%.1f") ; char *ptr = cjcbuf + cjcind ; cjcbuf[cjcind] = '(' ; if(cjcint) cjcind += 2 + snprintf(cjcbuf+cjcind+1,100,cjcbuf,(int)x) ; else cjcind += 2 + snprintf(cjcbuf+cjcind+1,100,cjcbuf,x) ; cjcbuf[cjcind-1] = ',' ; if(cjcint) cjcind += 2 + snprintf(cjcbuf+cjcind,100,cjcbuf,(int)y) ; else cjcind += 2 + snprintf(cjcbuf+cjcind,100,cjcbuf,y) ; cjcbuf[cjcind-2] = ')' ; cjcbuf[cjcind-1] = 0 ; if(cjcind>600) throw up("data overflow on printing an ordered pair") ; if(cjcind>500) cjcind = 40 ; return ptr ; } static char *cjcprint2(char *fmt,double x,double y) { cjcformat(fmt) ; return cjcprint2(x,y) ; } static char *cjcprint1(double x) { if(cjcbuf[0]==0) cjcformat((char *)"%.1f") ; char *ptr = cjcbuf + cjcind ; if(cjcint) cjcind += 1 + snprintf(cjcbuf+cjcind,100,cjcbuf,(int)x) ; else cjcind += 1 + snprintf(cjcbuf+cjcind,100,cjcbuf,x) ; if(cjcind>600) throw up("data overflow on printing") ; if(cjcind>500) cjcind = 40 ; return ptr ; } static char *cjcprint1(char *fmt,double x) { cjcformat(fmt) ; return cjcprint1(x) ; } struct complex { double re,im ; complex() { re = im = 0 ; } complex(double x) { re = x ; im = 0 ; } complex(double x,double y) { re = x ; im = y ; } complex &operator=(double x) { re = x ; im = 0 ; return *this ; } char *print(char *fmt) { return cjcprint2(fmt,re,im) ; } char *print() { return cjcprint2(re,im) ; } } ; struct xy { double x,y ; xy() { x = y = 0 ; } xy(double xx) { x = xx ; y = 0 ; } xy(double xx,double yy) { x = xx ; y = yy ; } xy(double xx,double(*f)(double)) { x = xx ; y = f(x) ; } xy &operator=(double xx) { x = xx ; y = 0 ; return *this ; } char *print(char *fmt) { return cjcprint2(fmt,x,y) ; } char *print() { return cjcprint2(x,y) ; } } ; inline bool operator==(xy a,xy b) { return a.x==b.x&&a.y==b.y ; } struct xi { double x ; int i ; xi() { x = i = 0 ; } xi(double a,int b) { x = a ; i = b ; } } ; struct ij { int i,j ; ij() { j = i = 0 ; } ij(int a,int b) { i = a ; j = b ; } } ; /* --------------------------------- settables ------------------------------ */ struct settable { private: double x ; public: bool set ; settable() { set = 0 ; } settable(double y) { if(abnormal(y)) throw up("setting a settable to %.1e",y) ; set = 1 ; x = y ; } settable unset() { return this[0] = settable() ; } operator double() { if(!set) throw up("accessing an unset settable") ; return x ; } settable &operator=(double y) { if(abnormal(y)) throw up("assigning %.1e to a settable",y) ; set = 1 ; x = y ; return *this ; } char *print() { if(set) return cjcprint1(x) ; char *ptr=cjcbuf+cjcind ; strcpy(ptr,"undef") ; cjcind += 6 ; if(cjcind>500) cjcind = 40 ; return ptr ; } char *print(char *fmt) { cjcformat(fmt) ; return print() ; } } ; inline bool operator==(settable x,settable y) { return (x.set==0&&y.set==0)||((double)x)==(double(y)) ; } inline bool operator==(settable x,double y) { return x.set && y==(double)x ; } inline bool operator==(double x,settable y) { return (y==x) ; } inline bool operator!=(settable x,settable y) { return !(x==y) ; } inline settable operator+=(settable &x,double y) { if(!x.set) throw up("incrementing an unset settable") ; return x = settable(x+y) ; } inline settable operator-=(settable &x,double y) { if(!x.set) throw up("decrementing an unset settable") ; return x = settable(x-y) ; } inline settable operator*=(settable &x,double y) { if(y==0) return x = settable(0) ; if(!x.set) throw up("*= applied to an unset settable") ; return x = settable(x*y) ; } inline settable operator/=(settable &x,double y) { if(y==0) throw up("settable divided by 0") ; if(!x.set) throw up("/= applied to an unset settable") ; return x = settable(x/y) ; } inline settable max(settable a,settable b) { if(a.set&&(!b.set||a>b)) return a ; else return b ; } inline settable min(settable a,settable b) { if(a.set&&(!b.set||a<b)) return a ; else return b ; } inline settable max(settable a,double b) { if(a.set&&a>b) return a ; else return b ; } inline settable min(settable a,double b) { if(a.set&&a<b) return a ; else return b ; } inline settable max(double a,settable b) { if(b.set&&b>a) return b ; else return a ; } inline settable min(double a,settable b) { if(b.set&&b<a) return b ; else return a ; } inline settable max(settable a,int b) { if(a.set&&a>b) return a ; else return b ; } inline settable min(settable a,int b) { if(a.set&&a<b) return a ; else return b ; } inline settable max(int a,settable b) { if(b.set&&b>a) return b ; else return a ; } inline settable min(int a,settable b) { if(b.set&&b<a) return b ; else return a ; } /* ------------------------------ variadic free() --------------------------- */ static void free(void *a,void *b) { free(a) ; free(b) ; } static void free(void *a,void *b,void *c) { free(a) ; free(b) ; free(c) ; } static void free(void *a,void *b,void *c,void *d) { free(a) ; free(b) ; free(c) ; free(d) ; } static void free(void *a,void *b,void *c,void *d,void *e) { free(a) ; free(b) ; free(c) ; free(d) ; free(e) ; } static void free(void *a,void *b,void *c,void *d,void *e,void *f) { free(a) ; free(b) ; free(c) ; free(d) ; free(e) ; free(f) ; } static void free(void *a,void *b,void *c,void *d,void *e,void *f,void *g) { free(a) ; free(b) ; free(c) ; free(d) ; free(e) ; free(f) ; free(g) ; } static void free(void *a,void *b,void *c,void *d, void *e,void *f,void *g,void *h) { free(a) ; free(b) ; free(c) ; free(d) ; free(e) ; free(f) ; free(g) ; free(h) ; } /* ------------------------- robust allocs ---------------------------- */ static void *cjcupalloc(int a,int b) { if(a<0||b<0) throw cjcup("negative length %d requested from cjcalloc.",a*b) ; void *p=calloc(a,b) ; if(p==0) throw cjcup("cjcalloc unable to allocate %d bytes of memory.",b) ; memset(p,0,a*b) ; return p ; } static void *cjcuprealloc(void *a,int b) { if(b<0) throw cjcup("negative length %d requested from cjcrealloc.",b) ; if(a==0&&b==0) return 0 ; void *p=realloc(a,b) ; if(b>0&&p==0) throw cjcup("cjcrealloc unable to reallocate %x to %d bytes.",a,b) ; return p ; } #define cjcalloc (cjcuplog(__FILE__,__LINE__,__PRETTY_FUNCTION__),cjcupalloc) #define cjcrealloc (cjcuplog(__FILE__,__LINE__,__PRETTY_FUNCTION__),cjcuprealloc) /* ---------------------------- generic matrix ------------------------------ */ #define genvector(type,vecname) \ static type *vecname(int n) \ { return (type*) cjcalloc(n,sizeof(type)) ; } \ static type *vecname(type *x,int n) \ { return (type *) cjcrealloc(x,n*sizeof(type)) ; } \ static void swap(type &a,type &b) { type c=b ; b = a ; a = c ; } #define genmatrix(type,vecname,name,freename) \ static type *vecname(int n) \ { return (type*) cjcalloc(n,sizeof(type)) ; } \ static type *vecname(type *x,int n) \ { return (type *) cjcrealloc(x,n*sizeof(type)) ; } \ static type **name(int m,int n) \ { type **a = (type **) cjcalloc(m,sizeof(type *)) ; \ a[0] = vecname(m*n) ; \ for(int i=1;i<m;i++) a[i] = a[i-1] + n ; \ return a ; \ } \ static type ***name(int m,int n,int l) \ { int i ; \ type ***a = (type ***) cjcalloc(m,sizeof(type **)) ; \ a[0] = (type **) cjcalloc(m*n,sizeof(type *)) ; \ for(i=1;i<m;i++) a[i] = a[i-1] + n ; \ a[0][0] = vecname(m*n*l) ; \ for(i=1;i<m*n;i++) a[0][i] = a[0][i-1] + l ; \ return a ; \ } \ static void freename(type **a) { if(a) free(a[0],a) ; } \ static void freename(type **a,type **b) \ { freename(a) ; freename(b) ; } \ static void freename(type **a,type **b,type **c) \ { freename(a) ; freename(b) ; freename(c) ; } \ static void freename(type **a,type **b,type **c,type **d) \ { freename(a) ; freename(b) ; freename(c) ; freename(d) ; } \ static void freename(type **a,type **b,type **c,type **d, \ type **e) \ { freename(a) ; freename(b) ; freename(c) ; freename(d) ; \ freename(e) ; } \ static void freename(type **a,type **b,type **c,type **d, \ type **e,type **f) \ { freename(a) ; freename(b) ; freename(c) ; freename(d) ; \ freename(e) ; freename(f) ; } \ static void freename(type ***a) { if(a) free(a[0][0],a[0],a) ; } \ static void swap(type &a,type &b) { type c=b ; b = a ; a = c ; } /* --------------------------- matrix instances ----------------------------- */ genmatrix(double,vector,matrix,freematrix) ; genmatrix(int,ivector,imatrix,freeimatrix) ; genmatrix(xi,xivector,ximatrix,freeximatrix) ; genmatrix(ij,ijvector,ijmatrix,freeijmatrix) ; genmatrix(xy,xyvector,xymatrix,freexymatrix) ; genmatrix(char,charvector,charmatrix,freecharmatrix) ; genmatrix(char*,strvector,strmatrix,freestrmatrix) ; genmatrix(short,shortvector,shortmatrix,freeshortmatrix) ; genmatrix(complex,cvector,cmatrix,freecmatrix) ; genmatrix(settable,setvector,setmatrix,freesetmatrix) ; // a couple of specials static char *charvector(char *c) { char *ret=charvector(1+strlen(c)) ; strcpy(ret,c) ; return ret ; } static xi *xivector(double *x,int n) { xi *y=xivector(n) ; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) y[i] = xi(x[i],i) ; return y ; } /* ----------------------------- generic sorts ------------------------------ */ #define shellsortup(x,n,type,field) \ { int i,j,inc ; type y ; \ for(inc=1;1+3*inc<(n);inc=1+3*inc) ; \ for(;inc>0;inc/=3) for(i=inc;i<(n);i++) \ { for(y=x[i],j=i;j>=inc;j-=inc) \ { if(y.field<x[j-inc].field) x[j] = x[j-inc] ; else break ; } \ x[j] = y ; \ } \ } #define shellsortdown(x,n,type,field) \ { int i,j,inc ; type y ; \ for(inc=1;1+3*inc<(n);inc=1+3*inc) ; \ for(;inc>0;inc/=3) for(i=inc;i<(n);i++) \ { for(y=x[i],j=i;j>=inc;j-=inc) \ { if(y.field>x[j-inc].field) x[j] = x[j-inc] ; else break ; } \ x[j] = y ; \ } \ } #define shsortup(x,n,type) \ { int i,j,inc ; type y ; \ for(inc=1;1+3*inc<(n);inc=1+3*inc) ; \ for(;inc>0;inc/=3) for(i=inc;i<(n);i++) \ { for(y=x[i],j=i;j>=inc;j-=inc) \ { if(y<x[j-inc]) x[j] = x[j-inc] ; else break ; } \ x[j] = y ; \ } \ } #define shsortdown(x,n,type) \ { int i,j,inc ; type y ; \ for(inc=1;1+3*inc<(n);inc=1+3*inc) ; \ for(;inc>0;inc/=3) for(i=inc;i<(n);i++) \ { for(y=x[i],j=i;j>=inc;j-=inc) \ { if(y>x[j-inc]) x[j] = x[j-inc] ; else break ; } \ x[j] = y ; \ } \ } /* ----------------------------- sundry sorts ------------------------------- */ static void isortup(int *u,int n) { shsortup(u,n,int) ; } static void realsort(double *u,int n) { shsortup(u,n,double) ; } static void realsortdown(double *u,int n) { shsortdown(u,n,double) ; } static void xysort(xy *u,int n) { shellsortup(u,n,xy,x) ; } static void xisort(xi *u,int n) { shellsortup(u,n,xi,x) ; } static void ijsort(ij *u,int n) { shellsortup(u,n,ij,i) ; } static void xisortdown(xi *u,int n) { shellsortdown(u,n,xi,x) ; } /* -------------------------- define robust fopens -------------------------- */ static FILE *fupopenread(char *name) { FILE *f ; if(name[0]=='-'&&name[1]=='-'&&name[2]==0) f = stdin ; else f = fopen(name,"r") ; if(f==0) { cjcperror = 1 ; throw cjcup("Your input file %s could not be found.",name) ; } return f ; } static FILE *fupopenwrite(char *name) { FILE *f ; if(name[0]=='-'&&name[1]=='-'&&name[2]==0) f = stdout ; else f = fopen(name,"w") ; if(f==0) { cjcperror = 1 ; throw cjcup("Unable to write to your file %s.",name) ; } return f ; } #define fopenread (cjcuplog(__FILE__,__LINE__,__PRETTY_FUNCTION__),fupopenread) #define fopenwrite (cjcuplog(__FILE__,__LINE__,__PRETTY_FUNCTION__),fupopenwrite) static char *freadline(FILE *ifl) { char *s=0 ; int slen,ns,c,i ; for(slen=ns=0;;) { c = fgetc(ifl) ; if(c==EOF||c=='\n') { if(slen>ns+1||(ns==0&&c=='\n')) s = charvector(s,ns+1) ; return s ; } if(ns>=slen-1) { slen += 20 + slen/2 ; s = charvector(s,slen) ; for(i=ns;i<slen;i++) s[i] = 0 ; } s[ns++] = (char) c ; } } static char *readline() { return freadline(stdin) ; } #endif
• lininterp • invlininterp • quadinterp • quadcoefs • quadslope • invquadinterp • quadreach • quadmax
static double lininterp(double x,xy A,xy B) { return A.y + (x-A.x)*(B.y-A.y)/(B.x-A.x) ; } static double invlininterp(double y,xy A,xy B) { return A.x + (y-A.y)*(B.x-A.x)/(B.y-A.y) ; } /* ------------------------------ quadinterp -------------------------------- */ // if a parabola takes values a,b,c at -1,0,1, then quadinterp returns // its value at x static double quadinterp(double x,double a,double b,double c) { return ( x*(x-1)*a - 2*(x+1)*(x-1)*b + x*(x+1)*c ) / 2 ; } static double quadinterp(double x,xy A,xy B,xy C) { double y,lam,mindif,c[2],d[2] ; int ind; if(A.x==B.x||B.x==C.x||A.x==C.x) throw up("two of the ordinates " "for quadinterp are equal: %.3f, %.3f, %.3f",A.x,B.x,C.x) ; ind = 0 ; mindif = fabs(x-A.x) ; y = A.y ; if(fabs(x-B.x)<mindif) { ind = 1 ; mindif = fabs(x-B.x) ; y = B.y ; } if(fabs(x-C.x)<mindif) { ind = 2 ; mindif = fabs(x-C.x) ; y = C.y ; } lam = (B.y-A.y) / (A.x-B.x) ; d[0] = (B.x-x) * lam ; c[0] = (A.x-x) * lam ; lam = (C.y-B.y) / (B.x-C.x) ; d[1] = (C.x-x) * lam ; c[1] = (B.x-x) * lam ; if(ind==0) y += c[0] ; else { ind -= 1 ; y += d[ind] ; } lam = (c[1]-d[0]) / (A.x-C.x) ; if(ind==0) y += (A.x-x)*lam ; else y += (C.x-x)*lam ; return y ; } static double quadinterp(double x,double *co) { return co[0] + x*(co[1]+x*co[2]) ; } /* ------------------------------- quadcoefs -------------------------------- */ static void quadcoefs(xy A,xy B,xy C,double *co) { int i,j ; double p[] = { A.x*B.x*C.x , -(A.x*B.x+A.x*C.x+B.x*C.x) , A.x+B.x+C.x } ; double q,u ; if(A.x==B.x||B.x==C.x||A.x==C.x) throw up("two of the ordinates " "for quadcoefs are equal: %.3f, %.3f, %.3f",A.x,B.x,C.x) ; for(q=3,j=2;j>0;j--) q = q*A.x - j*p[j] ; q = A.y / q ; for(u=1,j=2;j>=0;j--) { co[j] = u*q ; u = u*A.x - p[j] ; } for(q=3,j=2;j>0;j--) q = q*B.x - j*p[j] ; q = B.y / q ; for(u=1,j=2;j>=0;j--) { co[j] += u*q ; u = u*B.x - p[j] ; } for(q=3,j=2;j>0;j--) q = q*C.x - j*p[j] ; q = C.y / q ; for(u=1,j=2;j>=0;j--) { co[j] += u*q ; u = u*C.x - p[j] ; } } // linear embedded in a quadratic static void quadcoefs(xy A,xy B,double *co) { if(A.x==B.x) throw up("the ordinates for quadcoefs are equal: %.3e",A.x) ; co[2] = 0 ; co[1] = (B.y-A.y) / (B.x-A.x) ; co[0] = A.y - co[1]*A.x ; } static void quadcoefs(double a,double b,double c,double *co) { return quadcoefs(xy(-1,a),xy(0,b),xy(1,c),co) ; } // value at one point and value and gradient at a second static void quadcoefs(double x,double y,double dy,xy A,double *co) { if(A.x==x) throw up("equal ordinates supplied to quadcoefs: %.3f, %.3f",A.x,x) ; A = xy(A.x-x,A.y-y) ; co[2] = (A.y-dy*A.x) / (A.x*A.x) ; co[1] = dy - 2*x*co[2] ; co[0] = y - dy*x + co[2]*x*x ; } // two points and gradient at a third ordinate - not well conditioned static void quadcoefs(xy A,xy B,double x,double dy,double *co) { if(A.x==B.x||A.x==x||B.x==x) throw up("two of the ordinates " "for quadcoefs are equal: %.3f, %.3f, %.3f",A.x,B.x,x) ; co[2] = ( (B.y-A.y)/(B.x-A.x) ) ; co[2] = ( (B.y-A.y)/(B.x-A.x) - dy ) / ( (A.x-x)+(B.x-x) ) ; co[1] = dy - 2*co[2]*x ; co[0] = A.y - co[1]*A.x - co[2]*A.x*A.x ; } /* ------------------------------- quadslope -------------------------------- */ // if a parabola takes values a,b,c at -1,0,1, then quadslope returns // its gradient at x static double quadslope(double x,double a,double b,double c) { return ( (2*x-1)*a - 4*x*b + (2*x+1)*c ) / 2 ; } static double quadslope(double x,double *co) { return co[1]+2*x*co[2] ; } static double quadslope(double x,xy A,xy B,xy C) { double co[3] ; quadcoefs(A,B,C,co) ; return quadslope(x,co) ; } /* -------------------------- invquadinterp --------------------------------- */ // if a parabola takes values a,b,c at -1,0,1, then invquadinterp // returns the argument x such the parabola's value at x is y // (and given that there are two such, it chooses the one closer to 0) static double invquadinterp(double y,double a,double b,double c) { double t=b-y,u=(a-c)/4,v=(a-2*b+c)/2,q ; if(v==0) return (2*y-(c+a))/(c-a) ; q = u*u - t*v ; if(q<0) throw up("parabola through (%.2f,%.2f,%.2f) doesn\'t reach %.2f",a,b,c,y) ; q = sqrt(q) ; if(u>0) q = u + q ; else q = u - q ; if(q*q<fabs(t*v)) return q/v ; else return t/q ; } static double invquadinterp(double y,xy A,xy B,xy C) { double co[3],q,t,u,v,xmin=A.x,xmax=A.x ; quadcoefs(A,B,C,co) ; t = co[0] - y ; u = -co[1]/2 ; v = co[2] ; if(v==0) return -t/co[1] ; q = u*u - t*v ; if(q<0) throw up("parabola doesn\'t reach %.2f",y) ; q = sqrt(q) ; if(u>0) q = u + q ; else q = u - q ; if(B.x<xmin) xmin = B.x ; else if(B.x>xmax) xmax = B.x ; if(C.x<xmin) xmin = C.x ; else if(C.x>xmax) xmax = C.x ; u = q * v * (xmin+xmax) / 2 ; if(fabs(q*q-u)<fabs(t*v-u)) return q/v ; else return t/q ; } static xy invquadinterp(double y,double *co) { double q,t,u,v ; if(co[2]==0) { if(co[1]==0) throw up("invquadinterp called on constant quadratic %.2e",co[0]) ; q = (y-co[0]) / co[1] ; return xy(q,q) ; } t = co[0] - y ; u = -co[1]/2 ; v = co[2] ; if(v==0) { v = -t/co[1] ; return xy(v,v) ; } q = u*u - t*v ; if(q<0) throw up("parabola doesn\'t reach %.2e",y) ; q = sqrt(q) ; if(u>0) q = u + q ; else q = u - q ; if(q/v<t/q) return xy(q/v,t/q) ; else return xy(t/q,q/v) ; } static double invquadinterp(double y,double *co,double flag) { xy Z = invquadinterp(y,co) ; return (flag>=0)?Z.y:Z.x ; } /* -------------------------------- quadreach ------------------------------- */ // if a parabola takes values a,b,c at -1,0,1, then quadreach // returns 1 if it ever reaches the value y, and 0 otherwise static int quadreach(double y,double *coef) { if(coef[2]==0) return (coef[1]!=0) ; else return coef[1]*coef[1] >= 4*(coef[0]-y)*coef[2] ; } static int quadreach(double y,xy A,xy B,xy C) { double coef[3] ; quadcoefs(A,B,C,coef) ; return quadreach(y,coef) ; } static int quadreach(double y,double a,double b,double c) { return quadreach(y,xy(-1,a),xy(0,b),xy(1,c)) ; } /* --------------------------------- quadmax -------------------------------- */ // if a parabola takes values a,b,c at -1,0,1, then quadmax returns // the (x,y) values at its turning point (which may be a min or a max) static xy quadmax(double a,double b,double c) { double u=(a-c)/4,v=(a+c-2*b)/2 ; return xy(u/v,b-u*u/v) ; } static xy quadmax(xy A,xy B,xy C) { double co[3],t,u,v,x ; quadcoefs(A,B,C,co) ; t = co[0] ; u = -co[1]/2 ; v = co[2] ; x = u/v ; return xy(x,t+x*(v*x-2*u)) ; } static xy quadmax(double *co) { double t,u,v,x ; if(co[2]==0) throw up("quadmax called for a linear quadratic") ; t = co[0] ; u = -co[1]/2 ; v = co[2] ; x = u/v ; return xy(x,t+x*(v*x-2*u)) ; }
• parmimg • take • close • release • print • add • advance • parmkey • print • release • take • print • pathcat • nestitem • release • nestlist • add • subtract • munchline • munchgetparms • munchparmkey • munchpushlist • munchpoplist • munchsetlist • munchreadparms • getparmkey • getkparms • getparms • getfnparms • getmatparms • getparm • getfnparm • getaparm • munchparmloc
#include <ctype.h>
#include "memory.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "munchparms.h"
#ifndef DOS
#define DIRSEPARATOR '/'
#define DIRCURRENT "/./"
#define DIRPARENT "/../"
#else
#define DIRSEPARATOR '\\'
#define DIRCURRENT "\\.\\"
#define DIRPARENT "\\..\\"
#endif
#define extend(a,val,n,len) \
{ if(n>=len) \
{ len += 10 + len/2 ; a = (typeof a) cjcrealloc(a,len*sizeof(a[0])) ; } \
a[n++] = val ; \
}
/* ------------------------- parmimg methods ------------------------ */
parmimg::parmimg(char *img)
{ this[0] = parmimg() ; nbuf = strlen(buf=charvector(img)) ; }
void parmimg::take(char c) { extend(buf,c,nbuf,buflen) ; }
void parmimg::close()
{ take(0) ; buf = charvector(buf,buflen=nbuf) ; nbuf -= 1 ; }
void parmimg::release()
{ for(int i=0;i<nloc;i++) free(loc[i].file) ;
free(buf,loc) ;
this[0] = parmimg() ;
}
void parmimg::print()
{ for(int i=0;i<nloc;i++) // loop through nested includes
{ if(loc[i].file) printf("file=%s",loc[i].file) ; else printf("--") ;
printf(" line=%d: text begins: ",loc[i].lineno) ;
for(int pos=loc[i].start;pos<loc[i].start+20&&pos<nbuf;pos++)
{ if(i<nloc-1&&pos==loc[i+1].start) break ;
if(buf[pos]=='\n') printf("\n ") ; else printf("%c",buf[pos]) ;
}
printf("\n") ;
}
}
int parmimg::add(char *s,int st,int ln)
{ if(nloc==0||st>loc[nloc-1].start) extend(loc,parmloc(),nloc,loclen) ;
free(loc[nloc-1].file) ;
loc[nloc-1] = parmloc(charvector(s),st,ln) ;
return nloc-1 ;
}
/* this advances the pointer ind through buf until it finds the
start of a @keyword (or end of buffer), returning the character
pointed to, which will be either '@' or null. */
int parmimg::advance()
{ if(ind>=nbuf-1) return ind = nbuf ;
for(;ind<nbuf&&(buf[ind]!='@'||(ind>0&&buf[ind-1]!='\n'));ind++)
{ if(iloc<nloc-1&&ind==loc[iloc+1].start)
{ iloc += 1 ;
curl = loc[iloc].lineno ;
curf = loc[iloc].file ;
}
if(buf[ind]=='\n') curl += 1 ;
}
if(ind==nbuf) return ind ; else { ind += 1 ; return ind-1 ; }
}
/* ------------------------- parmkey methods ------------------------ */
parmkey::parmkey(char *k,char *v)
{ this[0] = parmkey() ; key = charvector(k) ; dat = charvector(v) ; }
void parmkey::print()
{ if(key) printf("@%s",key) ; else printf("@") ;
if(dat) printf(" %s",dat) ;
printf(" (%s -- %s:%d)\n",used?"used":"unused",file?file:"--",lineno) ;
}
/* ------------------------ parmlist methods ------------------------ */
void parmlist::release()
{ for(int i=0;i<nk;i++) k[i].release() ;
free(k) ;
k = 0 ;
nk = klen = 0 ;
}
int parmlist::take(parmkey p)
{ if(p.key==0&&p.dat==0) return 0 ; extend(k,p,nk,klen) ; return 1 ; }
void parmlist::print()
{ printf("--- %d keywords\n",nk) ; for(int i=0;i<nk;i++) k[i].print() ; }
/* --------------------------- munchparms --------------------------- */
static char *pathcat(char *p,char *s)
{ int plen,slen=strlen(s),i ;
char *pend=0,*r ;
if(p) pend = strrchr(p,DIRSEPARATOR) ;
if(pend)
{ plen = (pend+1) -p ;
r = charvector(slen+plen+1) ;
strncpy(r,p,plen) ;
strcpy(r+plen,s) ;
}
else { r = charvector(slen+1) ; strcpy(r,s) ; }
// GRO any initial "./" and any medial "/./"
while(r[0]=='.'&&r[1]==DIRSEPARATOR) for(i=0;(r[i]=r[i+2]);i++) ;
while((p=strstr(r,DIRCURRENT))) for(i=0;(p[i]=p[i+2]);i++) ;
// GRO any medial "/../"
while((p=strstr(r,DIRPARENT)))
{ p[0] = 0 ;
if((s=strrchr(r,DIRSEPARATOR))==0) s = r ; else s += 1 ;
for(i=0;(s[i]=p[4+i]);i++) ;
}
return r ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
struct nestitem
{ char *file ; FILE *fid ; int lineno ;
nestitem() { file = 0 ; fid = 0 ; lineno = 0 ; }
nestitem(char *f1,FILE *f2,int l) { file = f1 ; fid = f2 ; lineno = l ; }
void release() { fclose(fid) ; free(file) ; }
} ;
struct nestlist
{ int nitem,maxitem ; nestitem *item ;
nestlist() { nitem = maxitem = 0 ; item = 0 ; }
void add(char *s)
{ char *file = pathcat(nitem?item[nitem-1].file:0,s) ;
extend(item,nestitem(file,fopenread(file),1),nitem,maxitem) ;
}
void subtract()
{ nitem -= 1 ;
item[nitem].release() ;
if(nitem==0) { free(item) ; maxitem = 0 ; item = 0 ; }
}
} ;
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
// munchline processes a line of a parameter file, expanding macros and
// stripping out comments
static char *munchline(char *buf,int n,parmlist *macro)
{ int i,j,k,quoted,end,nl=0,llen=0 ;
char *l=0 ;
for(quoted=i=0;i<n;i++)
{ extend(l,buf[i],nl,llen) ;
if(buf[i]=='\"') quoted = 1 - quoted ;
else if(buf[i]=='#'&"ed==0) { nl -= 1 ; break ; }
else if(buf[i]!='\n'&&isspace(buf[i])) l[nl-1] = ' ' ;
else if( quoted==0 && macro && buf[i]=='$' && (i==0||isspace(buf[i-1])))
{ for(end=i+1;buf[end]&&isalnum(buf[end]);end++) ; // buf ends with '\n'
for(j=0;j<macro->nk;j++)
if(!strncmp(macro->k[j].key,buf+i+1,end-i-1)) break ;
if(j>=macro->nk) throw up("Undefined macro in\n%s",buf) ;
nl -= 1 ; // discard '$'
for(k=0;macro->k[j].dat[k];k++) extend(l,macro->k[j].dat[k],nl,llen) ;
macro->k[j].used = 1 ;
i = end-1 ;
}
}
if(quoted!=0) throw up("Mismatched \" in [%s].",buf) ;
if( n>0 && buf[0]=='@' && buf[1]!=0 && isspace(buf[1])!=0 )
throw up("Dangling \'@\' in %s\n",buf) ;
while(nl>0&&l[nl-1]==' ') l -= 1 ; // chop off terminating spaces
extend(l,0,nl,llen) ;
return l ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
// munchgetparms makes an image of the parameter file, actioning includes,
// expanding macros, and stripping out comments
parmimg munchgetparms(char *pfl,parmlist *macro)
{ int ind,end,ichar,i,j,k,np=0,plen=0 ;
char *p=0,*l ;
nestlist nest ;
parmimg pim ;
if(!pfl) throw up("null parmfile") ;
nest.add(pfl) ;
pim.add(pfl,0,1) ;
while(nest.nitem>0)
{ ichar = fgetc(nest.item[nest.nitem-1].fid) ;
if(ichar==EOF)
{ nest.subtract() ;
if(nest.nitem) pim.add(nest.item[nest.nitem-1].file,pim.nbuf,
nest.item[nest.nitem-1].lineno) ;
ichar = '\n' ;
}
extend(p,ichar,np,plen) ;
if(ichar!='\n'&&ichar!=EOF) continue ;
if(ichar=='\n'&&nest.nitem) nest.item[nest.nitem-1].lineno += 1 ;
// is it an #include line?
if(np>=9&&strncmp(p,"#include ",9)==0)
{ for(ind=9;p[ind]&&isspace(p[ind]);ind++) ;
if(!p[ind]) throw up("misformated #include line:\n%s",p) ;
// now at first nonspace
for(end=ind+1;p[end]&&!isspace(p[end]);end++) ;
p[end] = 0 ; // now at end or space - set NULL
nest.add(p+ind) ; // add filename
pim.add(nest.item[nest.nitem-1].file,pim.nbuf,
nest.item[nest.nitem-1].lineno) ;
}
else // now process a line of data in buf
{ l = munchline(p,np,macro) ;
k = strlen(l) ;
if(pim.buflen<k+pim.nbuf)
{ pim.buflen += pim.buflen/2 + 10*k ;
pim.buf = charvector(pim.buf,pim.buflen) ;
}
for(j=0;j<k;j++) pim.buf[pim.nbuf++] = l[j] ;
free(l) ;
}
np = 0 ;
}
free(p) ;
pim.close() ;
pim.curl = 1 ;
pim.curf = pim.loc[0].file ;
return pim ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
parmkey munchparmkey(parmimg *pim)
{ parmkey r ;
int i,quo,ind=pim->advance(),end,kind,cind,pind ;
if(pim->buf[ind]==0) return r ;
if(pim->ind!=1&&(pim->buf[ind]!='@'||pim->buf[ind-1]!='\n')) throw up
("munchparmkey called at an illegal position in parm image") ;
r.file = charvector(pim->curf) ;
r.lineno = pim->curl ;
end = pim->advance() ;
if(pim->buf[end]) pim->ind -= 1 ;
// ind now points to the '@' at the start of the keyword block
// and end to the '@' ending it
ind += 1 ; // now points to first char of kwd
for(kind=ind;
pim->buf[kind] && pim->buf[kind]!=' ' && pim->buf[kind]!='\n';
kind++) ;
if(kind==ind) throw up("Empty keyword") ;
r.key = charvector(1+kind-ind) ;
strncpy(r.key,pim->buf+ind,kind-ind) ;
for(cind=kind;cind<end&&isspace(pim->buf[cind]);cind++) ;
r.dat = charvector(1+end-cind) ;
for(i=0;cind<end;cind=1+kind)
{ for(kind=cind;kind<end&&pim->buf[kind]!='\n';kind++) ;
while(pim->buf[cind]==' '&&cind<kind) cind += 1 ;
for(quo=0,ind=kind,pind=cind;pind<kind;pind++)
{ if(pim->buf[pind]=='\"') quo = 1 - quo ;
else if(pim->buf[pind]=='#'&&quo==0) { ind = pind ; break ; }
}
if(quo!=0) throw up("unmatched quotation marks") ;
while(ind>cind&&pim->buf[ind-1]==' ') ind -= 1 ;
pim->buf[ind] = '\n' ;
strncpy(r.dat+i,pim->buf+cind,1+ind-cind) ;
i += 1+ind-cind ;
}
for(;i>0&&r.dat[i-1]=='\n';i--) r.dat[i-1] = 0 ;
return r ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
static parmlist *todayslist=0,**otherlist=0 ;
static parmkey *thiskey=0 ;
static int nother=0,otherlen=0 ;
void munchpushlist(parmlist *p)
{ if(todayslist) extend(otherlist,todayslist,nother,otherlen) ;
munchsetlist(p) ;
}
void munchpoplist()
{ if(nother<=0) throw up("popping an empty parmlist stack.") ;
nother -= 1 ;
todayslist = otherlist[nother] ;
if(nother==0) { otherlen = 0 ; free(otherlist) ; otherlist = 0 ; }
}
void munchsetlist(parmlist *p)
{ thiskey = 0 ;
if(p==0) { todayslist = 0 ; return ; }
else { for(int i=0;i<p->nk;i++) p->k[i].used = 0 ; todayslist = p ; }
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
parmlist *munchreadparms(char *file)
{ parmlist *parms = (parmlist *) cjcalloc(1,sizeof(parmlist)) ;
parms[0] = parmlist() ;
parmimg pim = munchgetparms(file,0) ;
while(parms->take(munchparmkey(&pim))) ;
munchsetlist(parms) ;
pim.release() ;
return parms ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
parmkey *getparmkey(char *k)
{ int i,klen,nk ;
char *key=0 ;
if(!todayslist) throw up("getparmblock called before munchsetlist\n") ;
parmkey *kk=todayslist->k ;
nk = todayslist->nk ;
if(k) key = charvector(k) ;
for(i=0;i<nk;i++) if(kk[i].used==0)
if(k==0||(kk[i].key&&strcmp(kk[i].key,key)==0)) break ;
free(key) ;
if(i==nk) return thiskey = 0 ;
else { kk[i].used = 1 ; return thiskey = kk+i ; }
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
static int getkparms(char **& p,parmkey *k) // line split by whitespace
{ int np,plen,i,j ;
char *q ;
if(k==0) return -1 ; else if(k->dat==0||k->dat[0]==0) return 0 ;
for(p=0,i=0,plen=np=0;k->dat[i];i=j)
{ while(k->dat[i]&&isspace(k->dat[i])) i++ ;
if(k->dat[i]==0) break ;
extend(p,0,np,plen) ;
if(k->dat[i]=='\"')
{ q = strchr(k->dat+i+1,'\"') ;
if(!q) throw up("unterminated \"quotes\":\n%s %s\n",k->key,k->dat) ;
j = q - k->dat ;
p[np-1] = charvector(j-i) ;
strncpy(p[np-1],k->dat+i+1,j-i-1) ;
j += 1 ;
}
else
{ for(j=i+1;k->dat[j]&&isspace(k->dat[j])==0;j++) ;
p[np-1] = charvector(j-i+1) ;
strncpy(p[np-1],k->dat+i,j-i) ;
}
}
return np ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* these are the routines to return an array of parameters */
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
int getparms(char **& p,char *key) // line split by whitespace
{ p = 0;
parmkey *k = getparmkey(key) ;
if(k==0) return -1 ; else return getkparms(p,k) ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
int getfnparms(char **& p,char *key)
{ int i,n=getparms(p,key) ;
char *r ;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ r = pathcat(thiskey->file,p[i]) ; free(p[i]) ; p[i] = r ; }
return n ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
#define genparms(ty,op) int getparms(ty *&p,char *key) \
{ char **pp ; \
int i,n=getparms(pp,key) ; \
if(n<=0) { p = 0 ; return n ; } \
p = (ty *) cjcalloc(n,sizeof(long)) ; \
for(i=0;i<n;i++) { p[i] = op(pp[i]) ; free(pp[i]) ; } \
free(pp) ; return n ; \
}
genparms(long,atol) ;
genparms(int,atoi) ;
genparms(double,atof) ;
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
int getmatparms(double **&p,char *key,int dim0)
{ char **pp ;
int i,n=getparms(pp,key),dim1 ;
if(n<=0) { p = 0 ; return n ; }
if(dim0>0) dim1 = n / dim0 ; else dim0 = dim1 = (int) sqrt(n) ;
if(n!=dim0*dim1) throw up("number of values supplied (%d) is not "
"a multiple of %d.",n,dim0) ;
p = matrix(dim0,dim1) ;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) { p[0][i] = atof(pp[i]) ; free(pp[i]) ; }
free(pp) ;
return n ;
}
int getmatparms(double **&p,char *key) { return getmatparms(p,key,0) ; }
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* these are the routines to return a single parameter */
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
void getparm(char *&val,char *key)
{ char **pp ;
int n=getparms(pp,key) ;
if(n<=0) throw up("no value supplied for %s",key) ;
if(n!=1) throw up("too many values supplied for %s",key) ;
val = pp[0] ;
free(pp) ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
#define genparm(ty,op) void getparm(ty &val,char *key) \
{ char *p ; getparm(p,key) ; val = op(p) ; free(p) ; }
genparm(int,atoi) ;
genparm(long,atol) ;
genparm(double,atof) ;
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
void getfnparm(char *&val,char *key)
{ char *s ;
getparm(val,key) ;
if(thiskey) s = pathcat(thiskey->file,val) ;
else s = pathcat(0,val) ;
free(val) ;
val = s ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* these are routines for a single parm allowed to default */
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
static int getaparm(char *&val,char *key)
{ char **pp ;
int n=getparms(pp,key) ;
if(n<=0) { val = 0 ; return n ; }
else if(n!=1) throw up("too many values supplied for %s",key) ;
val = pp[0] ;
free(pp) ;
return 1 ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
#define genaparm(ty,op) bool getparm(ty &val,char *key, ty def) \
{ char *p ; if(getaparm(p,key)>0) { val = op(p) ; free(p) ; return true ; } \
else { val = def ; return false ; } }
genaparm(double,atof) ;
genaparm(int,atoi) ;
genaparm(long,atol) ;
bool getparm(char *&val,char *key,char *def)
{ if(getaparm(val,key)>0) return true ;
if(def) val = charvector(def) ; else val = 0 ;
return false ;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* a simple existence test */
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
bool getparm(bool &val,char *key,bool def)
{ char *p ;
int resp = getaparm(p,key) ;
if(resp<0) { val = def ; return false ; }
else if(resp==0) { val = true ; return false ; }
if(strcmp(p,"true")==0) { val = true ; free(p) ; return true ; }
if(strcmp(p,"false")==0) { val = false ; free(p) ; return true ; }
if(strcmp(p,"true")!=0&&strcmp(p,"false")!=0)
throw up("invalid bool @%s %s\n",key,p) ;
return false;
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------ */
char *munchparmloc()
{ char *c ;
int flen ;
if(thiskey==0) return charvector(1) ;
if(thiskey->file==0)
{ c = charvector(20) ;
snprintf(c,19,"line %d",thiskey->lineno) ;
return c ;
}
flen = strlen(thiskey->file) ;
c = charvector(flen+20) ;
strcpy(c,thiskey->file) ;
snprintf(c+flen,flen+19,":%d",thiskey->lineno) ;
return c ;
}
• parmloc • parmimg • parmkey • release • parmlist
struct parmloc { char *file ; int start,lineno ; parmloc() { file = 0 ; start = lineno = 0 ; } parmloc(char *f,int s,int l) { file = f ; start = s ; lineno = l ; } } ; struct parmimg { char *buf,*curf ; parmloc *loc ; int nloc,loclen,ind,nbuf,buflen,curl,iloc ; parmimg() { buf = 0 ; loc = 0 ; nloc = loclen = nbuf = buflen = ind = iloc = 0 ; curf = (char *) "" ; curl = 1 ; } parmimg(char *img) ; int add(char *s,int st,int ln),advance() ; void take(char c),close(),release(),reloc(),print() ; } ; struct parmkey { char *dat,*key,*file ; int used,lineno ; parmkey() { dat = key = file = 0 ; used = 0 ; } parmkey(char *k,char *v) ; void print() ; void release() { free(dat,key,file) ; dat = key = file = 0 ; } } ; struct parmlist { parmkey *k ; int nk,klen ; parmlist() { k = 0 ; nk = klen = 0 ; } void release(),print() ; int take(parmkey p) ; } ; parmlist *munchreadparms(char *file),munchsubparms(parmkey *k) ; parmimg munchgetparms(char *pfl,parmlist *macro) ; parmkey munchparmkey(parmimg *p) ; void munchsetlist(parmlist *p) ; void munchpushlist(parmlist *p),munchpoplist() ; char *munchparmloc() ; // get unprocessed keyword data parmkey *getparmkey(char *k) ; // 1 // routines to return an array of values int getparms(char **&p,char *key) ; // 2 array of strings int getparms(long *&p,char *key) ; // 3 array of longs int getparms(int *&p,char *key) ; // 4 array of ints int getparms(double *&p,char *key) ; // 5 array of doubles // routines to return a two-dimensional matrix int getmatparms(double **&p,char *key,int dim0) ; // 6 int getmatparms(double **&p,char *key) ;// 7 must be square // arrays of strings subject to conversion int getlcparms(char **&p,char *key) ; // 8 lower case int getfnparms(char **&p,char *key) ; // 9 file path from cwd // routines to return a single value void getparm(char *&val,char *key) ; // 10 a string void getparm(int &val,char *key) ; // 11 an int void getparm(long &val,char *key) ; // 12 a long void getparm(double &val,char *key) ; // 13 a double // a single value allowing a default bool getparm(char *&val,char *key,char *def) ; // 14 a string bool getparm(double &val,char *key,double def) ;// 15 a double bool getparm(int &val,char *key,int def) ; // 16 an int bool getparm(long &val,char *key,long def) ; // 17 a long bool getparm(bool &val,char *key,bool def) ; // 18 a bool // a single string subject to conversion bool getlcparm(char *&val,char *key,char *def) ;// 19 lower case void getlcparm(char *&val,char *key) ; // 20 lower case void getfnparm(char *&val,char *key) ; // 21 path name
• compressmap • compress • rescale
#include "memory.h" #define uchar unsigned char struct mapitem { int i0,i1 ; double w0,w1 ; } ; genvector(uchar,ucharvector) ; genvector(mapitem,mapvector) ; /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ static mapitem *compressmap(int N,int n) { int i ; double q ; mapitem m , *maplist = mapvector(n) ; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if((i*N)%n==0) { m.i0 = (i*N)/n ; m.w0 = 1 ; } else { q = (i*N)/(double) n ; m.i0 = (int) q ; m.w0 = 1 - (q-m.i0) ; } if(((i+1)*N)%n==0) { m.i1 = ((i+1)*N)/n - 1 ; m.w1 = 1 ; } else { q = ((i+1)*N)/(double) n ; m.i1 = (int) q ; m.w1 = q - m.i1 ; } if(m.i1==m.i0) { m.w0 -= 1-m.w1 ; m.w1 = 0 ; } maplist[i] = m ; } return maplist ; } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ static void compress(uchar *x,int N,uchar *y,int n,mapitem *map) { int i,j ; mapitem m ; double q,r=n/(double)N ; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { for(m=map[i],q=x[m.i0]*m.w0+x[m.i1]*m.w1,j=m.i0+1;j<m.i1;j++) q += x[j] ; y[i] = q*r ; } } /* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ uchar *rescale(uchar *img,int W,int H,int w,int h,int ncol) { int i,j,k,col,n,offs ; mapitem *map ; uchar *img2 = ucharvector(ncol*h*w) , *img1 = ucharvector(ncol*H*w) ; uchar *xa = ucharvector(H>W?H:W) , *xb = ucharvector(h>w?h:w) ; for(col=0;col<ncol;col++) { // downsample width if(H*w<h*W) n = (int) (0.5+(H*w)/(double) h) ; else n = W ; map = compressmap(n,w) ; offs = (W-n)/2 ; for(i=0;i<H;i++) { k = col + ncol * ( offs + W*i ) ; for(j=0;j<n;j++) xa[j] = img[k+ncol*j] ; compress(xa,n,xb,w,map) ; k = col + ncol*i*w ; for(j=0;j<w;j++) img1[k+ncol*j] = xb[j] ; } free(map) ; // downsample height if(W*h<w*H) n = (int) (0.5+(W*h)/(double) w) ; else n = H ; map = compressmap(n,h) ; offs = (H-n)/2 ; for(j=0;j<w;j++) { k = col + ncol * ( j + w*offs ) ; for(i=0;i<n;i++) xa[i] = img1[ncol*w*i+k] ; compress(xa,n,xb,h,map) ; k = col + ncol*j ; for(i=0;i<h;i++) img2[ncol*w*i+k] = xb[i] ; } free(map) ; } free(img1,xa,xb) ; return img2 ; }
#include "readjpg.h" // nj_result_t: Result codes for njDecode(). typedef enum _nj_result { NJ_OK = 0, // no error, decoding successful NJ_NO_JPEG, // not a JPEG file NJ_UNSUPPORTED, // unsupported format NJ_OUT_OF_MEM, // out of memory NJ_INTERNAL_ERR, // internal error NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR, // syntax error __NJ_FINISHED, // used internally, will never be reported } nj_result_t; void njInit(void); nj_result_t njDecode(const void* jpeg, const int size); int njGetWidth(void); int njGetHeight(void); int njIsColor(void); unsigned char* njGetImage(void); int njGetImageSize(void); void njDone(void); extern bool jo_write_jpg(const char*,const void*,int,int,int,int) ; image readjpg(char *x) { int i,n ; FILE *ifl=fopen(x,"rb") ; char *buf,*whinge ; unsigned char *u ; image img ; if(!ifl) return img ; fseek(ifl,0,SEEK_END) ; n = (int) ftell(ifl) ; buf = charvector(n) ; fseek(ifl,0,SEEK_SET) ; n = fread(buf,1,n,ifl) ; fclose(ifl) ; njInit() ; nj_result_t resp = njDecode(buf,n) ; if(resp) { if(resp==NJ_NO_JPEG) whinge = "not jpeg" ; else if(resp==NJ_UNSUPPORTED) whinge = "not supported" ; else if(resp==NJ_OUT_OF_MEM) whinge = "out of memory" ; else if(resp==NJ_INTERNAL_ERR) whinge = "internal error" ; else if(resp==NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR) whinge = "syntax error" ; else whinge = "unspecified error" ; throw up("Error \"%s\" decoding %s",whinge,x) ; } free(buf) ; fclose(ifl) ; img = image(njGetWidth(),njGetHeight(),1+2*njIsColor(),0) ; n = img.w * img.h * img.ncol ; img.u = ucharvector(n) ; u = njGetImage() ; for(i=0;i<n;i++) img.u[i] = u[i] ; njDone() ; return img ; } void writejpg(image img,char *filename,int iqual) { jo_write_jpg(filename,img.u,img.w,img.h,img.ncol,iqual) ; }
#include "memory.h" #define uchar unsigned char genvector(uchar,ucharvector) ; struct image { uchar *u ; int w,h,ncol ; image() { u = 0 ; w = h = ncol = 0 ; } image(int a,int b,int c,uchar *d) { w = a ; h = b ; ncol = c ; u = d ; } } ; image readjpg(char *) ; void writejpg(image,char *,int) ;
• main • njFillMem • njCopyMem • njClip • njRowIDCT • njColIDCT • njShowBits • njSkipBits • njGetBits • njByteAlign • njSkip • njDecode16 • njDecodeLength • njSkipMarker • njDecodeSOF • njDecodeDHT • njDecodeDQT • njDecodeDRI • njGetVLC • njDecodeBlock • njDecodeScan • njUpsampleH • njUpsampleV • njUpsample • njConvert • njInit • njDone • njDecode • njGetWidth • njGetHeight • njIsColor • njGetImage • njGetImageSize
// NanoJPEG -- KeyJ's Tiny Baseline JPEG Decoder // version 1.3.5 (2016-11-14) // Copyright (c) 2009-2016 Martin J. Fiedler <martin.fiedler@gmx.net> // published under the terms of the MIT license // // Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy // of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to // deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the // rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or // sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is // furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: // // The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in // all copies or substantial portions of the Software. // // THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR // IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, // FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE // AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER // LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING // FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER // DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // DOCUMENTATION SECTION // // read this if you want to know what this is all about // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // INTRODUCTION // ============ // // This is a minimal decoder for baseline JPEG images. It accepts memory dumps // of JPEG files as input and generates either 8-bit grayscale or packed 24-bit // RGB images as output. It does not parse JFIF or Exif headers; all JPEG files // are assumed to be either grayscale or YCbCr. CMYK or other color spaces are // not supported. All YCbCr subsampling schemes with power-of-two ratios are // supported, as are restart intervals. Progressive or lossless JPEG is not // supported. // Summed up, NanoJPEG should be able to decode all images from digital cameras // and most common forms of other non-progressive JPEG images. // The decoder is not optimized for speed, it's optimized for simplicity and // small code. Image quality should be at a reasonable level. A bicubic chroma // upsampling filter ensures that subsampled YCbCr images are rendered in // decent quality. The decoder is not meant to deal with broken JPEG files in // a graceful manner; if anything is wrong with the bitstream, decoding will // simply fail. // The code should work with every modern C compiler without problems and // should not emit any warnings. It uses only (at least) 32-bit integer // arithmetic and is supposed to be endianness independent and 64-bit clean. // However, it is not thread-safe. // COMPILE-TIME CONFIGURATION // ========================== // // The following aspects of NanoJPEG can be controlled with preprocessor // defines: // // _NJ_EXAMPLE_PROGRAM = Compile a main() function with an example // program. // _NJ_INCLUDE_HEADER_ONLY = Don't compile anything, just act as a header // file for NanoJPEG. Example: // #define _NJ_INCLUDE_HEADER_ONLY // #include "nanojpeg.c" // int main(void) { // njInit(); // // your code here // njDone(); // } // NJ_USE_LIBC=1 = Use the malloc(), free(), memset() and memcpy() // functions from the standard C library (default). // NJ_USE_LIBC=0 = Don't use the standard C library. In this mode, // external functions njAlloc(), njFreeMem(), // njFillMem() and njCopyMem() need to be defined // and implemented somewhere. // NJ_USE_WIN32=0 = Normal mode (default). // NJ_USE_WIN32=1 = If compiling with MSVC for Win32 and // NJ_USE_LIBC=0, NanoJPEG will use its own // implementations of the required C library // functions (default if compiling with MSVC and // NJ_USE_LIBC=0). // NJ_CHROMA_FILTER=1 = Use the bicubic chroma upsampling filter // (default). // NJ_CHROMA_FILTER=0 = Use simple pixel repetition for chroma upsampling // (bad quality, but faster and less code). // API // === // // For API documentation, read the "header section" below. // EXAMPLE // ======= // // A few pages below, you can find an example program that uses NanoJPEG to // convert JPEG files into PGM or PPM. To compile it, use something like // gcc -O3 -D_NJ_EXAMPLE_PROGRAM -o nanojpeg nanojpeg.c // You may also add -std=c99 -Wall -Wextra -pedantic -Werror, if you want :) // The only thing you might need is -Wno-shift-negative-value, because this // code relies on the target machine using two's complement arithmetic, but // the C standard does not, even though *any* practically useful machine // nowadays uses two's complement. /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // HEADER SECTION // // copy and pase this into nanojpeg.h if you want // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifndef _NANOJPEG_H #define _NANOJPEG_H // nj_result_t: Result codes for njDecode(). typedef enum _nj_result { NJ_OK = 0, // no error, decoding successful NJ_NO_JPEG, // not a JPEG file NJ_UNSUPPORTED, // unsupported format NJ_OUT_OF_MEM, // out of memory NJ_INTERNAL_ERR, // internal error NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR, // syntax error __NJ_FINISHED, // used internally, will never be reported } nj_result_t; // njInit: Initialize NanoJPEG. // For safety reasons, this should be called at least one time before using // using any of the other NanoJPEG functions. void njInit(void); // njDecode: Decode a JPEG image. // Decodes a memory dump of a JPEG file into internal buffers. // Parameters: // jpeg = The pointer to the memory dump. // size = The size of the JPEG file. // Return value: The error code in case of failure, or NJ_OK (zero) on success. nj_result_t njDecode(const void* jpeg, const int size); // njGetWidth: Return the width (in pixels) of the most recently decoded // image. If njDecode() failed, the result of njGetWidth() is undefined. int njGetWidth(void); // njGetHeight: Return the height (in pixels) of the most recently decoded // image. If njDecode() failed, the result of njGetHeight() is undefined. int njGetHeight(void); // njIsColor: Return 1 if the most recently decoded image is a color image // (RGB) or 0 if it is a grayscale image. If njDecode() failed, the result // of njGetWidth() is undefined. int njIsColor(void); // njGetImage: Returns the decoded image data. // Returns a pointer to the most recently image. The memory layout it byte- // oriented, top-down, without any padding between lines. Pixels of color // images will be stored as three consecutive bytes for the red, green and // blue channels. This data format is thus compatible with the PGM or PPM // file formats and the OpenGL texture formats GL_LUMINANCE8 or GL_RGB8. // If njDecode() failed, the result of njGetImage() is undefined. unsigned char* njGetImage(void); // njGetImageSize: Returns the size (in bytes) of the image data returned // by njGetImage(). If njDecode() failed, the result of njGetImageSize() is // undefined. int njGetImageSize(void); // njDone: Uninitialize NanoJPEG. // Resets NanoJPEG's internal state and frees all memory that has been // allocated at run-time by NanoJPEG. It is still possible to decode another // image after a njDone() call. void njDone(void); #endif//_NANOJPEG_H /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // CONFIGURATION SECTION // // adjust the default settings for the NJ_ defines here // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifndef NJ_USE_LIBC #define NJ_USE_LIBC 1 #endif #ifndef NJ_USE_WIN32 #ifdef _MSC_VER #define NJ_USE_WIN32 (!NJ_USE_LIBC) #else #define NJ_USE_WIN32 0 #endif #endif #ifndef NJ_CHROMA_FILTER #define NJ_CHROMA_FILTER 1 #endif /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // EXAMPLE PROGRAM // // just define _NJ_EXAMPLE_PROGRAM to compile this (requires NJ_USE_LIBC) // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifdef _NJ_EXAMPLE_PROGRAM #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int size; char *buf; FILE *f; if (argc < 2) { printf("Usage: %s <input.jpg> [<output.ppm>]\n", argv[0]); return 2; } f = fopen(argv[1], "rb"); if (!f) { printf("Error opening the input file.\n"); return 1; } fseek(f, 0, SEEK_END); size = (int) ftell(f); buf = (char*) malloc(size); fseek(f, 0, SEEK_SET); size = (int) fread(buf, 1, size, f); fclose(f); njInit(); if (njDecode(buf, size)) { free((void*)buf); printf("Error decoding the input file.\n"); return 1; } free((void*)buf); f = fopen((argc > 2) ? argv[2] : (njIsColor() ? "nanojpeg_out.ppm" : "nanojpeg_out.pgm"), "wb"); if (!f) { printf("Error opening the output file.\n"); return 1; } fprintf(f, "P%d\n%d %d\n255\n", njIsColor() ? 6 : 5, njGetWidth(), njGetHeight()); fwrite(njGetImage(), 1, njGetImageSize(), f); fclose(f); njDone(); return 0; } #endif /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // IMPLEMENTATION SECTION // // you may stop reading here // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifndef _NJ_INCLUDE_HEADER_ONLY #ifdef _MSC_VER #define NJ_INLINE static __inline #define NJ_FORCE_INLINE static __forceinline #else #define NJ_INLINE static inline #define NJ_FORCE_INLINE static inline #endif #if NJ_USE_LIBC #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define njAllocMem malloc #define njFreeMem free #define njFillMem memset #define njCopyMem memcpy #elif NJ_USE_WIN32 #include <windows.h> #define njAllocMem(size) ((void*) LocalAlloc(LMEM_FIXED, (SIZE_T)(size))) #define njFreeMem(block) ((void) LocalFree((HLOCAL) block)) NJ_INLINE void njFillMem(void* block, unsigned char value, int count) { __asm { mov edi, block mov al, value mov ecx, count rep stosb } } NJ_INLINE void njCopyMem(void* dest, const void* src, int count) { __asm { mov edi, dest mov esi, src mov ecx, count rep movsb } } #else extern void* njAllocMem(int size); extern void njFreeMem(void* block); extern void njFillMem(void* block, unsigned char byte, int size); extern void njCopyMem(void* dest, const void* src, int size); #endif typedef struct _nj_code { unsigned char bits, code; } nj_vlc_code_t; typedef struct _nj_cmp { int cid; int ssx, ssy; int width, height; int stride; int qtsel; int actabsel, dctabsel; int dcpred; unsigned char *pixels; } nj_component_t; typedef struct _nj_ctx { nj_result_t error; const unsigned char *pos; int size; int length; int width, height; int mbwidth, mbheight; int mbsizex, mbsizey; int ncomp; nj_component_t comp[3]; int qtused, qtavail; unsigned char qtab[4][64]; nj_vlc_code_t vlctab[4][65536]; int buf, bufbits; int block[64]; int rstinterval; unsigned char *rgb; } nj_context_t; static nj_context_t nj; static const char njZZ[64] = { 0, 1, 8, 16, 9, 2, 3, 10, 17, 24, 32, 25, 18, 11, 4, 5, 12, 19, 26, 33, 40, 48, 41, 34, 27, 20, 13, 6, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 57, 50, 43, 36, 29, 22, 15, 23, 30, 37, 44, 51, 58, 59, 52, 45, 38, 31, 39, 46, 53, 60, 61, 54, 47, 55, 62, 63 }; NJ_FORCE_INLINE unsigned char njClip(const int x) { return (x < 0) ? 0 : ((x > 0xFF) ? 0xFF : (unsigned char) x); } #define W1 2841 #define W2 2676 #define W3 2408 #define W5 1609 #define W6 1108 #define W7 565 NJ_INLINE void njRowIDCT(int* blk) { int x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8; if (!((x1 = blk[4] << 11) | (x2 = blk[6]) | (x3 = blk[2]) | (x4 = blk[1]) | (x5 = blk[7]) | (x6 = blk[5]) | (x7 = blk[3]))) { blk[0] = blk[1] = blk[2] = blk[3] = blk[4] = blk[5] = blk[6] = blk[7] = blk[0] << 3; return; } x0 = (blk[0] << 11) + 128; x8 = W7 * (x4 + x5); x4 = x8 + (W1 - W7) * x4; x5 = x8 - (W1 + W7) * x5; x8 = W3 * (x6 + x7); x6 = x8 - (W3 - W5) * x6; x7 = x8 - (W3 + W5) * x7; x8 = x0 + x1; x0 -= x1; x1 = W6 * (x3 + x2); x2 = x1 - (W2 + W6) * x2; x3 = x1 + (W2 - W6) * x3; x1 = x4 + x6; x4 -= x6; x6 = x5 + x7; x5 -= x7; x7 = x8 + x3; x8 -= x3; x3 = x0 + x2; x0 -= x2; x2 = (181 * (x4 + x5) + 128) >> 8; x4 = (181 * (x4 - x5) + 128) >> 8; blk[0] = (x7 + x1) >> 8; blk[1] = (x3 + x2) >> 8; blk[2] = (x0 + x4) >> 8; blk[3] = (x8 + x6) >> 8; blk[4] = (x8 - x6) >> 8; blk[5] = (x0 - x4) >> 8; blk[6] = (x3 - x2) >> 8; blk[7] = (x7 - x1) >> 8; } NJ_INLINE void njColIDCT(const int* blk, unsigned char *out, int stride) { int x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8; if (!((x1 = blk[8*4] << 8) | (x2 = blk[8*6]) | (x3 = blk[8*2]) | (x4 = blk[8*1]) | (x5 = blk[8*7]) | (x6 = blk[8*5]) | (x7 = blk[8*3]))) { x1 = njClip(((blk[0] + 32) >> 6) + 128); for (x0 = 8; x0; --x0) { *out = (unsigned char) x1; out += stride; } return; } x0 = (blk[0] << 8) + 8192; x8 = W7 * (x4 + x5) + 4; x4 = (x8 + (W1 - W7) * x4) >> 3; x5 = (x8 - (W1 + W7) * x5) >> 3; x8 = W3 * (x6 + x7) + 4; x6 = (x8 - (W3 - W5) * x6) >> 3; x7 = (x8 - (W3 + W5) * x7) >> 3; x8 = x0 + x1; x0 -= x1; x1 = W6 * (x3 + x2) + 4; x2 = (x1 - (W2 + W6) * x2) >> 3; x3 = (x1 + (W2 - W6) * x3) >> 3; x1 = x4 + x6; x4 -= x6; x6 = x5 + x7; x5 -= x7; x7 = x8 + x3; x8 -= x3; x3 = x0 + x2; x0 -= x2; x2 = (181 * (x4 + x5) + 128) >> 8; x4 = (181 * (x4 - x5) + 128) >> 8; *out = njClip(((x7 + x1) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x3 + x2) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x0 + x4) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x8 + x6) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x8 - x6) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x0 - x4) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x3 - x2) >> 14) + 128); out += stride; *out = njClip(((x7 - x1) >> 14) + 128); } #define njThrow(e) do { nj.error = e; return; } while (0) #define njCheckError() do { if (nj.error) return; } while (0) static int njShowBits(int bits) { unsigned char newbyte; if (!bits) return 0; while (nj.bufbits < bits) { if (nj.size <= 0) { nj.buf = (nj.buf << 8) | 0xFF; nj.bufbits += 8; continue; } newbyte = *nj.pos++; nj.size--; nj.bufbits += 8; nj.buf = (nj.buf << 8) | newbyte; if (newbyte == 0xFF) { if (nj.size) { unsigned char marker = *nj.pos++; nj.size--; switch (marker) { case 0x00: case 0xFF: break; case 0xD9: nj.size = 0; break; default: if ((marker & 0xF8) != 0xD0) nj.error = NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR; else { nj.buf = (nj.buf << 8) | marker; nj.bufbits += 8; } } } else nj.error = NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR; } } return (nj.buf >> (nj.bufbits - bits)) & ((1 << bits) - 1); } NJ_INLINE void njSkipBits(int bits) { if (nj.bufbits < bits) (void) njShowBits(bits); nj.bufbits -= bits; } NJ_INLINE int njGetBits(int bits) { int res = njShowBits(bits); njSkipBits(bits); return res; } NJ_INLINE void njByteAlign(void) { nj.bufbits &= 0xF8; } static void njSkip(int count) { nj.pos += count; nj.size -= count; nj.length -= count; if (nj.size < 0) nj.error = NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR; } NJ_INLINE unsigned short njDecode16(const unsigned char *pos) { return (pos[0] << 8) | pos[1]; } static void njDecodeLength(void) { if (nj.size < 2) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); nj.length = njDecode16(nj.pos); if (nj.length > nj.size) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); njSkip(2); } NJ_INLINE void njSkipMarker(void) { njDecodeLength(); njSkip(nj.length); } NJ_INLINE void njDecodeSOF(void) { int i, ssxmax = 0, ssymax = 0; nj_component_t* c; njDecodeLength(); njCheckError(); if (nj.length < 9) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); if (nj.pos[0] != 8) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); nj.height = njDecode16(nj.pos+1); nj.width = njDecode16(nj.pos+3); if (!nj.width || !nj.height) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); nj.ncomp = nj.pos[5]; njSkip(6); switch (nj.ncomp) { case 1: case 3: break; default: njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); } if (nj.length < (nj.ncomp * 3)) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); for (i = 0, c = nj.comp; i < nj.ncomp; ++i, ++c) { c->cid = nj.pos[0]; if (!(c->ssx = nj.pos[1] >> 4)) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); if (c->ssx & (c->ssx - 1)) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); // non-power of two if (!(c->ssy = nj.pos[1] & 15)) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); if (c->ssy & (c->ssy - 1)) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); // non-power of two if ((c->qtsel = nj.pos[2]) & 0xFC) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); njSkip(3); nj.qtused |= 1 << c->qtsel; if (c->ssx > ssxmax) ssxmax = c->ssx; if (c->ssy > ssymax) ssymax = c->ssy; } if (nj.ncomp == 1) { c = nj.comp; c->ssx = c->ssy = ssxmax = ssymax = 1; } nj.mbsizex = ssxmax << 3; nj.mbsizey = ssymax << 3; nj.mbwidth = (nj.width + nj.mbsizex - 1) / nj.mbsizex; nj.mbheight = (nj.height + nj.mbsizey - 1) / nj.mbsizey; for (i = 0, c = nj.comp; i < nj.ncomp; ++i, ++c) { c->width = (nj.width * c->ssx + ssxmax - 1) / ssxmax; c->height = (nj.height * c->ssy + ssymax - 1) / ssymax; c->stride = nj.mbwidth * c->ssx << 3; if (((c->width < 3) && (c->ssx != ssxmax)) || ((c->height < 3) && (c->ssy != ssymax))) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); if (!(c->pixels = (unsigned char*) njAllocMem(c->stride * nj.mbheight * c->ssy << 3))) njThrow(NJ_OUT_OF_MEM); } if (nj.ncomp == 3) { nj.rgb = (unsigned char*) njAllocMem(nj.width * nj.height * nj.ncomp); if (!nj.rgb) njThrow(NJ_OUT_OF_MEM); } njSkip(nj.length); } NJ_INLINE void njDecodeDHT(void) { int codelen, currcnt, remain, spread, i, j; nj_vlc_code_t *vlc; static unsigned char counts[16]; njDecodeLength(); njCheckError(); while (nj.length >= 17) { i = nj.pos[0]; if (i & 0xEC) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); if (i & 0x02) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); i = (i | (i >> 3)) & 3; // combined DC/AC + tableid value for (codelen = 1; codelen <= 16; ++codelen) counts[codelen - 1] = nj.pos[codelen]; njSkip(17); vlc = &nj.vlctab[i][0]; remain = spread = 65536; for (codelen = 1; codelen <= 16; ++codelen) { spread >>= 1; currcnt = counts[codelen - 1]; if (!currcnt) continue; if (nj.length < currcnt) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); remain -= currcnt << (16 - codelen); if (remain < 0) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); for (i = 0; i < currcnt; ++i) { register unsigned char code = nj.pos[i]; for (j = spread; j; --j) { vlc->bits = (unsigned char) codelen; vlc->code = code; ++vlc; } } njSkip(currcnt); } while (remain--) { vlc->bits = 0; ++vlc; } } if (nj.length) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); } NJ_INLINE void njDecodeDQT(void) { int i; unsigned char *t; njDecodeLength(); njCheckError(); while (nj.length >= 65) { i = nj.pos[0]; if (i & 0xFC) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); nj.qtavail |= 1 << i; t = &nj.qtab[i][0]; for (i = 0; i < 64; ++i) t[i] = nj.pos[i + 1]; njSkip(65); } if (nj.length) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); } NJ_INLINE void njDecodeDRI(void) { njDecodeLength(); njCheckError(); if (nj.length < 2) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); nj.rstinterval = njDecode16(nj.pos); njSkip(nj.length); } static int njGetVLC(nj_vlc_code_t* vlc, unsigned char* code) { int value = njShowBits(16); int bits = vlc[value].bits; if (!bits) { nj.error = NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR; return 0; } njSkipBits(bits); value = vlc[value].code; if (code) *code = (unsigned char) value; bits = value & 15; if (!bits) return 0; value = njGetBits(bits); if (value < (1 << (bits - 1))) value += ((-1) << bits) + 1; return value; } NJ_INLINE void njDecodeBlock(nj_component_t* c, unsigned char* out) { unsigned char code = 0; int value, coef = 0; njFillMem(nj.block, 0, sizeof(nj.block)); c->dcpred += njGetVLC(&nj.vlctab[c->dctabsel][0], NULL); nj.block[0] = (c->dcpred) * nj.qtab[c->qtsel][0]; do { value = njGetVLC(&nj.vlctab[c->actabsel][0], &code); if (!code) break; // EOB if (!(code & 0x0F) && (code != 0xF0)) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); coef += (code >> 4) + 1; if (coef > 63) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); nj.block[(int) njZZ[coef]] = value * nj.qtab[c->qtsel][coef]; } while (coef < 63); for (coef = 0; coef < 64; coef += 8) njRowIDCT(&nj.block[coef]); for (coef = 0; coef < 8; ++coef) njColIDCT(&nj.block[coef], &out[coef], c->stride); } NJ_INLINE void njDecodeScan(void) { int i, mbx, mby, sbx, sby; int rstcount = nj.rstinterval, nextrst = 0; nj_component_t* c; njDecodeLength(); njCheckError(); if (nj.length < (4 + 2 * nj.ncomp)) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); if (nj.pos[0] != nj.ncomp) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); njSkip(1); for (i = 0, c = nj.comp; i < nj.ncomp; ++i, ++c) { if (nj.pos[0] != c->cid) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); if (nj.pos[1] & 0xEE) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); c->dctabsel = nj.pos[1] >> 4; c->actabsel = (nj.pos[1] & 1) | 2; njSkip(2); } if (nj.pos[0] || (nj.pos[1] != 63) || nj.pos[2]) njThrow(NJ_UNSUPPORTED); njSkip(nj.length); for (mbx = mby = 0;;) { for (i = 0, c = nj.comp; i < nj.ncomp; ++i, ++c) for (sby = 0; sby < c->ssy; ++sby) for (sbx = 0; sbx < c->ssx; ++sbx) { njDecodeBlock(c, &c->pixels[((mby * c->ssy + sby) * c->stride + mbx * c->ssx + sbx) << 3]); njCheckError(); } if (++mbx >= nj.mbwidth) { mbx = 0; if (++mby >= nj.mbheight) break; } if (nj.rstinterval && !(--rstcount)) { njByteAlign(); i = njGetBits(16); if (((i & 0xFFF8) != 0xFFD0) || ((i & 7) != nextrst)) njThrow(NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR); nextrst = (nextrst + 1) & 7; rstcount = nj.rstinterval; for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i) nj.comp[i].dcpred = 0; } } nj.error = __NJ_FINISHED; } #if NJ_CHROMA_FILTER #define CF4A (-9) #define CF4B (111) #define CF4C (29) #define CF4D (-3) #define CF3A (28) #define CF3B (109) #define CF3C (-9) #define CF3X (104) #define CF3Y (27) #define CF3Z (-3) #define CF2A (139) #define CF2B (-11) #define CF(x) njClip(((x) + 64) >> 7) NJ_INLINE void njUpsampleH(nj_component_t* c) { const int xmax = c->width - 3; unsigned char *out, *lin, *lout; int x, y; out = (unsigned char*) njAllocMem((c->width * c->height) << 1); if (!out) njThrow(NJ_OUT_OF_MEM); lin = c->pixels; lout = out; for (y = c->height; y; --y) { lout[0] = CF(CF2A * lin[0] + CF2B * lin[1]); lout[1] = CF(CF3X * lin[0] + CF3Y * lin[1] + CF3Z * lin[2]); lout[2] = CF(CF3A * lin[0] + CF3B * lin[1] + CF3C * lin[2]); for (x = 0; x < xmax; ++x) { lout[(x << 1) + 3] = CF(CF4A * lin[x] + CF4B * lin[x + 1] + CF4C * lin[x + 2] + CF4D * lin[x + 3]); lout[(x << 1) + 4] = CF(CF4D * lin[x] + CF4C * lin[x + 1] + CF4B * lin[x + 2] + CF4A * lin[x + 3]); } lin += c->stride; lout += c->width << 1; lout[-3] = CF(CF3A * lin[-1] + CF3B * lin[-2] + CF3C * lin[-3]); lout[-2] = CF(CF3X * lin[-1] + CF3Y * lin[-2] + CF3Z * lin[-3]); lout[-1] = CF(CF2A * lin[-1] + CF2B * lin[-2]); } c->width <<= 1; c->stride = c->width; njFreeMem((void*)c->pixels); c->pixels = out; } NJ_INLINE void njUpsampleV(nj_component_t* c) { const int w = c->width, s1 = c->stride, s2 = s1 + s1; unsigned char *out, *cin, *cout; int x, y; out = (unsigned char*) njAllocMem((c->width * c->height) << 1); if (!out) njThrow(NJ_OUT_OF_MEM); for (x = 0; x < w; ++x) { cin = &c->pixels[x]; cout = &out[x]; *cout = CF(CF2A * cin[0] + CF2B * cin[s1]); cout += w; *cout = CF(CF3X * cin[0] + CF3Y * cin[s1] + CF3Z * cin[s2]); cout += w; *cout = CF(CF3A * cin[0] + CF3B * cin[s1] + CF3C * cin[s2]); cout += w; cin += s1; for (y = c->height - 3; y; --y) { *cout = CF(CF4A * cin[-s1] + CF4B * cin[0] + CF4C * cin[s1] + CF4D * cin[s2]); cout += w; *cout = CF(CF4D * cin[-s1] + CF4C * cin[0] + CF4B * cin[s1] + CF4A * cin[s2]); cout += w; cin += s1; } cin += s1; *cout = CF(CF3A * cin[0] + CF3B * cin[-s1] + CF3C * cin[-s2]); cout += w; *cout = CF(CF3X * cin[0] + CF3Y * cin[-s1] + CF3Z * cin[-s2]); cout += w; *cout = CF(CF2A * cin[0] + CF2B * cin[-s1]); } c->height <<= 1; c->stride = c->width; njFreeMem((void*) c->pixels); c->pixels = out; } #else NJ_INLINE void njUpsample(nj_component_t* c) { int x, y, xshift = 0, yshift = 0; unsigned char *out, *lin, *lout; while (c->width < nj.width) { c->width <<= 1; ++xshift; } while (c->height < nj.height) { c->height <<= 1; ++yshift; } out = (unsigned char*) njAllocMem(c->width * c->height); if (!out) njThrow(NJ_OUT_OF_MEM); lin = c->pixels; lout = out; for (y = 0; y < c->height; ++y) { lin = &c->pixels[(y >> yshift) * c->stride]; for (x = 0; x < c->width; ++x) lout[x] = lin[x >> xshift]; lout += c->width; } c->stride = c->width; njFreeMem((void*) c->pixels); c->pixels = out; } #endif NJ_INLINE void njConvert(void) { int i; nj_component_t* c; for (i = 0, c = nj.comp; i < nj.ncomp; ++i, ++c) { #if NJ_CHROMA_FILTER while ((c->width < nj.width) || (c->height < nj.height)) { if (c->width < nj.width) njUpsampleH(c); njCheckError(); if (c->height < nj.height) njUpsampleV(c); njCheckError(); } #else if ((c->width < nj.width) || (c->height < nj.height)) njUpsample(c); #endif if ((c->width < nj.width) || (c->height < nj.height)) njThrow(NJ_INTERNAL_ERR); } if (nj.ncomp == 3) { // convert to RGB int x, yy; unsigned char *prgb = nj.rgb; const unsigned char *py = nj.comp[0].pixels; const unsigned char *pcb = nj.comp[1].pixels; const unsigned char *pcr = nj.comp[2].pixels; for (yy = nj.height; yy; --yy) { for (x = 0; x < nj.width; ++x) { register int y = py[x] << 8; register int cb = pcb[x] - 128; register int cr = pcr[x] - 128; *prgb++ = njClip((y + 359 * cr + 128) >> 8); *prgb++ = njClip((y - 88 * cb - 183 * cr + 128) >> 8); *prgb++ = njClip((y + 454 * cb + 128) >> 8); } py += nj.comp[0].stride; pcb += nj.comp[1].stride; pcr += nj.comp[2].stride; } } else if (nj.comp[0].width != nj.comp[0].stride) { // grayscale -> only remove stride unsigned char *pin = &nj.comp[0].pixels[nj.comp[0].stride]; unsigned char *pout = &nj.comp[0].pixels[nj.comp[0].width]; int y; for (y = nj.comp[0].height - 1; y; --y) { njCopyMem(pout, pin, nj.comp[0].width); pin += nj.comp[0].stride; pout += nj.comp[0].width; } nj.comp[0].stride = nj.comp[0].width; } } void njInit(void) { njFillMem(&nj, 0, sizeof(nj_context_t)); } void njDone(void) { int i; for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i) if (nj.comp[i].pixels) njFreeMem((void*) nj.comp[i].pixels); if (nj.rgb) njFreeMem((void*) nj.rgb); njInit(); } nj_result_t njDecode(const void* jpeg, const int size) { njDone(); nj.pos = (const unsigned char*) jpeg; nj.size = size & 0x7FFFFFFF; if (nj.size < 2) return NJ_NO_JPEG; if ((nj.pos[0] ^ 0xFF) | (nj.pos[1] ^ 0xD8)) return NJ_NO_JPEG; njSkip(2); while (!nj.error) { if ((nj.size < 2) || (nj.pos[0] != 0xFF)) return NJ_SYNTAX_ERROR; njSkip(2); switch (nj.pos[-1]) { case 0xC0: njDecodeSOF(); break; case 0xC4: njDecodeDHT(); break; case 0xDB: njDecodeDQT(); break; case 0xDD: njDecodeDRI(); break; case 0xDA: njDecodeScan(); break; case 0xFE: njSkipMarker(); break; default: if ((nj.pos[-1] & 0xF0) == 0xE0) njSkipMarker(); else return NJ_UNSUPPORTED; } } if (nj.error != __NJ_FINISHED) return nj.error; nj.error = NJ_OK; njConvert(); return nj.error; } int njGetWidth(void) { return nj.width; } int njGetHeight(void) { return nj.height; } int njIsColor(void) { return (nj.ncomp != 1); } unsigned char* njGetImage(void) { return (nj.ncomp == 1) ? nj.comp[0].pixels : nj.rgb; } int njGetImageSize(void) { return nj.width * nj.height * nj.ncomp; } #endif // _NJ_INCLUDE_HEADER_ONLY
• sft_version • sft_loadmem • sft_loadfile • sft_freefont • sft_lmetrics • sft_lookup • sft_gmetrics • sft_kerning • sft_render • reallocarray • fast_floor • fast_ceil • map_file • unmap_file • init_font • midpoint • return • transform_points • clip_points • init_outline • free_outline • grow_points • grow_curves • grow_lines • is_safe_offset • csearch • cmpu16 • cmpu32 • getu8 • geti8 • getu16 • geti16 • getu32 • gettable • cmap_fmt4 • cmap_fmt6 • cmap_fmt12_13 • glyph_id • hor_metrics • glyph_bbox • outline_offset • simple_flags • simple_points • decode_contour • simple_outline • compound_outline • decode_outline • is_flat • tesselate_curve • tesselate_curves • draw_line • draw_lines • post_process • render_outline
/* This file is part of libschrift. * * © 2019-2022 Thomas Oltmann and contributors * * Permission to use, copy, modify, and/or distribute this software for any * purpose with or without fee is hereby granted, provided that the above * copyright notice and this permission notice appear in all copies. * * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND THE AUTHOR DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES * WITH REGARD TO THIS SOFTWARE INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF * MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR * ANY SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES * WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN * ACTION OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE. */ #include <assert.h> #include <errno.h> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #if defined(_MSC_VER) # define restrict __restrict #endif #if defined(_WIN32) # define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN 1 # include <windows.h> #else # define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 1 # include <fcntl.h> # include <sys/mman.h> # include <sys/stat.h> # include <unistd.h> #endif #include "schrift.h" #define SCHRIFT_VERSION "0.10.2" #define FILE_MAGIC_ONE 0x00010000 #define FILE_MAGIC_TWO 0x74727565 #define HORIZONTAL_KERNING 0x01 #define MINIMUM_KERNING 0x02 #define CROSS_STREAM_KERNING 0x04 #define OVERRIDE_KERNING 0x08 #define POINT_IS_ON_CURVE 0x01 #define X_CHANGE_IS_SMALL 0x02 #define Y_CHANGE_IS_SMALL 0x04 #define REPEAT_FLAG 0x08 #define X_CHANGE_IS_ZERO 0x10 #define X_CHANGE_IS_POSITIVE 0x10 #define Y_CHANGE_IS_ZERO 0x20 #define Y_CHANGE_IS_POSITIVE 0x20 #define OFFSETS_ARE_LARGE 0x001 #define ACTUAL_XY_OFFSETS 0x002 #define GOT_A_SINGLE_SCALE 0x008 #define THERE_ARE_MORE_COMPONENTS 0x020 #define GOT_AN_X_AND_Y_SCALE 0x040 #define GOT_A_SCALE_MATRIX 0x080 /* macros */ #define MIN(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) #define SIGN(x) (((x) > 0) - ((x) < 0)) /* Allocate values on the stack if they are small enough, else spill to heap. */ #define STACK_ALLOC(var, type, thresh, count) \ type var##_stack_[thresh]; \ var = (count) <= (thresh) ? var##_stack_ : calloc(sizeof(type), count); #define STACK_FREE(var) \ if (var != var##_stack_) free(var); enum { SrcMapping, SrcUser }; /* structs */ typedef struct Point Point; typedef struct Line Line; typedef struct Curve Curve; typedef struct Cell Cell; typedef struct Outline Outline; typedef struct Raster Raster; struct Point { double x, y; }; struct Line { uint_least16_t beg, end; }; struct Curve { uint_least16_t beg, end, ctrl; }; struct Cell { double area, cover; }; struct Outline { Point *points; Curve *curves; Line *lines; uint_least16_t numPoints; uint_least16_t capPoints; uint_least16_t numCurves; uint_least16_t capCurves; uint_least16_t numLines; uint_least16_t capLines; }; struct Raster { Cell *cells; int width; int height; }; struct SFT_Font { const uint8_t *memory; uint_fast32_t size; #if defined(_WIN32) HANDLE mapping; #endif int source; uint_least16_t unitsPerEm; int_least16_t locaFormat; uint_least16_t numLongHmtx; }; /* function declarations */ /* generic utility functions */ static void *reallocarray(void *optr, size_t nmemb, size_t size); static inline int fast_floor(double x); static inline int fast_ceil (double x); /* file loading */ static int map_file (SFT_Font *font, const char *filename); static void unmap_file(SFT_Font *font); static int init_font (SFT_Font *font); /* simple mathematical operations */ static Point midpoint(Point a, Point b); static void transform_points(unsigned int numPts, Point *points, double trf[6]); static void clip_points(unsigned int numPts, Point *points, int width, int height); /* 'outline' data structure management */ static int init_outline(Outline *outl); static void free_outline(Outline *outl); static int grow_points (Outline *outl); static int grow_curves (Outline *outl); static int grow_lines (Outline *outl); /* TTF parsing utilities */ static inline int is_safe_offset(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, uint_fast32_t margin); static void *csearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nmemb, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void *)); static int cmpu16(const void *a, const void *b); static int cmpu32(const void *a, const void *b); static inline uint_least8_t getu8 (SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset); static inline int_least8_t geti8 (SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset); static inline uint_least16_t getu16(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset); static inline int_least16_t geti16(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset); static inline uint_least32_t getu32(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset); static int gettable(SFT_Font *font, char tag[4], uint_fast32_t *offset); /* codepoint to glyph id translation */ static int cmap_fmt4(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t table, SFT_UChar charCode, uint_fast32_t *glyph); static int cmap_fmt6(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t table, SFT_UChar charCode, uint_fast32_t *glyph); static int glyph_id(SFT_Font *font, SFT_UChar charCode, uint_fast32_t *glyph); /* glyph metrics lookup */ static int hor_metrics(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t glyph, int *advanceWidth, int *leftSideBearing); static int glyph_bbox(const SFT *sft, uint_fast32_t outline, int box[4]); /* decoding outlines */ static int outline_offset(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t glyph, uint_fast32_t *offset); static int simple_flags(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t *offset, uint_fast16_t numPts, uint8_t *flags); static int simple_points(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, uint_fast16_t numPts, uint8_t *flags, Point *points); static int decode_contour(uint8_t *flags, uint_fast16_t basePoint, uint_fast16_t count, Outline *outl); static int simple_outline(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, unsigned int numContours, Outline *outl); static int compound_outline(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, int recDepth, Outline *outl); static int decode_outline(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, int recDepth, Outline *outl); /* tesselation */ static int is_flat(Outline *outl, Curve curve); static int tesselate_curve(Curve curve, Outline *outl); static int tesselate_curves(Outline *outl); /* silhouette rasterization */ static void draw_line(Raster buf, Point origin, Point goal); static void draw_lines(Outline *outl, Raster buf); /* post-processing */ static void post_process(Raster buf, uint8_t *image); /* glyph rendering */ static int render_outline(Outline *outl, double transform[6], SFT_Image image); /* function implementations */ const char * sft_version(void) { return SCHRIFT_VERSION; } /* Loads a font from a user-supplied memory range. */ SFT_Font * sft_loadmem(const void *mem, size_t size) { SFT_Font *font; if (size > UINT32_MAX) { return NULL; } if (!(font = calloc(1, sizeof *font))) { return NULL; } font->memory = mem; font->size = (uint_fast32_t) size; font->source = SrcUser; if (init_font(font) < 0) { sft_freefont(font); return NULL; } return font; } /* Loads a font from the file system. To do so, it has to map the entire font into memory. */ SFT_Font * sft_loadfile(char const *filename) { SFT_Font *font; if (!(font = calloc(1, sizeof *font))) { return NULL; } if (map_file(font, filename) < 0) { free(font); return NULL; } if (init_font(font) < 0) { sft_freefont(font); return NULL; } return font; } void sft_freefont(SFT_Font *font) { if (!font) return; /* Only unmap if we mapped it ourselves. */ if (font->source == SrcMapping) unmap_file(font); free(font); } int sft_lmetrics(const SFT *sft, SFT_LMetrics *metrics) { double factor; uint_fast32_t hhea; memset(metrics, 0, sizeof *metrics); if (gettable(sft->font, "hhea", &hhea) < 0) return -1; if (!is_safe_offset(sft->font, hhea, 36)) return -1; factor = sft->yScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; metrics->ascender = geti16(sft->font, hhea + 4) * factor; metrics->descender = geti16(sft->font, hhea + 6) * factor; metrics->lineGap = geti16(sft->font, hhea + 8) * factor; return 0; } int sft_lookup(const SFT *sft, SFT_UChar codepoint, SFT_Glyph *glyph) { return glyph_id(sft->font, codepoint, glyph); } int sft_gmetrics(const SFT *sft, SFT_Glyph glyph, SFT_GMetrics *metrics) { int adv, lsb; double xScale = sft->xScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; uint_fast32_t outline; int bbox[4]; memset(metrics, 0, sizeof *metrics); if (hor_metrics(sft->font, glyph, &adv, &lsb) < 0) return -1; metrics->advanceWidth = adv * xScale; metrics->leftSideBearing = lsb * xScale + sft->xOffset; if (outline_offset(sft->font, glyph, &outline) < 0) return -1; if (!outline) return 0; if (glyph_bbox(sft, outline, bbox) < 0) return -1; metrics->minWidth = bbox[2] - bbox[0] + 1; metrics->minHeight = bbox[3] - bbox[1] + 1; metrics->yOffset = sft->flags & SFT_DOWNWARD_Y ? -bbox[3] : bbox[1]; return 0; } int sft_kerning(const SFT *sft, SFT_Glyph leftGlyph, SFT_Glyph rightGlyph, SFT_Kerning *kerning) { void *match; uint_fast32_t offset; unsigned int numTables, numPairs, length, format, flags; int value; uint8_t key[4]; memset(kerning, 0, sizeof *kerning); if (gettable(sft->font, "kern", &offset) < 0) return 0; /* Read kern table header. */ if (!is_safe_offset(sft->font, offset, 4)) return -1; if (getu16(sft->font, offset) != 0) return 0; numTables = getu16(sft->font, offset + 2); offset += 4; while (numTables > 0) { /* Read subtable header. */ if (!is_safe_offset(sft->font, offset, 6)) return -1; length = getu16(sft->font, offset + 2); format = getu8 (sft->font, offset + 4); flags = getu8 (sft->font, offset + 5); offset += 6; if (format == 0 && (flags & HORIZONTAL_KERNING) && !(flags & MINIMUM_KERNING)) { /* Read format 0 header. */ if (!is_safe_offset(sft->font, offset, 8)) return -1; numPairs = getu16(sft->font, offset); offset += 8; /* Look up character code pair via binary search. */ key[0] = (leftGlyph >> 8) & 0xFF; key[1] = leftGlyph & 0xFF; key[2] = (rightGlyph >> 8) & 0xFF; key[3] = rightGlyph & 0xFF; if ((match = bsearch(key, sft->font->memory + offset, numPairs, 6, cmpu32)) != NULL) { value = geti16(sft->font, (uint_fast32_t) ((uint8_t *) match - sft->font->memory + 4)); if (flags & CROSS_STREAM_KERNING) { kerning->yShift += value; } else { kerning->xShift += value; } } } offset += length; --numTables; } kerning->xShift = kerning->xShift / sft->font->unitsPerEm * sft->xScale; kerning->yShift = kerning->yShift / sft->font->unitsPerEm * sft->yScale; return 0; } int sft_render(const SFT *sft, SFT_Glyph glyph, SFT_Image image) { uint_fast32_t outline; double transform[6]; int bbox[4]; Outline outl; if (outline_offset(sft->font, glyph, &outline) < 0) return -1; if (!outline) return 0; if (glyph_bbox(sft, outline, bbox) < 0) return -1; /* Set up the transformation matrix such that * the transformed bounding boxes min corner lines * up with the (0, 0) point. */ transform[0] = sft->xScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; transform[1] = 0.0; transform[2] = 0.0; transform[4] = sft->xOffset - bbox[0]; if (sft->flags & SFT_DOWNWARD_Y) { transform[3] = -sft->yScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; transform[5] = bbox[3] - sft->yOffset; } else { transform[3] = +sft->yScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; transform[5] = sft->yOffset - bbox[1]; } memset(&outl, 0, sizeof outl); if (init_outline(&outl) < 0) goto failure; if (decode_outline(sft->font, outline, 0, &outl) < 0) goto failure; if (render_outline(&outl, transform, image) < 0) goto failure; free_outline(&outl); return 0; failure: free_outline(&outl); return -1; } /* This is sqrt(SIZE_MAX+1), as s1*s2 <= SIZE_MAX * if both s1 < MUL_NO_OVERFLOW and s2 < MUL_NO_OVERFLOW */ #define MUL_NO_OVERFLOW ((size_t)1 << (sizeof(size_t) * 4)) /* OpenBSD's reallocarray() standard libary function. * A wrapper for realloc() that takes two size args like calloc(). * Useful because it eliminates common integer overflow bugs. */ static void * reallocarray(void *optr, size_t nmemb, size_t size) { if ((nmemb >= MUL_NO_OVERFLOW || size >= MUL_NO_OVERFLOW) && nmemb > 0 && SIZE_MAX / nmemb < size) { errno = ENOMEM; return NULL; } return realloc(optr, size * nmemb); } /* TODO maybe we should use long here instead of int. */ static inline int fast_floor(double x) { int i = (int) x; return i - (i > x); } static inline int fast_ceil(double x) { int i = (int) x; return i + (i < x); } #if defined(_WIN32) static int map_file(SFT_Font *font, const char *filename) { HANDLE file; DWORD high, low; font->mapping = NULL; font->memory = NULL; file = CreateFileA(filename, GENERIC_READ, FILE_SHARE_READ, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, 0, NULL); if (file == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) { return -1; } low = GetFileSize(file, &high); if (low == INVALID_FILE_SIZE) { CloseHandle(file); return -1; } font->size = (size_t)high << (8 * sizeof(DWORD)) | low; font->mapping = CreateFileMapping(file, NULL, PAGE_READONLY, high, low, NULL); if (!font->mapping) { CloseHandle(file); return -1; } CloseHandle(file); font->memory = MapViewOfFile(font->mapping, FILE_MAP_READ, 0, 0, 0); if (!font->memory) { CloseHandle(font->mapping); font->mapping = NULL; return -1; } return 0; } static void unmap_file(SFT_Font *font) { if (font->memory) { UnmapViewOfFile(font->memory); font->memory = NULL; } if (font->mapping) { CloseHandle(font->mapping); font->mapping = NULL; } } #else static int map_file(SFT_Font *font, const char *filename) { struct stat info; int fd; font->memory = MAP_FAILED; font->size = 0; font->source = SrcMapping; if ((fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY)) < 0) { return -1; } if (fstat(fd, &info) < 0) { close(fd); return -1; } /* FIXME do some basic validation on info.st_size maybe - it is signed for example, so it *could* be negative .. */ font->memory = mmap(NULL, (size_t) info.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, fd, 0); font->size = (uint_fast32_t) info.st_size; close(fd); return font->memory == MAP_FAILED ? -1 : 0; } static void unmap_file(SFT_Font *font) { assert(font->memory != MAP_FAILED); munmap((void *) font->memory, font->size); } #endif static int init_font(SFT_Font *font) { uint_fast32_t scalerType, head, hhea; if (!is_safe_offset(font, 0, 12)) return -1; /* Check for a compatible scalerType (magic number). */ scalerType = getu32(font, 0); if (scalerType != FILE_MAGIC_ONE && scalerType != FILE_MAGIC_TWO) return -1; if (gettable(font, "head", &head) < 0) return -1; if (!is_safe_offset(font, head, 54)) return -1; font->unitsPerEm = getu16(font, head + 18); font->locaFormat = geti16(font, head + 50); if (gettable(font, "hhea", &hhea) < 0) return -1; if (!is_safe_offset(font, hhea, 36)) return -1; font->numLongHmtx = getu16(font, hhea + 34); return 0; } static Point midpoint(Point a, Point b) { return (Point) { 0.5 * (a.x + b.x), 0.5 * (a.y + b.y) }; } /* Applies an affine linear transformation matrix to a set of points. */ static void transform_points(unsigned int numPts, Point *points, double trf[6]) { Point pt; unsigned int i; for (i = 0; i < numPts; ++i) { pt = points[i]; points[i] = (Point) { pt.x * trf[0] + pt.y * trf[2] + trf[4], pt.x * trf[1] + pt.y * trf[3] + trf[5] }; } } static void clip_points(unsigned int numPts, Point *points, int width, int height) { Point pt; unsigned int i; for (i = 0; i < numPts; ++i) { pt = points[i]; if (pt.x < 0.0) { points[i].x = 0.0; } if (pt.x >= width) { points[i].x = nextafter(width, 0.0); } if (pt.y < 0.0) { points[i].y = 0.0; } if (pt.y >= height) { points[i].y = nextafter(height, 0.0); } } } static int init_outline(Outline *outl) { /* TODO Smaller initial allocations */ outl->numPoints = 0; outl->capPoints = 64; if (!(outl->points = malloc(outl->capPoints * sizeof *outl->points))) return -1; outl->numCurves = 0; outl->capCurves = 64; if (!(outl->curves = malloc(outl->capCurves * sizeof *outl->curves))) return -1; outl->numLines = 0; outl->capLines = 64; if (!(outl->lines = malloc(outl->capLines * sizeof *outl->lines))) return -1; return 0; } static void free_outline(Outline *outl) { free(outl->points); free(outl->curves); free(outl->lines); } static int grow_points(Outline *outl) { void *mem; uint_fast16_t cap; assert(outl->capPoints); /* Since we use uint_fast16_t for capacities, we have to be extra careful not to trigger integer overflow. */ if (outl->capPoints > UINT16_MAX / 2) return -1; cap = (uint_fast16_t) (2U * outl->capPoints); if (!(mem = reallocarray(outl->points, cap, sizeof *outl->points))) return -1; outl->capPoints = (uint_least16_t) cap; outl->points = mem; return 0; } static int grow_curves(Outline *outl) { void *mem; uint_fast16_t cap; assert(outl->capCurves); if (outl->capCurves > UINT16_MAX / 2) return -1; cap = (uint_fast16_t) (2U * outl->capCurves); if (!(mem = reallocarray(outl->curves, cap, sizeof *outl->curves))) return -1; outl->capCurves = (uint_least16_t) cap; outl->curves = mem; return 0; } static int grow_lines(Outline *outl) { void *mem; uint_fast16_t cap; assert(outl->capLines); if (outl->capLines > UINT16_MAX / 2) return -1; cap = (uint_fast16_t) (2U * outl->capLines); if (!(mem = reallocarray(outl->lines, cap, sizeof *outl->lines))) return -1; outl->capLines = (uint_least16_t) cap; outl->lines = mem; return 0; } static inline int is_safe_offset(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, uint_fast32_t margin) { if (offset > font->size) return 0; if (font->size - offset < margin) return 0; return 1; } /* Like bsearch(), but returns the next highest element if key could not be found. */ static void * csearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nmemb, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void *)) { const uint8_t *bytes = base, *sample; size_t low = 0, high = nmemb - 1, mid; if (!nmemb) return NULL; while (low != high) { mid = low + (high - low) / 2; sample = bytes + mid * size; if (compar(key, sample) > 0) { low = mid + 1; } else { high = mid; } } return (uint8_t *) bytes + low * size; } /* Used as a comparison function for [bc]search(). */ static int cmpu16(const void *a, const void *b) { return memcmp(a, b, 2); } /* Used as a comparison function for [bc]search(). */ static int cmpu32(const void *a, const void *b) { return memcmp(a, b, 4); } static inline uint_least8_t getu8(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset) { assert(offset + 1 <= font->size); return *(font->memory + offset); } static inline int_least8_t geti8(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset) { return (int_least8_t) getu8(font, offset); } static inline uint_least16_t getu16(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset) { assert(offset + 2 <= font->size); const uint8_t *base = font->memory + offset; uint_least16_t b1 = base[0], b0 = base[1]; return (uint_least16_t) (b1 << 8 | b0); } static inline int16_t geti16(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset) { return (int_least16_t) getu16(font, offset); } static inline uint32_t getu32(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset) { assert(offset + 4 <= font->size); const uint8_t *base = font->memory + offset; uint_least32_t b3 = base[0], b2 = base[1], b1 = base[2], b0 = base[3]; return (uint_least32_t) (b3 << 24 | b2 << 16 | b1 << 8 | b0); } static int gettable(SFT_Font *font, char tag[4], uint_fast32_t *offset) { void *match; unsigned int numTables; /* No need to bounds-check access to the first 12 bytes - this gets already checked by init_font(). */ numTables = getu16(font, 4); if (!is_safe_offset(font, 12, (uint_fast32_t) numTables * 16)) return -1; if (!(match = bsearch(tag, font->memory + 12, numTables, 16, cmpu32))) return -1; *offset = getu32(font, (uint_fast32_t) ((uint8_t *) match - font->memory + 8)); return 0; } static int cmap_fmt4(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t table, SFT_UChar charCode, SFT_Glyph *glyph) { const uint8_t *segPtr; uint_fast32_t segIdxX2; uint_fast32_t endCodes, startCodes, idDeltas, idRangeOffsets, idOffset; uint_fast16_t segCountX2, idRangeOffset, startCode, shortCode, idDelta, id; uint8_t key[2] = { (uint8_t) (charCode >> 8), (uint8_t) charCode }; /* cmap format 4 only supports the Unicode BMP. */ if (charCode > 0xFFFF) { *glyph = 0; return 0; } shortCode = (uint_fast16_t) charCode; if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, 8)) return -1; segCountX2 = getu16(font, table); if ((segCountX2 & 1) || !segCountX2) return -1; /* Find starting positions of the relevant arrays. */ endCodes = table + 8; startCodes = endCodes + segCountX2 + 2; idDeltas = startCodes + segCountX2; idRangeOffsets = idDeltas + segCountX2; if (!is_safe_offset(font, idRangeOffsets, segCountX2)) return -1; /* Find the segment that contains shortCode by binary searching over * the highest codes in the segments. */ segPtr = csearch(key, font->memory + endCodes, segCountX2 / 2, 2, cmpu16); segIdxX2 = (uint_fast32_t) (segPtr - (font->memory + endCodes)); /* Look up segment info from the arrays & short circuit if the spec requires. */ if ((startCode = getu16(font, startCodes + segIdxX2)) > shortCode) return 0; idDelta = getu16(font, idDeltas + segIdxX2); if (!(idRangeOffset = getu16(font, idRangeOffsets + segIdxX2))) { /* Intentional integer under- and overflow. */ *glyph = (shortCode + idDelta) & 0xFFFF; return 0; } /* Calculate offset into glyph array and determine ultimate value. */ idOffset = idRangeOffsets + segIdxX2 + idRangeOffset + 2U * (unsigned int) (shortCode - startCode); if (!is_safe_offset(font, idOffset, 2)) return -1; id = getu16(font, idOffset); /* Intentional integer under- and overflow. */ *glyph = id ? (id + idDelta) & 0xFFFF : 0; return 0; } static int cmap_fmt6(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t table, SFT_UChar charCode, SFT_Glyph *glyph) { unsigned int firstCode, entryCount; /* cmap format 6 only supports the Unicode BMP. */ if (charCode > 0xFFFF) { *glyph = 0; return 0; } if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, 4)) return -1; firstCode = getu16(font, table); entryCount = getu16(font, table + 2); if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, 4 + 2 * entryCount)) return -1; if (charCode < firstCode) return -1; charCode -= firstCode; if (!(charCode < entryCount)) return -1; *glyph = getu16(font, table + 4 + 2 * charCode); return 0; } static int cmap_fmt12_13(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t table, SFT_UChar charCode, SFT_Glyph *glyph, int which) { uint32_t len, numEntries; uint_fast32_t i; *glyph = 0; /* check that the entire header is present */ if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, 16)) return -1; len = getu32(font, table + 4); /* A minimal header is 16 bytes */ if (len < 16) return -1; if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, len)) return -1; numEntries = getu32(font, table + 12); for (i = 0; i < numEntries; ++i) { uint32_t firstCode, lastCode, glyphOffset; firstCode = getu32(font, table + (i * 12) + 16); lastCode = getu32(font, table + (i * 12) + 16 + 4); if (charCode < firstCode || charCode > lastCode) continue; glyphOffset = getu32(font, table + (i * 12) + 16 + 8); if (which == 12) *glyph = (charCode-firstCode) + glyphOffset; else *glyph = glyphOffset; return 0; } return 0; } /* Maps Unicode code points to glyph indices. */ static int glyph_id(SFT_Font *font, SFT_UChar charCode, SFT_Glyph *glyph) { uint_fast32_t cmap, entry, table; unsigned int idx, numEntries; int type, format; *glyph = 0; if (gettable(font, "cmap", &cmap) < 0) return -1; if (!is_safe_offset(font, cmap, 4)) return -1; numEntries = getu16(font, cmap + 2); if (!is_safe_offset(font, cmap, 4 + numEntries * 8)) return -1; /* First look for a 'full repertoire'/non-BMP map. */ for (idx = 0; idx < numEntries; ++idx) { entry = cmap + 4 + idx * 8; type = getu16(font, entry) * 0100 + getu16(font, entry + 2); /* Complete unicode map */ if (type == 0004 || type == 0312) { table = cmap + getu32(font, entry + 4); if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, 8)) return -1; /* Dispatch based on cmap format. */ format = getu16(font, table); switch (format) { case 12: return cmap_fmt12_13(font, table, charCode, glyph, 12); default: return -1; } } } /* If no 'full repertoire' cmap was found, try looking for a BMP map. */ for (idx = 0; idx < numEntries; ++idx) { entry = cmap + 4 + idx * 8; type = getu16(font, entry) * 0100 + getu16(font, entry + 2); /* Unicode BMP */ if (type == 0003 || type == 0301) { table = cmap + getu32(font, entry + 4); if (!is_safe_offset(font, table, 6)) return -1; /* Dispatch based on cmap format. */ switch (getu16(font, table)) { case 4: return cmap_fmt4(font, table + 6, charCode, glyph); case 6: return cmap_fmt6(font, table + 6, charCode, glyph); default: return -1; } } } return -1; } static int hor_metrics(SFT_Font *font, SFT_Glyph glyph, int *advanceWidth, int *leftSideBearing) { uint_fast32_t hmtx, offset, boundary; if (gettable(font, "hmtx", &hmtx) < 0) return -1; if (glyph < font->numLongHmtx) { /* glyph is inside long metrics segment. */ offset = hmtx + 4 * glyph; if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 4)) return -1; *advanceWidth = getu16(font, offset); *leftSideBearing = geti16(font, offset + 2); return 0; } else { /* glyph is inside short metrics segment. */ boundary = hmtx + 4U * (uint_fast32_t) font->numLongHmtx; if (boundary < 4) return -1; offset = boundary - 4; if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 4)) return -1; *advanceWidth = getu16(font, offset); offset = boundary + 2 * (glyph - font->numLongHmtx); if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 2)) return -1; *leftSideBearing = geti16(font, offset); return 0; } } static int glyph_bbox(const SFT *sft, uint_fast32_t outline, int box[4]) { double xScale, yScale; /* Read the bounding box from the font file verbatim. */ if (!is_safe_offset(sft->font, outline, 10)) return -1; box[0] = geti16(sft->font, outline + 2); box[1] = geti16(sft->font, outline + 4); box[2] = geti16(sft->font, outline + 6); box[3] = geti16(sft->font, outline + 8); if (box[2] <= box[0] || box[3] <= box[1]) return -1; /* Transform the bounding box into SFT coordinate space. */ xScale = sft->xScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; yScale = sft->yScale / sft->font->unitsPerEm; box[0] = (int) floor(box[0] * xScale + sft->xOffset); box[1] = (int) floor(box[1] * yScale + sft->yOffset); box[2] = (int) ceil (box[2] * xScale + sft->xOffset); box[3] = (int) ceil (box[3] * yScale + sft->yOffset); return 0; } /* Returns the offset into the font that the glyph's outline is stored at. */ static int outline_offset(SFT_Font *font, SFT_Glyph glyph, uint_fast32_t *offset) { uint_fast32_t loca, glyf; uint_fast32_t base, this, next; if (gettable(font, "loca", &loca) < 0) return -1; if (gettable(font, "glyf", &glyf) < 0) return -1; if (font->locaFormat == 0) { base = loca + 2 * glyph; if (!is_safe_offset(font, base, 4)) return -1; this = 2U * (uint_fast32_t) getu16(font, base); next = 2U * (uint_fast32_t) getu16(font, base + 2); } else { base = loca + 4 * glyph; if (!is_safe_offset(font, base, 8)) return -1; this = getu32(font, base); next = getu32(font, base + 4); } *offset = this == next ? 0 : glyf + this; return 0; } /* For a 'simple' outline, determines each point of the outline with a set of flags. */ static int simple_flags(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t *offset, uint_fast16_t numPts, uint8_t *flags) { uint_fast32_t off = *offset; uint_fast16_t i; uint8_t value = 0, repeat = 0; for (i = 0; i < numPts; ++i) { if (repeat) { --repeat; } else { if (!is_safe_offset(font, off, 1)) return -1; value = getu8(font, off++); if (value & REPEAT_FLAG) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, off, 1)) return -1; repeat = getu8(font, off++); } } flags[i] = value; } *offset = off; return 0; } /* For a 'simple' outline, decodes both X and Y coordinates for each point of the outline. */ static int simple_points(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, uint_fast16_t numPts, uint8_t *flags, Point *points) { long accum, value, bit; uint_fast16_t i; accum = 0L; for (i = 0; i < numPts; ++i) { if (flags[i] & X_CHANGE_IS_SMALL) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 1)) return -1; value = (long) getu8(font, offset++); bit = !!(flags[i] & X_CHANGE_IS_POSITIVE); accum -= (value ^ -bit) + bit; } else if (!(flags[i] & X_CHANGE_IS_ZERO)) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 2)) return -1; accum += geti16(font, offset); offset += 2; } points[i].x = (double) accum; } accum = 0L; for (i = 0; i < numPts; ++i) { if (flags[i] & Y_CHANGE_IS_SMALL) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 1)) return -1; value = (long) getu8(font, offset++); bit = !!(flags[i] & Y_CHANGE_IS_POSITIVE); accum -= (value ^ -bit) + bit; } else if (!(flags[i] & Y_CHANGE_IS_ZERO)) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 2)) return -1; accum += geti16(font, offset); offset += 2; } points[i].y = (double) accum; } return 0; } static int decode_contour(uint8_t *flags, uint_fast16_t basePoint, uint_fast16_t count, Outline *outl) { uint_fast16_t i; uint_least16_t looseEnd, beg, ctrl, center, cur; unsigned int gotCtrl; /* Skip contours with less than two points, since the following algorithm can't handle them and * they should appear invisible either way (because they don't have any area). */ if (count < 2) return 0; assert(basePoint <= UINT16_MAX - count); if (flags[0] & POINT_IS_ON_CURVE) { looseEnd = (uint_least16_t) basePoint++; ++flags; --count; } else if (flags[count - 1] & POINT_IS_ON_CURVE) { looseEnd = (uint_least16_t) (basePoint + --count); } else { if (outl->numPoints >= outl->capPoints && grow_points(outl) < 0) return -1; looseEnd = outl->numPoints; outl->points[outl->numPoints++] = midpoint( outl->points[basePoint], outl->points[basePoint + count - 1]); } beg = looseEnd; gotCtrl = 0; for (i = 0; i < count; ++i) { /* cur can't overflow because we ensure that basePoint + count < 0xFFFF before calling decode_contour(). */ cur = (uint_least16_t) (basePoint + i); /* NOTE clang-analyzer will often flag this and another piece of code because it thinks that flags and * outl->points + basePoint don't always get properly initialized -- even when you explicitly loop over both * and set every element to zero (but not when you use memset). This is a known clang-analyzer bug: * http://clang-developers.42468.n3.nabble.com/StaticAnalyzer-False-positive-with-loop-handling-td4053875.html */ if (flags[i] & POINT_IS_ON_CURVE) { if (gotCtrl) { if (outl->numCurves >= outl->capCurves && grow_curves(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->curves[outl->numCurves++] = (Curve) { beg, cur, ctrl }; } else { if (outl->numLines >= outl->capLines && grow_lines(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->lines[outl->numLines++] = (Line) { beg, cur }; } beg = cur; gotCtrl = 0; } else { if (gotCtrl) { center = outl->numPoints; if (outl->numPoints >= outl->capPoints && grow_points(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->points[center] = midpoint(outl->points[ctrl], outl->points[cur]); ++outl->numPoints; if (outl->numCurves >= outl->capCurves && grow_curves(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->curves[outl->numCurves++] = (Curve) { beg, center, ctrl }; beg = center; } ctrl = cur; gotCtrl = 1; } } if (gotCtrl) { if (outl->numCurves >= outl->capCurves && grow_curves(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->curves[outl->numCurves++] = (Curve) { beg, looseEnd, ctrl }; } else { if (outl->numLines >= outl->capLines && grow_lines(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->lines[outl->numLines++] = (Line) { beg, looseEnd }; } return 0; } static int simple_outline(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, unsigned int numContours, Outline *outl) { uint_fast16_t *endPts = NULL; uint8_t *flags = NULL; uint_fast16_t numPts; unsigned int i; assert(numContours > 0); uint_fast16_t basePoint = outl->numPoints; if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, numContours * 2 + 2)) goto failure; numPts = getu16(font, offset + (numContours - 1) * 2); if (numPts >= UINT16_MAX) goto failure; numPts++; if (outl->numPoints > UINT16_MAX - numPts) goto failure; while (outl->capPoints < basePoint + numPts) { if (grow_points(outl) < 0) goto failure; } STACK_ALLOC(endPts, uint_fast16_t, 16, numContours); if (endPts == NULL) goto failure; STACK_ALLOC(flags, uint8_t, 128, numPts); if (flags == NULL) goto failure; for (i = 0; i < numContours; ++i) { endPts[i] = getu16(font, offset); offset += 2; } /* Ensure that endPts are never falling. * Falling endPts have no sensible interpretation and most likely only occur in malicious input. * Therefore, we bail, should we ever encounter such input. */ for (i = 0; i < numContours - 1; ++i) { if (endPts[i + 1] < endPts[i] + 1) goto failure; } offset += 2U + getu16(font, offset); if (simple_flags(font, &offset, numPts, flags) < 0) goto failure; if (simple_points(font, offset, numPts, flags, outl->points + basePoint) < 0) goto failure; outl->numPoints = (uint_least16_t) (outl->numPoints + numPts); uint_fast16_t beg = 0; for (i = 0; i < numContours; ++i) { uint_fast16_t count = endPts[i] - beg + 1; if (decode_contour(flags + beg, basePoint + beg, count, outl) < 0) goto failure; beg = endPts[i] + 1; } STACK_FREE(endPts); STACK_FREE(flags); return 0; failure: STACK_FREE(endPts); STACK_FREE(flags); return -1; } static int compound_outline(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, int recDepth, Outline *outl) { double local[6]; uint_fast32_t outline; unsigned int flags, glyph, basePoint; /* Guard against infinite recursion (compound glyphs that have themselves as component). */ if (recDepth >= 4) return -1; do { memset(local, 0, sizeof local); if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 4)) return -1; flags = getu16(font, offset); glyph = getu16(font, offset + 2); offset += 4; /* We don't implement point matching, and neither does stb_truetype for that matter. */ if (!(flags & ACTUAL_XY_OFFSETS)) return -1; /* Read additional X and Y offsets (in FUnits) of this component. */ if (flags & OFFSETS_ARE_LARGE) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 4)) return -1; local[4] = geti16(font, offset); local[5] = geti16(font, offset + 2); offset += 4; } else { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 2)) return -1; local[4] = geti8(font, offset); local[5] = geti8(font, offset + 1); offset += 2; } if (flags & GOT_A_SINGLE_SCALE) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 2)) return -1; local[0] = geti16(font, offset) / 16384.0; local[3] = local[0]; offset += 2; } else if (flags & GOT_AN_X_AND_Y_SCALE) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 4)) return -1; local[0] = geti16(font, offset + 0) / 16384.0; local[3] = geti16(font, offset + 2) / 16384.0; offset += 4; } else if (flags & GOT_A_SCALE_MATRIX) { if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 8)) return -1; local[0] = geti16(font, offset + 0) / 16384.0; local[1] = geti16(font, offset + 2) / 16384.0; local[2] = geti16(font, offset + 4) / 16384.0; local[3] = geti16(font, offset + 6) / 16384.0; offset += 8; } else { local[0] = 1.0; local[3] = 1.0; } /* At this point, Apple's spec more or less tells you to scale the matrix by its own L1 norm. * But stb_truetype scales by the L2 norm. And FreeType2 doesn't scale at all. * Furthermore, Microsoft's spec doesn't even mention anything like this. * It's almost as if nobody ever uses this feature anyway. */ if (outline_offset(font, glyph, &outline) < 0) return -1; if (outline) { basePoint = outl->numPoints; if (decode_outline(font, outline, recDepth + 1, outl) < 0) return -1; transform_points(outl->numPoints - basePoint, outl->points + basePoint, local); } } while (flags & THERE_ARE_MORE_COMPONENTS); return 0; } static int decode_outline(SFT_Font *font, uint_fast32_t offset, int recDepth, Outline *outl) { int numContours; if (!is_safe_offset(font, offset, 10)) return -1; numContours = geti16(font, offset); if (numContours > 0) { /* Glyph has a 'simple' outline consisting of a number of contours. */ return simple_outline(font, offset + 10, (unsigned int) numContours, outl); } else if (numContours < 0) { /* Glyph has a compound outline combined from mutiple other outlines. */ return compound_outline(font, offset + 10, recDepth, outl); } else { return 0; } } /* A heuristic to tell whether a given curve can be approximated closely enough by a line. */ static int is_flat(Outline *outl, Curve curve) { const double maxArea2 = 2.0; Point a = outl->points[curve.beg]; Point b = outl->points[curve.ctrl]; Point c = outl->points[curve.end]; Point g = { b.x-a.x, b.y-a.y }; Point h = { c.x-a.x, c.y-a.y }; double area2 = fabs(g.x*h.y-h.x*g.y); return area2 <= maxArea2; } static int tesselate_curve(Curve curve, Outline *outl) { /* From my tests I can conclude that this stack barely reaches a top height * of 4 elements even for the largest font sizes I'm willing to support. And * as space requirements should only grow logarithmically, I think 10 is * more than enough. */ #define STACK_SIZE 10 Curve stack[STACK_SIZE]; unsigned int top = 0; for (;;) { if (is_flat(outl, curve) || top >= STACK_SIZE) { if (outl->numLines >= outl->capLines && grow_lines(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->lines[outl->numLines++] = (Line) { curve.beg, curve.end }; if (top == 0) break; curve = stack[--top]; } else { uint_least16_t ctrl0 = outl->numPoints; if (outl->numPoints >= outl->capPoints && grow_points(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->points[ctrl0] = midpoint(outl->points[curve.beg], outl->points[curve.ctrl]); ++outl->numPoints; uint_least16_t ctrl1 = outl->numPoints; if (outl->numPoints >= outl->capPoints && grow_points(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->points[ctrl1] = midpoint(outl->points[curve.ctrl], outl->points[curve.end]); ++outl->numPoints; uint_least16_t pivot = outl->numPoints; if (outl->numPoints >= outl->capPoints && grow_points(outl) < 0) return -1; outl->points[pivot] = midpoint(outl->points[ctrl0], outl->points[ctrl1]); ++outl->numPoints; stack[top++] = (Curve) { curve.beg, pivot, ctrl0 }; curve = (Curve) { pivot, curve.end, ctrl1 }; } } return 0; #undef STACK_SIZE } static int tesselate_curves(Outline *outl) { unsigned int i; for (i = 0; i < outl->numCurves; ++i) { if (tesselate_curve(outl->curves[i], outl) < 0) return -1; } return 0; } /* Draws a line into the buffer. Uses a custom 2D raycasting algorithm to do so. */ static void draw_line(Raster buf, Point origin, Point goal) { Point delta; Point nextCrossing; Point crossingIncr; double halfDeltaX; double prevDistance = 0.0, nextDistance; double xAverage, yDifference; struct { int x, y; } pixel; struct { int x, y; } dir; int step, numSteps = 0; Cell *restrict cptr, cell; delta.x = goal.x - origin.x; delta.y = goal.y - origin.y; dir.x = SIGN(delta.x); dir.y = SIGN(delta.y); if (!dir.y) { return; } crossingIncr.x = dir.x ? fabs(1.0 / delta.x) : 1.0; crossingIncr.y = fabs(1.0 / delta.y); if (!dir.x) { pixel.x = fast_floor(origin.x); nextCrossing.x = 100.0; } else { if (dir.x > 0) { pixel.x = fast_floor(origin.x); nextCrossing.x = (origin.x - pixel.x) * crossingIncr.x; nextCrossing.x = crossingIncr.x - nextCrossing.x; numSteps += fast_ceil(goal.x) - fast_floor(origin.x) - 1; } else { pixel.x = fast_ceil(origin.x) - 1; nextCrossing.x = (origin.x - pixel.x) * crossingIncr.x; numSteps += fast_ceil(origin.x) - fast_floor(goal.x) - 1; } } if (dir.y > 0) { pixel.y = fast_floor(origin.y); nextCrossing.y = (origin.y - pixel.y) * crossingIncr.y; nextCrossing.y = crossingIncr.y - nextCrossing.y; numSteps += fast_ceil(goal.y) - fast_floor(origin.y) - 1; } else { pixel.y = fast_ceil(origin.y) - 1; nextCrossing.y = (origin.y - pixel.y) * crossingIncr.y; numSteps += fast_ceil(origin.y) - fast_floor(goal.y) - 1; } nextDistance = MIN(nextCrossing.x, nextCrossing.y); halfDeltaX = 0.5 * delta.x; for (step = 0; step < numSteps; ++step) { xAverage = origin.x + (prevDistance + nextDistance) * halfDeltaX; yDifference = (nextDistance - prevDistance) * delta.y; cptr = &buf.cells[pixel.y * buf.width + pixel.x]; cell = *cptr; cell.cover += yDifference; xAverage -= (double) pixel.x; cell.area += (1.0 - xAverage) * yDifference; *cptr = cell; prevDistance = nextDistance; int alongX = nextCrossing.x < nextCrossing.y; pixel.x += alongX ? dir.x : 0; pixel.y += alongX ? 0 : dir.y; nextCrossing.x += alongX ? crossingIncr.x : 0.0; nextCrossing.y += alongX ? 0.0 : crossingIncr.y; nextDistance = MIN(nextCrossing.x, nextCrossing.y); } xAverage = origin.x + (prevDistance + 1.0) * halfDeltaX; yDifference = (1.0 - prevDistance) * delta.y; cptr = &buf.cells[pixel.y * buf.width + pixel.x]; cell = *cptr; cell.cover += yDifference; xAverage -= (double) pixel.x; cell.area += (1.0 - xAverage) * yDifference; *cptr = cell; } static void draw_lines(Outline *outl, Raster buf) { unsigned int i; for (i = 0; i < outl->numLines; ++i) { Line line = outl->lines[i]; Point origin = outl->points[line.beg]; Point goal = outl->points[line.end]; draw_line(buf, origin, goal); } } /* Integrate the values in the buffer to arrive at the final grayscale image. */ static void post_process(Raster buf, uint8_t *image) { Cell cell; double accum = 0.0, value; unsigned int i, num; num = (unsigned int) buf.width * (unsigned int) buf.height; for (i = 0; i < num; ++i) { cell = buf.cells[i]; value = fabs(accum + cell.area); value = MIN(value, 1.0); value = value * 255.0 + 0.5; image[i] = (uint8_t) value; accum += cell.cover; } } static int render_outline(Outline *outl, double transform[6], SFT_Image image) { Cell *cells = NULL; Raster buf; unsigned int numPixels; numPixels = (unsigned int) image.width * (unsigned int) image.height; STACK_ALLOC(cells, Cell, 128 * 128, numPixels); if (!cells) { return -1; } memset(cells, 0, numPixels * sizeof *cells); buf.cells = cells; buf.width = image.width; buf.height = image.height; transform_points(outl->numPoints, outl->points, transform); clip_points(outl->numPoints, outl->points, image.width, image.height); if (tesselate_curves(outl) < 0) { STACK_FREE(cells); return -1; } draw_lines(outl, buf); post_process(buf, image.pixels); STACK_FREE(cells); return 0; }
/* This file is part of libschrift. * * © 2019-2022 Thomas Oltmann and contributors * * Permission to use, copy, modify, and/or distribute this software for any * purpose with or without fee is hereby granted, provided that the above * copyright notice and this permission notice appear in all copies. * * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND THE AUTHOR DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES * WITH REGARD TO THIS SOFTWARE INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF * MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR * ANY SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES * WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN * ACTION OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE. */ #ifndef SCHRIFT_H #define SCHRIFT_H 1 #include <stddef.h> /* size_t */ #include <stdint.h> /* uint_fast32_t, uint_least32_t */ #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif #define SFT_DOWNWARD_Y 0x01 typedef struct SFT SFT; typedef struct SFT_Font SFT_Font; typedef uint_least32_t SFT_UChar; /* Guaranteed to be compatible with char32_t. */ typedef uint_fast32_t SFT_Glyph; typedef struct SFT_LMetrics SFT_LMetrics; typedef struct SFT_GMetrics SFT_GMetrics; typedef struct SFT_Kerning SFT_Kerning; typedef struct SFT_Image SFT_Image; struct SFT { SFT_Font *font; double xScale; double yScale; double xOffset; double yOffset; int flags; }; struct SFT_LMetrics { double ascender; double descender; double lineGap; }; struct SFT_GMetrics { double advanceWidth; double leftSideBearing; int yOffset; int minWidth; int minHeight; }; struct SFT_Kerning { double xShift; double yShift; }; struct SFT_Image { void *pixels; int width; int height; }; const char *sft_version(void); SFT_Font *sft_loadmem (const void *mem, size_t size); SFT_Font *sft_loadfile(const char *filename); void sft_freefont(SFT_Font *font); int sft_lmetrics(const SFT *sft, SFT_LMetrics *metrics); int sft_lookup (const SFT *sft, SFT_UChar codepoint, SFT_Glyph *glyph); int sft_gmetrics(const SFT *sft, SFT_Glyph glyph, SFT_GMetrics *metrics); int sft_kerning (const SFT *sft, SFT_Glyph leftGlyph, SFT_Glyph rightGlyph, SFT_Kerning *kerning); int sft_render (const SFT *sft, SFT_Glyph glyph, SFT_Image image); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif
• spng__malloc • spng__calloc • spng__realloc • spng__free • spng__zfree • read_u16 • read_u32 • read_s32 • write_u16 • write_u32 • write_s32 • spng__iter_init • get_sample • u16_row_to_host • u16_row_to_bigendian • rgb8_row_to_rgba8 • num_channels • calculate_scanline_width • calculate_subimages • check_decode_fmt • calculate_image_width • calculate_image_size • increase_cache_usage • decrease_cache_usage • is_critical_chunk • decode_err • encode_err • read_data • require_bytes • write_data • write_header • trim_chunk • finish_chunk • write_chunk • write_iend • write_unknown_chunks • read_and_check_crc • read_header • read_chunk_bytes • read_chunk_bytes2 • discard_chunk_bytes • spng__inflate_init • spng__deflate_init • spng__inflate_stream • read_idat_bytes • read_scanline_bytes • paeth • defilter_up • defilter_scanline • filter_scanline • filter_sum • get_best_filter • sample_to_target • gamma_correct_row • trns_row • scale_row • expand_row • unpack_scanline • check_ihdr • check_plte • check_sbit • check_chrm_int • check_phys • check_time • check_offs • check_exif • check_png_keyword • check_png_text • is_small_chunk • read_ihdr • splt_undo • text_undo • chunk_undo • read_non_idat_chunks • read_chunks • read_scanline • update_row_info • spng_decode_scanline • spng_decode_row • spng_decode_chunks • spng_decode_image • spng_get_row_info • write_chunks_before_idat • write_chunks_after_idat • write_idat_bytes • finish_idat • encode_scanline • encode_row • spng_encode_scanline • spng_encode_row • spng_encode_chunks • spng_encode_image • spng_ctx_new • spng_ctx_new2 • spng_ctx_free • buffer_read_fn • file_read_fn • file_write_fn • spng_set_png_buffer • spng_set_png_stream • spng_set_png_file • spng_get_png_buffer • spng_set_image_limits • spng_get_image_limits • spng_set_chunk_limits • spng_get_chunk_limits • spng_set_crc_action • spng_set_option • spng_get_option • spng_decoded_image_size • spng_get_ihdr • spng_get_plte • spng_get_trns • spng_get_chrm • spng_get_chrm_int • spng_get_gama • spng_get_gama_int • spng_get_iccp • spng_get_sbit • spng_get_srgb • spng_get_text • spng_get_bkgd • spng_get_hist • spng_get_phys • spng_get_splt • spng_get_time • spng_get_unknown_chunks • spng_get_offs • spng_get_exif • spng_set_ihdr • spng_set_plte • spng_set_trns • spng_set_chrm • spng_set_chrm_int • spng_set_gama • spng_set_gama_int • spng_set_iccp • spng_set_sbit • spng_set_srgb • spng_set_text • spng_set_bkgd • spng_set_hist • spng_set_phys • spng_set_splt • spng_set_time • spng_set_unknown_chunks • spng_set_offs • spng_set_exif • spng_strerror • spng_version_string • load4 • store4 • load3 • store3 • defilter_sub3 • defilter_sub4 • defilter_avg3 • defilter_avg4 • abs_i16 • if_then_else • defilter_paeth3 • defilter_paeth4 • paeth_arm • expand_palette_rgba8_neon • expand_palette_rgb8_neon
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: (BSD-2-Clause AND libpng-2.0) */ #define SPNG__BUILD #include "spng.h" #include <limits.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #define ZLIB_CONST #ifdef __FRAMAC__ #define SPNG_DISABLE_OPT #include "tests/framac_stubs.h" #else #ifdef SPNG_USE_MINIZ #include <miniz.h> #else #include <zlib.h> #endif #endif #ifdef SPNG_MULTITHREADING #include <pthread.h> #endif /* Not build options, edit at your own risk! */ #define SPNG_READ_SIZE (8192) #define SPNG_WRITE_SIZE SPNG_READ_SIZE #define SPNG_MAX_CHUNK_COUNT (1000) #define SPNG_TARGET_CLONES(x) #ifndef SPNG_DISABLE_OPT #if defined(__i386__) || defined(__x86_64__) || defined(_M_IX86) || defined(_M_X64) #define SPNG_X86 #if defined(__x86_64__) || defined(_M_X64) #define SPNG_X86_64 #endif #elif defined(__aarch64__) || defined(_M_ARM64) /* || defined(__ARM_NEON) */ #define SPNG_ARM /* NOTE: only arm64 builds are tested! */ #else #pragma message "disabling SIMD optimizations for unknown target" #define SPNG_DISABLE_OPT #endif #if defined(SPNG_X86_64) && defined(SPNG_ENABLE_TARGET_CLONES) #undef SPNG_TARGET_CLONES #define SPNG_TARGET_CLONES(x) __attribute__((target_clones(x))) #else #define SPNG_TARGET_CLONES(x) #endif #ifndef SPNG_DISABLE_OPT static void defilter_sub3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row); static void defilter_sub4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row); static void defilter_avg3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev); static void defilter_avg4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev); static void defilter_paeth3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev); static void defilter_paeth4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev); #if defined(SPNG_ARM) static uint32_t expand_palette_rgba8_neon(unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *scanline, const unsigned char *plte, uint32_t width); static uint32_t expand_palette_rgb8_neon(unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *scanline, const unsigned char *plte, uint32_t width); #endif #endif #endif #if defined(_MSC_VER) #pragma warning(push) #pragma warning(disable: 4244) #endif #if (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__) || defined(__BIG_ENDIAN__) #define SPNG_BIG_ENDIAN #else #define SPNG_LITTLE_ENDIAN #endif enum spng_state { SPNG_STATE_INVALID = 0, SPNG_STATE_INIT = 1, /* No PNG buffer/stream is set */ SPNG_STATE_INPUT, /* Decoder input PNG was set */ SPNG_STATE_OUTPUT = SPNG_STATE_INPUT, /* Encoder output was set */ SPNG_STATE_IHDR, /* IHDR was read/written */ SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT, /* Encoded up to / reached first IDAT */ SPNG_STATE_DECODE_INIT, /* Decoder is ready for progressive reads */ SPNG_STATE_ENCODE_INIT = SPNG_STATE_DECODE_INIT, SPNG_STATE_EOI, /* Reached the last scanline/row */ SPNG_STATE_LAST_IDAT, /* Reached last IDAT, set at end of decode_image() */ SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT, /* */ SPNG_STATE_IEND, /* Reached IEND */ }; enum spng__internal { SPNG__IO_SIGNAL = 1 << 9, SPNG__CTX_FLAGS_ALL = (SPNG_CTX_IGNORE_ADLER32 | SPNG_CTX_ENCODER) }; #define SPNG_STR(x) _SPNG_STR(x) #define _SPNG_STR(x) #x #define SPNG_VERSION_STRING SPNG_STR(SPNG_VERSION_MAJOR) "." \ SPNG_STR(SPNG_VERSION_MINOR) "." \ SPNG_STR(SPNG_VERSION_PATCH) #define SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chunk) \ if(ctx == NULL) return 1; \ int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 0); \ if(ret) return ret; \ if(!ctx->stored.chunk) return SPNG_ECHUNKAVAIL; \ if(chunk == NULL) return 1 #define SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chunk) \ if(ctx == NULL || chunk == NULL) return 1; \ if(ctx->data == NULL && !ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ENOSRC; \ int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 0); \ if(ret) return ret /* Determine if the spng_option can be overriden/optimized */ #define spng__optimize(option) (ctx->optimize_option & (1 << option)) struct spng_subimage { uint32_t width; uint32_t height; size_t out_width; /* byte width based on output format */ size_t scanline_width; }; struct spng_text2 { int type; char *keyword; char *text; size_t text_length; uint8_t compression_flag; /* iTXt only */ char *language_tag; /* iTXt only */ char *translated_keyword; /* iTXt only */ size_t cache_usage; char user_keyword_storage[80]; }; struct decode_flags { unsigned apply_trns: 1; unsigned apply_gamma: 1; unsigned use_sbit: 1; unsigned indexed: 1; unsigned do_scaling: 1; unsigned interlaced: 1; unsigned same_layout: 1; unsigned zerocopy: 1; unsigned unpack: 1; }; struct encode_flags { unsigned interlace: 1; unsigned same_layout: 1; unsigned to_bigendian: 1; unsigned progressive: 1; unsigned finalize: 1; enum spng_filter_choice filter_choice; }; struct spng_chunk_bitfield { unsigned ihdr: 1; unsigned plte: 1; unsigned chrm: 1; unsigned iccp: 1; unsigned gama: 1; unsigned sbit: 1; unsigned srgb: 1; unsigned text: 1; unsigned bkgd: 1; unsigned hist: 1; unsigned trns: 1; unsigned phys: 1; unsigned splt: 1; unsigned time: 1; unsigned offs: 1; unsigned exif: 1; unsigned unknown: 1; }; /* Packed sample iterator */ struct spng__iter { const uint8_t mask; unsigned shift_amount; const unsigned initial_shift, bit_depth; const unsigned char *samples; }; union spng__decode_plte { struct spng_plte_entry rgba[256]; unsigned char rgb[256 * 3]; unsigned char raw[256 * 4]; uint32_t align_this; }; struct spng__zlib_options { int compression_level; int window_bits; int mem_level; int strategy; int data_type; }; typedef void spng__undo(spng_ctx *ctx); struct spng_ctx { size_t data_size; size_t bytes_read; size_t stream_buf_size; unsigned char *stream_buf; const unsigned char *data; /* User-defined pointers for streaming */ spng_read_fn *read_fn; spng_write_fn *write_fn; void *stream_user_ptr; /* Used for buffer reads */ const unsigned char *png_base; size_t bytes_left; size_t last_read_size; /* Used for encoding */ int user_owns_out_png; unsigned char *out_png; unsigned char *write_ptr; size_t out_png_size; size_t bytes_encoded; /* These are updated by read/write_header()/read_chunk_bytes() */ struct spng_chunk current_chunk; uint32_t cur_chunk_bytes_left; uint32_t cur_actual_crc; struct spng_alloc alloc; enum spng_ctx_flags flags; enum spng_format fmt; enum spng_state state; unsigned streaming: 1; unsigned internal_buffer: 1; /* encoding to internal buffer */ unsigned inflate: 1; unsigned deflate: 1; unsigned encode_only: 1; unsigned strict: 1; unsigned discard: 1; unsigned skip_crc: 1; unsigned keep_unknown: 1; unsigned prev_was_idat: 1; struct spng__zlib_options image_options; struct spng__zlib_options text_options; spng__undo *undo; /* input file contains this chunk */ struct spng_chunk_bitfield file; /* chunk was stored with spng_set_*() */ struct spng_chunk_bitfield user; /* chunk was stored by reading or with spng_set_*() */ struct spng_chunk_bitfield stored; /* used to reset the above in case of an error */ struct spng_chunk_bitfield prev_stored; struct spng_chunk first_idat, last_idat; uint32_t max_width, max_height; size_t max_chunk_size; size_t chunk_cache_limit; size_t chunk_cache_usage; uint32_t chunk_count_limit; uint32_t chunk_count_total; int crc_action_critical; int crc_action_ancillary; uint32_t optimize_option; struct spng_ihdr ihdr; struct spng_plte plte; struct spng_chrm_int chrm_int; struct spng_iccp iccp; uint32_t gama; struct spng_sbit sbit; uint8_t srgb_rendering_intent; uint32_t n_text; struct spng_text2 *text_list; struct spng_bkgd bkgd; struct spng_hist hist; struct spng_trns trns; struct spng_phys phys; uint32_t n_splt; struct spng_splt *splt_list; struct spng_time time; struct spng_offs offs; struct spng_exif exif; uint32_t n_chunks; struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunk_list; struct spng_subimage subimage[7]; z_stream zstream; unsigned char *scanline_buf, *prev_scanline_buf, *row_buf, *filtered_scanline_buf; unsigned char *scanline, *prev_scanline, *row, *filtered_scanline; /* based on fmt */ size_t image_size; /* may be zero */ size_t image_width; unsigned bytes_per_pixel; /* derived from ihdr */ unsigned pixel_size; /* derived from spng_format+ihdr */ int widest_pass; int last_pass; /* last non-empty pass */ uint16_t *gamma_lut; /* points to either _lut8 or _lut16 */ uint16_t *gamma_lut16; uint16_t gamma_lut8[256]; unsigned char trns_px[8]; union spng__decode_plte decode_plte; struct spng_sbit decode_sb; struct decode_flags decode_flags; struct spng_row_info row_info; struct encode_flags encode_flags; }; static const uint32_t spng_u32max = INT32_MAX; static const uint32_t adam7_x_start[7] = { 0, 4, 0, 2, 0, 1, 0 }; static const uint32_t adam7_y_start[7] = { 0, 0, 4, 0, 2, 0, 1 }; static const uint32_t adam7_x_delta[7] = { 8, 8, 4, 4, 2, 2, 1 }; static const uint32_t adam7_y_delta[7] = { 8, 8, 8, 4, 4, 2, 2 }; static const uint8_t spng_signature[8] = { 137, 80, 78, 71, 13, 10, 26, 10 }; static const uint8_t type_ihdr[4] = { 73, 72, 68, 82 }; static const uint8_t type_plte[4] = { 80, 76, 84, 69 }; static const uint8_t type_idat[4] = { 73, 68, 65, 84 }; static const uint8_t type_iend[4] = { 73, 69, 78, 68 }; static const uint8_t type_trns[4] = { 116, 82, 78, 83 }; static const uint8_t type_chrm[4] = { 99, 72, 82, 77 }; static const uint8_t type_gama[4] = { 103, 65, 77, 65 }; static const uint8_t type_iccp[4] = { 105, 67, 67, 80 }; static const uint8_t type_sbit[4] = { 115, 66, 73, 84 }; static const uint8_t type_srgb[4] = { 115, 82, 71, 66 }; static const uint8_t type_text[4] = { 116, 69, 88, 116 }; static const uint8_t type_ztxt[4] = { 122, 84, 88, 116 }; static const uint8_t type_itxt[4] = { 105, 84, 88, 116 }; static const uint8_t type_bkgd[4] = { 98, 75, 71, 68 }; static const uint8_t type_hist[4] = { 104, 73, 83, 84 }; static const uint8_t type_phys[4] = { 112, 72, 89, 115 }; static const uint8_t type_splt[4] = { 115, 80, 76, 84 }; static const uint8_t type_time[4] = { 116, 73, 77, 69 }; static const uint8_t type_offs[4] = { 111, 70, 70, 115 }; static const uint8_t type_exif[4] = { 101, 88, 73, 102 }; static inline void *spng__malloc(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t size) { return ctx->alloc.malloc_fn(size); } static inline void *spng__calloc(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t nmemb, size_t size) { return ctx->alloc.calloc_fn(nmemb, size); } static inline void *spng__realloc(spng_ctx *ctx, void *ptr, size_t size) { return ctx->alloc.realloc_fn(ptr, size); } static inline void spng__free(spng_ctx *ctx, void *ptr) { ctx->alloc.free_fn(ptr); } #if defined(SPNG_USE_MINIZ) static void *spng__zalloc(void *opaque, size_t items, size_t size) #else static void *spng__zalloc(void *opaque, uInt items, uInt size) #endif { spng_ctx *ctx = opaque; if(size > SIZE_MAX / items) return NULL; size_t len = (size_t)items * size; return spng__malloc(ctx, len); } static void spng__zfree(void *opqaue, void *ptr) { spng_ctx *ctx = opqaue; spng__free(ctx, ptr); } static inline uint16_t read_u16(const void *src) { const unsigned char *data = src; return (data[0] & 0xFFU) << 8 | (data[1] & 0xFFU); } static inline uint32_t read_u32(const void *src) { const unsigned char *data = src; return (data[0] & 0xFFUL) << 24 | (data[1] & 0xFFUL) << 16 | (data[2] & 0xFFUL) << 8 | (data[3] & 0xFFUL); } static inline int32_t read_s32(const void *src) { int32_t ret = (int32_t)read_u32(src); return ret; } static inline void write_u16(void *dest, uint16_t x) { unsigned char *data = dest; data[0] = x >> 8; data[1] = x & 0xFF; } static inline void write_u32(void *dest, uint32_t x) { unsigned char *data = dest; data[0] = (x >> 24); data[1] = (x >> 16) & 0xFF; data[2] = (x >> 8) & 0xFF; data[3] = x & 0xFF; } static inline void write_s32(void *dest, int32_t x) { uint32_t n = x; write_u32(dest, n); } /* Returns an iterator for 1,2,4,8-bit samples */ static struct spng__iter spng__iter_init(unsigned bit_depth, const unsigned char *samples) { struct spng__iter iter = { .mask = (uint32_t)(1 << bit_depth) - 1, .shift_amount = 8 - bit_depth, .initial_shift = 8 - bit_depth, .bit_depth = bit_depth, .samples = samples }; return iter; } /* Returns the current sample unpacked, iterates to the next one */ static inline uint8_t get_sample(struct spng__iter *iter) { uint8_t x = (iter->samples[0] >> iter->shift_amount) & iter->mask; iter->shift_amount -= iter->bit_depth; if(iter->shift_amount > 7) { iter->shift_amount = iter->initial_shift; iter->samples++; } return x; } static void u16_row_to_host(void *row, size_t size) { uint16_t *px = row; size_t i, n = size / 2; for(i=0; i < n; i++) { px[i] = read_u16(&px[i]); } } static void u16_row_to_bigendian(void *row, size_t size) { uint16_t *px = (uint16_t*)row; size_t i, n = size / 2; for(i=0; i < n; i++) { write_u16(&px[i], px[i]); } } static void rgb8_row_to_rgba8(const unsigned char *row, unsigned char *out, uint32_t n) { uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < n; i++) { memcpy(out + i * 4, row + i * 3, 3); out[i*4+3] = 255; } } static unsigned num_channels(const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr) { switch(ihdr->color_type) { case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR: return 3; case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA: return 2; case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA: return 4; case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE: case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED: return 1; default: return 0; } } /* Calculate scanline width in bits, round up to the nearest byte */ static int calculate_scanline_width(const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr, uint32_t width, size_t *scanline_width) { if(ihdr == NULL || !width) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; size_t res = num_channels(ihdr) * ihdr->bit_depth; if(res > SIZE_MAX / width) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; res = res * width; res += 15; /* Filter byte + 7 for rounding */ if(res < 15) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; res /= 8; if(res > UINT32_MAX) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; *scanline_width = res; return 0; } static int calculate_subimages(struct spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; struct spng_ihdr *ihdr = &ctx->ihdr; struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; if(ihdr->interlace_method == 1) { sub[0].width = (ihdr->width + 7) >> 3; sub[0].height = (ihdr->height + 7) >> 3; sub[1].width = (ihdr->width + 3) >> 3; sub[1].height = (ihdr->height + 7) >> 3; sub[2].width = (ihdr->width + 3) >> 2; sub[2].height = (ihdr->height + 3) >> 3; sub[3].width = (ihdr->width + 1) >> 2; sub[3].height = (ihdr->height + 3) >> 2; sub[4].width = (ihdr->width + 1) >> 1; sub[4].height = (ihdr->height + 1) >> 2; sub[5].width = ihdr->width >> 1; sub[5].height = (ihdr->height + 1) >> 1; sub[6].width = ihdr->width; sub[6].height = ihdr->height >> 1; } else { sub[0].width = ihdr->width; sub[0].height = ihdr->height; } int i; for(i=0; i < 7; i++) { if(sub[i].width == 0 || sub[i].height == 0) continue; int ret = calculate_scanline_width(ihdr, sub[i].width, &sub[i].scanline_width); if(ret) return ret; if(sub[ctx->widest_pass].scanline_width < sub[i].scanline_width) ctx->widest_pass = i; ctx->last_pass = i; } return 0; } static int check_decode_fmt(const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr, const int fmt) { switch(fmt) { case SPNG_FMT_RGBA8: case SPNG_FMT_RGBA16: case SPNG_FMT_RGB8: case SPNG_FMT_PNG: case SPNG_FMT_RAW: return 0; case SPNG_FMT_G8: case SPNG_FMT_GA8: if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE && ihdr->bit_depth <= 8) return 0; else return SPNG_EFMT; case SPNG_FMT_GA16: if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE && ihdr->bit_depth == 16) return 0; else return SPNG_EFMT; default: return SPNG_EFMT; } } static int calculate_image_width(const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr, int fmt, size_t *len) { if(ihdr == NULL || len == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; size_t res = ihdr->width; unsigned bytes_per_pixel; switch(fmt) { case SPNG_FMT_RGBA8: case SPNG_FMT_GA16: bytes_per_pixel = 4; break; case SPNG_FMT_RGBA16: bytes_per_pixel = 8; break; case SPNG_FMT_RGB8: bytes_per_pixel = 3; break; case SPNG_FMT_PNG: case SPNG_FMT_RAW: { int ret = calculate_scanline_width(ihdr, ihdr->width, &res); if(ret) return ret; res -= 1; /* exclude filter byte */ bytes_per_pixel = 1; break; } case SPNG_FMT_G8: bytes_per_pixel = 1; break; case SPNG_FMT_GA8: bytes_per_pixel = 2; break; default: return SPNG_EINTERNAL; } if(res > SIZE_MAX / bytes_per_pixel) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; res = res * bytes_per_pixel; *len = res; return 0; } static int calculate_image_size(const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr, int fmt, size_t *len) { if(ihdr == NULL || len == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; size_t res = 0; int ret = calculate_image_width(ihdr, fmt, &res); if(ret) return ret; if(res > SIZE_MAX / ihdr->height) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; res = res * ihdr->height; *len = res; return 0; } static int increase_cache_usage(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t bytes, int new_chunk) { if(ctx == NULL || !bytes) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(new_chunk) { ctx->chunk_count_total++; if(ctx->chunk_count_total < 1) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(ctx->chunk_count_total > ctx->chunk_count_limit) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; } size_t new_usage = ctx->chunk_cache_usage + bytes; if(new_usage < ctx->chunk_cache_usage) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(new_usage > ctx->chunk_cache_limit) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; ctx->chunk_cache_usage = new_usage; return 0; } static int decrease_cache_usage(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t usage) { if(ctx == NULL || !usage) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(usage > ctx->chunk_cache_usage) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; ctx->chunk_cache_usage -= usage; return 0; } static int is_critical_chunk(struct spng_chunk *chunk) { if(chunk == NULL) return 0; if((chunk->type[0] & (1 << 5)) == 0) return 1; return 0; } static int decode_err(spng_ctx *ctx, int err) { ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_INVALID; return err; } static int encode_err(spng_ctx *ctx, int err) { ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_INVALID; return err; } static inline int read_data(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t bytes) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!bytes) return 0; if(ctx->streaming && (bytes > SPNG_READ_SIZE)) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret = ctx->read_fn(ctx, ctx->stream_user_ptr, ctx->stream_buf, bytes); if(ret) { if(ret > 0 || ret < SPNG_IO_ERROR) ret = SPNG_IO_ERROR; return ret; } ctx->bytes_read += bytes; if(ctx->bytes_read < bytes) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; return 0; } /* Ensure there is enough space for encoding starting at ctx->write_ptr */ static int require_bytes(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t bytes) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(ctx->streaming) { if(bytes > ctx->stream_buf_size) { size_t new_size = ctx->stream_buf_size; /* Start at default IDAT size + header + crc */ if(new_size < (SPNG_WRITE_SIZE + 12)) new_size = SPNG_WRITE_SIZE + 12; if(new_size < bytes) new_size = bytes; void *temp = spng__realloc(ctx, ctx->stream_buf, new_size); if(temp == NULL) return encode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); ctx->stream_buf = temp; ctx->stream_buf_size = bytes; ctx->write_ptr = ctx->stream_buf; } return 0; } if(!ctx->internal_buffer) return SPNG_ENODST; size_t required = ctx->bytes_encoded + bytes; if(required < bytes) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(required > ctx->out_png_size) { size_t new_size = ctx->out_png_size; /* Start with a size that doesn't require a realloc() 100% of the time */ if(new_size < (SPNG_WRITE_SIZE * 2)) new_size = SPNG_WRITE_SIZE * 2; /* Prefer the next power of two over the requested size */ while(new_size < required) { if(new_size / SIZE_MAX > 2) return encode_err(ctx, SPNG_EOVERFLOW); new_size *= 2; } void *temp = spng__realloc(ctx, ctx->out_png, new_size); if(temp == NULL) return encode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); ctx->out_png = temp; ctx->out_png_size = new_size; ctx->write_ptr = ctx->out_png + ctx->bytes_encoded; } return 0; } static int write_data(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *data, size_t bytes) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!bytes) return 0; if(ctx->streaming) { if(bytes > SPNG_WRITE_SIZE) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret = ctx->write_fn(ctx, ctx->stream_user_ptr, (void*)data, bytes); if(ret) { if(ret > 0 || ret < SPNG_IO_ERROR) ret = SPNG_IO_ERROR; return encode_err(ctx, ret); } } else { int ret = require_bytes(ctx, bytes); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); memcpy(ctx->write_ptr, data, bytes); ctx->write_ptr += bytes; } ctx->bytes_encoded += bytes; if(ctx->bytes_encoded < bytes) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; return 0; } static int write_header(spng_ctx *ctx, const uint8_t chunk_type[4], size_t chunk_length, unsigned char **data) { if(ctx == NULL || chunk_type == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(chunk_length > spng_u32max) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; size_t total = chunk_length + 12; int ret = require_bytes(ctx, total); if(ret) return ret; uint32_t crc = crc32(0, NULL, 0); ctx->current_chunk.crc = crc32(crc, chunk_type, 4); memcpy(&ctx->current_chunk.type, chunk_type, 4); ctx->current_chunk.length = (uint32_t)chunk_length; if(!data) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(ctx->streaming) *data = ctx->stream_buf + 8; else *data = ctx->write_ptr + 8; return 0; } static int trim_chunk(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t length) { if(length > spng_u32max) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(length > ctx->current_chunk.length) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; ctx->current_chunk.length = length; return 0; } static int finish_chunk(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; struct spng_chunk *chunk = &ctx->current_chunk; unsigned char *header; unsigned char *chunk_data; if(ctx->streaming) { chunk_data = ctx->stream_buf + 8; header = ctx->stream_buf; } else { chunk_data = ctx->write_ptr + 8; header = ctx->write_ptr; } write_u32(header, chunk->length); memcpy(header + 4, chunk->type, 4); chunk->crc = crc32(chunk->crc, chunk_data, chunk->length); write_u32(chunk_data + chunk->length, chunk->crc); if(ctx->streaming) { const unsigned char *ptr = ctx->stream_buf; uint32_t bytes_left = chunk->length + 12; uint32_t len = 0; while(bytes_left) { ptr += len; len = SPNG_WRITE_SIZE; if(len > bytes_left) len = bytes_left; int ret = write_data(ctx, ptr, len); if(ret) return ret; bytes_left -= len; } } else { ctx->bytes_encoded += chunk->length; if(ctx->bytes_encoded < chunk->length) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; ctx->bytes_encoded += 12; if(ctx->bytes_encoded < 12) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; ctx->write_ptr += chunk->length + 12; } return 0; } static int write_chunk(spng_ctx *ctx, const uint8_t type[4], const void *data, size_t length) { if(ctx == NULL || type == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(length && data == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; unsigned char *write_ptr; int ret = write_header(ctx, type, length, &write_ptr); if(ret) return ret; if(length) memcpy(write_ptr, data, length); return finish_chunk(ctx); } static int write_iend(spng_ctx *ctx) { unsigned char iend_chunk[12] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 73, 69, 78, 68, 174, 66, 96, 130 }; return write_data(ctx, iend_chunk, 12); } static int write_unknown_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx, enum spng_location location) { if(!ctx->stored.unknown) return 0; const struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunk = ctx->chunk_list; uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < ctx->n_chunks; i++, chunk++) { if(chunk->location != location) continue; int ret = write_chunk(ctx, chunk->type, chunk->data, chunk->length); if(ret) return ret; } return 0; } /* Read and check the current chunk's crc, returns -SPNG_CRC_DISCARD if the chunk should be discarded */ static inline int read_and_check_crc(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret; ret = read_data(ctx, 4); if(ret) return ret; ctx->current_chunk.crc = read_u32(ctx->data); if(ctx->skip_crc) return 0; if(ctx->cur_actual_crc != ctx->current_chunk.crc) { if(is_critical_chunk(&ctx->current_chunk)) { if(ctx->crc_action_critical == SPNG_CRC_USE) return 0; } else { if(ctx->crc_action_ancillary == SPNG_CRC_USE) return 0; if(ctx->crc_action_ancillary == SPNG_CRC_DISCARD) return -SPNG_CRC_DISCARD; } return SPNG_ECHUNK_CRC; } return 0; } /* Read and validate the current chunk's crc and the next chunk header */ static inline int read_header(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret; struct spng_chunk chunk = { 0 }; ret = read_and_check_crc(ctx); if(ret) { if(ret == -SPNG_CRC_DISCARD) { ctx->discard = 1; } else return ret; } ret = read_data(ctx, 8); if(ret) return ret; chunk.offset = ctx->bytes_read - 8; chunk.length = read_u32(ctx->data); memcpy(&chunk.type, ctx->data + 4, 4); if(chunk.length > spng_u32max) return SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN; ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left = chunk.length; if(is_critical_chunk(&chunk) && ctx->crc_action_critical == SPNG_CRC_USE) ctx->skip_crc = 1; else if(ctx->crc_action_ancillary == SPNG_CRC_USE) ctx->skip_crc = 1; else ctx->skip_crc = 0; if(!ctx->skip_crc) { ctx->cur_actual_crc = crc32(0, NULL, 0); ctx->cur_actual_crc = crc32(ctx->cur_actual_crc, chunk.type, 4); } ctx->current_chunk = chunk; return 0; } /* Read chunk bytes and update crc */ static int read_chunk_bytes(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t bytes) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left || !bytes) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(bytes > ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; /* XXX: more specific error? */ int ret; ret = read_data(ctx, bytes); if(ret) return ret; if(!ctx->skip_crc) ctx->cur_actual_crc = crc32(ctx->cur_actual_crc, ctx->data, bytes); ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left -= bytes; return ret; } /* read_chunk_bytes() + read_data() with custom output buffer */ static int read_chunk_bytes2(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, uint32_t bytes) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left || !bytes) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(bytes > ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; /* XXX: more specific error? */ int ret; uint32_t len = bytes; if(ctx->streaming && len > SPNG_READ_SIZE) len = SPNG_READ_SIZE; while(bytes) { if(len > bytes) len = bytes; ret = ctx->read_fn(ctx, ctx->stream_user_ptr, out, len); if(ret) return ret; if(!ctx->streaming) memcpy(out, ctx->data, len); ctx->bytes_read += len; if(ctx->bytes_read < len) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(!ctx->skip_crc) ctx->cur_actual_crc = crc32(ctx->cur_actual_crc, out, len); ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left -= len; out = (char*)out + len; bytes -= len; len = SPNG_READ_SIZE; } return 0; } static int discard_chunk_bytes(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t bytes) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!bytes) return 0; int ret; if(ctx->streaming) /* Do small, consecutive reads */ { while(bytes) { uint32_t len = SPNG_READ_SIZE; if(len > bytes) len = bytes; ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, len); if(ret) return ret; bytes -= len; } } else { ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, bytes); if(ret) return ret; } return 0; } static int spng__inflate_init(spng_ctx *ctx, int window_bits) { if(ctx->zstream.state) inflateEnd(&ctx->zstream); ctx->inflate = 1; ctx->zstream.zalloc = spng__zalloc; ctx->zstream.zfree = spng__zfree; ctx->zstream.opaque = ctx; if(inflateInit2(&ctx->zstream, window_bits) != Z_OK) return SPNG_EZLIB_INIT; #if ZLIB_VERNUM >= 0x1290 && !defined(SPNG_USE_MINIZ) int validate = 1; if(ctx->flags & SPNG_CTX_IGNORE_ADLER32) validate = 0; if(is_critical_chunk(&ctx->current_chunk)) { if(ctx->crc_action_critical == SPNG_CRC_USE) validate = 0; } else /* ancillary */ { if(ctx->crc_action_ancillary == SPNG_CRC_USE) validate = 0; } if(inflateValidate(&ctx->zstream, validate)) return SPNG_EZLIB_INIT; #else /* This requires zlib >= 1.2.11 */ #pragma message ("inflateValidate() not available, SPNG_CTX_IGNORE_ADLER32 will be ignored") #endif return 0; } static int spng__deflate_init(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng__zlib_options *options) { if(ctx->zstream.state) deflateEnd(&ctx->zstream); ctx->deflate = 1; z_stream *zstream = &ctx->zstream; zstream->zalloc = spng__zalloc; zstream->zfree = spng__zfree; zstream->opaque = ctx; zstream->data_type = options->data_type; int ret = deflateInit2(zstream, options->compression_level, Z_DEFLATED, options->window_bits, options->mem_level, options->strategy); if(ret != Z_OK) return SPNG_EZLIB_INIT; return 0; } /* Inflate a zlib stream starting with start_buf if non-NULL, continuing from the datastream till an end marker, allocating and writing the inflated stream to *out, leaving "extra" bytes at the end, final buffer length is *len. Takes into account the chunk size and cache limits. */ static int spng__inflate_stream(spng_ctx *ctx, char **out, size_t *len, size_t extra, const void *start_buf, size_t start_len) { int ret = spng__inflate_init(ctx, 15); if(ret) return ret; size_t max = ctx->chunk_cache_limit - ctx->chunk_cache_usage; if(ctx->max_chunk_size < max) max = ctx->max_chunk_size; if(extra > max) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; max -= extra; uint32_t read_size; size_t size = 8 * 1024; void *t, *buf = spng__malloc(ctx, size); if(buf == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; z_stream *stream = &ctx->zstream; if(start_buf != NULL && start_len) { stream->avail_in = (uInt)start_len; stream->next_in = start_buf; } else { stream->avail_in = 0; stream->next_in = NULL; } stream->avail_out = (uInt)size; stream->next_out = buf; while(ret != Z_STREAM_END) { ret = inflate(stream, Z_NO_FLUSH); if(ret == Z_STREAM_END) break; if(ret != Z_OK && ret != Z_BUF_ERROR) { ret = SPNG_EZLIB; goto err; } if(!stream->avail_out) /* Resize buffer */ { /* overflow or reached chunk/cache limit */ if( (2 > SIZE_MAX / size) || (size > max / 2) ) { ret = SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; goto err; } size *= 2; t = spng__realloc(ctx, buf, size); if(t == NULL) goto mem; buf = t; stream->avail_out = (uInt)size / 2; stream->next_out = (unsigned char*)buf + size / 2; } else if(!stream->avail_in) /* Read more chunk bytes */ { read_size = ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left; if(ctx->streaming && read_size > SPNG_READ_SIZE) read_size = SPNG_READ_SIZE; ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, read_size); if(ret) { if(!read_size) ret = SPNG_EZLIB; goto err; } stream->avail_in = read_size; stream->next_in = ctx->data; } } size = stream->total_out; if(!size) { ret = SPNG_EZLIB; goto err; } size += extra; if(size < extra) goto mem; t = spng__realloc(ctx, buf, size); if(t == NULL) goto mem; buf = t; (void)increase_cache_usage(ctx, size, 0); *out = buf; *len = size; return 0; mem: ret = SPNG_EMEM; err: spng__free(ctx, buf); return ret; } /* Read at least one byte from the IDAT stream */ static int read_idat_bytes(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t *bytes_read) { if(ctx == NULL || bytes_read == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(memcmp(ctx->current_chunk.type, type_idat, 4)) return SPNG_EIDAT_TOO_SHORT; int ret; uint32_t len; while(!ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left) { ret = read_header(ctx); if(ret) return ret; if(memcmp(ctx->current_chunk.type, type_idat, 4)) return SPNG_EIDAT_TOO_SHORT; } if(ctx->streaming) {/* TODO: estimate bytes to read for progressive reads */ len = SPNG_READ_SIZE; if(len > ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left) len = ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left; } else len = ctx->current_chunk.length; ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, len); *bytes_read = len; return ret; } static int read_scanline_bytes(spng_ctx *ctx, unsigned char *dest, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || dest == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret = Z_OK; uint32_t bytes_read; z_stream *zstream = &ctx->zstream; zstream->avail_out = (uInt)len; zstream->next_out = dest; while(zstream->avail_out != 0) { ret = inflate(zstream, Z_NO_FLUSH); if(ret == Z_OK) continue; if(ret == Z_STREAM_END) /* Reached an end-marker */ { if(zstream->avail_out != 0) return SPNG_EIDAT_TOO_SHORT; } else if(ret == Z_BUF_ERROR) /* Read more IDAT bytes */ { ret = read_idat_bytes(ctx, &bytes_read); if(ret) return ret; zstream->avail_in = bytes_read; zstream->next_in = ctx->data; } else return SPNG_EIDAT_STREAM; } return 0; } static uint8_t paeth(uint8_t a, uint8_t b, uint8_t c) { int16_t p = a + b - c; int16_t pa = abs(p - a); int16_t pb = abs(p - b); int16_t pc = abs(p - c); if(pa <= pb && pa <= pc) return a; else if(pb <= pc) return b; return c; } SPNG_TARGET_CLONES("default,avx2") static void defilter_up(size_t bytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev) { size_t i; for(i=0; i < bytes; i++) { row[i] += prev[i]; } } /* Defilter *scanline in-place. *prev_scanline and *scanline should point to the first pixel, scanline_width is the width of the scanline including the filter byte. */ static int defilter_scanline(const unsigned char *prev_scanline, unsigned char *scanline, size_t scanline_width, unsigned bytes_per_pixel, unsigned filter) { if(prev_scanline == NULL || scanline == NULL || !scanline_width) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; size_t i; scanline_width--; if(filter == 0) return 0; #ifndef SPNG_DISABLE_OPT if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_UP) goto no_opt; if(bytes_per_pixel == 4) { if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_SUB) defilter_sub4(scanline_width, scanline); else if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_AVERAGE) defilter_avg4(scanline_width, scanline, prev_scanline); else if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_PAETH) defilter_paeth4(scanline_width, scanline, prev_scanline); else return SPNG_EFILTER; return 0; } else if(bytes_per_pixel == 3) { if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_SUB) defilter_sub3(scanline_width, scanline); else if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_AVERAGE) defilter_avg3(scanline_width, scanline, prev_scanline); else if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_PAETH) defilter_paeth3(scanline_width, scanline, prev_scanline); else return SPNG_EFILTER; return 0; } no_opt: #endif if(filter == SPNG_FILTER_UP) { defilter_up(scanline_width, scanline, prev_scanline); return 0; } for(i=0; i < scanline_width; i++) { uint8_t x, a, b, c; if(i >= bytes_per_pixel) { a = scanline[i - bytes_per_pixel]; b = prev_scanline[i]; c = prev_scanline[i - bytes_per_pixel]; } else /* First pixel in row */ { a = 0; b = prev_scanline[i]; c = 0; } x = scanline[i]; switch(filter) { case SPNG_FILTER_SUB: { x = x + a; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_AVERAGE: { uint16_t avg = (a + b) / 2; x = x + avg; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_PAETH: { x = x + paeth(a,b,c); break; } } scanline[i] = x; } return 0; } static int filter_scanline(unsigned char *filtered, const unsigned char *prev_scanline, const unsigned char *scanline, size_t scanline_width, unsigned bytes_per_pixel, const unsigned filter) { if(prev_scanline == NULL || scanline == NULL || scanline_width <= 1) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(filter > 4) return SPNG_EFILTER; if(filter == 0) return 0; scanline_width--; uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < scanline_width; i++) { uint8_t x, a, b, c; if(i >= bytes_per_pixel) { a = scanline[i - bytes_per_pixel]; b = prev_scanline[i]; c = prev_scanline[i - bytes_per_pixel]; } else /* first pixel in row */ { a = 0; b = prev_scanline[i]; c = 0; } x = scanline[i]; switch(filter) { case SPNG_FILTER_SUB: { x = x - a; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_UP: { x = x - b; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_AVERAGE: { uint16_t avg = (a + b) / 2; x = x - avg; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_PAETH: { x = x - paeth(a,b,c); break; } } filtered[i] = x; } return 0; } static int32_t filter_sum(const unsigned char *prev_scanline, const unsigned char *scanline, size_t size, unsigned bytes_per_pixel, const unsigned filter) { /* prevent potential over/underflow, bails out at a width of ~8M pixels for RGBA8 */ if(size > (INT32_MAX / 128)) return INT32_MAX; uint32_t i; int32_t sum = 0; uint8_t x, a, b, c; for(i=0; i < size; i++) { if(i >= bytes_per_pixel) { a = scanline[i - bytes_per_pixel]; b = prev_scanline[i]; c = prev_scanline[i - bytes_per_pixel]; } else /* first pixel in row */ { a = 0; b = prev_scanline[i]; c = 0; } x = scanline[i]; switch(filter) { case SPNG_FILTER_NONE: { break; } case SPNG_FILTER_SUB: { x = x - a; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_UP: { x = x - b; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_AVERAGE: { uint16_t avg = (a + b) / 2; x = x - avg; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_PAETH: { x = x - paeth(a,b,c); break; } } sum += 128 - abs((int)x - 128); } return sum; } static unsigned get_best_filter(const unsigned char *prev_scanline, const unsigned char *scanline, size_t scanline_width, unsigned bytes_per_pixel, const int choices) { if(!choices) return SPNG_FILTER_NONE; scanline_width--; int i; unsigned int best_filter = 0; enum spng_filter_choice flag; int32_t sum, best_score = INT32_MAX; int32_t filter_scores[5] = { INT32_MAX, INT32_MAX, INT32_MAX, INT32_MAX, INT32_MAX }; if( !(choices & (choices - 1)) ) {/* only one choice/bit is set */ for(i=0; i < 5; i++) { if(choices == 1 << (i + 3)) return i; } } for(i=0; i < 5; i++) { flag = 1 << (i + 3); if(choices & flag) sum = filter_sum(prev_scanline, scanline, scanline_width, bytes_per_pixel, i); else continue; filter_scores[i] = abs(sum); if(filter_scores[i] < best_score) { best_score = filter_scores[i]; best_filter = i; } } return best_filter; } /* Scale "sbits" significant bits in "sample" from "bit_depth" to "target" "bit_depth" must be a valid PNG depth "sbits" must be less than or equal to "bit_depth" "target" must be between 1 and 16 */ static uint16_t sample_to_target(uint16_t sample, unsigned bit_depth, unsigned sbits, unsigned target) { if(bit_depth == sbits) { if(target == sbits) return sample; /* No scaling */ }/* bit_depth > sbits */ else sample = sample >> (bit_depth - sbits); /* Shift significant bits to bottom */ /* Downscale */ if(target < sbits) return sample >> (sbits - target); /* Upscale using left bit replication */ int8_t shift_amount = target - sbits; uint16_t sample_bits = sample; sample = 0; while(shift_amount >= 0) { sample = sample | (sample_bits << shift_amount); shift_amount -= sbits; } int8_t partial = shift_amount + (int8_t)sbits; if(partial != 0) sample = sample | (sample_bits >> abs(shift_amount)); return sample; } static inline void gamma_correct_row(unsigned char *row, uint32_t pixels, int fmt, const uint16_t *gamma_lut) { uint32_t i; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) { unsigned char *px; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { px = row + i * 4; px[0] = gamma_lut[px[0]]; px[1] = gamma_lut[px[1]]; px[2] = gamma_lut[px[2]]; } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) { for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { uint16_t px[4]; memcpy(px, row + i * 8, 8); px[0] = gamma_lut[px[0]]; px[1] = gamma_lut[px[1]]; px[2] = gamma_lut[px[2]]; memcpy(row + i * 8, px, 8); } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) { unsigned char *px; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { px = row + i * 3; px[0] = gamma_lut[px[0]]; px[1] = gamma_lut[px[1]]; px[2] = gamma_lut[px[2]]; } } } /* Apply transparency to output row */ static inline void trns_row(unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *scanline, const unsigned char *trns, unsigned scanline_stride, struct spng_ihdr *ihdr, uint32_t pixels, int fmt) { uint32_t i; unsigned row_stride; unsigned depth = ihdr->bit_depth; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE) return; /* already applied in the decoding loop */ row_stride = 4; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++, scanline+=scanline_stride, row+=row_stride) { if(!memcmp(scanline, trns, scanline_stride)) row[3] = 0; } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE) return; /* already applied in the decoding loop */ row_stride = 8; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++, scanline+=scanline_stride, row+=row_stride) { if(!memcmp(scanline, trns, scanline_stride)) memset(row + 6, 0, 2); } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8) { row_stride = 2; if(depth == 16) { for(i=0; i < pixels; i++, scanline+=scanline_stride, row+=row_stride) { if(!memcmp(scanline, trns, scanline_stride)) memset(row + 1, 0, 1); } } else /* depth <= 8 */ { struct spng__iter iter = spng__iter_init(depth, scanline); for(i=0; i < pixels; i++, row+=row_stride) { if(trns[0] == get_sample(&iter)) row[1] = 0; } } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA16) { row_stride = 4; if(depth == 16) { for(i=0; i< pixels; i++, scanline+=scanline_stride, row+=row_stride) { if(!memcmp(scanline, trns, 2)) memset(row + 2, 0, 2); } } else { struct spng__iter iter = spng__iter_init(depth, scanline); for(i=0; i< pixels; i++, row+=row_stride) { if(trns[0] == get_sample(&iter)) memset(row + 2, 0, 2); } } } else return; } static inline void scale_row(unsigned char *row, uint32_t pixels, int fmt, unsigned depth, const struct spng_sbit *sbit) { uint32_t i; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) { unsigned char px[4]; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { memcpy(px, row + i * 4, 4); px[0] = sample_to_target(px[0], depth, sbit->red_bits, 8); px[1] = sample_to_target(px[1], depth, sbit->green_bits, 8); px[2] = sample_to_target(px[2], depth, sbit->blue_bits, 8); px[3] = sample_to_target(px[3], depth, sbit->alpha_bits, 8); memcpy(row + i * 4, px, 4); } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) { uint16_t px[4]; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { memcpy(px, row + i * 8, 8); px[0] = sample_to_target(px[0], depth, sbit->red_bits, 16); px[1] = sample_to_target(px[1], depth, sbit->green_bits, 16); px[2] = sample_to_target(px[2], depth, sbit->blue_bits, 16); px[3] = sample_to_target(px[3], depth, sbit->alpha_bits, 16); memcpy(row + i * 8, px, 8); } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) { unsigned char px[4]; for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { memcpy(px, row + i * 3, 3); px[0] = sample_to_target(px[0], depth, sbit->red_bits, 8); px[1] = sample_to_target(px[1], depth, sbit->green_bits, 8); px[2] = sample_to_target(px[2], depth, sbit->blue_bits, 8); memcpy(row + i * 3, px, 3); } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_G8) { for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { row[i] = sample_to_target(row[i], depth, sbit->grayscale_bits, 8); } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8) { for(i=0; i < pixels; i++) { row[i*2] = sample_to_target(row[i*2], depth, sbit->grayscale_bits, 8); } } } /* Expand to *row using 8-bit palette indices from *scanline */ static void expand_row(unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *scanline, const union spng__decode_plte *decode_plte, uint32_t width, int fmt) { uint32_t i = 0; unsigned char *px; unsigned char entry; const struct spng_plte_entry *plte = decode_plte->rgba; #if defined(SPNG_ARM) if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) i = expand_palette_rgba8_neon(row, scanline, decode_plte->raw, width); else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) { i = expand_palette_rgb8_neon(row, scanline, decode_plte->raw, width); for(; i < width; i++) {/* In this case the LUT is 3 bytes packed */ px = row + i * 3; entry = scanline[i]; px[0] = decode_plte->raw[entry * 3 + 0]; px[1] = decode_plte->raw[entry * 3 + 1]; px[2] = decode_plte->raw[entry * 3 + 2]; } return; } #endif if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) { for(; i < width; i++) { px = row + i * 4; entry = scanline[i]; px[0] = plte[entry].red; px[1] = plte[entry].green; px[2] = plte[entry].blue; px[3] = plte[entry].alpha; } } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) { for(; i < width; i++) { px = row + i * 3; entry = scanline[i]; px[0] = plte[entry].red; px[1] = plte[entry].green; px[2] = plte[entry].blue; } } } /* Unpack 1/2/4/8-bit samples to G8/GA8/GA16 or G16 -> GA16 */ static void unpack_scanline(unsigned char *out, const unsigned char *scanline, uint32_t width, unsigned bit_depth, int fmt) { struct spng__iter iter = spng__iter_init(bit_depth, scanline); uint32_t i; uint16_t sample, alpha = 65535; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8) goto ga8; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA16) goto ga16; /* 1/2/4-bit -> 8-bit */ for(i=0; i < width; i++) out[i] = get_sample(&iter); return; ga8: /* 1/2/4/8-bit -> GA8 */ for(i=0; i < width; i++) { out[i*2] = get_sample(&iter); out[i*2 + 1] = 255; } return; ga16: /* 16 -> GA16 */ if(bit_depth == 16) { for(i=0; i < width; i++) { memcpy(out + i * 4, scanline + i * 2, 2); memcpy(out + i * 4 + 2, &alpha, 2); } return; } /* 1/2/4/8-bit -> GA16 */ for(i=0; i < width; i++) { sample = get_sample(&iter); memcpy(out + i * 4, &sample, 2); memcpy(out + i * 4 + 2, &alpha, 2); } } static int check_ihdr(const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr, uint32_t max_width, uint32_t max_height) { if(ihdr->width > spng_u32max || !ihdr->width) return SPNG_EWIDTH; if(ihdr->height > spng_u32max || !ihdr->height) return SPNG_EHEIGHT; if(ihdr->width > max_width) return SPNG_EUSER_WIDTH; if(ihdr->height > max_height) return SPNG_EUSER_HEIGHT; switch(ihdr->color_type) { case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE: { if( !(ihdr->bit_depth == 1 || ihdr->bit_depth == 2 || ihdr->bit_depth == 4 || ihdr->bit_depth == 8 || ihdr->bit_depth == 16) ) return SPNG_EBIT_DEPTH; break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR: case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA: case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA: { if( !(ihdr->bit_depth == 8 || ihdr->bit_depth == 16) ) return SPNG_EBIT_DEPTH; break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED: { if( !(ihdr->bit_depth == 1 || ihdr->bit_depth == 2 || ihdr->bit_depth == 4 || ihdr->bit_depth == 8) ) return SPNG_EBIT_DEPTH; break; } default: return SPNG_ECOLOR_TYPE; } if(ihdr->compression_method) return SPNG_ECOMPRESSION_METHOD; if(ihdr->filter_method) return SPNG_EFILTER_METHOD; if(ihdr->interlace_method > 1) return SPNG_EINTERLACE_METHOD; return 0; } static int check_plte(const struct spng_plte *plte, const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr) { if(plte == NULL || ihdr == NULL) return 1; if(plte->n_entries == 0) return 1; if(plte->n_entries > 256) return 1; if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED) { if(plte->n_entries > (1U << ihdr->bit_depth)) return 1; } return 0; } static int check_sbit(const struct spng_sbit *sbit, const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr) { if(sbit == NULL || ihdr == NULL) return 1; if(ihdr->color_type == 0) { if(sbit->grayscale_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->grayscale_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; } else if(ihdr->color_type == 2 || ihdr->color_type == 3) { if(sbit->red_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->green_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->blue_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; uint8_t bit_depth; if(ihdr->color_type == 3) bit_depth = 8; else bit_depth = ihdr->bit_depth; if(sbit->red_bits > bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->green_bits > bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->blue_bits > bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; } else if(ihdr->color_type == 4) { if(sbit->grayscale_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->alpha_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->grayscale_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->alpha_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; } else if(ihdr->color_type == 6) { if(sbit->red_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->green_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->blue_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->alpha_bits == 0) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->red_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->green_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->blue_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; if(sbit->alpha_bits > ihdr->bit_depth) return SPNG_ESBIT; } return 0; } static int check_chrm_int(const struct spng_chrm_int *chrm_int) { if(chrm_int == NULL) return 1; if(chrm_int->white_point_x > spng_u32max || chrm_int->white_point_y > spng_u32max || chrm_int->red_x > spng_u32max || chrm_int->red_y > spng_u32max || chrm_int->green_x > spng_u32max || chrm_int->green_y > spng_u32max || chrm_int->blue_x > spng_u32max || chrm_int->blue_y > spng_u32max) return SPNG_ECHRM; return 0; } static int check_phys(const struct spng_phys *phys) { if(phys == NULL) return 1; if(phys->unit_specifier > 1) return SPNG_EPHYS; if(phys->ppu_x > spng_u32max) return SPNG_EPHYS; if(phys->ppu_y > spng_u32max) return SPNG_EPHYS; return 0; } static int check_time(const struct spng_time *time) { if(time == NULL) return 1; if(time->month == 0 || time->month > 12) return 1; if(time->day == 0 || time->day > 31) return 1; if(time->hour > 23) return 1; if(time->minute > 59) return 1; if(time->second > 60) return 1; return 0; } static int check_offs(const struct spng_offs *offs) { if(offs == NULL) return 1; if(offs->unit_specifier > 1) return 1; return 0; } static int check_exif(const struct spng_exif *exif) { if(exif == NULL) return 1; if(exif->data == NULL) return 1; if(exif->length < 4) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(exif->length > spng_u32max) return SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN; const uint8_t exif_le[4] = { 73, 73, 42, 0 }; const uint8_t exif_be[4] = { 77, 77, 0, 42 }; if(memcmp(exif->data, exif_le, 4) && memcmp(exif->data, exif_be, 4)) return 1; return 0; } /* Validate PNG keyword */ static int check_png_keyword(const char *str) { if(str == NULL) return 1; size_t len = strlen(str); const char *end = str + len; if(!len) return 1; if(len > 79) return 1; if(str[0] == ' ') return 1; /* Leading space */ if(end[-1] == ' ') return 1; /* Trailing space */ if(strstr(str, " ") != NULL) return 1; /* Consecutive spaces */ uint8_t c; while(str != end) { memcpy(&c, str, 1); if( (c >= 32 && c <= 126) || (c >= 161) ) str++; else return 1; /* Invalid character */ } return 0; } /* Validate PNG text *str up to 'len' bytes */ static int check_png_text(const char *str, size_t len) {/* XXX: are consecutive newlines permitted? */ if(str == NULL || len == 0) return 1; uint8_t c; size_t i = 0; while(i < len) { memcpy(&c, str + i, 1); if( (c >= 32 && c <= 126) || (c >= 161) || c == 10) i++; else return 1; /* Invalid character */ } return 0; } /* Returns non-zero for standard chunks which are stored without allocating memory */ static int is_small_chunk(uint8_t type[4]) { if(!memcmp(type, type_plte, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_chrm, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_gama, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_sbit, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_srgb, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_bkgd, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_trns, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_hist, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_phys, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_time, 4)) return 1; else if(!memcmp(type, type_offs, 4)) return 1; else return 0; } static int read_ihdr(spng_ctx *ctx) { int ret; struct spng_chunk *chunk = &ctx->current_chunk; const unsigned char *data; chunk->offset = 8; chunk->length = 13; size_t sizeof_sig_ihdr = 29; ret = read_data(ctx, sizeof_sig_ihdr); if(ret) return ret; data = ctx->data; if(memcmp(data, spng_signature, sizeof(spng_signature))) return SPNG_ESIGNATURE; chunk->length = read_u32(data + 8); memcpy(&chunk->type, data + 12, 4); if(chunk->length != 13) return SPNG_EIHDR_SIZE; if(memcmp(chunk->type, type_ihdr, 4)) return SPNG_ENOIHDR; ctx->cur_actual_crc = crc32(0, NULL, 0); ctx->cur_actual_crc = crc32(ctx->cur_actual_crc, data + 12, 17); ctx->ihdr.width = read_u32(data + 16); ctx->ihdr.height = read_u32(data + 20); ctx->ihdr.bit_depth = data[24]; ctx->ihdr.color_type = data[25]; ctx->ihdr.compression_method = data[26]; ctx->ihdr.filter_method = data[27]; ctx->ihdr.interlace_method = data[28]; ret = check_ihdr(&ctx->ihdr, ctx->max_width, ctx->max_height); if(ret) return ret; ctx->file.ihdr = 1; ctx->stored.ihdr = 1; if(ctx->ihdr.bit_depth < 8) ctx->bytes_per_pixel = 1; else ctx->bytes_per_pixel = num_channels(&ctx->ihdr) * (ctx->ihdr.bit_depth / 8); ret = calculate_subimages(ctx); if(ret) return ret; return 0; } static void splt_undo(spng_ctx *ctx) { struct spng_splt *splt = &ctx->splt_list[ctx->n_splt - 1]; spng__free(ctx, splt->entries); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, sizeof(struct spng_splt)); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, splt->n_entries * sizeof(struct spng_splt_entry)); splt->entries = NULL; ctx->n_splt--; } static void text_undo(spng_ctx *ctx) { struct spng_text2 *text = &ctx->text_list[ctx->n_text - 1]; spng__free(ctx, text->keyword); if(text->compression_flag) spng__free(ctx, text->text); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, text->cache_usage); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, sizeof(struct spng_text2)); text->keyword = NULL; text->text = NULL; ctx->n_text--; } static void chunk_undo(spng_ctx *ctx) { struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunk = &ctx->chunk_list[ctx->n_chunks - 1]; spng__free(ctx, chunk->data); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, chunk->length); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, sizeof(struct spng_unknown_chunk)); chunk->data = NULL; ctx->n_chunks--; } static int read_non_idat_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx) { int ret; struct spng_chunk chunk; const unsigned char *data; ctx->discard = 0; ctx->undo = NULL; ctx->prev_stored = ctx->stored; while( !(ret = read_header(ctx))) { if(ctx->discard) { if(ctx->undo) ctx->undo(ctx); ctx->stored = ctx->prev_stored; } ctx->discard = 0; ctx->undo = NULL; ctx->prev_stored = ctx->stored; chunk = ctx->current_chunk; if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_idat, 4)) { if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT) { if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 3 && !ctx->stored.plte) return SPNG_ENOPLTE; ctx->first_idat = chunk; return 0; } if(ctx->prev_was_idat) { /* Ignore extra IDAT's */ ret = discard_chunk_bytes(ctx, chunk.length); if(ret) return ret; continue; } else return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; /* IDAT chunk not at the end of the IDAT sequence */ } ctx->prev_was_idat = 0; if(is_small_chunk(chunk.type)) { /* None of the known chunks can be zero length */ if(!chunk.length) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; /* The largest of these chunks is PLTE with 256 entries */ ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, chunk.length > 768 ? 768 : chunk.length); if(ret) return ret; } data = ctx->data; if(is_critical_chunk(&chunk)) { if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_plte, 4)) { if(ctx->file.trns || ctx->file.hist || ctx->file.bkgd) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(chunk.length % 3 != 0) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->plte.n_entries = chunk.length / 3; if(check_plte(&ctx->plte, &ctx->ihdr)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; /* XXX: EPLTE? */ size_t i; for(i=0; i < ctx->plte.n_entries; i++) { ctx->plte.entries[i].red = data[i * 3]; ctx->plte.entries[i].green = data[i * 3 + 1]; ctx->plte.entries[i].blue = data[i * 3 + 2]; } ctx->file.plte = 1; ctx->stored.plte = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_iend, 4)) { if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) { if(chunk.length) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ret = read_and_check_crc(ctx); if(ret == -SPNG_CRC_DISCARD) ret = 0; return ret; } else return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_ihdr, 4)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; else return SPNG_ECHUNK_UNKNOWN_CRITICAL; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_chrm, 4)) /* Ancillary chunks */ { if(ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.chrm) return SPNG_EDUP_CHRM; if(chunk.length != 32) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->chrm_int.white_point_x = read_u32(data); ctx->chrm_int.white_point_y = read_u32(data + 4); ctx->chrm_int.red_x = read_u32(data + 8); ctx->chrm_int.red_y = read_u32(data + 12); ctx->chrm_int.green_x = read_u32(data + 16); ctx->chrm_int.green_y = read_u32(data + 20); ctx->chrm_int.blue_x = read_u32(data + 24); ctx->chrm_int.blue_y = read_u32(data + 28); if(check_chrm_int(&ctx->chrm_int)) return SPNG_ECHRM; ctx->file.chrm = 1; ctx->stored.chrm = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_gama, 4)) { if(ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.gama) return SPNG_EDUP_GAMA; if(chunk.length != 4) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->gama = read_u32(data); if(!ctx->gama) return SPNG_EGAMA; if(ctx->gama > spng_u32max) return SPNG_EGAMA; ctx->file.gama = 1; ctx->stored.gama = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_sbit, 4)) { if(ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.sbit) return SPNG_EDUP_SBIT; if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 0) { if(chunk.length != 1) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->sbit.grayscale_bits = data[0]; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 2 || ctx->ihdr.color_type == 3) { if(chunk.length != 3) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->sbit.red_bits = data[0]; ctx->sbit.green_bits = data[1]; ctx->sbit.blue_bits = data[2]; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 4) { if(chunk.length != 2) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->sbit.grayscale_bits = data[0]; ctx->sbit.alpha_bits = data[1]; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 6) { if(chunk.length != 4) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->sbit.red_bits = data[0]; ctx->sbit.green_bits = data[1]; ctx->sbit.blue_bits = data[2]; ctx->sbit.alpha_bits = data[3]; } if(check_sbit(&ctx->sbit, &ctx->ihdr)) return SPNG_ESBIT; ctx->file.sbit = 1; ctx->stored.sbit = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_srgb, 4)) { if(ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.srgb) return SPNG_EDUP_SRGB; if(chunk.length != 1) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->srgb_rendering_intent = data[0]; if(ctx->srgb_rendering_intent > 3) return SPNG_ESRGB; ctx->file.srgb = 1; ctx->stored.srgb = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_bkgd, 4)) { if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.bkgd) return SPNG_EDUP_BKGD; if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 0 || ctx->ihdr.color_type == 4) { if(chunk.length != 2) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->bkgd.gray = read_u16(data); } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 2 || ctx->ihdr.color_type == 6) { if(chunk.length != 6) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->bkgd.red = read_u16(data); ctx->bkgd.green = read_u16(data + 2); ctx->bkgd.blue = read_u16(data + 4); } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 3) { if(chunk.length != 1) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(!ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_EBKGD_NO_PLTE; ctx->bkgd.plte_index = data[0]; if(ctx->bkgd.plte_index >= ctx->plte.n_entries) return SPNG_EBKGD_PLTE_IDX; } ctx->file.bkgd = 1; ctx->stored.bkgd = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_trns, 4)) { if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.trns) return SPNG_EDUP_TRNS; if(!chunk.length) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 0) { if(chunk.length != 2) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->trns.gray = read_u16(data); } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 2) { if(chunk.length != 6) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->trns.red = read_u16(data); ctx->trns.green = read_u16(data + 2); ctx->trns.blue = read_u16(data + 4); } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 3) { if(chunk.length > ctx->plte.n_entries) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(!ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_ETRNS_NO_PLTE; memcpy(ctx->trns.type3_alpha, data, chunk.length); ctx->trns.n_type3_entries = chunk.length; } if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 4 || ctx->ihdr.color_type == 6) return SPNG_ETRNS_COLOR_TYPE; ctx->file.trns = 1; ctx->stored.trns = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_hist, 4)) { if(!ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_EHIST_NO_PLTE; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.hist) return SPNG_EDUP_HIST; if( (chunk.length / 2) != (ctx->plte.n_entries) ) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; size_t k; for(k=0; k < (chunk.length / 2); k++) { ctx->hist.frequency[k] = read_u16(data + k*2); } ctx->file.hist = 1; ctx->stored.hist = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_phys, 4)) { if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.phys) return SPNG_EDUP_PHYS; if(chunk.length != 9) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->phys.ppu_x = read_u32(data); ctx->phys.ppu_y = read_u32(data + 4); ctx->phys.unit_specifier = data[8]; if(check_phys(&ctx->phys)) return SPNG_EPHYS; ctx->file.phys = 1; ctx->stored.phys = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_time, 4)) { if(ctx->file.time) return SPNG_EDUP_TIME; if(chunk.length != 7) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; struct spng_time time; time.year = read_u16(data); time.month = data[2]; time.day = data[3]; time.hour = data[4]; time.minute = data[5]; time.second = data[6]; if(check_time(&time)) return SPNG_ETIME; ctx->file.time = 1; if(!ctx->user.time) ctx->time = time; ctx->stored.time = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_offs, 4)) { if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.offs) return SPNG_EDUP_OFFS; if(chunk.length != 9) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->offs.x = read_s32(data); ctx->offs.y = read_s32(data + 4); ctx->offs.unit_specifier = data[8]; if(check_offs(&ctx->offs)) return SPNG_EOFFS; ctx->file.offs = 1; ctx->stored.offs = 1; } else /* Arbitrary-length chunk */ { if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_exif, 4)) { if(ctx->file.exif) return SPNG_EDUP_EXIF; if(!chunk.length) return SPNG_EEXIF; ctx->file.exif = 1; if(ctx->user.exif) goto discard; if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, chunk.length, 1)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; struct spng_exif exif; exif.length = chunk.length; exif.data = spng__malloc(ctx, chunk.length); if(exif.data == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ret = read_chunk_bytes2(ctx, exif.data, chunk.length); if(ret) { spng__free(ctx, exif.data); return ret; } if(check_exif(&exif)) { spng__free(ctx, exif.data); return SPNG_EEXIF; } ctx->exif = exif; ctx->stored.exif = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_iccp, 4)) {/* TODO: add test file with color profile */ if(ctx->file.plte) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->file.iccp) return SPNG_EDUP_ICCP; if(!chunk.length) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->file.iccp = 1; uint32_t peek_bytes = 81 > chunk.length ? chunk.length : 81; ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, peek_bytes); if(ret) return ret; unsigned char *keyword_nul = memchr(ctx->data, '\0', peek_bytes); if(keyword_nul == NULL) return SPNG_EICCP_NAME; uint32_t keyword_len = keyword_nul - ctx->data; if(keyword_len > 79) return SPNG_EICCP_NAME; memcpy(ctx->iccp.profile_name, ctx->data, keyword_len); if(check_png_keyword(ctx->iccp.profile_name)) return SPNG_EICCP_NAME; if(chunk.length < (keyword_len + 2)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(ctx->data[keyword_len + 1] != 0) return SPNG_EICCP_COMPRESSION_METHOD; ret = spng__inflate_stream(ctx, &ctx->iccp.profile, &ctx->iccp.profile_len, 0, ctx->data + keyword_len + 2, peek_bytes - (keyword_len + 2)); if(ret) return ret; ctx->stored.iccp = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_text, 4) || !memcmp(chunk.type, type_ztxt, 4) || !memcmp(chunk.type, type_itxt, 4)) { if(!chunk.length) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->file.text = 1; if(ctx->user.text) goto discard; if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, sizeof(struct spng_text2), 1)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; ctx->n_text++; if(ctx->n_text < 1) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(sizeof(struct spng_text2) > SIZE_MAX / ctx->n_text) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; void *buf = spng__realloc(ctx, ctx->text_list, ctx->n_text * sizeof(struct spng_text2)); if(buf == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ctx->text_list = buf; struct spng_text2 *text = &ctx->text_list[ctx->n_text - 1]; memset(text, 0, sizeof(struct spng_text2)); ctx->undo = text_undo; uint32_t text_offset = 0, language_tag_offset = 0, translated_keyword_offset = 0; uint32_t peek_bytes = 256; /* enough for 3 80-byte keywords and some text bytes */ uint32_t keyword_len; if(peek_bytes > chunk.length) peek_bytes = chunk.length; ret = read_chunk_bytes(ctx, peek_bytes); if(ret) return ret; data = ctx->data; const unsigned char *zlib_stream = NULL; const unsigned char *peek_end = data + peek_bytes; const unsigned char *keyword_nul = memchr(data, 0, chunk.length > 80 ? 80 : chunk.length); if(keyword_nul == NULL) return SPNG_ETEXT_KEYWORD; keyword_len = keyword_nul - data; if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_text, 4)) { text->type = SPNG_TEXT; text->text_length = chunk.length - keyword_len - 1; text_offset = keyword_len; /* increment past nul if there is a text field */ if(text->text_length) text_offset++; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_ztxt, 4)) { text->type = SPNG_ZTXT; if((peek_bytes - keyword_len) <= 2) return SPNG_EZTXT; if(keyword_nul[1]) return SPNG_EZTXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD; text->compression_flag = 1; text_offset = keyword_len + 2; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_itxt, 4)) { text->type = SPNG_ITXT; /* at least two 1-byte fields, two >=0 length strings, and one byte of (compressed) text */ if((peek_bytes - keyword_len) < 5) return SPNG_EITXT; text->compression_flag = keyword_nul[1]; if(text->compression_flag > 1) return SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_FLAG; if(keyword_nul[2]) return SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD; language_tag_offset = keyword_len + 3; const unsigned char *term; term = memchr(data + language_tag_offset, 0, peek_bytes - language_tag_offset); if(term == NULL) return SPNG_EITXT_LANG_TAG; if((peek_end - term) < 2) return SPNG_EITXT; translated_keyword_offset = term - data + 1; zlib_stream = memchr(data + translated_keyword_offset, 0, peek_bytes - translated_keyword_offset); if(zlib_stream == NULL) return SPNG_EITXT; if(zlib_stream == peek_end) return SPNG_EITXT; text_offset = zlib_stream - data + 1; text->text_length = chunk.length - text_offset; } else return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(text->compression_flag) { /* cache usage = peek_bytes + decompressed text size + nul */ if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, peek_bytes, 0)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; text->keyword = spng__calloc(ctx, 1, peek_bytes); if(text->keyword == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; memcpy(text->keyword, data, peek_bytes); zlib_stream = ctx->data + text_offset; ret = spng__inflate_stream(ctx, &text->text, &text->text_length, 1, zlib_stream, peek_bytes - text_offset); if(ret) return ret; text->text[text->text_length - 1] = '\0'; text->cache_usage = text->text_length + peek_bytes; } else { if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, chunk.length + 1, 0)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; text->keyword = spng__malloc(ctx, chunk.length + 1); if(text->keyword == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; memcpy(text->keyword, data, peek_bytes); if(chunk.length > peek_bytes) { ret = read_chunk_bytes2(ctx, text->keyword + peek_bytes, chunk.length - peek_bytes); if(ret) return ret; } text->text = text->keyword + text_offset; text->text_length = chunk.length - text_offset; text->text[text->text_length] = '\0'; text->cache_usage = chunk.length + 1; } if(check_png_keyword(text->keyword)) return SPNG_ETEXT_KEYWORD; text->text_length = strlen(text->text); if(text->type != SPNG_ITXT) { language_tag_offset = keyword_len; translated_keyword_offset = keyword_len; if(ctx->strict && check_png_text(text->text, text->text_length)) { if(text->type == SPNG_ZTXT) return SPNG_EZTXT; else return SPNG_ETEXT; } } text->language_tag = text->keyword + language_tag_offset; text->translated_keyword = text->keyword + translated_keyword_offset; ctx->stored.text = 1; } else if(!memcmp(chunk.type, type_splt, 4)) { if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; if(ctx->user.splt) goto discard; /* XXX: could check profile names for uniqueness */ if(!chunk.length) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; ctx->file.splt = 1; /* chunk.length + sizeof(struct spng_splt) + splt->n_entries * sizeof(struct spng_splt_entry) */ if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, chunk.length + sizeof(struct spng_splt), 1)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; ctx->n_splt++; if(ctx->n_splt < 1) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(sizeof(struct spng_splt) > SIZE_MAX / ctx->n_splt) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; void *buf = spng__realloc(ctx, ctx->splt_list, ctx->n_splt * sizeof(struct spng_splt)); if(buf == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ctx->splt_list = buf; struct spng_splt *splt = &ctx->splt_list[ctx->n_splt - 1]; memset(splt, 0, sizeof(struct spng_splt)); ctx->undo = splt_undo; void *t = spng__malloc(ctx, chunk.length); if(t == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; splt->entries = t; /* simplifies error handling */ data = t; ret = read_chunk_bytes2(ctx, t, chunk.length); if(ret) return ret; uint32_t keyword_len = chunk.length < 80 ? chunk.length : 80; const unsigned char *keyword_nul = memchr(data, 0, keyword_len); if(keyword_nul == NULL) return SPNG_ESPLT_NAME; keyword_len = keyword_nul - data; memcpy(splt->name, data, keyword_len); if(check_png_keyword(splt->name)) return SPNG_ESPLT_NAME; uint32_t j; for(j=0; j < (ctx->n_splt - 1); j++) { if(!strcmp(ctx->splt_list[j].name, splt->name)) return SPNG_ESPLT_DUP_NAME; } if( (chunk.length - keyword_len) <= 2) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; splt->sample_depth = data[keyword_len + 1]; uint32_t entries_len = chunk.length - keyword_len - 2; if(!entries_len) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(splt->sample_depth == 16) { if(entries_len % 10 != 0) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; splt->n_entries = entries_len / 10; } else if(splt->sample_depth == 8) { if(entries_len % 6 != 0) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; splt->n_entries = entries_len / 6; } else return SPNG_ESPLT_DEPTH; if(!splt->n_entries) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; size_t list_size = splt->n_entries; if(list_size > SIZE_MAX / sizeof(struct spng_splt_entry)) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; list_size *= sizeof(struct spng_splt_entry); if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, list_size, 0)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; splt->entries = spng__malloc(ctx, list_size); if(splt->entries == NULL) { spng__free(ctx, t); return SPNG_EMEM; } data = (unsigned char*)t + keyword_len + 2; uint32_t k; if(splt->sample_depth == 16) { for(k=0; k < splt->n_entries; k++) { splt->entries[k].red = read_u16(data + k * 10); splt->entries[k].green = read_u16(data + k * 10 + 2); splt->entries[k].blue = read_u16(data + k * 10 + 4); splt->entries[k].alpha = read_u16(data + k * 10 + 6); splt->entries[k].frequency = read_u16(data + k * 10 + 8); } } else if(splt->sample_depth == 8) { for(k=0; k < splt->n_entries; k++) { splt->entries[k].red = data[k * 6]; splt->entries[k].green = data[k * 6 + 1]; splt->entries[k].blue = data[k * 6 + 2]; splt->entries[k].alpha = data[k * 6 + 3]; splt->entries[k].frequency = read_u16(data + k * 6 + 4); } } spng__free(ctx, t); decrease_cache_usage(ctx, chunk.length); ctx->stored.splt = 1; } else /* Unknown chunk */ { ctx->file.unknown = 1; if(!ctx->keep_unknown) goto discard; if(ctx->user.unknown) goto discard; if(increase_cache_usage(ctx, chunk.length + sizeof(struct spng_unknown_chunk), 1)) return SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS; ctx->n_chunks++; if(ctx->n_chunks < 1) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(sizeof(struct spng_unknown_chunk) > SIZE_MAX / ctx->n_chunks) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; void *buf = spng__realloc(ctx, ctx->chunk_list, ctx->n_chunks * sizeof(struct spng_unknown_chunk)); if(buf == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ctx->chunk_list = buf; struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunkp = &ctx->chunk_list[ctx->n_chunks - 1]; memset(chunkp, 0, sizeof(struct spng_unknown_chunk)); ctx->undo = chunk_undo; memcpy(chunkp->type, chunk.type, 4); if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT) { if(ctx->file.plte) chunkp->location = SPNG_AFTER_PLTE; else chunkp->location = SPNG_AFTER_IHDR; } else if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) chunkp->location = SPNG_AFTER_IDAT; if(chunk.length > 0) { void *t = spng__malloc(ctx, chunk.length); if(t == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ret = read_chunk_bytes2(ctx, t, chunk.length); if(ret) { spng__free(ctx, t); return ret; } chunkp->length = chunk.length; chunkp->data = t; } ctx->stored.unknown = 1; } discard: ret = discard_chunk_bytes(ctx, ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left); if(ret) return ret; } } return ret; } /* Read chunks before or after the IDAT chunks depending on state */ static int read_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx, int only_ihdr) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; if(ctx->data == NULL) { if(ctx->encode_only) return 0; else return SPNG_EINTERNAL; } int ret = 0; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_INPUT) { ret = read_ihdr(ctx); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_IHDR; } if(only_ihdr) return 0; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_EOI) { ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT; ctx->prev_was_idat = 1; } while(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT || ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) { ret = read_non_idat_chunks(ctx); if(!ret) { if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT) ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT; else if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_AFTER_IDAT) ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_IEND; } else { switch(ret) { case SPNG_ECHUNK_POS: case SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE: /* size != expected size, SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN = invalid size */ case SPNG_EDUP_PLTE: case SPNG_EDUP_CHRM: case SPNG_EDUP_GAMA: case SPNG_EDUP_ICCP: case SPNG_EDUP_SBIT: case SPNG_EDUP_SRGB: case SPNG_EDUP_BKGD: case SPNG_EDUP_HIST: case SPNG_EDUP_TRNS: case SPNG_EDUP_PHYS: case SPNG_EDUP_TIME: case SPNG_EDUP_OFFS: case SPNG_EDUP_EXIF: case SPNG_ECHRM: case SPNG_ETRNS_COLOR_TYPE: case SPNG_ETRNS_NO_PLTE: case SPNG_EGAMA: case SPNG_EICCP_NAME: case SPNG_EICCP_COMPRESSION_METHOD: case SPNG_ESBIT: case SPNG_ESRGB: case SPNG_ETEXT: case SPNG_ETEXT_KEYWORD: case SPNG_EZTXT: case SPNG_EZTXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD: case SPNG_EITXT: case SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_FLAG: case SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD: case SPNG_EITXT_LANG_TAG: case SPNG_EITXT_TRANSLATED_KEY: case SPNG_EBKGD_NO_PLTE: case SPNG_EBKGD_PLTE_IDX: case SPNG_EHIST_NO_PLTE: case SPNG_EPHYS: case SPNG_ESPLT_NAME: case SPNG_ESPLT_DUP_NAME: case SPNG_ESPLT_DEPTH: case SPNG_ETIME: case SPNG_EOFFS: case SPNG_EEXIF: case SPNG_EZLIB: { if(!ctx->strict && !is_critical_chunk(&ctx->current_chunk)) { ret = discard_chunk_bytes(ctx, ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); if(ctx->undo) ctx->undo(ctx); ctx->stored = ctx->prev_stored; ctx->discard = 0; ctx->undo = NULL; continue; } else return decode_err(ctx, ret); break; } default: return decode_err(ctx, ret); } } } return ret; } static int read_scanline(spng_ctx *ctx) { int ret, pass = ctx->row_info.pass; struct spng_row_info *ri = &ctx->row_info; const struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; size_t scanline_width = sub[pass].scanline_width; uint32_t scanline_idx = ri->scanline_idx; uint8_t next_filter = 0; if(scanline_idx == (sub[pass].height - 1) && ri->pass == ctx->last_pass) { ret = read_scanline_bytes(ctx, ctx->scanline, scanline_width - 1); } else { ret = read_scanline_bytes(ctx, ctx->scanline, scanline_width); if(ret) return ret; next_filter = ctx->scanline[scanline_width - 1]; if(next_filter > 4) ret = SPNG_EFILTER; } if(ret) return ret; if(!scanline_idx && ri->filter > 1) { /* prev_scanline is all zeros for the first scanline */ memset(ctx->prev_scanline, 0, scanline_width); } if(ctx->ihdr.bit_depth == 16 && ctx->fmt != SPNG_FMT_RAW) u16_row_to_host(ctx->scanline, scanline_width - 1); ret = defilter_scanline(ctx->prev_scanline, ctx->scanline, scanline_width, ctx->bytes_per_pixel, ri->filter); if(ret) return ret; ri->filter = next_filter; return 0; } static int update_row_info(spng_ctx *ctx) { int interlacing = ctx->ihdr.interlace_method; struct spng_row_info *ri = &ctx->row_info; const struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; if(ri->scanline_idx == (sub[ri->pass].height - 1)) /* Last scanline */ { if(ri->pass == ctx->last_pass) { ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_EOI; return SPNG_EOI; } ri->scanline_idx = 0; ri->pass++; /* Skip empty passes */ while( (!sub[ri->pass].width || !sub[ri->pass].height) && (ri->pass < ctx->last_pass)) ri->pass++; } else { ri->row_num++; ri->scanline_idx++; } if(interlacing) ri->row_num = adam7_y_start[ri->pass] + ri->scanline_idx * adam7_y_delta[ri->pass]; return 0; } int spng_decode_scanline(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || out == NULL) return 1; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_EOI) return SPNG_EOI; struct decode_flags f = ctx->decode_flags; struct spng_row_info *ri = &ctx->row_info; const struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr = &ctx->ihdr; const uint16_t *gamma_lut = ctx->gamma_lut; unsigned char *trns_px = ctx->trns_px; const struct spng_sbit *sb = &ctx->decode_sb; const struct spng_plte_entry *plte = ctx->decode_plte.rgba; struct spng__iter iter = spng__iter_init(ihdr->bit_depth, ctx->scanline); const unsigned char *scanline; const int pass = ri->pass; const int fmt = ctx->fmt; const size_t scanline_width = sub[pass].scanline_width; const uint32_t width = sub[pass].width; uint32_t k; uint8_t r_8, g_8, b_8, a_8, gray_8; uint16_t r_16, g_16, b_16, a_16, gray_16; r_8=0; g_8=0; b_8=0; a_8=0; gray_8=0; r_16=0; g_16=0; b_16=0; a_16=0; gray_16=0; size_t pixel_size = 4; /* SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 */ size_t pixel_offset = 0; unsigned char *pixel; unsigned processing_depth = ihdr->bit_depth; if(f.indexed) processing_depth = 8; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) pixel_size = 8; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) pixel_size = 3; if(len < sub[pass].out_width) return SPNG_EBUFSIZ; int ret = read_scanline(ctx); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); scanline = ctx->scanline; for(k=0; k < width; k++) { pixel = (unsigned char*)out + pixel_offset; pixel_offset += pixel_size; if(f.same_layout) { if(f.zerocopy) break; memcpy(out, scanline, scanline_width - 1); break; } if(f.unpack) { unpack_scanline(out, scanline, width, ihdr->bit_depth, fmt); break; } if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { memcpy(&r_16, scanline + (k * 6), 2); memcpy(&g_16, scanline + (k * 6) + 2, 2); memcpy(&b_16, scanline + (k * 6) + 4, 2); a_16 = 65535; } else /* == 8 */ { if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) { rgb8_row_to_rgba8(scanline, out, width); break; } r_8 = scanline[k * 3]; g_8 = scanline[k * 3 + 1]; b_8 = scanline[k * 3 + 2]; a_8 = 255; } } else if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED) { uint8_t entry = 0; if(ihdr->bit_depth == 8) { if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGB8)) { expand_row(out, scanline, &ctx->decode_plte, width, fmt); break; } entry = scanline[k]; } else /* < 8 */ { entry = get_sample(&iter); } if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGB8)) { pixel[0] = plte[entry].red; pixel[1] = plte[entry].green; pixel[2] = plte[entry].blue; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) pixel[3] = plte[entry].alpha; continue; } else /* RGBA16 */ { r_16 = plte[entry].red; g_16 = plte[entry].green; b_16 = plte[entry].blue; a_16 = plte[entry].alpha; r_16 = (r_16 << 8) | r_16; g_16 = (g_16 << 8) | g_16; b_16 = (b_16 << 8) | b_16; a_16 = (a_16 << 8) | a_16; memcpy(pixel, &r_16, 2); memcpy(pixel + 2, &g_16, 2); memcpy(pixel + 4, &b_16, 2); memcpy(pixel + 6, &a_16, 2); continue; } } else if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { memcpy(&r_16, scanline + (k * 8), 2); memcpy(&g_16, scanline + (k * 8) + 2, 2); memcpy(&b_16, scanline + (k * 8) + 4, 2); memcpy(&a_16, scanline + (k * 8) + 6, 2); } else /* == 8 */ { r_8 = scanline[k * 4]; g_8 = scanline[k * 4 + 1]; b_8 = scanline[k * 4 + 2]; a_8 = scanline[k * 4 + 3]; } } else if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { memcpy(&gray_16, scanline + k * 2, 2); if(f.apply_trns && ctx->trns.gray == gray_16) a_16 = 0; else a_16 = 65535; r_16 = gray_16; g_16 = gray_16; b_16 = gray_16; } else /* <= 8 */ { gray_8 = get_sample(&iter); if(f.apply_trns && ctx->trns.gray == gray_8) a_8 = 0; else a_8 = 255; r_8 = gray_8; g_8 = gray_8; b_8 = gray_8; } } else if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { memcpy(&gray_16, scanline + (k * 4), 2); memcpy(&a_16, scanline + (k * 4) + 2, 2); r_16 = gray_16; g_16 = gray_16; b_16 = gray_16; } else /* == 8 */ { gray_8 = scanline[k * 2]; a_8 = scanline[k * 2 + 1]; r_8 = gray_8; g_8 = gray_8; b_8 = gray_8; } } if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGB8)) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { r_8 = r_16 >> 8; g_8 = g_16 >> 8; b_8 = b_16 >> 8; a_8 = a_16 >> 8; } pixel[0] = r_8; pixel[1] = g_8; pixel[2] = b_8; if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA8) pixel[3] = a_8; } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) { if(ihdr->bit_depth != 16) { r_16 = r_8; g_16 = g_8; b_16 = b_8; a_16 = a_8; } memcpy(pixel, &r_16, 2); memcpy(pixel + 2, &g_16, 2); memcpy(pixel + 4, &b_16, 2); memcpy(pixel + 6, &a_16, 2); } }/* for(k=0; k < width; k++) */ if(f.apply_trns) trns_row(out, scanline, trns_px, ctx->bytes_per_pixel, &ctx->ihdr, width, fmt); if(f.do_scaling) scale_row(out, width, fmt, processing_depth, sb); if(f.apply_gamma) gamma_correct_row(out, width, fmt, gamma_lut); /* The previous scanline is always defiltered */ void *t = ctx->prev_scanline; ctx->prev_scanline = ctx->scanline; ctx->scanline = t; ret = update_row_info(ctx); if(ret == SPNG_EOI) { if(ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left) /* zlib stream ended before an IDAT chunk boundary */ {/* Discard the rest of the chunk */ int error = discard_chunk_bytes(ctx, ctx->cur_chunk_bytes_left); if(error) return decode_err(ctx, error); } ctx->last_idat = ctx->current_chunk; } return ret; } int spng_decode_row(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || out == NULL) return 1; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_EOI) return SPNG_EOI; if(len < ctx->image_width) return SPNG_EBUFSIZ; const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr = &ctx->ihdr; int ret, pass = ctx->row_info.pass; unsigned char *outptr = out; if(!ihdr->interlace_method || pass == 6) return spng_decode_scanline(ctx, out, len); ret = spng_decode_scanline(ctx, ctx->row, ctx->image_width); if(ret && ret != SPNG_EOI) return ret; uint32_t k; unsigned pixel_size = 4; /* RGBA8 */ if(ctx->fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) pixel_size = 8; else if(ctx->fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) pixel_size = 3; else if(ctx->fmt == SPNG_FMT_G8) pixel_size = 1; else if(ctx->fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8) pixel_size = 2; else if(ctx->fmt & (SPNG_FMT_PNG | SPNG_FMT_RAW)) { if(ihdr->bit_depth < 8) { struct spng__iter iter = spng__iter_init(ihdr->bit_depth, ctx->row); const uint8_t samples_per_byte = 8 / ihdr->bit_depth; uint8_t sample; for(k=0; k < ctx->subimage[pass].width; k++) { sample = get_sample(&iter); size_t ioffset = adam7_x_start[pass] + k * adam7_x_delta[pass]; sample = sample << (iter.initial_shift - ioffset * ihdr->bit_depth % 8); ioffset /= samples_per_byte; outptr[ioffset] |= sample; } return 0; } else pixel_size = ctx->bytes_per_pixel; } for(k=0; k < ctx->subimage[pass].width; k++) { size_t ioffset = (adam7_x_start[pass] + (size_t) k * adam7_x_delta[pass]) * pixel_size; memcpy(outptr + ioffset, ctx->row + k * pixel_size, pixel_size); } return 0; } int spng_decode_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_INPUT) return SPNG_ENOSRC; if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_IEND) return 0; return read_chunks(ctx, 0); } int spng_decode_image(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, size_t len, int fmt, int flags) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_EOI) return SPNG_EOI; const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr = &ctx->ihdr; int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 0); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); ret = check_decode_fmt(ihdr, fmt); if(ret) return ret; ret = calculate_image_width(ihdr, fmt, &ctx->image_width); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); if(ctx->image_width > SIZE_MAX / ihdr->height) ctx->image_size = 0; /* overflow */ else ctx->image_size = ctx->image_width * ihdr->height; if( !(flags & SPNG_DECODE_PROGRESSIVE) ) { if(out == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->image_size) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(len < ctx->image_size) return SPNG_EBUFSIZ; } uint32_t bytes_read = 0; ret = read_idat_bytes(ctx, &bytes_read); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); if(bytes_read > 1) { int valid = read_u16(ctx->data) % 31 ? 0 : 1; unsigned flg = ctx->data[1]; unsigned flevel = flg >> 6; int compression_level = Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION; if(flevel == 0) compression_level = 0; /* fastest */ else if(flevel == 1) compression_level = 1; /* fast */ else if(flevel == 2) compression_level = 6; /* default */ else if(flevel == 3) compression_level = 9; /* slowest, max compression */ if(valid) ctx->image_options.compression_level = compression_level; } ret = spng__inflate_init(ctx, ctx->image_options.window_bits); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); ctx->zstream.avail_in = bytes_read; ctx->zstream.next_in = ctx->data; size_t scanline_buf_size = ctx->subimage[ctx->widest_pass].scanline_width; scanline_buf_size += 32; if(scanline_buf_size < 32) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; ctx->scanline_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, scanline_buf_size); ctx->prev_scanline_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, scanline_buf_size); ctx->scanline = ctx->scanline_buf; ctx->prev_scanline = ctx->prev_scanline_buf; struct decode_flags f = {0}; ctx->fmt = fmt; if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED) f.indexed = 1; unsigned processing_depth = ihdr->bit_depth; if(f.indexed) processing_depth = 8; if(ihdr->interlace_method) { f.interlaced = 1; ctx->row_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, ctx->image_width); ctx->row = ctx->row_buf; if(ctx->row == NULL) return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); } if(ctx->scanline == NULL || ctx->prev_scanline == NULL) { return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); } f.do_scaling = 1; if(f.indexed) f.do_scaling = 0; unsigned depth_target = 8; /* FMT_RGBA8, G8 */ if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) depth_target = 16; if(flags & SPNG_DECODE_TRNS && ctx->stored.trns) f.apply_trns = 1; else flags &= ~SPNG_DECODE_TRNS; if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA || ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA) flags &= ~SPNG_DECODE_TRNS; if(flags & SPNG_DECODE_GAMMA && ctx->stored.gama) f.apply_gamma = 1; else flags &= ~SPNG_DECODE_GAMMA; if(flags & SPNG_DECODE_USE_SBIT && ctx->stored.sbit) f.use_sbit = 1; else flags &= ~SPNG_DECODE_USE_SBIT; if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGBA16)) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA && ihdr->bit_depth == depth_target) f.same_layout = 1; } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR && ihdr->bit_depth == depth_target) f.same_layout = 1; f.apply_trns = 0; /* not applicable */ } else if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_PNG | SPNG_FMT_RAW)) { f.same_layout = 1; f.do_scaling = 0; f.apply_gamma = 0; /* for now */ f.apply_trns = 0; } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_G8 && ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE && ihdr->bit_depth <= 8) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == depth_target) f.same_layout = 1; else if(ihdr->bit_depth < 8) f.unpack = 1; f.apply_trns = 0; } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8 && ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE && ihdr->bit_depth <= 8) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA && ihdr->bit_depth == depth_target) f.same_layout = 1; else if(ihdr->bit_depth <= 8) f.unpack = 1; } else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA16 && ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE && ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA && ihdr->bit_depth == depth_target) f.same_layout = 1; else if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) f.unpack = 1; } /*if(f.same_layout && !flags && !f.interlaced) f.zerocopy = 1;*/ uint16_t *gamma_lut = NULL; if(f.apply_gamma) { float file_gamma = (float)ctx->gama / 100000.0f; float max; unsigned lut_entries; if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGB8)) { lut_entries = 256; max = 255.0f; gamma_lut = ctx->gamma_lut8; ctx->gamma_lut = ctx->gamma_lut8; } else /* SPNG_FMT_RGBA16 */ { lut_entries = 65536; max = 65535.0f; ctx->gamma_lut16 = spng__malloc(ctx, lut_entries * sizeof(uint16_t)); if(ctx->gamma_lut16 == NULL) return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); gamma_lut = ctx->gamma_lut16; ctx->gamma_lut = ctx->gamma_lut16; } float screen_gamma = 2.2f; float exponent = file_gamma * screen_gamma; if(FP_ZERO == fpclassify(exponent)) return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_EGAMA); exponent = 1.0f / exponent; unsigned i; for(i=0; i < lut_entries; i++) { float c = pow((float)i / max, exponent) * max; if(c > max) c = max; gamma_lut[i] = (uint16_t)c; } } struct spng_sbit *sb = &ctx->decode_sb; sb->red_bits = processing_depth; sb->green_bits = processing_depth; sb->blue_bits = processing_depth; sb->alpha_bits = processing_depth; sb->grayscale_bits = processing_depth; if(f.use_sbit) { if(ihdr->color_type == 0) { sb->grayscale_bits = ctx->sbit.grayscale_bits; sb->alpha_bits = ihdr->bit_depth; } else if(ihdr->color_type == 2 || ihdr->color_type == 3) { sb->red_bits = ctx->sbit.red_bits; sb->green_bits = ctx->sbit.green_bits; sb->blue_bits = ctx->sbit.blue_bits; sb->alpha_bits = ihdr->bit_depth; } else if(ihdr->color_type == 4) { sb->grayscale_bits = ctx->sbit.grayscale_bits; sb->alpha_bits = ctx->sbit.alpha_bits; } else /* == 6 */ { sb->red_bits = ctx->sbit.red_bits; sb->green_bits = ctx->sbit.green_bits; sb->blue_bits = ctx->sbit.blue_bits; sb->alpha_bits = ctx->sbit.alpha_bits; } } if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16 && fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGB8)) {/* samples are scaled down by 8 bits in the decode loop */ sb->red_bits -= 8; sb->green_bits -= 8; sb->blue_bits -= 8; sb->alpha_bits -= 8; sb->grayscale_bits -= 8; processing_depth = 8; } /* Prevent infinite loops in sample_to_target() */ if(!depth_target || depth_target > 16 || !processing_depth || processing_depth > 16 || !sb->grayscale_bits || sb->grayscale_bits > processing_depth || !sb->alpha_bits || sb->alpha_bits > processing_depth || !sb->red_bits || sb->red_bits > processing_depth || !sb->green_bits || sb->green_bits > processing_depth || !sb->blue_bits || sb->blue_bits > processing_depth) { return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_ESBIT); } if(sb->red_bits == sb->green_bits && sb->green_bits == sb->blue_bits && sb->blue_bits == sb->alpha_bits && sb->alpha_bits == processing_depth && processing_depth == depth_target) f.do_scaling = 0; struct spng_plte_entry *plte = ctx->decode_plte.rgba; /* Pre-process palette entries */ if(f.indexed) { uint8_t red, green, blue, alpha; uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < 256; i++) { if(f.apply_trns && i < ctx->trns.n_type3_entries) ctx->plte.entries[i].alpha = ctx->trns.type3_alpha[i]; else ctx->plte.entries[i].alpha = 255; red = sample_to_target(ctx->plte.entries[i].red, 8, sb->red_bits, 8); green = sample_to_target(ctx->plte.entries[i].green, 8, sb->green_bits, 8); blue = sample_to_target(ctx->plte.entries[i].blue, 8, sb->blue_bits, 8); alpha = sample_to_target(ctx->plte.entries[i].alpha, 8, sb->alpha_bits, 8); #if defined(SPNG_ARM) if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8 && ihdr->bit_depth == 8) {/* Working with 3 bytes at a time is more of an ARM thing */ ctx->decode_plte.rgb[i * 3 + 0] = red; ctx->decode_plte.rgb[i * 3 + 1] = green; ctx->decode_plte.rgb[i * 3 + 2] = blue; continue; } #endif plte[i].red = red; plte[i].green = green; plte[i].blue = blue; plte[i].alpha = alpha; } f.apply_trns = 0; } unsigned char *trns_px = ctx->trns_px; if(f.apply_trns) { uint16_t mask = ~0; if(ctx->ihdr.bit_depth < 16) mask = (1 << ctx->ihdr.bit_depth) - 1; if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 | SPNG_FMT_RGBA16)) { if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR) { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { memcpy(trns_px, &ctx->trns.red, 2); memcpy(trns_px + 2, &ctx->trns.green, 2); memcpy(trns_px + 4, &ctx->trns.blue, 2); } else { trns_px[0] = ctx->trns.red & mask; trns_px[1] = ctx->trns.green & mask; trns_px[2] = ctx->trns.blue & mask; } } } else if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE) // fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8 && { if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16) { memcpy(trns_px, &ctx->trns.gray, 2); } else { trns_px[0] = ctx->trns.gray & mask; } } } ctx->decode_flags = f; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_DECODE_INIT; struct spng_row_info *ri = &ctx->row_info; struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; while(!sub[ri->pass].width || !sub[ri->pass].height) ri->pass++; if(f.interlaced) ri->row_num = adam7_y_start[ri->pass]; unsigned pixel_size = 4; /* SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 */ if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) pixel_size = 8; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) pixel_size = 3; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_G8) pixel_size = 1; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8) pixel_size = 2; int i; for(i=ri->pass; i <= ctx->last_pass; i++) { if(!sub[i].scanline_width) continue; if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_PNG | SPNG_FMT_RAW)) sub[i].out_width = sub[i].scanline_width - 1; else sub[i].out_width = (size_t)sub[i].width * pixel_size; if(sub[i].out_width > UINT32_MAX) return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_EOVERFLOW); } /* Read the first filter byte, offsetting all reads by 1 byte. The scanlines will be aligned with the start of the array with the next scanline's filter byte at the end, the last scanline will end up being 1 byte "shorter". */ ret = read_scanline_bytes(ctx, &ri->filter, 1); if(ret) return decode_err(ctx, ret); if(ri->filter > 4) return decode_err(ctx, SPNG_EFILTER); if(flags & SPNG_DECODE_PROGRESSIVE) { return 0; } do { size_t ioffset = ri->row_num * ctx->image_width; ret = spng_decode_row(ctx, (unsigned char*)out + ioffset, ctx->image_width); }while(!ret); if(ret != SPNG_EOI) return decode_err(ctx, ret); return 0; } int spng_get_row_info(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_row_info *row_info) { if(ctx == NULL || row_info == NULL || ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_DECODE_INIT) return 1; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_EOI) return SPNG_EOI; *row_info = ctx->row_info; return 0; } static int write_chunks_before_idat(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret; uint32_t i; size_t length; const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr = &ctx->ihdr; unsigned char *data = ctx->decode_plte.raw; ret = write_data(ctx, spng_signature, 8); if(ret) return ret; write_u32(data, ihdr->width); write_u32(data + 4, ihdr->height); data[8] = ihdr->bit_depth; data[9] = ihdr->color_type; data[10] = ihdr->compression_method; data[11] = ihdr->filter_method; data[12] = ihdr->interlace_method; ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_ihdr, data, 13); if(ret) return ret; if(ctx->stored.chrm) { write_u32(data, ctx->chrm_int.white_point_x); write_u32(data + 4, ctx->chrm_int.white_point_y); write_u32(data + 8, ctx->chrm_int.red_x); write_u32(data + 12, ctx->chrm_int.red_y); write_u32(data + 16, ctx->chrm_int.green_x); write_u32(data + 20, ctx->chrm_int.green_y); write_u32(data + 24, ctx->chrm_int.blue_x); write_u32(data + 28, ctx->chrm_int.blue_y); ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_chrm, data, 32); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.gama) { write_u32(data, ctx->gama); ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_gama, data, 4); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.iccp) { uLongf dest_len = compressBound((uLong)ctx->iccp.profile_len); Bytef *buf = spng__malloc(ctx, dest_len); if(buf == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ret = compress2(buf, &dest_len, (void*)ctx->iccp.profile, (uLong)ctx->iccp.profile_len, Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION); if(ret != Z_OK) { spng__free(ctx, buf); return SPNG_EZLIB; } size_t name_len = strlen(ctx->iccp.profile_name); length = name_len + 2; length += dest_len; if(dest_len > length) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; unsigned char *cdata = NULL; ret = write_header(ctx, type_iccp, length, &cdata); if(ret) { spng__free(ctx, buf); return ret; } memcpy(cdata, ctx->iccp.profile_name, name_len + 1); cdata[name_len + 1] = 0; /* compression method */ memcpy(cdata + name_len + 2, buf, dest_len); spng__free(ctx, buf); ret = finish_chunk(ctx); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.sbit) { switch(ctx->ihdr.color_type) { case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE: { length = 1; data[0] = ctx->sbit.grayscale_bits; break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR: case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED: { length = 3; data[0] = ctx->sbit.red_bits; data[1] = ctx->sbit.green_bits; data[2] = ctx->sbit.blue_bits; break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA: { length = 2; data[0] = ctx->sbit.grayscale_bits; data[1] = ctx->sbit.alpha_bits; break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA: { length = 4; data[0] = ctx->sbit.red_bits; data[1] = ctx->sbit.green_bits; data[2] = ctx->sbit.blue_bits; data[3] = ctx->sbit.alpha_bits; break; } default: return SPNG_EINTERNAL; } ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_sbit, data, length); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.srgb) { ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_srgb, &ctx->srgb_rendering_intent, 1); if(ret) return ret; } ret = write_unknown_chunks(ctx, SPNG_AFTER_IHDR); if(ret) return ret; if(ctx->stored.plte) { for(i=0; i < ctx->plte.n_entries; i++) { data[i * 3 + 0] = ctx->plte.entries[i].red; data[i * 3 + 1] = ctx->plte.entries[i].green; data[i * 3 + 2] = ctx->plte.entries[i].blue; } ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_plte, data, ctx->plte.n_entries * 3); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.bkgd) { switch(ctx->ihdr.color_type) { case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE: case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA: { length = 2; write_u16(data, ctx->bkgd.gray); break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR: case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA: { length = 6; write_u16(data, ctx->bkgd.red); write_u16(data + 2, ctx->bkgd.green); write_u16(data + 4, ctx->bkgd.blue); break; } case SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED: { length = 1; data[0] = ctx->bkgd.plte_index; break; } default: return SPNG_EINTERNAL; } ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_bkgd, data, length); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.hist) { length = ctx->plte.n_entries * 2; for(i=0; i < ctx->plte.n_entries; i++) { write_u16(data + i * 2, ctx->hist.frequency[i]); } ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_hist, data, length); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.trns) { if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE) { write_u16(data, ctx->trns.gray); ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_trns, data, 2); } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR) { write_u16(data, ctx->trns.red); write_u16(data + 2, ctx->trns.green); write_u16(data + 4, ctx->trns.blue); ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_trns, data, 6); } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED) { ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_trns, ctx->trns.type3_alpha, ctx->trns.n_type3_entries); } if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.phys) { write_u32(data, ctx->phys.ppu_x); write_u32(data + 4, ctx->phys.ppu_y); data[8] = ctx->phys.unit_specifier; ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_phys, data, 9); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.splt) { const struct spng_splt *splt; unsigned char *cdata = NULL; uint32_t k; for(i=0; i < ctx->n_splt; i++) { splt = &ctx->splt_list[i]; size_t name_len = strlen(splt->name); length = name_len + 1; if(splt->sample_depth == 8) length += splt->n_entries * 6 + 1; else if(splt->sample_depth == 16) length += splt->n_entries * 10 + 1; ret = write_header(ctx, type_splt, length, &cdata); if(ret) return ret; memcpy(cdata, splt->name, name_len + 1); cdata += name_len + 2; cdata[-1] = splt->sample_depth; if(splt->sample_depth == 8) { for(k=0; k < splt->n_entries; k++) { cdata[k * 6 + 0] = splt->entries[k].red; cdata[k * 6 + 1] = splt->entries[k].green; cdata[k * 6 + 2] = splt->entries[k].blue; cdata[k * 6 + 3] = splt->entries[k].alpha; write_u16(cdata + k * 6 + 4, splt->entries[k].frequency); } } else if(splt->sample_depth == 16) { for(k=0; k < splt->n_entries; k++) { write_u16(cdata + k * 10 + 0, splt->entries[k].red); write_u16(cdata + k * 10 + 2, splt->entries[k].green); write_u16(cdata + k * 10 + 4, splt->entries[k].blue); write_u16(cdata + k * 10 + 6, splt->entries[k].alpha); write_u16(cdata + k * 10 + 8, splt->entries[k].frequency); } } ret = finish_chunk(ctx); if(ret) return ret; } } if(ctx->stored.time) { write_u16(data, ctx->time.year); data[2] = ctx->time.month; data[3] = ctx->time.day; data[4] = ctx->time.hour; data[5] = ctx->time.minute; data[6] = ctx->time.second; ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_time, data, 7); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.text) { unsigned char *cdata = NULL; const struct spng_text2 *text; const uint8_t *text_type_array[4] = { 0, type_text, type_ztxt, type_itxt }; for(i=0; i < ctx->n_text; i++) { text = &ctx->text_list[i]; const uint8_t *text_chunk_type = text_type_array[text->type]; Bytef *compressed_text = NULL; size_t keyword_len = 0; size_t language_tag_len = 0; size_t translated_keyword_len = 0; size_t compressed_length = 0; size_t text_length = 0; keyword_len = strlen(text->keyword); text_length = strlen(text->text); length = keyword_len + 1; if(text->type == SPNG_ZTXT) { length += 1; /* compression method */ } else if(text->type == SPNG_ITXT) { if(!text->language_tag || !text->translated_keyword) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; language_tag_len = strlen(text->language_tag); translated_keyword_len = strlen(text->translated_keyword); length += language_tag_len; if(length < language_tag_len) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; length += translated_keyword_len; if(length < translated_keyword_len) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; length += 4; /* compression flag + method + nul for the two strings */ if(length < 4) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; } if(text->compression_flag) { ret = spng__deflate_init(ctx, &ctx->text_options); if(ret) return ret; z_stream *zstream = &ctx->zstream; uLongf dest_len = deflateBound(zstream, (uLong)text_length); compressed_text = spng__malloc(ctx, dest_len); if(compressed_text == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; zstream->next_in = (void*)text->text; zstream->avail_in = (uInt)text_length; zstream->next_out = compressed_text; zstream->avail_out = dest_len; ret = deflate(zstream, Z_FINISH); if(ret != Z_STREAM_END) { spng__free(ctx, compressed_text); return SPNG_EZLIB; } compressed_length = zstream->total_out; length += compressed_length; if(length < compressed_length) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; } else { text_length = strlen(text->text); length += text_length; if(length < text_length) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; } ret = write_header(ctx, text_chunk_type, length, &cdata); if(ret) { spng__free(ctx, compressed_text); return ret; } memcpy(cdata, text->keyword, keyword_len + 1); cdata += keyword_len + 1; if(text->type == SPNG_ITXT) { cdata[0] = text->compression_flag; cdata[1] = 0; /* compression method */ cdata += 2; memcpy(cdata, text->language_tag, language_tag_len + 1); cdata += language_tag_len + 1; memcpy(cdata, text->translated_keyword, translated_keyword_len + 1); cdata += translated_keyword_len + 1; } else if(text->type == SPNG_ZTXT) { cdata[0] = 0; /* compression method */ cdata++; } if(text->compression_flag) memcpy(cdata, compressed_text, compressed_length); else memcpy(cdata, text->text, text_length); spng__free(ctx, compressed_text); ret = finish_chunk(ctx); if(ret) return ret; } } if(ctx->stored.offs) { write_s32(data, ctx->offs.x); write_s32(data + 4, ctx->offs.y); data[8] = ctx->offs.unit_specifier; ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_offs, data, 9); if(ret) return ret; } if(ctx->stored.exif) { ret = write_chunk(ctx, type_exif, ctx->exif.data, ctx->exif.length); if(ret) return ret; } ret = write_unknown_chunks(ctx, SPNG_AFTER_PLTE); if(ret) return ret; return 0; } static int write_chunks_after_idat(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret = write_unknown_chunks(ctx, SPNG_AFTER_IDAT); if(ret) return ret; return write_iend(ctx); } /* Compress and write scanline to IDAT stream */ static int write_idat_bytes(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *scanline, size_t len, int flush) { if(ctx == NULL || scanline == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; if(len > UINT_MAX) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret = 0; unsigned char *data = NULL; z_stream *zstream = &ctx->zstream; uint32_t idat_length = SPNG_WRITE_SIZE; zstream->next_in = scanline; zstream->avail_in = (uInt)len; do { ret = deflate(zstream, flush); if(zstream->avail_out == 0) { ret = finish_chunk(ctx); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); ret = write_header(ctx, type_idat, idat_length, &data); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); zstream->next_out = data; zstream->avail_out = idat_length; } }while(zstream->avail_in); if(ret != Z_OK) return SPNG_EZLIB; return 0; } static int finish_idat(spng_ctx *ctx) { int ret = 0; unsigned char *data = NULL; z_stream *zstream = &ctx->zstream; uint32_t idat_length = SPNG_WRITE_SIZE; while(ret != Z_STREAM_END) { ret = deflate(zstream, Z_FINISH); if(ret) { if(ret == Z_STREAM_END) break; if(ret != Z_BUF_ERROR) return SPNG_EZLIB; } if(zstream->avail_out == 0) { ret = finish_chunk(ctx); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); ret = write_header(ctx, type_idat, idat_length, &data); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); zstream->next_out = data; zstream->avail_out = idat_length; } } uint32_t trimmed_length = idat_length - zstream->avail_out; ret = trim_chunk(ctx, trimmed_length); if(ret) return ret; return finish_chunk(ctx); } static int encode_scanline(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *scanline, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || scanline == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; int ret, pass = ctx->row_info.pass; uint8_t filter = 0; struct spng_row_info *ri = &ctx->row_info; const struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; struct encode_flags f = ctx->encode_flags; unsigned char *filtered_scanline = ctx->filtered_scanline; size_t scanline_width = sub[pass].scanline_width; if(len < scanline_width - 1) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; /* encode_row() interlaces directly to ctx->scanline */ if(scanline != ctx->scanline) memcpy(ctx->scanline, scanline, scanline_width - 1); if(f.to_bigendian) u16_row_to_bigendian(ctx->scanline, scanline_width - 1); const int requires_previous = f.filter_choice & (SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_UP | SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_AVG | SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_PAETH); /* XXX: exclude 'requires_previous' filters by default for first scanline? */ if(!ri->scanline_idx && requires_previous) { /* prev_scanline is all zeros for the first scanline */ memset(ctx->prev_scanline, 0, scanline_width); } filter = get_best_filter(ctx->prev_scanline, ctx->scanline, scanline_width, ctx->bytes_per_pixel, f.filter_choice); if(!filter) filtered_scanline = ctx->scanline; filtered_scanline[-1] = filter; if(filter) { ret = filter_scanline(filtered_scanline, ctx->prev_scanline, ctx->scanline, scanline_width, ctx->bytes_per_pixel, filter); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); } ret = write_idat_bytes(ctx, filtered_scanline - 1, scanline_width, Z_NO_FLUSH); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); /* The previous scanline is always unfiltered */ void *t = ctx->prev_scanline; ctx->prev_scanline = ctx->scanline; ctx->scanline = t; ret = update_row_info(ctx); if(ret == SPNG_EOI) { int error = finish_idat(ctx); if(error) encode_err(ctx, error); if(f.finalize) { error = spng_encode_chunks(ctx); if(error) return encode_err(ctx, error); } } return ret; } static int encode_row(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *row, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || row == NULL) return SPNG_EINTERNAL; const int pass = ctx->row_info.pass; if(!ctx->ihdr.interlace_method || pass == 6) return encode_scanline(ctx, row, len); uint32_t k; const unsigned pixel_size = ctx->pixel_size; const unsigned bit_depth = ctx->ihdr.bit_depth; if(bit_depth < 8) { const unsigned samples_per_byte = 8 / bit_depth; const uint8_t mask = (1 << bit_depth) - 1; const unsigned initial_shift = 8 - bit_depth; unsigned shift_amount = initial_shift; unsigned char *scanline = ctx->scanline; const unsigned char *row_uc = row; uint8_t sample; memset(scanline, 0, ctx->subimage[pass].scanline_width); for(k=0; k < ctx->subimage[pass].width; k++) { size_t ioffset = adam7_x_start[pass] + k * adam7_x_delta[pass]; sample = row_uc[ioffset / samples_per_byte]; sample = sample >> (initial_shift - ioffset * bit_depth % 8); sample = sample & mask; sample = sample << shift_amount; scanline[0] |= sample; shift_amount -= bit_depth; if(shift_amount > 7) { shift_amount = initial_shift; scanline++; } } return encode_scanline(ctx, ctx->scanline, len); } for(k=0; k < ctx->subimage[pass].width; k++) { size_t ioffset = (adam7_x_start[pass] + (size_t) k * adam7_x_delta[pass]) * pixel_size; memcpy(ctx->scanline + k * pixel_size, (unsigned char*)row + ioffset, pixel_size); } return encode_scanline(ctx, ctx->scanline, len); } int spng_encode_scanline(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *scanline, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || scanline == NULL) return SPNG_EINVAL; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_EOI) return SPNG_EOI; if(len < (ctx->subimage[ctx->row_info.pass].scanline_width -1) ) return SPNG_EBUFSIZ; return encode_scanline(ctx, scanline, len); } int spng_encode_row(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *row, size_t len) { if(ctx == NULL || row == NULL) return SPNG_EINVAL; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_EOI) return SPNG_EOI; if(len < ctx->image_width) return SPNG_EBUFSIZ; return encode_row(ctx, row, len); } int spng_encode_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_OUTPUT) return SPNG_ENODST; if(!ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; int ret = 0; if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT) { if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return SPNG_ENOIHDR; ret = write_chunks_before_idat(ctx); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT; } else if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_FIRST_IDAT) { return 0; } else if(ctx->state == SPNG_STATE_EOI) { ret = write_chunks_after_idat(ctx); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_IEND; } else return SPNG_EOPSTATE; return 0; } int spng_encode_image(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *img, size_t len, int fmt, int flags) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; if(!ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return SPNG_ENOIHDR; if( !(fmt == SPNG_FMT_PNG || fmt == SPNG_FMT_RAW) ) return SPNG_EFMT; int ret = 0; const struct spng_ihdr *ihdr = &ctx->ihdr; struct encode_flags *encode_flags = &ctx->encode_flags; if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED && !ctx->stored.plte) return SPNG_ENOPLTE; ret = calculate_image_width(ihdr, fmt, &ctx->image_width); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); if(ctx->image_width > SIZE_MAX / ihdr->height) ctx->image_size = 0; /* overflow */ else ctx->image_size = ctx->image_width * ihdr->height; if( !(flags & SPNG_ENCODE_PROGRESSIVE) ) { if(img == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->image_size) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; if(len != ctx->image_size) return SPNG_EBUFSIZ; } ret = spng_encode_chunks(ctx); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); ret = calculate_subimages(ctx); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); if(ihdr->bit_depth < 8) ctx->bytes_per_pixel = 1; else ctx->bytes_per_pixel = num_channels(ihdr) * (ihdr->bit_depth / 8); if(spng__optimize(SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE)) { /* Filtering would make no difference */ if(!ctx->image_options.compression_level) { encode_flags->filter_choice = SPNG_DISABLE_FILTERING; } /* Palette indices and low bit-depth images do not benefit from filtering */ if(ihdr->color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED || ihdr->bit_depth < 8) { encode_flags->filter_choice = SPNG_DISABLE_FILTERING; } } /* This is technically the same as disabling filtering */ if(encode_flags->filter_choice == SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_NONE) { encode_flags->filter_choice = SPNG_DISABLE_FILTERING; } if(!encode_flags->filter_choice && spng__optimize(SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY)) { ctx->image_options.strategy = Z_DEFAULT_STRATEGY; } ret = spng__deflate_init(ctx, &ctx->image_options); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); size_t scanline_buf_size = ctx->subimage[ctx->widest_pass].scanline_width; scanline_buf_size += 32; if(scanline_buf_size < 32) return SPNG_EOVERFLOW; ctx->scanline_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, scanline_buf_size); ctx->prev_scanline_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, scanline_buf_size); if(ctx->scanline_buf == NULL || ctx->prev_scanline_buf == NULL) return encode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); /* Maintain alignment for pixels, filter at [-1] */ ctx->scanline = ctx->scanline_buf + 16; ctx->prev_scanline = ctx->prev_scanline_buf + 16; if(encode_flags->filter_choice) { ctx->filtered_scanline_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, scanline_buf_size); if(ctx->filtered_scanline_buf == NULL) return encode_err(ctx, SPNG_EMEM); ctx->filtered_scanline = ctx->filtered_scanline_buf + 16; } struct spng_subimage *sub = ctx->subimage; struct spng_row_info *ri = &ctx->row_info; ctx->fmt = fmt; z_stream *zstream = &ctx->zstream; zstream->avail_out = SPNG_WRITE_SIZE; ret = write_header(ctx, type_idat, zstream->avail_out, &zstream->next_out); if(ret) return encode_err(ctx, ret); if(ihdr->interlace_method) encode_flags->interlace = 1; if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_PNG | SPNG_FMT_RAW) ) encode_flags->same_layout = 1; if(ihdr->bit_depth == 16 && fmt != SPNG_FMT_RAW) encode_flags->to_bigendian = 1; if(flags & SPNG_ENCODE_FINALIZE) encode_flags->finalize = 1; while(!sub[ri->pass].width || !sub[ri->pass].height) ri->pass++; if(encode_flags->interlace) ri->row_num = adam7_y_start[ri->pass]; ctx->pixel_size = 4; /* SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 */ if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGBA16) ctx->pixel_size = 8; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_RGB8) ctx->pixel_size = 3; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_G8) ctx->pixel_size = 1; else if(fmt == SPNG_FMT_GA8) ctx->pixel_size = 2; else if(fmt & (SPNG_FMT_PNG | SPNG_FMT_RAW)) ctx->pixel_size = ctx->bytes_per_pixel; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_ENCODE_INIT; if(flags & SPNG_ENCODE_PROGRESSIVE) { encode_flags->progressive = 1; return 0; } do { size_t ioffset = ri->row_num * ctx->image_width; ret = encode_row(ctx, (unsigned char*)img + ioffset, ctx->image_width); }while(!ret); if(ret != SPNG_EOI) return encode_err(ctx, ret); return 0; } spng_ctx *spng_ctx_new(int flags) { struct spng_alloc alloc = { .malloc_fn = malloc, .realloc_fn = realloc, .calloc_fn = calloc, .free_fn = free }; return spng_ctx_new2(&alloc, flags); } spng_ctx *spng_ctx_new2(struct spng_alloc *alloc, int flags) { if(alloc == NULL) return NULL; if(flags != (flags & SPNG__CTX_FLAGS_ALL)) return NULL; if(alloc->malloc_fn == NULL) return NULL; if(alloc->realloc_fn == NULL) return NULL; if(alloc->calloc_fn == NULL) return NULL; if(alloc->free_fn == NULL) return NULL; spng_ctx *ctx = alloc->calloc_fn(1, sizeof(spng_ctx)); if(ctx == NULL) return NULL; ctx->alloc = *alloc; ctx->max_width = spng_u32max; ctx->max_height = spng_u32max; ctx->max_chunk_size = spng_u32max; ctx->chunk_cache_limit = SIZE_MAX; ctx->chunk_count_limit = SPNG_MAX_CHUNK_COUNT; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_INIT; ctx->crc_action_critical = SPNG_CRC_ERROR; ctx->crc_action_ancillary = SPNG_CRC_DISCARD; const struct spng__zlib_options image_defaults = { .compression_level = Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION, .window_bits = 15, .mem_level = 8, .strategy = Z_FILTERED, .data_type = 0 /* Z_BINARY */ }; const struct spng__zlib_options text_defaults = { .compression_level = Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION, .window_bits = 15, .mem_level = 8, .strategy = Z_DEFAULT_STRATEGY, .data_type = 1 /* Z_TEXT */ }; ctx->image_options = image_defaults; ctx->text_options = text_defaults; ctx->optimize_option = ~0; ctx->encode_flags.filter_choice = SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_ALL; ctx->flags = flags; if(flags & SPNG_CTX_ENCODER) ctx->encode_only = 1; return ctx; } void spng_ctx_free(spng_ctx *ctx) { if(ctx == NULL) return; if(ctx->streaming && ctx->stream_buf != NULL) spng__free(ctx, ctx->stream_buf); if(!ctx->user.exif) spng__free(ctx, ctx->exif.data); if(!ctx->user.iccp) spng__free(ctx, ctx->iccp.profile); uint32_t i; if(ctx->splt_list != NULL && !ctx->user.splt) { for(i=0; i < ctx->n_splt; i++) { spng__free(ctx, ctx->splt_list[i].entries); } spng__free(ctx, ctx->splt_list); } if(ctx->text_list != NULL) { for(i=0; i< ctx->n_text; i++) { if(ctx->user.text) break; spng__free(ctx, ctx->text_list[i].keyword); if(ctx->text_list[i].compression_flag) spng__free(ctx, ctx->text_list[i].text); } spng__free(ctx, ctx->text_list); } if(ctx->chunk_list != NULL && !ctx->user.unknown) { for(i=0; i< ctx->n_chunks; i++) { spng__free(ctx, ctx->chunk_list[i].data); } spng__free(ctx, ctx->chunk_list); } if(ctx->deflate) deflateEnd(&ctx->zstream); else inflateEnd(&ctx->zstream); if(!ctx->user_owns_out_png) spng__free(ctx, ctx->out_png); spng__free(ctx, ctx->gamma_lut16); spng__free(ctx, ctx->row_buf); spng__free(ctx, ctx->scanline_buf); spng__free(ctx, ctx->prev_scanline_buf); spng__free(ctx, ctx->filtered_scanline_buf); spng_free_fn *free_fn = ctx->alloc.free_fn; memset(ctx, 0, sizeof(spng_ctx)); free_fn(ctx); } static int buffer_read_fn(spng_ctx *ctx, void *user, void *data, size_t n) { if(n > ctx->bytes_left) return SPNG_IO_EOF; (void)user; (void)data; ctx->data = ctx->data + ctx->last_read_size; ctx->last_read_size = n; ctx->bytes_left -= n; return 0; } static int file_read_fn(spng_ctx *ctx, void *user, void *data, size_t n) { FILE *file = user; (void)ctx; if(fread(data, n, 1, file) != 1) { if(feof(file)) return SPNG_IO_EOF; else return SPNG_IO_ERROR; } return 0; } static int file_write_fn(spng_ctx *ctx, void *user, void *data, size_t n) { FILE *file = user; (void)ctx; if(fwrite(data, n, 1, file) != 1) return SPNG_IO_ERROR; return 0; } int spng_set_png_buffer(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *buf, size_t size) { if(ctx == NULL || buf == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; if(ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; /* not supported */ if(ctx->data != NULL) return SPNG_EBUF_SET; ctx->data = buf; ctx->png_base = buf; ctx->data_size = size; ctx->bytes_left = size; ctx->read_fn = buffer_read_fn; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_INPUT; return 0; } int spng_set_png_stream(spng_ctx *ctx, spng_rw_fn *rw_func, void *user) { if(ctx == NULL || rw_func == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; /* SPNG_STATE_OUTPUT shares the same value */ if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_INPUT) return SPNG_EBUF_SET; if(ctx->encode_only) { if(ctx->out_png != NULL) return SPNG_EBUF_SET; ctx->write_fn = rw_func; ctx->write_ptr = ctx->stream_buf; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_OUTPUT; } else { ctx->stream_buf = spng__malloc(ctx, SPNG_READ_SIZE); if(ctx->stream_buf == NULL) return SPNG_EMEM; ctx->read_fn = rw_func; ctx->data = ctx->stream_buf; ctx->data_size = SPNG_READ_SIZE; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_INPUT; } ctx->stream_user_ptr = user; ctx->streaming = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_png_file(spng_ctx *ctx, FILE *file) { if(file == NULL) return 1; if(ctx->encode_only) return spng_set_png_stream(ctx, file_write_fn, file); return spng_set_png_stream(ctx, file_read_fn, file); } void *spng_get_png_buffer(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t *len, int *error) { int tmp = 0; error = error ? error : &tmp; *error = 0; if(ctx == NULL || !len) *error = SPNG_EINVAL; if(*error) return NULL; if(!ctx->encode_only) *error = SPNG_ECTXTYPE; else if(!ctx->state) *error = SPNG_EBADSTATE; else if(!ctx->internal_buffer) *error = SPNG_EOPSTATE; else if(ctx->state < SPNG_STATE_EOI) *error = SPNG_EOPSTATE; else if(ctx->state != SPNG_STATE_IEND) *error = SPNG_ENOTFINAL; if(*error) return NULL; ctx->user_owns_out_png = 1; *len = ctx->bytes_encoded; return ctx->out_png; } int spng_set_image_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t width, uint32_t height) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(width > spng_u32max || height > spng_u32max) return 1; ctx->max_width = width; ctx->max_height = height; return 0; } int spng_get_image_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t *width, uint32_t *height) { if(ctx == NULL || width == NULL || height == NULL) return 1; *width = ctx->max_width; *height = ctx->max_height; return 0; } int spng_set_chunk_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t chunk_size, size_t cache_limit) { if(ctx == NULL || chunk_size > spng_u32max || chunk_size > cache_limit) return 1; ctx->max_chunk_size = chunk_size; ctx->chunk_cache_limit = cache_limit; return 0; } int spng_get_chunk_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t *chunk_size, size_t *cache_limit) { if(ctx == NULL || chunk_size == NULL || cache_limit == NULL) return 1; *chunk_size = ctx->max_chunk_size; *cache_limit = ctx->chunk_cache_limit; return 0; } int spng_set_crc_action(spng_ctx *ctx, int critical, int ancillary) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; if(critical > 2 || critical < 0) return 1; if(ancillary > 2 || ancillary < 0) return 1; if(critical == SPNG_CRC_DISCARD) return 1; ctx->crc_action_critical = critical; ctx->crc_action_ancillary = ancillary; return 0; } int spng_set_option(spng_ctx *ctx, enum spng_option option, int value) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; switch(option) { case SPNG_KEEP_UNKNOWN_CHUNKS: { ctx->keep_unknown = value ? 1 : 0; break; } case SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_LEVEL: { ctx->image_options.compression_level = value; break; } case SPNG_IMG_WINDOW_BITS: { ctx->image_options.window_bits = value; break; } case SPNG_IMG_MEM_LEVEL: { ctx->image_options.mem_level = value; break; } case SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY: { ctx->image_options.strategy = value; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_COMPRESSION_LEVEL: { ctx->text_options.compression_level = value; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_WINDOW_BITS: { ctx->text_options.window_bits = value; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_MEM_LEVEL: { ctx->text_options.mem_level = value; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY: { ctx->text_options.strategy = value; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE: { if(value & ~SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_ALL) return 1; ctx->encode_flags.filter_choice = value; break; } case SPNG_CHUNK_COUNT_LIMIT: { if(value < 0) return 1; if(value > (int)ctx->chunk_count_total) return 1; ctx->chunk_count_limit = value; break; } case SPNG_ENCODE_TO_BUFFER: { if(value < 0) return 1; if(!ctx->encode_only) return SPNG_ECTXTYPE; if(ctx->state >= SPNG_STATE_OUTPUT) return SPNG_EOPSTATE; if(!value) break; ctx->internal_buffer = 1; ctx->state = SPNG_STATE_OUTPUT; break; } default: return 1; } /* Option can no longer be overriden by the library */ if(option < 32) ctx->optimize_option &= ~(1 << option); return 0; } int spng_get_option(spng_ctx *ctx, enum spng_option option, int *value) { if(ctx == NULL || value == NULL) return 1; if(!ctx->state) return SPNG_EBADSTATE; switch(option) { case SPNG_KEEP_UNKNOWN_CHUNKS: { *value = ctx->keep_unknown; break; } case SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_LEVEL: { *value = ctx->image_options.compression_level; break; } case SPNG_IMG_WINDOW_BITS: { *value = ctx->image_options.window_bits; break; } case SPNG_IMG_MEM_LEVEL: { *value = ctx->image_options.mem_level; break; } case SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY: { *value = ctx->image_options.strategy; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_COMPRESSION_LEVEL: { *value = ctx->text_options.compression_level; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_WINDOW_BITS: { *value = ctx->text_options.window_bits; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_MEM_LEVEL: { *value = ctx->text_options.mem_level; break; } case SPNG_TEXT_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY: { *value = ctx->text_options.strategy; break; } case SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE: { *value = ctx->encode_flags.filter_choice; break; } case SPNG_CHUNK_COUNT_LIMIT: { *value = ctx->chunk_count_limit; break; } case SPNG_ENCODE_TO_BUFFER: { if(ctx->internal_buffer) *value = 1; else *value = 0; break; } default: return 1; } return 0; } int spng_decoded_image_size(spng_ctx *ctx, int fmt, size_t *len) { if(ctx == NULL || len == NULL) return 1; int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 1); if(ret) return ret; ret = check_decode_fmt(&ctx->ihdr, fmt); if(ret) return ret; return calculate_image_size(&ctx->ihdr, fmt, len); } int spng_get_ihdr(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_ihdr *ihdr) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 1); if(ret) return ret; if(ihdr == NULL) return 1; *ihdr = ctx->ihdr; return 0; } int spng_get_plte(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_plte *plte) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(plte); *plte = ctx->plte; return 0; } int spng_get_trns(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_trns *trns) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(trns); *trns = ctx->trns; return 0; } int spng_get_chrm(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm *chrm) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chrm); chrm->white_point_x = (double)ctx->chrm_int.white_point_x / 100000.0; chrm->white_point_y = (double)ctx->chrm_int.white_point_y / 100000.0; chrm->red_x = (double)ctx->chrm_int.red_x / 100000.0; chrm->red_y = (double)ctx->chrm_int.red_y / 100000.0; chrm->blue_y = (double)ctx->chrm_int.blue_y / 100000.0; chrm->blue_x = (double)ctx->chrm_int.blue_x / 100000.0; chrm->green_x = (double)ctx->chrm_int.green_x / 100000.0; chrm->green_y = (double)ctx->chrm_int.green_y / 100000.0; return 0; } int spng_get_chrm_int(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm_int *chrm) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chrm); *chrm = ctx->chrm_int; return 0; } int spng_get_gama(spng_ctx *ctx, double *gamma) { double *gama = gamma; SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(gama); *gama = (double)ctx->gama / 100000.0; return 0; } int spng_get_gama_int(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t *gama_int) { uint32_t *gama = gama_int; SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(gama); *gama_int = ctx->gama; return 0; } int spng_get_iccp(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_iccp *iccp) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(iccp); *iccp = ctx->iccp; return 0; } int spng_get_sbit(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_sbit *sbit) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(sbit); *sbit = ctx->sbit; return 0; } int spng_get_srgb(spng_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *rendering_intent) { uint8_t *srgb = rendering_intent; SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(srgb); *srgb = ctx->srgb_rendering_intent; return 0; } int spng_get_text(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_text *text, uint32_t *n_text) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 0); if(ret) return ret; if(!ctx->stored.text) return SPNG_ECHUNKAVAIL; if(n_text == NULL) return 1; if(text == NULL) { *n_text = ctx->n_text; return 0; } if(*n_text < ctx->n_text) return 1; uint32_t i; for(i=0; i< ctx->n_text; i++) { text[i].type = ctx->text_list[i].type; memcpy(&text[i].keyword, ctx->text_list[i].keyword, strlen(ctx->text_list[i].keyword) + 1); text[i].compression_method = 0; text[i].compression_flag = ctx->text_list[i].compression_flag; text[i].language_tag = ctx->text_list[i].language_tag; text[i].translated_keyword = ctx->text_list[i].translated_keyword; text[i].length = ctx->text_list[i].text_length; text[i].text = ctx->text_list[i].text; } return ret; } int spng_get_bkgd(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_bkgd *bkgd) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(bkgd); *bkgd = ctx->bkgd; return 0; } int spng_get_hist(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_hist *hist) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(hist); *hist = ctx->hist; return 0; } int spng_get_phys(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_phys *phys) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(phys); *phys = ctx->phys; return 0; } int spng_get_splt(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_splt *splt, uint32_t *n_splt) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 0); if(ret) return ret; if(!ctx->stored.splt) return SPNG_ECHUNKAVAIL; if(n_splt == NULL) return 1; if(splt == NULL) { *n_splt = ctx->n_splt; return 0; } if(*n_splt < ctx->n_splt) return 1; memcpy(splt, ctx->splt_list, ctx->n_splt * sizeof(struct spng_splt)); return 0; } int spng_get_time(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_time *time) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(time); *time = ctx->time; return 0; } int spng_get_unknown_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunks, uint32_t *n_chunks) { if(ctx == NULL) return 1; int ret = read_chunks(ctx, 0); if(ret) return ret; if(!ctx->stored.unknown) return SPNG_ECHUNKAVAIL; if(n_chunks == NULL) return 1; if(chunks == NULL) { *n_chunks = ctx->n_chunks; return 0; } if(*n_chunks < ctx->n_chunks) return 1; memcpy(chunks, ctx->chunk_list, sizeof(struct spng_unknown_chunk)); return 0; } int spng_get_offs(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_offs *offs) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(offs); *offs = ctx->offs; return 0; } int spng_get_exif(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_exif *exif) { SPNG_GET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(exif); *exif = ctx->exif; return 0; } int spng_set_ihdr(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_ihdr *ihdr) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(ihdr); if(ctx->stored.ihdr) return 1; ret = check_ihdr(ihdr, ctx->max_width, ctx->max_height); if(ret) return ret; ctx->ihdr = *ihdr; ctx->stored.ihdr = 1; ctx->user.ihdr = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_plte(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_plte *plte) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(plte); if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return 1; if(check_plte(plte, &ctx->ihdr)) return 1; ctx->plte.n_entries = plte->n_entries; memcpy(ctx->plte.entries, plte->entries, plte->n_entries * sizeof(struct spng_plte_entry)); ctx->stored.plte = 1; ctx->user.plte = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_trns(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_trns *trns) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(trns); if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return SPNG_ENOIHDR; if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE) { ctx->trns.gray = trns->gray; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR) { ctx->trns.red = trns->red; ctx->trns.green = trns->green; ctx->trns.blue = trns->blue; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED) { if(!ctx->stored.plte) return SPNG_ETRNS_NO_PLTE; if(trns->n_type3_entries > ctx->plte.n_entries) return 1; ctx->trns.n_type3_entries = trns->n_type3_entries; memcpy(ctx->trns.type3_alpha, trns->type3_alpha, trns->n_type3_entries); } else return SPNG_ETRNS_COLOR_TYPE; ctx->stored.trns = 1; ctx->user.trns = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_chrm(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm *chrm) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chrm); struct spng_chrm_int chrm_int; chrm_int.white_point_x = (uint32_t)(chrm->white_point_x * 100000.0); chrm_int.white_point_y = (uint32_t)(chrm->white_point_y * 100000.0); chrm_int.red_x = (uint32_t)(chrm->red_x * 100000.0); chrm_int.red_y = (uint32_t)(chrm->red_y * 100000.0); chrm_int.green_x = (uint32_t)(chrm->green_x * 100000.0); chrm_int.green_y = (uint32_t)(chrm->green_y * 100000.0); chrm_int.blue_x = (uint32_t)(chrm->blue_x * 100000.0); chrm_int.blue_y = (uint32_t)(chrm->blue_y * 100000.0); if(check_chrm_int(&chrm_int)) return SPNG_ECHRM; ctx->chrm_int = chrm_int; ctx->stored.chrm = 1; ctx->user.chrm = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_chrm_int(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm_int *chrm_int) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chrm_int); if(check_chrm_int(chrm_int)) return SPNG_ECHRM; ctx->chrm_int = *chrm_int; ctx->stored.chrm = 1; ctx->user.chrm = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_gama(spng_ctx *ctx, double gamma) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(ctx); uint32_t gama = gamma * 100000.0; if(!gama) return 1; if(gama > spng_u32max) return 1; ctx->gama = gama; ctx->stored.gama = 1; ctx->user.gama = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_gama_int(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t gamma) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(ctx); if(!gamma) return 1; if(gamma > spng_u32max) return 1; ctx->gama = gamma; ctx->stored.gama = 1; ctx->user.gama = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_iccp(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_iccp *iccp) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(iccp); if(check_png_keyword(iccp->profile_name)) return SPNG_EICCP_NAME; if(!iccp->profile_len) return SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE; if(iccp->profile_len > spng_u32max) return SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN; if(ctx->iccp.profile && !ctx->user.iccp) spng__free(ctx, ctx->iccp.profile); ctx->iccp = *iccp; ctx->stored.iccp = 1; ctx->user.iccp = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_sbit(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_sbit *sbit) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(sbit); if(check_sbit(sbit, &ctx->ihdr)) return 1; if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return 1; ctx->sbit = *sbit; ctx->stored.sbit = 1; ctx->user.sbit = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_srgb(spng_ctx *ctx, uint8_t rendering_intent) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(ctx); if(rendering_intent > 3) return 1; ctx->srgb_rendering_intent = rendering_intent; ctx->stored.srgb = 1; ctx->user.srgb = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_text(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_text *text, uint32_t n_text) { if(!n_text) return 1; SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(text); uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < n_text; i++) { if(check_png_keyword(text[i].keyword)) return SPNG_ETEXT_KEYWORD; if(!text[i].length) return 1; if(text[i].length > UINT_MAX) return 1; if(text[i].text == NULL) return 1; if(text[i].type == SPNG_TEXT) { if(ctx->strict && check_png_text(text[i].text, text[i].length)) return 1; } else if(text[i].type == SPNG_ZTXT) { if(ctx->strict && check_png_text(text[i].text, text[i].length)) return 1; if(text[i].compression_method != 0) return SPNG_EZTXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD; } else if(text[i].type == SPNG_ITXT) { if(text[i].compression_flag > 1) return SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_FLAG; if(text[i].compression_method != 0) return SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD; if(text[i].language_tag == NULL) return SPNG_EITXT_LANG_TAG; if(text[i].translated_keyword == NULL) return SPNG_EITXT_TRANSLATED_KEY; } else return 1; } struct spng_text2 *text_list = spng__calloc(ctx, sizeof(struct spng_text2), n_text); if(!text_list) return SPNG_EMEM; if(ctx->text_list != NULL) { for(i=0; i < ctx->n_text; i++) { if(ctx->user.text) break; spng__free(ctx, ctx->text_list[i].keyword); if(ctx->text_list[i].compression_flag) spng__free(ctx, ctx->text_list[i].text); } spng__free(ctx, ctx->text_list); } for(i=0; i < n_text; i++) { text_list[i].type = text[i].type; /* Prevent issues with spng_text.keyword[80] going out of scope */ text_list[i].keyword = text_list[i].user_keyword_storage; memcpy(text_list[i].user_keyword_storage, text[i].keyword, strlen(text[i].keyword)); text_list[i].text = text[i].text; text_list[i].text_length = text[i].length; if(text[i].type == SPNG_ZTXT) { text_list[i].compression_flag = 1; } else if(text[i].type == SPNG_ITXT) { text_list[i].compression_flag = text[i].compression_flag; text_list[i].language_tag = text[i].language_tag; text_list[i].translated_keyword = text[i].translated_keyword; } } ctx->text_list = text_list; ctx->n_text = n_text; ctx->stored.text = 1; ctx->user.text = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_bkgd(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_bkgd *bkgd) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(bkgd); if(!ctx->stored.ihdr) return 1; if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 0 || ctx->ihdr.color_type == 4) { ctx->bkgd.gray = bkgd->gray; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 2 || ctx->ihdr.color_type == 6) { ctx->bkgd.red = bkgd->red; ctx->bkgd.green = bkgd->green; ctx->bkgd.blue = bkgd->blue; } else if(ctx->ihdr.color_type == 3) { if(!ctx->stored.plte) return SPNG_EBKGD_NO_PLTE; if(bkgd->plte_index >= ctx->plte.n_entries) return SPNG_EBKGD_PLTE_IDX; ctx->bkgd.plte_index = bkgd->plte_index; } ctx->stored.bkgd = 1; ctx->user.bkgd = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_hist(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_hist *hist) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(hist); if(!ctx->stored.plte) return SPNG_EHIST_NO_PLTE; ctx->hist = *hist; ctx->stored.hist = 1; ctx->user.hist = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_phys(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_phys *phys) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(phys); if(check_phys(phys)) return SPNG_EPHYS; ctx->phys = *phys; ctx->stored.phys = 1; ctx->user.phys = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_splt(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_splt *splt, uint32_t n_splt) { if(!n_splt) return 1; SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(splt); uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < n_splt; i++) { if(check_png_keyword(splt[i].name)) return SPNG_ESPLT_NAME; if( !(splt[i].sample_depth == 8 || splt[i].sample_depth == 16) ) return SPNG_ESPLT_DEPTH; } if(ctx->stored.splt && !ctx->user.splt) { for(i=0; i < ctx->n_splt; i++) { if(ctx->splt_list[i].entries != NULL) spng__free(ctx, ctx->splt_list[i].entries); } spng__free(ctx, ctx->splt_list); } ctx->splt_list = splt; ctx->n_splt = n_splt; ctx->stored.splt = 1; ctx->user.splt = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_time(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_time *time) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(time); if(check_time(time)) return SPNG_ETIME; ctx->time = *time; ctx->stored.time = 1; ctx->user.time = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_unknown_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunks, uint32_t n_chunks) { if(!n_chunks) return 1; SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(chunks); uint32_t i; for(i=0; i < n_chunks; i++) { if(chunks[i].length > spng_u32max) return SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN; if(chunks[i].length && chunks[i].data == NULL) return 1; switch(chunks[i].location) { case SPNG_AFTER_IHDR: case SPNG_AFTER_PLTE: case SPNG_AFTER_IDAT: break; default: return SPNG_ECHUNK_POS; } } if(ctx->stored.unknown && !ctx->user.unknown) { for(i=0; i < ctx->n_chunks; i++) { spng__free(ctx, ctx->chunk_list[i].data); } spng__free(ctx, ctx->chunk_list); } ctx->chunk_list = chunks; ctx->n_chunks = n_chunks; ctx->stored.unknown = 1; ctx->user.unknown = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_offs(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_offs *offs) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(offs); if(check_offs(offs)) return SPNG_EOFFS; ctx->offs = *offs; ctx->stored.offs = 1; ctx->user.offs = 1; return 0; } int spng_set_exif(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_exif *exif) { SPNG_SET_CHUNK_BOILERPLATE(exif); if(check_exif(exif)) return SPNG_EEXIF; if(ctx->exif.data != NULL && !ctx->user.exif) spng__free(ctx, ctx->exif.data); ctx->exif = *exif; ctx->stored.exif = 1; ctx->user.exif = 1; return 0; } const char *spng_strerror(int err) { switch(err) { case SPNG_IO_EOF: return "end of stream"; case SPNG_IO_ERROR: return "stream error"; case SPNG_OK: return "success"; case SPNG_EINVAL: return "invalid argument"; case SPNG_EMEM: return "out of memory"; case SPNG_EOVERFLOW: return "arithmetic overflow"; case SPNG_ESIGNATURE: return "invalid signature"; case SPNG_EWIDTH: return "invalid image width"; case SPNG_EHEIGHT: return "invalid image height"; case SPNG_EUSER_WIDTH: return "image width exceeds user limit"; case SPNG_EUSER_HEIGHT: return "image height exceeds user limit"; case SPNG_EBIT_DEPTH: return "invalid bit depth"; case SPNG_ECOLOR_TYPE: return "invalid color type"; case SPNG_ECOMPRESSION_METHOD: return "invalid compression method"; case SPNG_EFILTER_METHOD: return "invalid filter method"; case SPNG_EINTERLACE_METHOD: return "invalid interlace method"; case SPNG_EIHDR_SIZE: return "invalid IHDR chunk size"; case SPNG_ENOIHDR: return "missing IHDR chunk"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_POS: return "invalid chunk position"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE: return "invalid chunk length"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_CRC: return "invalid chunk checksum"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_TYPE: return "invalid chunk type"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_UNKNOWN_CRITICAL: return "unknown critical chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_PLTE: return "duplicate PLTE chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_CHRM: return "duplicate cHRM chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_GAMA: return "duplicate gAMA chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_ICCP: return "duplicate iCCP chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_SBIT: return "duplicate sBIT chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_SRGB: return "duplicate sRGB chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_BKGD: return "duplicate bKGD chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_HIST: return "duplicate hIST chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_TRNS: return "duplicate tRNS chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_PHYS: return "duplicate pHYs chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_TIME: return "duplicate tIME chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_OFFS: return "duplicate oFFs chunk"; case SPNG_EDUP_EXIF: return "duplicate eXIf chunk"; case SPNG_ECHRM: return "invalid cHRM chunk"; case SPNG_EPLTE_IDX: return "invalid palette (PLTE) index"; case SPNG_ETRNS_COLOR_TYPE: return "tRNS chunk with incompatible color type"; case SPNG_ETRNS_NO_PLTE: return "missing palette (PLTE) for tRNS chunk"; case SPNG_EGAMA: return "invalid gAMA chunk"; case SPNG_EICCP_NAME: return "invalid iCCP profile name"; case SPNG_EICCP_COMPRESSION_METHOD: return "invalid iCCP compression method"; case SPNG_ESBIT: return "invalid sBIT chunk"; case SPNG_ESRGB: return "invalid sRGB chunk"; case SPNG_ETEXT: return "invalid tEXt chunk"; case SPNG_ETEXT_KEYWORD: return "invalid tEXt keyword"; case SPNG_EZTXT: return "invalid zTXt chunk"; case SPNG_EZTXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD: return "invalid zTXt compression method"; case SPNG_EITXT: return "invalid iTXt chunk"; case SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_FLAG: return "invalid iTXt compression flag"; case SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD: return "invalid iTXt compression method"; case SPNG_EITXT_LANG_TAG: return "invalid iTXt language tag"; case SPNG_EITXT_TRANSLATED_KEY: return "invalid iTXt translated key"; case SPNG_EBKGD_NO_PLTE: return "missing palette for bKGD chunk"; case SPNG_EBKGD_PLTE_IDX: return "invalid palette index for bKGD chunk"; case SPNG_EHIST_NO_PLTE: return "missing palette for hIST chunk"; case SPNG_EPHYS: return "invalid pHYs chunk"; case SPNG_ESPLT_NAME: return "invalid suggested palette name"; case SPNG_ESPLT_DUP_NAME: return "duplicate suggested palette (sPLT) name"; case SPNG_ESPLT_DEPTH: return "invalid suggested palette (sPLT) sample depth"; case SPNG_ETIME: return "invalid tIME chunk"; case SPNG_EOFFS: return "invalid oFFs chunk"; case SPNG_EEXIF: return "invalid eXIf chunk"; case SPNG_EIDAT_TOO_SHORT: return "IDAT stream too short"; case SPNG_EIDAT_STREAM: return "IDAT stream error"; case SPNG_EZLIB: return "zlib error"; case SPNG_EFILTER: return "invalid scanline filter"; case SPNG_EBUFSIZ: return "invalid buffer size"; case SPNG_EIO: return "i/o error"; case SPNG_EOF: return "end of file"; case SPNG_EBUF_SET: return "buffer already set"; case SPNG_EBADSTATE: return "non-recoverable state"; case SPNG_EFMT: return "invalid format"; case SPNG_EFLAGS: return "invalid flags"; case SPNG_ECHUNKAVAIL: return "chunk not available"; case SPNG_ENCODE_ONLY: return "encode only context"; case SPNG_EOI: return "reached end-of-image state"; case SPNG_ENOPLTE: return "missing PLTE for indexed image"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS: return "reached chunk/cache limits"; case SPNG_EZLIB_INIT: return "zlib init error"; case SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN: return "chunk exceeds maximum standard length"; case SPNG_EINTERNAL: return "internal error"; case SPNG_ECTXTYPE: return "invalid operation for context type"; case SPNG_ENOSRC: return "source PNG not set"; case SPNG_ENODST: return "PNG output not set"; case SPNG_EOPSTATE: return "invalid operation for state"; case SPNG_ENOTFINAL: return "PNG not finalized"; default: return "unknown error"; } } const char *spng_version_string(void) { return SPNG_VERSION_STRING; } #if defined(_MSC_VER) #pragma warning(pop) #endif /* The following SIMD optimizations are derived from libpng source code. */ /* * PNG Reference Library License version 2 * * Copyright (c) 1995-2019 The PNG Reference Library Authors. * Copyright (c) 2018-2019 Cosmin Truta. * Copyright (c) 2000-2002, 2004, 2006-2018 Glenn Randers-Pehrson. * Copyright (c) 1996-1997 Andreas Dilger. * Copyright (c) 1995-1996 Guy Eric Schalnat, Group 42, Inc. * * The software is supplied "as is", without warranty of any kind, * express or implied, including, without limitation, the warranties * of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, title, and * non-infringement. In no event shall the Copyright owners, or * anyone distributing the software, be liable for any damages or * other liability, whether in contract, tort or otherwise, arising * from, out of, or in connection with the software, or the use or * other dealings in the software, even if advised of the possibility * of such damage. * * Permission is hereby granted to use, copy, modify, and distribute * this software, or portions hereof, for any purpose, without fee, * subject to the following restrictions: * * 1. The origin of this software must not be misrepresented; you * must not claim that you wrote the original software. If you * use this software in a product, an acknowledgment in the product * documentation would be appreciated, but is not required. * * 2. Altered source versions must be plainly marked as such, and must * not be misrepresented as being the original software. * * 3. This Copyright notice may not be removed or altered from any * source or altered source distribution. */ #if defined(SPNG_X86) #ifndef SPNG_SSE #define SPNG_SSE 1 #endif #if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) #if SPNG_SSE == 3 #pragma GCC target("ssse3") #elif SPNG_SSE == 4 #pragma GCC target("sse4.1") #else #pragma GCC target("sse2") #endif #endif /* SSE2 optimised filter functions * Derived from filter_neon_intrinsics.c * * Copyright (c) 2018 Cosmin Truta * Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Glenn Randers-Pehrson * Written by Mike Klein and Matt Sarett * Derived from arm/filter_neon_intrinsics.c * * This code is derived from libpng source code. * For conditions of distribution and use, see the disclaimer * and license above. */ #include <immintrin.h> #include <inttypes.h> #include <string.h> /* Functions in this file look at most 3 pixels (a,b,c) to predict the 4th (d). * They're positioned like this: * prev: c b * row: a d * The Sub filter predicts d=a, Avg d=(a+b)/2, and Paeth predicts d to be * whichever of a, b, or c is closest to p=a+b-c. */ static __m128i load4(const void* p) { int tmp; memcpy(&tmp, p, sizeof(tmp)); return _mm_cvtsi32_si128(tmp); } static void store4(void* p, __m128i v) { int tmp = _mm_cvtsi128_si32(v); memcpy(p, &tmp, sizeof(int)); } static __m128i load3(const void* p) { uint32_t tmp = 0; memcpy(&tmp, p, 3); return _mm_cvtsi32_si128(tmp); } static void store3(void* p, __m128i v) { int tmp = _mm_cvtsi128_si32(v); memcpy(p, &tmp, 3); } static void defilter_sub3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row) { /* The Sub filter predicts each pixel as the previous pixel, a. * There is no pixel to the left of the first pixel. It's encoded directly. * That works with our main loop if we just say that left pixel was zero. */ size_t rb = rowbytes; __m128i a, d = _mm_setzero_si128(); while(rb >= 4) { a = d; d = load4(row); d = _mm_add_epi8(d, a); store3(row, d); row += 3; rb -= 3; } if(rb > 0) { a = d; d = load3(row); d = _mm_add_epi8(d, a); store3(row, d); } } static void defilter_sub4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row) { /* The Sub filter predicts each pixel as the previous pixel, a. * There is no pixel to the left of the first pixel. It's encoded directly. * That works with our main loop if we just say that left pixel was zero. */ size_t rb = rowbytes+4; __m128i a, d = _mm_setzero_si128(); while(rb > 4) { a = d; d = load4(row); d = _mm_add_epi8(d, a); store4(row, d); row += 4; rb -= 4; } } static void defilter_avg3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev) { /* The Avg filter predicts each pixel as the (truncated) average of a and b. * There's no pixel to the left of the first pixel. Luckily, it's * predicted to be half of the pixel above it. So again, this works * perfectly with our loop if we make sure a starts at zero. */ size_t rb = rowbytes; const __m128i zero = _mm_setzero_si128(); __m128i b; __m128i a, d = zero; while(rb >= 4) { __m128i avg; b = load4(prev); a = d; d = load4(row ); /* PNG requires a truncating average, so we can't just use _mm_avg_epu8 */ avg = _mm_avg_epu8(a,b); /* ...but we can fix it up by subtracting off 1 if it rounded up. */ avg = _mm_sub_epi8(avg, _mm_and_si128(_mm_xor_si128(a, b), _mm_set1_epi8(1))); d = _mm_add_epi8(d, avg); store3(row, d); prev += 3; row += 3; rb -= 3; } if(rb > 0) { __m128i avg; b = load3(prev); a = d; d = load3(row ); /* PNG requires a truncating average, so we can't just use _mm_avg_epu8 */ avg = _mm_avg_epu8(a, b); /* ...but we can fix it up by subtracting off 1 if it rounded up. */ avg = _mm_sub_epi8(avg, _mm_and_si128(_mm_xor_si128(a, b), _mm_set1_epi8(1))); d = _mm_add_epi8(d, avg); store3(row, d); } } static void defilter_avg4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev) { /* The Avg filter predicts each pixel as the (truncated) average of a and b. * There's no pixel to the left of the first pixel. Luckily, it's * predicted to be half of the pixel above it. So again, this works * perfectly with our loop if we make sure a starts at zero. */ size_t rb = rowbytes+4; const __m128i zero = _mm_setzero_si128(); __m128i b; __m128i a, d = zero; while(rb > 4) { __m128i avg; b = load4(prev); a = d; d = load4(row ); /* PNG requires a truncating average, so we can't just use _mm_avg_epu8 */ avg = _mm_avg_epu8(a,b); /* ...but we can fix it up by subtracting off 1 if it rounded up. */ avg = _mm_sub_epi8(avg, _mm_and_si128(_mm_xor_si128(a, b), _mm_set1_epi8(1))); d = _mm_add_epi8(d, avg); store4(row, d); prev += 4; row += 4; rb -= 4; } } /* Returns |x| for 16-bit lanes. */ #if (SPNG_SSE >= 3) && !defined(_MSC_VER) __attribute__((target("ssse3"))) #endif static __m128i abs_i16(__m128i x) { #if SPNG_SSE >= 3 return _mm_abs_epi16(x); #else /* Read this all as, return x<0 ? -x : x. * To negate two's complement, you flip all the bits then add 1. */ __m128i is_negative = _mm_cmplt_epi16(x, _mm_setzero_si128()); /* Flip negative lanes. */ x = _mm_xor_si128(x, is_negative); /* +1 to negative lanes, else +0. */ x = _mm_sub_epi16(x, is_negative); return x; #endif } /* Bytewise c ? t : e. */ static __m128i if_then_else(__m128i c, __m128i t, __m128i e) { #if SPNG_SSE >= 4 return _mm_blendv_epi8(e, t, c); #else return _mm_or_si128(_mm_and_si128(c, t), _mm_andnot_si128(c, e)); #endif } static void defilter_paeth3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev) { /* Paeth tries to predict pixel d using the pixel to the left of it, a, * and two pixels from the previous row, b and c: * prev: c b * row: a d * The Paeth function predicts d to be whichever of a, b, or c is nearest to * p=a+b-c. * * The first pixel has no left context, and so uses an Up filter, p = b. * This works naturally with our main loop's p = a+b-c if we force a and c * to zero. * Here we zero b and d, which become c and a respectively at the start of * the loop. */ size_t rb = rowbytes; const __m128i zero = _mm_setzero_si128(); __m128i c, b = zero, a, d = zero; while(rb >= 4) { /* It's easiest to do this math (particularly, deal with pc) with 16-bit * intermediates. */ __m128i pa,pb,pc,smallest,nearest; c = b; b = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(load4(prev), zero); a = d; d = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(load4(row ), zero); /* (p-a) == (a+b-c - a) == (b-c) */ pa = _mm_sub_epi16(b, c); /* (p-b) == (a+b-c - b) == (a-c) */ pb = _mm_sub_epi16(a, c); /* (p-c) == (a+b-c - c) == (a+b-c-c) == (b-c)+(a-c) */ pc = _mm_add_epi16(pa, pb); pa = abs_i16(pa); /* |p-a| */ pb = abs_i16(pb); /* |p-b| */ pc = abs_i16(pc); /* |p-c| */ smallest = _mm_min_epi16(pc, _mm_min_epi16(pa, pb)); /* Paeth breaks ties favoring a over b over c. */ nearest = if_then_else(_mm_cmpeq_epi16(smallest, pa), a, if_then_else(_mm_cmpeq_epi16(smallest, pb), b, c)); /* Note `_epi8`: we need addition to wrap modulo 255. */ d = _mm_add_epi8(d, nearest); store3(row, _mm_packus_epi16(d, d)); prev += 3; row += 3; rb -= 3; } if(rb > 0) { /* It's easiest to do this math (particularly, deal with pc) with 16-bit * intermediates. */ __m128i pa, pb, pc, smallest, nearest; c = b; b = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(load3(prev), zero); a = d; d = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(load3(row ), zero); /* (p-a) == (a+b-c - a) == (b-c) */ pa = _mm_sub_epi16(b, c); /* (p-b) == (a+b-c - b) == (a-c) */ pb = _mm_sub_epi16(a, c); /* (p-c) == (a+b-c - c) == (a+b-c-c) == (b-c)+(a-c) */ pc = _mm_add_epi16(pa, pb); pa = abs_i16(pa); /* |p-a| */ pb = abs_i16(pb); /* |p-b| */ pc = abs_i16(pc); /* |p-c| */ smallest = _mm_min_epi16(pc, _mm_min_epi16(pa, pb)); /* Paeth breaks ties favoring a over b over c. */ nearest = if_then_else(_mm_cmpeq_epi16(smallest, pa), a, if_then_else(_mm_cmpeq_epi16(smallest, pb), b, c)); /* Note `_epi8`: we need addition to wrap modulo 255. */ d = _mm_add_epi8(d, nearest); store3(row, _mm_packus_epi16(d, d)); } } static void defilter_paeth4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev) { /* Paeth tries to predict pixel d using the pixel to the left of it, a, * and two pixels from the previous row, b and c: * prev: c b * row: a d * The Paeth function predicts d to be whichever of a, b, or c is nearest to * p=a+b-c. * * The first pixel has no left context, and so uses an Up filter, p = b. * This works naturally with our main loop's p = a+b-c if we force a and c * to zero. * Here we zero b and d, which become c and a respectively at the start of * the loop. */ size_t rb = rowbytes+4; const __m128i zero = _mm_setzero_si128(); __m128i pa, pb, pc, smallest, nearest; __m128i c, b = zero, a, d = zero; while(rb > 4) { /* It's easiest to do this math (particularly, deal with pc) with 16-bit * intermediates. */ c = b; b = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(load4(prev), zero); a = d; d = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(load4(row ), zero); /* (p-a) == (a+b-c - a) == (b-c) */ pa = _mm_sub_epi16(b, c); /* (p-b) == (a+b-c - b) == (a-c) */ pb = _mm_sub_epi16(a, c); /* (p-c) == (a+b-c - c) == (a+b-c-c) == (b-c)+(a-c) */ pc = _mm_add_epi16(pa, pb); pa = abs_i16(pa); /* |p-a| */ pb = abs_i16(pb); /* |p-b| */ pc = abs_i16(pc); /* |p-c| */ smallest = _mm_min_epi16(pc, _mm_min_epi16(pa, pb)); /* Paeth breaks ties favoring a over b over c. */ nearest = if_then_else(_mm_cmpeq_epi16(smallest, pa), a, if_then_else(_mm_cmpeq_epi16(smallest, pb), b, c)); /* Note `_epi8`: we need addition to wrap modulo 255. */ d = _mm_add_epi8(d, nearest); store4(row, _mm_packus_epi16(d, d)); prev += 4; row += 4; rb -= 4; } } #endif /* SPNG_X86 */ #if defined(SPNG_ARM) /* NEON optimised filter functions * Derived from filter_neon_intrinsics.c * * Copyright (c) 2018 Cosmin Truta * Copyright (c) 2014,2016 Glenn Randers-Pehrson * Written by James Yu <james.yu at linaro.org>, October 2013. * Based on filter_neon.S, written by Mans Rullgard, 2011. * * This code is derived from libpng source code. * For conditions of distribution and use, see the disclaimer * and license in this file. */ #define png_aligncast(type, value) ((void*)(value)) #define png_aligncastconst(type, value) ((const void*)(value)) /* libpng row pointers are not necessarily aligned to any particular boundary, * however this code will only work with appropriate alignment. mips/mips_init.c * checks for this (and will not compile unless it is done). This code uses * variants of png_aligncast to avoid compiler warnings. */ #define png_ptr(type,pointer) png_aligncast(type *,pointer) #define png_ptrc(type,pointer) png_aligncastconst(const type *,pointer) /* The following relies on a variable 'temp_pointer' being declared with type * 'type'. This is written this way just to hide the GCC strict aliasing * warning; note that the code is safe because there never is an alias between * the input and output pointers. */ #define png_ldr(type,pointer)\ (temp_pointer = png_ptr(type,pointer), *temp_pointer) #if defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(__clang__) && defined(_M_ARM64) #include <arm64_neon.h> #else #include <arm_neon.h> #endif static void defilter_sub3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row) { unsigned char *rp = row; unsigned char *rp_stop = row + rowbytes; uint8x16_t vtmp = vld1q_u8(rp); uint8x8x2_t *vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t, &vtmp); uint8x8x2_t vrp = *vrpt; uint8x8x4_t vdest; vdest.val[3] = vdup_n_u8(0); for (; rp < rp_stop;) { uint8x8_t vtmp1, vtmp2; uint32x2_t *temp_pointer; vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[0], vrp.val[1], 3); vdest.val[0] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vrp.val[0]); vtmp2 = vext_u8(vrp.val[0], vrp.val[1], 6); vdest.val[1] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vtmp1); vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[1], vrp.val[1], 1); vdest.val[2] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vtmp2); vdest.val[3] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vtmp1); vtmp = vld1q_u8(rp + 12); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t, &vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[0]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[1]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[2]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[3]), 0); rp += 3; } } static void defilter_sub4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row) { unsigned char *rp = row; unsigned char *rp_stop = row + rowbytes; uint8x8x4_t vdest; vdest.val[3] = vdup_n_u8(0); for (; rp < rp_stop; rp += 16) { uint32x2x4_t vtmp = vld4_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp)); uint8x8x4_t *vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x4_t,&vtmp); uint8x8x4_t vrp = *vrpt; uint32x2x4_t *temp_pointer; uint32x2x4_t vdest_val; vdest.val[0] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vrp.val[0]); vdest.val[1] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vrp.val[1]); vdest.val[2] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vrp.val[2]); vdest.val[3] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vrp.val[3]); vdest_val = png_ldr(uint32x2x4_t, &vdest); vst4_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), vdest_val, 0); } } static void defilter_avg3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev_row) { unsigned char *rp = row; const unsigned char *pp = prev_row; unsigned char *rp_stop = row + rowbytes; uint8x16_t vtmp; uint8x8x2_t *vrpt; uint8x8x2_t vrp; uint8x8x4_t vdest; vdest.val[3] = vdup_n_u8(0); vtmp = vld1q_u8(rp); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t,&vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; for (; rp < rp_stop; pp += 12) { uint8x8_t vtmp1, vtmp2, vtmp3; uint8x8x2_t *vppt; uint8x8x2_t vpp; uint32x2_t *temp_pointer; vtmp = vld1q_u8(pp); vppt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t,&vtmp); vpp = *vppt; vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[0], vrp.val[1], 3); vdest.val[0] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vpp.val[0]); vdest.val[0] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vrp.val[0]); vtmp2 = vext_u8(vpp.val[0], vpp.val[1], 3); vtmp3 = vext_u8(vrp.val[0], vrp.val[1], 6); vdest.val[1] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vtmp2); vdest.val[1] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vtmp1); vtmp2 = vext_u8(vpp.val[0], vpp.val[1], 6); vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[1], vrp.val[1], 1); vtmp = vld1q_u8(rp + 12); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t,&vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; vdest.val[2] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vtmp2); vdest.val[2] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vtmp3); vtmp2 = vext_u8(vpp.val[1], vpp.val[1], 1); vdest.val[3] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vtmp2); vdest.val[3] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vtmp1); vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[0]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[1]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[2]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[3]), 0); rp += 3; } } static void defilter_avg4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev_row) { unsigned char *rp = row; unsigned char *rp_stop = row + rowbytes; const unsigned char *pp = prev_row; uint8x8x4_t vdest; vdest.val[3] = vdup_n_u8(0); for (; rp < rp_stop; rp += 16, pp += 16) { uint32x2x4_t vtmp; uint8x8x4_t *vrpt, *vppt; uint8x8x4_t vrp, vpp; uint32x2x4_t *temp_pointer; uint32x2x4_t vdest_val; vtmp = vld4_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp)); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x4_t,&vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; vtmp = vld4_u32(png_ptrc(uint32_t,pp)); vppt = png_ptr(uint8x8x4_t,&vtmp); vpp = *vppt; vdest.val[0] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vpp.val[0]); vdest.val[0] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vrp.val[0]); vdest.val[1] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vpp.val[1]); vdest.val[1] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vrp.val[1]); vdest.val[2] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vpp.val[2]); vdest.val[2] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vrp.val[2]); vdest.val[3] = vhadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vpp.val[3]); vdest.val[3] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vrp.val[3]); vdest_val = png_ldr(uint32x2x4_t, &vdest); vst4_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), vdest_val, 0); } } static uint8x8_t paeth_arm(uint8x8_t a, uint8x8_t b, uint8x8_t c) { uint8x8_t d, e; uint16x8_t p1, pa, pb, pc; p1 = vaddl_u8(a, b); /* a + b */ pc = vaddl_u8(c, c); /* c * 2 */ pa = vabdl_u8(b, c); /* pa */ pb = vabdl_u8(a, c); /* pb */ pc = vabdq_u16(p1, pc); /* pc */ p1 = vcleq_u16(pa, pb); /* pa <= pb */ pa = vcleq_u16(pa, pc); /* pa <= pc */ pb = vcleq_u16(pb, pc); /* pb <= pc */ p1 = vandq_u16(p1, pa); /* pa <= pb && pa <= pc */ d = vmovn_u16(pb); e = vmovn_u16(p1); d = vbsl_u8(d, b, c); e = vbsl_u8(e, a, d); return e; } static void defilter_paeth3(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev_row) { unsigned char *rp = row; const unsigned char *pp = prev_row; unsigned char *rp_stop = row + rowbytes; uint8x16_t vtmp; uint8x8x2_t *vrpt; uint8x8x2_t vrp; uint8x8_t vlast = vdup_n_u8(0); uint8x8x4_t vdest; vdest.val[3] = vdup_n_u8(0); vtmp = vld1q_u8(rp); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t,&vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; for (; rp < rp_stop; pp += 12) { uint8x8x2_t *vppt; uint8x8x2_t vpp; uint8x8_t vtmp1, vtmp2, vtmp3; uint32x2_t *temp_pointer; vtmp = vld1q_u8(pp); vppt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t,&vtmp); vpp = *vppt; vdest.val[0] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[3], vpp.val[0], vlast); vdest.val[0] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vrp.val[0]); vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[0], vrp.val[1], 3); vtmp2 = vext_u8(vpp.val[0], vpp.val[1], 3); vdest.val[1] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[0], vtmp2, vpp.val[0]); vdest.val[1] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vtmp1); vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[0], vrp.val[1], 6); vtmp3 = vext_u8(vpp.val[0], vpp.val[1], 6); vdest.val[2] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[1], vtmp3, vtmp2); vdest.val[2] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vtmp1); vtmp1 = vext_u8(vrp.val[1], vrp.val[1], 1); vtmp2 = vext_u8(vpp.val[1], vpp.val[1], 1); vtmp = vld1q_u8(rp + 12); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x2_t,&vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; vdest.val[3] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[2], vtmp2, vtmp3); vdest.val[3] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vtmp1); vlast = vtmp2; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[0]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[1]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[2]), 0); rp += 3; vst1_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), png_ldr(uint32x2_t,&vdest.val[3]), 0); rp += 3; } } static void defilter_paeth4(size_t rowbytes, unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *prev_row) { unsigned char *rp = row; unsigned char *rp_stop = row + rowbytes; const unsigned char *pp = prev_row; uint8x8_t vlast = vdup_n_u8(0); uint8x8x4_t vdest; vdest.val[3] = vdup_n_u8(0); for (; rp < rp_stop; rp += 16, pp += 16) { uint32x2x4_t vtmp; uint8x8x4_t *vrpt, *vppt; uint8x8x4_t vrp, vpp; uint32x2x4_t *temp_pointer; uint32x2x4_t vdest_val; vtmp = vld4_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp)); vrpt = png_ptr(uint8x8x4_t,&vtmp); vrp = *vrpt; vtmp = vld4_u32(png_ptrc(uint32_t,pp)); vppt = png_ptr(uint8x8x4_t,&vtmp); vpp = *vppt; vdest.val[0] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[3], vpp.val[0], vlast); vdest.val[0] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[0], vrp.val[0]); vdest.val[1] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[0], vpp.val[1], vpp.val[0]); vdest.val[1] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[1], vrp.val[1]); vdest.val[2] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[1], vpp.val[2], vpp.val[1]); vdest.val[2] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[2], vrp.val[2]); vdest.val[3] = paeth_arm(vdest.val[2], vpp.val[3], vpp.val[2]); vdest.val[3] = vadd_u8(vdest.val[3], vrp.val[3]); vlast = vpp.val[3]; vdest_val = png_ldr(uint32x2x4_t, &vdest); vst4_lane_u32(png_ptr(uint32_t,rp), vdest_val, 0); } } /* NEON optimised palette expansion functions * Derived from palette_neon_intrinsics.c * * Copyright (c) 2018-2019 Cosmin Truta * Copyright (c) 2017-2018 Arm Holdings. All rights reserved. * Written by Richard Townsend <Richard.Townsend@arm.com>, February 2017. * * This code is derived from libpng source code. * For conditions of distribution and use, see the disclaimer * and license in this file. * * Related: https://developer.arm.com/documentation/101964/latest/Color-palette-expansion * * The functions were refactored to iterate forward. * */ /* Expands a palettized row into RGBA8. */ static uint32_t expand_palette_rgba8_neon(unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *scanline, const unsigned char *plte, uint32_t width) { const uint32_t scanline_stride = 4; const uint32_t row_stride = scanline_stride * 4; const uint32_t count = width / scanline_stride; const uint32_t *palette = (const uint32_t*)plte; if(!count) return 0; uint32_t i; uint32x4_t cur; for(i=0; i < count; i++, scanline += scanline_stride) { cur = vld1q_dup_u32 (palette + scanline[0]); cur = vld1q_lane_u32(palette + scanline[1], cur, 1); cur = vld1q_lane_u32(palette + scanline[2], cur, 2); cur = vld1q_lane_u32(palette + scanline[3], cur, 3); vst1q_u32((uint32_t*)(row + i * row_stride), cur); } return count * scanline_stride; } /* Expands a palettized row into RGB8. */ static uint32_t expand_palette_rgb8_neon(unsigned char *row, const unsigned char *scanline, const unsigned char *plte, uint32_t width) { const uint32_t scanline_stride = 8; const uint32_t row_stride = scanline_stride * 3; const uint32_t count = width / scanline_stride; if(!count) return 0; uint32_t i; uint8x8x3_t cur; for(i=0; i < count; i++, scanline += scanline_stride) { cur = vld3_dup_u8 (plte + 3 * scanline[0]); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[1], cur, 1); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[2], cur, 2); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[3], cur, 3); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[4], cur, 4); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[5], cur, 5); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[6], cur, 6); cur = vld3_lane_u8(plte + 3 * scanline[7], cur, 7); vst3_u8(row + i * row_stride, cur); } return count * scanline_stride; } #endif /* SPNG_ARM */
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-2-Clause */ #ifndef SPNG_H #define SPNG_H #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif #if (defined(_WIN32) || defined(__CYGWIN__)) && !defined(SPNG_STATIC) #if defined(SPNG__BUILD) #define SPNG_API __declspec(dllexport) #else #define SPNG_API __declspec(dllimport) #endif #else #define SPNG_API #endif #if defined(_MSC_VER) #define SPNG_CDECL __cdecl #else #define SPNG_CDECL #endif #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stdio.h> #define SPNG_VERSION_MAJOR 0 #define SPNG_VERSION_MINOR 7 #define SPNG_VERSION_PATCH 4 enum spng_errno { SPNG_IO_ERROR = -2, SPNG_IO_EOF = -1, SPNG_OK = 0, SPNG_EINVAL, SPNG_EMEM, SPNG_EOVERFLOW, SPNG_ESIGNATURE, SPNG_EWIDTH, SPNG_EHEIGHT, SPNG_EUSER_WIDTH, SPNG_EUSER_HEIGHT, SPNG_EBIT_DEPTH, SPNG_ECOLOR_TYPE, SPNG_ECOMPRESSION_METHOD, SPNG_EFILTER_METHOD, SPNG_EINTERLACE_METHOD, SPNG_EIHDR_SIZE, SPNG_ENOIHDR, SPNG_ECHUNK_POS, SPNG_ECHUNK_SIZE, SPNG_ECHUNK_CRC, SPNG_ECHUNK_TYPE, SPNG_ECHUNK_UNKNOWN_CRITICAL, SPNG_EDUP_PLTE, SPNG_EDUP_CHRM, SPNG_EDUP_GAMA, SPNG_EDUP_ICCP, SPNG_EDUP_SBIT, SPNG_EDUP_SRGB, SPNG_EDUP_BKGD, SPNG_EDUP_HIST, SPNG_EDUP_TRNS, SPNG_EDUP_PHYS, SPNG_EDUP_TIME, SPNG_EDUP_OFFS, SPNG_EDUP_EXIF, SPNG_ECHRM, SPNG_EPLTE_IDX, SPNG_ETRNS_COLOR_TYPE, SPNG_ETRNS_NO_PLTE, SPNG_EGAMA, SPNG_EICCP_NAME, SPNG_EICCP_COMPRESSION_METHOD, SPNG_ESBIT, SPNG_ESRGB, SPNG_ETEXT, SPNG_ETEXT_KEYWORD, SPNG_EZTXT, SPNG_EZTXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD, SPNG_EITXT, SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_FLAG, SPNG_EITXT_COMPRESSION_METHOD, SPNG_EITXT_LANG_TAG, SPNG_EITXT_TRANSLATED_KEY, SPNG_EBKGD_NO_PLTE, SPNG_EBKGD_PLTE_IDX, SPNG_EHIST_NO_PLTE, SPNG_EPHYS, SPNG_ESPLT_NAME, SPNG_ESPLT_DUP_NAME, SPNG_ESPLT_DEPTH, SPNG_ETIME, SPNG_EOFFS, SPNG_EEXIF, SPNG_EIDAT_TOO_SHORT, SPNG_EIDAT_STREAM, SPNG_EZLIB, SPNG_EFILTER, SPNG_EBUFSIZ, SPNG_EIO, SPNG_EOF, SPNG_EBUF_SET, SPNG_EBADSTATE, SPNG_EFMT, SPNG_EFLAGS, SPNG_ECHUNKAVAIL, SPNG_ENCODE_ONLY, SPNG_EOI, SPNG_ENOPLTE, SPNG_ECHUNK_LIMITS, SPNG_EZLIB_INIT, SPNG_ECHUNK_STDLEN, SPNG_EINTERNAL, SPNG_ECTXTYPE, SPNG_ENOSRC, SPNG_ENODST, SPNG_EOPSTATE, SPNG_ENOTFINAL, }; enum spng_text_type { SPNG_TEXT = 1, SPNG_ZTXT = 2, SPNG_ITXT = 3 }; enum spng_color_type { SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE = 0, SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR = 2, SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_INDEXED = 3, SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAYSCALE_ALPHA = 4, SPNG_COLOR_TYPE_TRUECOLOR_ALPHA = 6 }; enum spng_filter { SPNG_FILTER_NONE = 0, SPNG_FILTER_SUB = 1, SPNG_FILTER_UP = 2, SPNG_FILTER_AVERAGE = 3, SPNG_FILTER_PAETH = 4 }; enum spng_filter_choice { SPNG_DISABLE_FILTERING = 0, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_NONE = 8, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_SUB = 16, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_UP = 32, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_AVG = 64, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_PAETH = 128, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE_ALL = (8|16|32|64|128) }; enum spng_interlace_method { SPNG_INTERLACE_NONE = 0, SPNG_INTERLACE_ADAM7 = 1 }; /* Channels are always in byte-order */ enum spng_format { SPNG_FMT_RGBA8 = 1, SPNG_FMT_RGBA16 = 2, SPNG_FMT_RGB8 = 4, /* Partially implemented, see documentation */ SPNG_FMT_GA8 = 16, SPNG_FMT_GA16 = 32, SPNG_FMT_G8 = 64, /* No conversion or scaling */ SPNG_FMT_PNG = 256, SPNG_FMT_RAW = 512 /* big-endian (everything else is host-endian) */ }; enum spng_ctx_flags { SPNG_CTX_IGNORE_ADLER32 = 1, /* Ignore checksum in DEFLATE streams */ SPNG_CTX_ENCODER = 2 /* Create an encoder context */ }; enum spng_decode_flags { SPNG_DECODE_USE_TRNS = 1, /* Deprecated */ SPNG_DECODE_USE_GAMA = 2, /* Deprecated */ SPNG_DECODE_USE_SBIT = 8, /* Undocumented */ SPNG_DECODE_TRNS = 1, /* Apply transparency */ SPNG_DECODE_GAMMA = 2, /* Apply gamma correction */ SPNG_DECODE_PROGRESSIVE = 256 /* Initialize for progressive reads */ }; enum spng_crc_action { /* Default for critical chunks */ SPNG_CRC_ERROR = 0, /* Discard chunk, invalid for critical chunks. Since v0.6.2: default for ancillary chunks */ SPNG_CRC_DISCARD = 1, /* Ignore and don't calculate checksum. Since v0.6.2: also ignores checksums in DEFLATE streams */ SPNG_CRC_USE = 2 }; enum spng_encode_flags { SPNG_ENCODE_PROGRESSIVE = 1, /* Initialize for progressive writes */ SPNG_ENCODE_FINALIZE = 2, /* Finalize PNG after encoding image */ }; struct spng_ihdr { uint32_t width; uint32_t height; uint8_t bit_depth; uint8_t color_type; uint8_t compression_method; uint8_t filter_method; uint8_t interlace_method; }; struct spng_plte_entry { uint8_t red; uint8_t green; uint8_t blue; uint8_t alpha; /* Reserved for internal use */ }; struct spng_plte { uint32_t n_entries; struct spng_plte_entry entries[256]; }; struct spng_trns { uint16_t gray; uint16_t red; uint16_t green; uint16_t blue; uint32_t n_type3_entries; uint8_t type3_alpha[256]; }; struct spng_chrm_int { uint32_t white_point_x; uint32_t white_point_y; uint32_t red_x; uint32_t red_y; uint32_t green_x; uint32_t green_y; uint32_t blue_x; uint32_t blue_y; }; struct spng_chrm { double white_point_x; double white_point_y; double red_x; double red_y; double green_x; double green_y; double blue_x; double blue_y; }; struct spng_iccp { char profile_name[80]; size_t profile_len; char *profile; }; struct spng_sbit { uint8_t grayscale_bits; uint8_t red_bits; uint8_t green_bits; uint8_t blue_bits; uint8_t alpha_bits; }; struct spng_text { char keyword[80]; int type; size_t length; char *text; uint8_t compression_flag; /* iTXt only */ uint8_t compression_method; /* iTXt, ztXt only */ char *language_tag; /* iTXt only */ char *translated_keyword; /* iTXt only */ }; struct spng_bkgd { uint16_t gray; /* Only for gray/gray alpha */ uint16_t red; uint16_t green; uint16_t blue; uint16_t plte_index; /* Only for indexed color */ }; struct spng_hist { uint16_t frequency[256]; }; struct spng_phys { uint32_t ppu_x, ppu_y; uint8_t unit_specifier; }; struct spng_splt_entry { uint16_t red; uint16_t green; uint16_t blue; uint16_t alpha; uint16_t frequency; }; struct spng_splt { char name[80]; uint8_t sample_depth; uint32_t n_entries; struct spng_splt_entry *entries; }; struct spng_time { uint16_t year; uint8_t month; uint8_t day; uint8_t hour; uint8_t minute; uint8_t second; }; struct spng_offs { int32_t x, y; uint8_t unit_specifier; }; struct spng_exif { size_t length; char *data; }; struct spng_chunk { size_t offset; uint32_t length; uint8_t type[4]; uint32_t crc; }; enum spng_location { SPNG_AFTER_IHDR = 1, SPNG_AFTER_PLTE = 2, SPNG_AFTER_IDAT = 8, }; struct spng_unknown_chunk { uint8_t type[4]; size_t length; void *data; enum spng_location location; }; enum spng_option { SPNG_KEEP_UNKNOWN_CHUNKS = 1, SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_LEVEL, SPNG_IMG_WINDOW_BITS, SPNG_IMG_MEM_LEVEL, SPNG_IMG_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY, SPNG_TEXT_COMPRESSION_LEVEL, SPNG_TEXT_WINDOW_BITS, SPNG_TEXT_MEM_LEVEL, SPNG_TEXT_COMPRESSION_STRATEGY, SPNG_FILTER_CHOICE, SPNG_CHUNK_COUNT_LIMIT, SPNG_ENCODE_TO_BUFFER, }; typedef void* SPNG_CDECL spng_malloc_fn(size_t size); typedef void* SPNG_CDECL spng_realloc_fn(void* ptr, size_t size); typedef void* SPNG_CDECL spng_calloc_fn(size_t count, size_t size); typedef void SPNG_CDECL spng_free_fn(void* ptr); struct spng_alloc { spng_malloc_fn *malloc_fn; spng_realloc_fn *realloc_fn; spng_calloc_fn *calloc_fn; spng_free_fn *free_fn; }; struct spng_row_info { uint32_t scanline_idx; uint32_t row_num; /* deinterlaced row index */ int pass; uint8_t filter; }; typedef struct spng_ctx spng_ctx; typedef int spng_read_fn(spng_ctx *ctx, void *user, void *dest, size_t length); typedef int spng_write_fn(spng_ctx *ctx, void *user, void *src, size_t length); typedef int spng_rw_fn(spng_ctx *ctx, void *user, void *dst_src, size_t length); SPNG_API spng_ctx *spng_ctx_new(int flags); SPNG_API spng_ctx *spng_ctx_new2(struct spng_alloc *alloc, int flags); SPNG_API void spng_ctx_free(spng_ctx *ctx); SPNG_API int spng_set_png_buffer(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *buf, size_t size); SPNG_API int spng_set_png_stream(spng_ctx *ctx, spng_rw_fn *rw_func, void *user); SPNG_API int spng_set_png_file(spng_ctx *ctx, FILE *file); SPNG_API void *spng_get_png_buffer(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t *len, int *error); SPNG_API int spng_set_image_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t width, uint32_t height); SPNG_API int spng_get_image_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t *width, uint32_t *height); SPNG_API int spng_set_chunk_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t chunk_size, size_t cache_size); SPNG_API int spng_get_chunk_limits(spng_ctx *ctx, size_t *chunk_size, size_t *cache_size); SPNG_API int spng_set_crc_action(spng_ctx *ctx, int critical, int ancillary); SPNG_API int spng_set_option(spng_ctx *ctx, enum spng_option option, int value); SPNG_API int spng_get_option(spng_ctx *ctx, enum spng_option option, int *value); SPNG_API int spng_decoded_image_size(spng_ctx *ctx, int fmt, size_t *len); /* Decode */ SPNG_API int spng_decode_image(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, size_t len, int fmt, int flags); /* Progressive decode */ SPNG_API int spng_decode_scanline(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, size_t len); SPNG_API int spng_decode_row(spng_ctx *ctx, void *out, size_t len); SPNG_API int spng_decode_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx); /* Encode/decode */ SPNG_API int spng_get_row_info(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_row_info *row_info); /* Encode */ SPNG_API int spng_encode_image(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *img, size_t len, int fmt, int flags); /* Progressive encode */ SPNG_API int spng_encode_scanline(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *scanline, size_t len); SPNG_API int spng_encode_row(spng_ctx *ctx, const void *row, size_t len); SPNG_API int spng_encode_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx); SPNG_API int spng_get_ihdr(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_ihdr *ihdr); SPNG_API int spng_get_plte(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_plte *plte); SPNG_API int spng_get_trns(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_trns *trns); SPNG_API int spng_get_chrm(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm *chrm); SPNG_API int spng_get_chrm_int(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm_int *chrm_int); SPNG_API int spng_get_gama(spng_ctx *ctx, double *gamma); SPNG_API int spng_get_gama_int(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t *gama_int); SPNG_API int spng_get_iccp(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_iccp *iccp); SPNG_API int spng_get_sbit(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_sbit *sbit); SPNG_API int spng_get_srgb(spng_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *rendering_intent); SPNG_API int spng_get_text(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_text *text, uint32_t *n_text); SPNG_API int spng_get_bkgd(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_bkgd *bkgd); SPNG_API int spng_get_hist(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_hist *hist); SPNG_API int spng_get_phys(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_phys *phys); SPNG_API int spng_get_splt(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_splt *splt, uint32_t *n_splt); SPNG_API int spng_get_time(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_time *time); SPNG_API int spng_get_unknown_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunks, uint32_t *n_chunks); /* Official extensions */ SPNG_API int spng_get_offs(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_offs *offs); SPNG_API int spng_get_exif(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_exif *exif); SPNG_API int spng_set_ihdr(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_ihdr *ihdr); SPNG_API int spng_set_plte(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_plte *plte); SPNG_API int spng_set_trns(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_trns *trns); SPNG_API int spng_set_chrm(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm *chrm); SPNG_API int spng_set_chrm_int(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_chrm_int *chrm_int); SPNG_API int spng_set_gama(spng_ctx *ctx, double gamma); SPNG_API int spng_set_gama_int(spng_ctx *ctx, uint32_t gamma); SPNG_API int spng_set_iccp(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_iccp *iccp); SPNG_API int spng_set_sbit(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_sbit *sbit); SPNG_API int spng_set_srgb(spng_ctx *ctx, uint8_t rendering_intent); SPNG_API int spng_set_text(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_text *text, uint32_t n_text); SPNG_API int spng_set_bkgd(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_bkgd *bkgd); SPNG_API int spng_set_hist(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_hist *hist); SPNG_API int spng_set_phys(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_phys *phys); SPNG_API int spng_set_splt(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_splt *splt, uint32_t n_splt); SPNG_API int spng_set_time(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_time *time); SPNG_API int spng_set_unknown_chunks(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_unknown_chunk *chunks, uint32_t n_chunks); /* Official extensions */ SPNG_API int spng_set_offs(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_offs *offs); SPNG_API int spng_set_exif(spng_ctx *ctx, struct spng_exif *exif); SPNG_API const char *spng_strerror(int err); SPNG_API const char *spng_version_string(void); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif /* SPNG_H */
• DO1 • adler32_z • adler32 • adler32_combine_ • adler32_combine • adler32_combine64
/* adler32.c -- compute the Adler-32 checksum of a data stream * Copyright (C) 1995-2011, 2016 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #include "zutil.h" #define BASE 65521U /* largest prime smaller than 65536 */ #define NMAX 5552 /* NMAX is the largest n such that 255n(n+1)/2 + (n+1)(BASE-1) <= 2^32-1 */ #define DO1(buf,i) {adler += (buf)[i]; sum2 += adler;} #define DO2(buf,i) DO1(buf,i); DO1(buf,i+1); #define DO4(buf,i) DO2(buf,i); DO2(buf,i+2); #define DO8(buf,i) DO4(buf,i); DO4(buf,i+4); #define DO16(buf) DO8(buf,0); DO8(buf,8); /* use NO_DIVIDE if your processor does not do division in hardware -- try it both ways to see which is faster */ #ifdef NO_DIVIDE /* note that this assumes BASE is 65521, where 65536 % 65521 == 15 (thank you to John Reiser for pointing this out) */ # define CHOP(a) \ do { \ unsigned long tmp = a >> 16; \ a &= 0xffffUL; \ a += (tmp << 4) - tmp; \ } while (0) # define MOD28(a) \ do { \ CHOP(a); \ if (a >= BASE) a -= BASE; \ } while (0) # define MOD(a) \ do { \ CHOP(a); \ MOD28(a); \ } while (0) # define MOD63(a) \ do { /* this assumes a is not negative */ \ z_off64_t tmp = a >> 32; \ a &= 0xffffffffL; \ a += (tmp << 8) - (tmp << 5) + tmp; \ tmp = a >> 16; \ a &= 0xffffL; \ a += (tmp << 4) - tmp; \ tmp = a >> 16; \ a &= 0xffffL; \ a += (tmp << 4) - tmp; \ if (a >= BASE) a -= BASE; \ } while (0) #else # define MOD(a) a %= BASE # define MOD28(a) a %= BASE # define MOD63(a) a %= BASE #endif /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT adler32_z(uLong adler, const Bytef *buf, z_size_t len) { unsigned long sum2; unsigned n; /* split Adler-32 into component sums */ sum2 = (adler >> 16) & 0xffff; adler &= 0xffff; /* in case user likes doing a byte at a time, keep it fast */ if (len == 1) { adler += buf[0]; if (adler >= BASE) adler -= BASE; sum2 += adler; if (sum2 >= BASE) sum2 -= BASE; return adler | (sum2 << 16); } /* initial Adler-32 value (deferred check for len == 1 speed) */ if (buf == Z_NULL) return 1L; /* in case short lengths are provided, keep it somewhat fast */ if (len < 16) { while (len--) { adler += *buf++; sum2 += adler; } if (adler >= BASE) adler -= BASE; MOD28(sum2); /* only added so many BASE's */ return adler | (sum2 << 16); } /* do length NMAX blocks -- requires just one modulo operation */ while (len >= NMAX) { len -= NMAX; n = NMAX / 16; /* NMAX is divisible by 16 */ do { DO16(buf); /* 16 sums unrolled */ buf += 16; } while (--n); MOD(adler); MOD(sum2); } /* do remaining bytes (less than NMAX, still just one modulo) */ if (len) { /* avoid modulos if none remaining */ while (len >= 16) { len -= 16; DO16(buf); buf += 16; } while (len--) { adler += *buf++; sum2 += adler; } MOD(adler); MOD(sum2); } /* return recombined sums */ return adler | (sum2 << 16); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT adler32(uLong adler, const Bytef *buf, uInt len) { return adler32_z(adler, buf, len); } /* ========================================================================= */ local uLong adler32_combine_(uLong adler1, uLong adler2, z_off64_t len2) { unsigned long sum1; unsigned long sum2; unsigned rem; /* for negative len, return invalid adler32 as a clue for debugging */ if (len2 < 0) return 0xffffffffUL; /* the derivation of this formula is left as an exercise for the reader */ MOD63(len2); /* assumes len2 >= 0 */ rem = (unsigned)len2; sum1 = adler1 & 0xffff; sum2 = rem * sum1; MOD(sum2); sum1 += (adler2 & 0xffff) + BASE - 1; sum2 += ((adler1 >> 16) & 0xffff) + ((adler2 >> 16) & 0xffff) + BASE - rem; if (sum1 >= BASE) sum1 -= BASE; if (sum1 >= BASE) sum1 -= BASE; if (sum2 >= ((unsigned long)BASE << 1)) sum2 -= ((unsigned long)BASE << 1); if (sum2 >= BASE) sum2 -= BASE; return sum1 | (sum2 << 16); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine(uLong adler1, uLong adler2, z_off_t len2) { return adler32_combine_(adler1, adler2, len2); } uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine64(uLong adler1, uLong adler2, z_off64_t len2) { return adler32_combine_(adler1, adler2, len2); }
• compress2 • compress • compressBound
/* compress.c -- compress a memory buffer * Copyright (C) 1995-2005, 2014, 2016 Jean-loup Gailly, Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #define ZLIB_INTERNAL #include "zlib.h" /* =========================================================================== Compresses the source buffer into the destination buffer. The level parameter has the same meaning as in deflateInit. sourceLen is the byte length of the source buffer. Upon entry, destLen is the total size of the destination buffer, which must be at least 0.1% larger than sourceLen plus 12 bytes. Upon exit, destLen is the actual size of the compressed buffer. compress2 returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough room in the output buffer, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the level parameter is invalid. */ int ZEXPORT compress2(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen, int level) { z_stream stream; int err; const uInt max = (uInt)-1; uLong left; left = *destLen; *destLen = 0; stream.zalloc = (alloc_func)0; stream.zfree = (free_func)0; stream.opaque = (voidpf)0; err = deflateInit(&stream, level); if (err != Z_OK) return err; stream.next_out = dest; stream.avail_out = 0; stream.next_in = (z_const Bytef *)source; stream.avail_in = 0; do { if (stream.avail_out == 0) { stream.avail_out = left > (uLong)max ? max : (uInt)left; left -= stream.avail_out; } if (stream.avail_in == 0) { stream.avail_in = sourceLen > (uLong)max ? max : (uInt)sourceLen; sourceLen -= stream.avail_in; } err = deflate(&stream, sourceLen ? Z_NO_FLUSH : Z_FINISH); } while (err == Z_OK); *destLen = stream.total_out; deflateEnd(&stream); return err == Z_STREAM_END ? Z_OK : err; } /* =========================================================================== */ int ZEXPORT compress(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen) { return compress2(dest, destLen, source, sourceLen, Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION); } /* =========================================================================== If the default memLevel or windowBits for deflateInit() is changed, then this function needs to be updated. */ uLong ZEXPORT compressBound(uLong sourceLen) { return sourceLen + (sourceLen >> 12) + (sourceLen >> 14) + (sourceLen >> 25) + 13; }
• byte_swap • multmodp • x2nmodp • once • test_and_set • make_crc_table • write_table • write_table32hi • write_table64 • main • braid • get_crc_table • crc32_z • crc_word • crc_word_big • crc32 • crc32_combine64 • crc32_combine • crc32_combine_gen64 • crc32_combine_gen • crc32_combine_op
/* crc32.c -- compute the CRC-32 of a data stream * Copyright (C) 1995-2022 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h * * This interleaved implementation of a CRC makes use of pipelined multiple * arithmetic-logic units, commonly found in modern CPU cores. It is due to * Kadatch and Jenkins (2010). See doc/crc-doc.1.0.pdf in this distribution. */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ /* Note on the use of DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE: there is no mutex or semaphore protection on the static variables used to control the first-use generation of the crc tables. Therefore, if you #define DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE, you should first call get_crc_table() to initialize the tables before allowing more than one thread to use crc32(). MAKECRCH can be #defined to write out crc32.h. A main() routine is also produced, so that this one source file can be compiled to an executable. */ #ifdef MAKECRCH # include <stdio.h> # ifndef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE # define DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE # endif /* !DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ #endif /* MAKECRCH */ #include "zutil.h" /* for Z_U4, Z_U8, z_crc_t, and FAR definitions */ /* A CRC of a message is computed on N braids of words in the message, where each word consists of W bytes (4 or 8). If N is 3, for example, then three running sparse CRCs are calculated respectively on each braid, at these indices in the array of words: 0, 3, 6, ..., 1, 4, 7, ..., and 2, 5, 8, ... This is done starting at a word boundary, and continues until as many blocks of N * W bytes as are available have been processed. The results are combined into a single CRC at the end. For this code, N must be in the range 1..6 and W must be 4 or 8. The upper limit on N can be increased if desired by adding more #if blocks, extending the patterns apparent in the code. In addition, crc32.h would need to be regenerated, if the maximum N value is increased. N and W are chosen empirically by benchmarking the execution time on a given processor. The choices for N and W below were based on testing on Intel Kaby Lake i7, AMD Ryzen 7, ARM Cortex-A57, Sparc64-VII, PowerPC POWER9, and MIPS64 Octeon II processors. The Intel, AMD, and ARM processors were all fastest with N=5, W=8. The Sparc, PowerPC, and MIPS64 were all fastest at N=5, W=4. They were all tested with either gcc or clang, all using the -O3 optimization level. Your mileage may vary. */ /* Define N */ #ifdef Z_TESTN # define N Z_TESTN #else # define N 5 #endif #if N < 1 || N > 6 # error N must be in 1..6 #endif /* z_crc_t must be at least 32 bits. z_word_t must be at least as long as z_crc_t. It is assumed here that z_word_t is either 32 bits or 64 bits, and that bytes are eight bits. */ /* Define W and the associated z_word_t type. If W is not defined, then a braided calculation is not used, and the associated tables and code are not compiled. */ #ifdef Z_TESTW # if Z_TESTW-1 != -1 # define W Z_TESTW # endif #else # ifdef MAKECRCH # define W 8 /* required for MAKECRCH */ # else # if defined(__x86_64__) || defined(__aarch64__) # define W 8 # else # define W 4 # endif # endif #endif #ifdef W # if W == 8 && defined(Z_U8) typedef Z_U8 z_word_t; # elif defined(Z_U4) # undef W # define W 4 typedef Z_U4 z_word_t; # else # undef W # endif #endif /* If available, use the ARM processor CRC32 instruction. */ #if defined(__aarch64__) && defined(__ARM_FEATURE_CRC32) && W == 8 # define ARMCRC32 #endif #if defined(W) && (!defined(ARMCRC32) || defined(DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE)) /* Swap the bytes in a z_word_t to convert between little and big endian. Any self-respecting compiler will optimize this to a single machine byte-swap instruction, if one is available. This assumes that word_t is either 32 bits or 64 bits. */ local z_word_t byte_swap(z_word_t word) { # if W == 8 return (word & 0xff00000000000000) >> 56 | (word & 0xff000000000000) >> 40 | (word & 0xff0000000000) >> 24 | (word & 0xff00000000) >> 8 | (word & 0xff000000) << 8 | (word & 0xff0000) << 24 | (word & 0xff00) << 40 | (word & 0xff) << 56; # else /* W == 4 */ return (word & 0xff000000) >> 24 | (word & 0xff0000) >> 8 | (word & 0xff00) << 8 | (word & 0xff) << 24; # endif } #endif #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE /* ========================================================================= * Table of powers of x for combining CRC-32s, filled in by make_crc_table() * below. */ local z_crc_t FAR x2n_table[32]; #else /* ========================================================================= * Tables for byte-wise and braided CRC-32 calculations, and a table of powers * of x for combining CRC-32s, all made by make_crc_table(). */ # include "crc32.h" #endif /* CRC polynomial. */ #define POLY 0xedb88320 /* p(x) reflected, with x^32 implied */ /* Return a(x) multiplied by b(x) modulo p(x), where p(x) is the CRC polynomial, reflected. For speed, this requires that a not be zero. */ local z_crc_t multmodp(z_crc_t a, z_crc_t b) { z_crc_t m, p; m = (z_crc_t)1 << 31; p = 0; for (;;) { if (a & m) { p ^= b; if ((a & (m - 1)) == 0) break; } m >>= 1; b = b & 1 ? (b >> 1) ^ POLY : b >> 1; } return p; } /* Return x^(n * 2^k) modulo p(x). Requires that x2n_table[] has been initialized. */ local z_crc_t x2nmodp(z_off64_t n, unsigned k) { z_crc_t p; p = (z_crc_t)1 << 31; /* x^0 == 1 */ while (n) { if (n & 1) p = multmodp(x2n_table[k & 31], p); n >>= 1; k++; } return p; } #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE /* ========================================================================= * Build the tables for byte-wise and braided CRC-32 calculations, and a table * of powers of x for combining CRC-32s. */ local z_crc_t FAR crc_table[256]; #ifdef W local z_word_t FAR crc_big_table[256]; local z_crc_t FAR crc_braid_table[W][256]; local z_word_t FAR crc_braid_big_table[W][256]; local void braid(z_crc_t [][256], z_word_t [][256], int, int); #endif #ifdef MAKECRCH local void write_table(FILE *, const z_crc_t FAR *, int); local void write_table32hi(FILE *, const z_word_t FAR *, int); local void write_table64(FILE *, const z_word_t FAR *, int); #endif /* MAKECRCH */ /* Define a once() function depending on the availability of atomics. If this is compiled with DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE defined, and if CRCs will be computed in multiple threads, and if atomics are not available, then get_crc_table() must be called to initialize the tables and must return before any threads are allowed to compute or combine CRCs. */ /* Definition of once functionality. */ typedef struct once_s once_t; /* Check for the availability of atomics. */ #if defined(__STDC__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L && \ !defined(__STDC_NO_ATOMICS__) #include <stdatomic.h> /* Structure for once(), which must be initialized with ONCE_INIT. */ struct once_s { atomic_flag begun; atomic_int done; }; #define ONCE_INIT {ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT, 0} /* Run the provided init() function exactly once, even if multiple threads invoke once() at the same time. The state must be a once_t initialized with ONCE_INIT. */ local void once(once_t *state, void (*init)(void)) { if (!atomic_load(&state->done)) { if (atomic_flag_test_and_set(&state->begun)) while (!atomic_load(&state->done)) ; else { init(); atomic_store(&state->done, 1); } } } #else /* no atomics */ /* Structure for once(), which must be initialized with ONCE_INIT. */ struct once_s { volatile int begun; volatile int done; }; #define ONCE_INIT {0, 0} /* Test and set. Alas, not atomic, but tries to minimize the period of vulnerability. */ local int test_and_set(int volatile *flag) { int was; was = *flag; *flag = 1; return was; } /* Run the provided init() function once. This is not thread-safe. */ local void once(once_t *state, void (*init)(void)) { if (!state->done) { if (test_and_set(&state->begun)) while (!state->done) ; else { init(); state->done = 1; } } } #endif /* State for once(). */ local once_t made = ONCE_INIT; /* Generate tables for a byte-wise 32-bit CRC calculation on the polynomial: x^32+x^26+x^23+x^22+x^16+x^12+x^11+x^10+x^8+x^7+x^5+x^4+x^2+x+1. Polynomials over GF(2) are represented in binary, one bit per coefficient, with the lowest powers in the most significant bit. Then adding polynomials is just exclusive-or, and multiplying a polynomial by x is a right shift by one. If we call the above polynomial p, and represent a byte as the polynomial q, also with the lowest power in the most significant bit (so the byte 0xb1 is the polynomial x^7+x^3+x^2+1), then the CRC is (q*x^32) mod p, where a mod b means the remainder after dividing a by b. This calculation is done using the shift-register method of multiplying and taking the remainder. The register is initialized to zero, and for each incoming bit, x^32 is added mod p to the register if the bit is a one (where x^32 mod p is p+x^32 = x^26+...+1), and the register is multiplied mod p by x (which is shifting right by one and adding x^32 mod p if the bit shifted out is a one). We start with the highest power (least significant bit) of q and repeat for all eight bits of q. The table is simply the CRC of all possible eight bit values. This is all the information needed to generate CRCs on data a byte at a time for all combinations of CRC register values and incoming bytes. */ local void make_crc_table(void) { unsigned i, j, n; z_crc_t p; /* initialize the CRC of bytes tables */ for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { p = i; for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) p = p & 1 ? (p >> 1) ^ POLY : p >> 1; crc_table[i] = p; #ifdef W crc_big_table[i] = byte_swap(p); #endif } /* initialize the x^2^n mod p(x) table */ p = (z_crc_t)1 << 30; /* x^1 */ x2n_table[0] = p; for (n = 1; n < 32; n++) x2n_table[n] = p = multmodp(p, p); #ifdef W /* initialize the braiding tables -- needs x2n_table[] */ braid(crc_braid_table, crc_braid_big_table, N, W); #endif #ifdef MAKECRCH { /* The crc32.h header file contains tables for both 32-bit and 64-bit z_word_t's, and so requires a 64-bit type be available. In that case, z_word_t must be defined to be 64-bits. This code then also generates and writes out the tables for the case that z_word_t is 32 bits. */ #if !defined(W) || W != 8 # error Need a 64-bit integer type in order to generate crc32.h. #endif FILE *out; int k, n; z_crc_t ltl[8][256]; z_word_t big[8][256]; out = fopen("crc32.h", "w"); if (out == NULL) return; /* write out little-endian CRC table to crc32.h */ fprintf(out, "/* crc32.h -- tables for rapid CRC calculation\n" " * Generated automatically by crc32.c\n */\n" "\n" "local const z_crc_t FAR crc_table[] = {\n" " "); write_table(out, crc_table, 256); fprintf(out, "};\n"); /* write out big-endian CRC table for 64-bit z_word_t to crc32.h */ fprintf(out, "\n" "#ifdef W\n" "\n" "#if W == 8\n" "\n" "local const z_word_t FAR crc_big_table[] = {\n" " "); write_table64(out, crc_big_table, 256); fprintf(out, "};\n"); /* write out big-endian CRC table for 32-bit z_word_t to crc32.h */ fprintf(out, "\n" "#else /* W == 4 */\n" "\n" "local const z_word_t FAR crc_big_table[] = {\n" " "); write_table32hi(out, crc_big_table, 256); fprintf(out, "};\n" "\n" "#endif\n"); /* write out braid tables for each value of N */ for (n = 1; n <= 6; n++) { fprintf(out, "\n" "#if N == %d\n", n); /* compute braid tables for this N and 64-bit word_t */ braid(ltl, big, n, 8); /* write out braid tables for 64-bit z_word_t to crc32.h */ fprintf(out, "\n" "#if W == 8\n" "\n" "local const z_crc_t FAR crc_braid_table[][256] = {\n"); for (k = 0; k < 8; k++) { fprintf(out, " {"); write_table(out, ltl[k], 256); fprintf(out, "}%s", k < 7 ? ",\n" : ""); } fprintf(out, "};\n" "\n" "local const z_word_t FAR crc_braid_big_table[][256] = {\n"); for (k = 0; k < 8; k++) { fprintf(out, " {"); write_table64(out, big[k], 256); fprintf(out, "}%s", k < 7 ? ",\n" : ""); } fprintf(out, "};\n"); /* compute braid tables for this N and 32-bit word_t */ braid(ltl, big, n, 4); /* write out braid tables for 32-bit z_word_t to crc32.h */ fprintf(out, "\n" "#else /* W == 4 */\n" "\n" "local const z_crc_t FAR crc_braid_table[][256] = {\n"); for (k = 0; k < 4; k++) { fprintf(out, " {"); write_table(out, ltl[k], 256); fprintf(out, "}%s", k < 3 ? ",\n" : ""); } fprintf(out, "};\n" "\n" "local const z_word_t FAR crc_braid_big_table[][256] = {\n"); for (k = 0; k < 4; k++) { fprintf(out, " {"); write_table32hi(out, big[k], 256); fprintf(out, "}%s", k < 3 ? ",\n" : ""); } fprintf(out, "};\n" "\n" "#endif\n" "\n" "#endif\n"); } fprintf(out, "\n" "#endif\n"); /* write out zeros operator table to crc32.h */ fprintf(out, "\n" "local const z_crc_t FAR x2n_table[] = {\n" " "); write_table(out, x2n_table, 32); fprintf(out, "};\n"); fclose(out); } #endif /* MAKECRCH */ } #ifdef MAKECRCH /* Write the 32-bit values in table[0..k-1] to out, five per line in hexadecimal separated by commas. */ local void write_table(FILE *out, const z_crc_t FAR *table, int k) { int n; for (n = 0; n < k; n++) fprintf(out, "%s0x%08lx%s", n == 0 || n % 5 ? "" : " ", (unsigned long)(table[n]), n == k - 1 ? "" : (n % 5 == 4 ? ",\n" : ", ")); } /* Write the high 32-bits of each value in table[0..k-1] to out, five per line in hexadecimal separated by commas. */ local void write_table32hi(FILE *out, const z_word_t FAR *table, int k) { int n; for (n = 0; n < k; n++) fprintf(out, "%s0x%08lx%s", n == 0 || n % 5 ? "" : " ", (unsigned long)(table[n] >> 32), n == k - 1 ? "" : (n % 5 == 4 ? ",\n" : ", ")); } /* Write the 64-bit values in table[0..k-1] to out, three per line in hexadecimal separated by commas. This assumes that if there is a 64-bit type, then there is also a long long integer type, and it is at least 64 bits. If not, then the type cast and format string can be adjusted accordingly. */ local void write_table64(FILE *out, const z_word_t FAR *table, int k) { int n; for (n = 0; n < k; n++) fprintf(out, "%s0x%016llx%s", n == 0 || n % 3 ? "" : " ", (unsigned long long)(table[n]), n == k - 1 ? "" : (n % 3 == 2 ? ",\n" : ", ")); } /* Actually do the deed. */ int main(void) { make_crc_table(); return 0; } #endif /* MAKECRCH */ #ifdef W /* Generate the little and big-endian braid tables for the given n and z_word_t size w. Each array must have room for w blocks of 256 elements. */ local void braid(z_crc_t ltl[][256], z_word_t big[][256], int n, int w) { int k; z_crc_t i, p, q; for (k = 0; k < w; k++) { p = x2nmodp((n * w + 3 - k) << 3, 0); ltl[k][0] = 0; big[w - 1 - k][0] = 0; for (i = 1; i < 256; i++) { ltl[k][i] = q = multmodp(i << 24, p); big[w - 1 - k][i] = byte_swap(q); } } } #endif #endif /* DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ /* ========================================================================= * This function can be used by asm versions of crc32(), and to force the * generation of the CRC tables in a threaded application. */ const z_crc_t FAR * ZEXPORT get_crc_table(void) { #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE once(&made, make_crc_table); #endif /* DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ return (const z_crc_t FAR *)crc_table; } /* ========================================================================= * Use ARM machine instructions if available. This will compute the CRC about * ten times faster than the braided calculation. This code does not check for * the presence of the CRC instruction at run time. __ARM_FEATURE_CRC32 will * only be defined if the compilation specifies an ARM processor architecture * that has the instructions. For example, compiling with -march=armv8.1-a or * -march=armv8-a+crc, or -march=native if the compile machine has the crc32 * instructions. */ #ifdef ARMCRC32 /* Constants empirically determined to maximize speed. These values are from measurements on a Cortex-A57. Your mileage may vary. */ #define Z_BATCH 3990 /* number of words in a batch */ #define Z_BATCH_ZEROS 0xa10d3d0c /* computed from Z_BATCH = 3990 */ #define Z_BATCH_MIN 800 /* fewest words in a final batch */ unsigned long ZEXPORT crc32_z(unsigned long crc, const unsigned char FAR *buf, z_size_t len) { z_crc_t val; z_word_t crc1, crc2; const z_word_t *word; z_word_t val0, val1, val2; z_size_t last, last2, i; z_size_t num; /* Return initial CRC, if requested. */ if (buf == Z_NULL) return 0; #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE once(&made, make_crc_table); #endif /* DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ /* Pre-condition the CRC */ crc = (~crc) & 0xffffffff; /* Compute the CRC up to a word boundary. */ while (len && ((z_size_t)buf & 7) != 0) { len--; val = *buf++; __asm__ volatile("crc32b %w0, %w0, %w1" : "+r"(crc) : "r"(val)); } /* Prepare to compute the CRC on full 64-bit words word[0..num-1]. */ word = (z_word_t const *)buf; num = len >> 3; len &= 7; /* Do three interleaved CRCs to realize the throughput of one crc32x instruction per cycle. Each CRC is calculated on Z_BATCH words. The three CRCs are combined into a single CRC after each set of batches. */ while (num >= 3 * Z_BATCH) { crc1 = 0; crc2 = 0; for (i = 0; i < Z_BATCH; i++) { val0 = word[i]; val1 = word[i + Z_BATCH]; val2 = word[i + 2 * Z_BATCH]; __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc) : "r"(val0)); __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc1) : "r"(val1)); __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc2) : "r"(val2)); } word += 3 * Z_BATCH; num -= 3 * Z_BATCH; crc = multmodp(Z_BATCH_ZEROS, crc) ^ crc1; crc = multmodp(Z_BATCH_ZEROS, crc) ^ crc2; } /* Do one last smaller batch with the remaining words, if there are enough to pay for the combination of CRCs. */ last = num / 3; if (last >= Z_BATCH_MIN) { last2 = last << 1; crc1 = 0; crc2 = 0; for (i = 0; i < last; i++) { val0 = word[i]; val1 = word[i + last]; val2 = word[i + last2]; __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc) : "r"(val0)); __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc1) : "r"(val1)); __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc2) : "r"(val2)); } word += 3 * last; num -= 3 * last; val = x2nmodp(last, 6); crc = multmodp(val, crc) ^ crc1; crc = multmodp(val, crc) ^ crc2; } /* Compute the CRC on any remaining words. */ for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { val0 = word[i]; __asm__ volatile("crc32x %w0, %w0, %x1" : "+r"(crc) : "r"(val0)); } word += num; /* Complete the CRC on any remaining bytes. */ buf = (const unsigned char FAR *)word; while (len) { len--; val = *buf++; __asm__ volatile("crc32b %w0, %w0, %w1" : "+r"(crc) : "r"(val)); } /* Return the CRC, post-conditioned. */ return crc ^ 0xffffffff; } #else #ifdef W /* Return the CRC of the W bytes in the word_t data, taking the least-significant byte of the word as the first byte of data, without any pre or post conditioning. This is used to combine the CRCs of each braid. */ local z_crc_t crc_word(z_word_t data) { int k; for (k = 0; k < W; k++) data = (data >> 8) ^ crc_table[data & 0xff]; return (z_crc_t)data; } local z_word_t crc_word_big(z_word_t data) { int k; for (k = 0; k < W; k++) data = (data << 8) ^ crc_big_table[(data >> ((W - 1) << 3)) & 0xff]; return data; } #endif /* ========================================================================= */ unsigned long ZEXPORT crc32_z(unsigned long crc, const unsigned char FAR *buf, z_size_t len) { /* Return initial CRC, if requested. */ if (buf == Z_NULL) return 0; #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE once(&made, make_crc_table); #endif /* DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ /* Pre-condition the CRC */ crc = (~crc) & 0xffffffff; #ifdef W /* If provided enough bytes, do a braided CRC calculation. */ if (len >= N * W + W - 1) { z_size_t blks; z_word_t const *words; unsigned endian; int k; /* Compute the CRC up to a z_word_t boundary. */ while (len && ((z_size_t)buf & (W - 1)) != 0) { len--; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; } /* Compute the CRC on as many N z_word_t blocks as are available. */ blks = len / (N * W); len -= blks * N * W; words = (z_word_t const *)buf; /* Do endian check at execution time instead of compile time, since ARM processors can change the endianness at execution time. If the compiler knows what the endianness will be, it can optimize out the check and the unused branch. */ endian = 1; if (*(unsigned char *)&endian) { /* Little endian. */ z_crc_t crc0; z_word_t word0; #if N > 1 z_crc_t crc1; z_word_t word1; #if N > 2 z_crc_t crc2; z_word_t word2; #if N > 3 z_crc_t crc3; z_word_t word3; #if N > 4 z_crc_t crc4; z_word_t word4; #if N > 5 z_crc_t crc5; z_word_t word5; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif /* Initialize the CRC for each braid. */ crc0 = crc; #if N > 1 crc1 = 0; #if N > 2 crc2 = 0; #if N > 3 crc3 = 0; #if N > 4 crc4 = 0; #if N > 5 crc5 = 0; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif /* Process the first blks-1 blocks, computing the CRCs on each braid independently. */ while (--blks) { /* Load the word for each braid into registers. */ word0 = crc0 ^ words[0]; #if N > 1 word1 = crc1 ^ words[1]; #if N > 2 word2 = crc2 ^ words[2]; #if N > 3 word3 = crc3 ^ words[3]; #if N > 4 word4 = crc4 ^ words[4]; #if N > 5 word5 = crc5 ^ words[5]; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif words += N; /* Compute and update the CRC for each word. The loop should get unrolled. */ crc0 = crc_braid_table[0][word0 & 0xff]; #if N > 1 crc1 = crc_braid_table[0][word1 & 0xff]; #if N > 2 crc2 = crc_braid_table[0][word2 & 0xff]; #if N > 3 crc3 = crc_braid_table[0][word3 & 0xff]; #if N > 4 crc4 = crc_braid_table[0][word4 & 0xff]; #if N > 5 crc5 = crc_braid_table[0][word5 & 0xff]; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif for (k = 1; k < W; k++) { crc0 ^= crc_braid_table[k][(word0 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 1 crc1 ^= crc_braid_table[k][(word1 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 2 crc2 ^= crc_braid_table[k][(word2 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 3 crc3 ^= crc_braid_table[k][(word3 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 4 crc4 ^= crc_braid_table[k][(word4 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 5 crc5 ^= crc_braid_table[k][(word5 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif } } /* Process the last block, combining the CRCs of the N braids at the same time. */ crc = crc_word(crc0 ^ words[0]); #if N > 1 crc = crc_word(crc1 ^ words[1] ^ crc); #if N > 2 crc = crc_word(crc2 ^ words[2] ^ crc); #if N > 3 crc = crc_word(crc3 ^ words[3] ^ crc); #if N > 4 crc = crc_word(crc4 ^ words[4] ^ crc); #if N > 5 crc = crc_word(crc5 ^ words[5] ^ crc); #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif words += N; } else { /* Big endian. */ z_word_t crc0, word0, comb; #if N > 1 z_word_t crc1, word1; #if N > 2 z_word_t crc2, word2; #if N > 3 z_word_t crc3, word3; #if N > 4 z_word_t crc4, word4; #if N > 5 z_word_t crc5, word5; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif /* Initialize the CRC for each braid. */ crc0 = byte_swap(crc); #if N > 1 crc1 = 0; #if N > 2 crc2 = 0; #if N > 3 crc3 = 0; #if N > 4 crc4 = 0; #if N > 5 crc5 = 0; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif /* Process the first blks-1 blocks, computing the CRCs on each braid independently. */ while (--blks) { /* Load the word for each braid into registers. */ word0 = crc0 ^ words[0]; #if N > 1 word1 = crc1 ^ words[1]; #if N > 2 word2 = crc2 ^ words[2]; #if N > 3 word3 = crc3 ^ words[3]; #if N > 4 word4 = crc4 ^ words[4]; #if N > 5 word5 = crc5 ^ words[5]; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif words += N; /* Compute and update the CRC for each word. The loop should get unrolled. */ crc0 = crc_braid_big_table[0][word0 & 0xff]; #if N > 1 crc1 = crc_braid_big_table[0][word1 & 0xff]; #if N > 2 crc2 = crc_braid_big_table[0][word2 & 0xff]; #if N > 3 crc3 = crc_braid_big_table[0][word3 & 0xff]; #if N > 4 crc4 = crc_braid_big_table[0][word4 & 0xff]; #if N > 5 crc5 = crc_braid_big_table[0][word5 & 0xff]; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif for (k = 1; k < W; k++) { crc0 ^= crc_braid_big_table[k][(word0 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 1 crc1 ^= crc_braid_big_table[k][(word1 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 2 crc2 ^= crc_braid_big_table[k][(word2 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 3 crc3 ^= crc_braid_big_table[k][(word3 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 4 crc4 ^= crc_braid_big_table[k][(word4 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #if N > 5 crc5 ^= crc_braid_big_table[k][(word5 >> (k << 3)) & 0xff]; #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif } } /* Process the last block, combining the CRCs of the N braids at the same time. */ comb = crc_word_big(crc0 ^ words[0]); #if N > 1 comb = crc_word_big(crc1 ^ words[1] ^ comb); #if N > 2 comb = crc_word_big(crc2 ^ words[2] ^ comb); #if N > 3 comb = crc_word_big(crc3 ^ words[3] ^ comb); #if N > 4 comb = crc_word_big(crc4 ^ words[4] ^ comb); #if N > 5 comb = crc_word_big(crc5 ^ words[5] ^ comb); #endif #endif #endif #endif #endif words += N; crc = byte_swap(comb); } /* Update the pointer to the remaining bytes to process. */ buf = (unsigned char const *)words; } #endif /* W */ /* Complete the computation of the CRC on any remaining bytes. */ while (len >= 8) { len -= 8; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; } while (len) { len--; crc = (crc >> 8) ^ crc_table[(crc ^ *buf++) & 0xff]; } /* Return the CRC, post-conditioned. */ return crc ^ 0xffffffff; } #endif /* ========================================================================= */ unsigned long ZEXPORT crc32(unsigned long crc, const unsigned char FAR *buf, uInt len) { return crc32_z(crc, buf, len); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine64(uLong crc1, uLong crc2, z_off64_t len2) { #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE once(&made, make_crc_table); #endif /* DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ return multmodp(x2nmodp(len2, 3), crc1) ^ (crc2 & 0xffffffff); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine(uLong crc1, uLong crc2, z_off_t len2) { return crc32_combine64(crc1, crc2, (z_off64_t)len2); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen64(z_off64_t len2) { #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE once(&made, make_crc_table); #endif /* DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE */ return x2nmodp(len2, 3); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen(z_off_t len2) { return crc32_combine_gen64((z_off64_t)len2); } /* ========================================================================= */ uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_op(uLong crc1, uLong crc2, uLong op) { return multmodp(op, crc1) ^ (crc2 & 0xffffffff); }
• slide_hash • read_buf • fill_window • deflateInit_ • deflateInit2_ • deflateStateCheck • deflateSetDictionary • deflateGetDictionary • deflateResetKeep • lm_init • deflateReset • deflateSetHeader • deflatePending • deflatePrime • deflateParams • deflateTune • deflateBound • putShortMSB • flush_pending • deflate • deflateEnd • deflateCopy • longest_match • check_match • FLUSH_BLOCK_ONLY • FLUSH_BLOCK • deflate_stored • deflate_fast • deflate_slow • deflate_rle • deflate_huff
/* deflate.c -- compress data using the deflation algorithm * Copyright (C) 1995-2024 Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* * ALGORITHM * * The "deflation" process depends on being able to identify portions * of the input text which are identical to earlier input (within a * sliding window trailing behind the input currently being processed). * * The most straightforward technique turns out to be the fastest for * most input files: try all possible matches and select the longest. * The key feature of this algorithm is that insertions into the string * dictionary are very simple and thus fast, and deletions are avoided * completely. Insertions are performed at each input character, whereas * string matches are performed only when the previous match ends. So it * is preferable to spend more time in matches to allow very fast string * insertions and avoid deletions. The matching algorithm for small * strings is inspired from that of Rabin & Karp. A brute force approach * is used to find longer strings when a small match has been found. * A similar algorithm is used in comic (by Jan-Mark Wams) and freeze * (by Leonid Broukhis). * A previous version of this file used a more sophisticated algorithm * (by Fiala and Greene) which is guaranteed to run in linear amortized * time, but has a larger average cost, uses more memory and is patented. * However the F&G algorithm may be faster for some highly redundant * files if the parameter max_chain_length (described below) is too large. * * ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS * * The idea of lazy evaluation of matches is due to Jan-Mark Wams, and * I found it in 'freeze' written by Leonid Broukhis. * Thanks to many people for bug reports and testing. * * REFERENCES * * Deutsch, L.P.,"DEFLATE Compressed Data Format Specification". * Available in http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1951 * * A description of the Rabin and Karp algorithm is given in the book * "Algorithms" by R. Sedgewick, Addison-Wesley, p252. * * Fiala,E.R., and Greene,D.H. * Data Compression with Finite Windows, Comm.ACM, 32,4 (1989) 490-595 * */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #include "deflate.h" const char deflate_copyright[] = " deflate 1.3.1 Copyright 1995-2024 Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler "; /* If you use the zlib library in a product, an acknowledgment is welcome in the documentation of your product. If for some reason you cannot include such an acknowledgment, I would appreciate that you keep this copyright string in the executable of your product. */ typedef enum { need_more, /* block not completed, need more input or more output */ block_done, /* block flush performed */ finish_started, /* finish started, need only more output at next deflate */ finish_done /* finish done, accept no more input or output */ } block_state; typedef block_state (*compress_func)(deflate_state *s, int flush); /* Compression function. Returns the block state after the call. */ local block_state deflate_stored(deflate_state *s, int flush); local block_state deflate_fast(deflate_state *s, int flush); #ifndef FASTEST local block_state deflate_slow(deflate_state *s, int flush); #endif local block_state deflate_rle(deflate_state *s, int flush); local block_state deflate_huff(deflate_state *s, int flush); /* =========================================================================== * Local data */ #define NIL 0 /* Tail of hash chains */ #ifndef TOO_FAR # define TOO_FAR 4096 #endif /* Matches of length 3 are discarded if their distance exceeds TOO_FAR */ /* Values for max_lazy_match, good_match and max_chain_length, depending on * the desired pack level (0..9). The values given below have been tuned to * exclude worst case performance for pathological files. Better values may be * found for specific files. */ typedef struct config_s { ush good_length; /* reduce lazy search above this match length */ ush max_lazy; /* do not perform lazy search above this match length */ ush nice_length; /* quit search above this match length */ ush max_chain; compress_func func; } config; #ifdef FASTEST local const config configuration_table[2] = { /* good lazy nice chain */ /* 0 */ {0, 0, 0, 0, deflate_stored}, /* store only */ /* 1 */ {4, 4, 8, 4, deflate_fast}}; /* max speed, no lazy matches */ #else local const config configuration_table[10] = { /* good lazy nice chain */ /* 0 */ {0, 0, 0, 0, deflate_stored}, /* store only */ /* 1 */ {4, 4, 8, 4, deflate_fast}, /* max speed, no lazy matches */ /* 2 */ {4, 5, 16, 8, deflate_fast}, /* 3 */ {4, 6, 32, 32, deflate_fast}, /* 4 */ {4, 4, 16, 16, deflate_slow}, /* lazy matches */ /* 5 */ {8, 16, 32, 32, deflate_slow}, /* 6 */ {8, 16, 128, 128, deflate_slow}, /* 7 */ {8, 32, 128, 256, deflate_slow}, /* 8 */ {32, 128, 258, 1024, deflate_slow}, /* 9 */ {32, 258, 258, 4096, deflate_slow}}; /* max compression */ #endif /* Note: the deflate() code requires max_lazy >= MIN_MATCH and max_chain >= 4 * For deflate_fast() (levels <= 3) good is ignored and lazy has a different * meaning. */ /* rank Z_BLOCK between Z_NO_FLUSH and Z_PARTIAL_FLUSH */ #define RANK(f) (((f) * 2) - ((f) > 4 ? 9 : 0)) /* =========================================================================== * Update a hash value with the given input byte * IN assertion: all calls to UPDATE_HASH are made with consecutive input * characters, so that a running hash key can be computed from the previous * key instead of complete recalculation each time. */ #define UPDATE_HASH(s,h,c) (h = (((h) << s->hash_shift) ^ (c)) & s->hash_mask) /* =========================================================================== * Insert string str in the dictionary and set match_head to the previous head * of the hash chain (the most recent string with same hash key). Return * the previous length of the hash chain. * If this file is compiled with -DFASTEST, the compression level is forced * to 1, and no hash chains are maintained. * IN assertion: all calls to INSERT_STRING are made with consecutive input * characters and the first MIN_MATCH bytes of str are valid (except for * the last MIN_MATCH-1 bytes of the input file). */ #ifdef FASTEST #define INSERT_STRING(s, str, match_head) \ (UPDATE_HASH(s, s->ins_h, s->window[(str) + (MIN_MATCH-1)]), \ match_head = s->head[s->ins_h], \ s->head[s->ins_h] = (Pos)(str)) #else #define INSERT_STRING(s, str, match_head) \ (UPDATE_HASH(s, s->ins_h, s->window[(str) + (MIN_MATCH-1)]), \ match_head = s->prev[(str) & s->w_mask] = s->head[s->ins_h], \ s->head[s->ins_h] = (Pos)(str)) #endif /* =========================================================================== * Initialize the hash table (avoiding 64K overflow for 16 bit systems). * prev[] will be initialized on the fly. */ #define CLEAR_HASH(s) \ do { \ s->head[s->hash_size - 1] = NIL; \ zmemzero((Bytef *)s->head, \ (unsigned)(s->hash_size - 1)*sizeof(*s->head)); \ } while (0) /* =========================================================================== * Slide the hash table when sliding the window down (could be avoided with 32 * bit values at the expense of memory usage). We slide even when level == 0 to * keep the hash table consistent if we switch back to level > 0 later. */ #if defined(__has_feature) # if __has_feature(memory_sanitizer) __attribute__((no_sanitize("memory"))) # endif #endif local void slide_hash(deflate_state *s) { unsigned n, m; Posf *p; uInt wsize = s->w_size; n = s->hash_size; p = &s->head[n]; do { m = *--p; *p = (Pos)(m >= wsize ? m - wsize : NIL); } while (--n); n = wsize; #ifndef FASTEST p = &s->prev[n]; do { m = *--p; *p = (Pos)(m >= wsize ? m - wsize : NIL); /* If n is not on any hash chain, prev[n] is garbage but * its value will never be used. */ } while (--n); #endif } /* =========================================================================== * Read a new buffer from the current input stream, update the adler32 * and total number of bytes read. All deflate() input goes through * this function so some applications may wish to modify it to avoid * allocating a large strm->next_in buffer and copying from it. * (See also flush_pending()). */ local unsigned read_buf(z_streamp strm, Bytef *buf, unsigned size) { unsigned len = strm->avail_in; if (len > size) len = size; if (len == 0) return 0; strm->avail_in -= len; zmemcpy(buf, strm->next_in, len); if (strm->state->wrap == 1) { strm->adler = adler32(strm->adler, buf, len); } #ifdef GZIP else if (strm->state->wrap == 2) { strm->adler = crc32(strm->adler, buf, len); } #endif strm->next_in += len; strm->total_in += len; return len; } /* =========================================================================== * Fill the window when the lookahead becomes insufficient. * Updates strstart and lookahead. * * IN assertion: lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD * OUT assertions: strstart <= window_size-MIN_LOOKAHEAD * At least one byte has been read, or avail_in == 0; reads are * performed for at least two bytes (required for the zip translate_eol * option -- not supported here). */ local void fill_window(deflate_state *s) { unsigned n; unsigned more; /* Amount of free space at the end of the window. */ uInt wsize = s->w_size; Assert(s->lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD, "already enough lookahead"); do { more = (unsigned)(s->window_size -(ulg)s->lookahead -(ulg)s->strstart); /* Deal with !@#$% 64K limit: */ if (sizeof(int) <= 2) { if (more == 0 && s->strstart == 0 && s->lookahead == 0) { more = wsize; } else if (more == (unsigned)(-1)) { /* Very unlikely, but possible on 16 bit machine if * strstart == 0 && lookahead == 1 (input done a byte at time) */ more--; } } /* If the window is almost full and there is insufficient lookahead, * move the upper half to the lower one to make room in the upper half. */ if (s->strstart >= wsize + MAX_DIST(s)) { zmemcpy(s->window, s->window + wsize, (unsigned)wsize - more); s->match_start -= wsize; s->strstart -= wsize; /* we now have strstart >= MAX_DIST */ s->block_start -= (long) wsize; if (s->insert > s->strstart) s->insert = s->strstart; slide_hash(s); more += wsize; } if (s->strm->avail_in == 0) break; /* If there was no sliding: * strstart <= WSIZE+MAX_DIST-1 && lookahead <= MIN_LOOKAHEAD - 1 && * more == window_size - lookahead - strstart * => more >= window_size - (MIN_LOOKAHEAD-1 + WSIZE + MAX_DIST-1) * => more >= window_size - 2*WSIZE + 2 * In the BIG_MEM or MMAP case (not yet supported), * window_size == input_size + MIN_LOOKAHEAD && * strstart + s->lookahead <= input_size => more >= MIN_LOOKAHEAD. * Otherwise, window_size == 2*WSIZE so more >= 2. * If there was sliding, more >= WSIZE. So in all cases, more >= 2. */ Assert(more >= 2, "more < 2"); n = read_buf(s->strm, s->window + s->strstart + s->lookahead, more); s->lookahead += n; /* Initialize the hash value now that we have some input: */ if (s->lookahead + s->insert >= MIN_MATCH) { uInt str = s->strstart - s->insert; s->ins_h = s->window[str]; UPDATE_HASH(s, s->ins_h, s->window[str + 1]); #if MIN_MATCH != 3 Call UPDATE_HASH() MIN_MATCH-3 more times #endif while (s->insert) { UPDATE_HASH(s, s->ins_h, s->window[str + MIN_MATCH-1]); #ifndef FASTEST s->prev[str & s->w_mask] = s->head[s->ins_h]; #endif s->head[s->ins_h] = (Pos)str; str++; s->insert--; if (s->lookahead + s->insert < MIN_MATCH) break; } } /* If the whole input has less than MIN_MATCH bytes, ins_h is garbage, * but this is not important since only literal bytes will be emitted. */ } while (s->lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD && s->strm->avail_in != 0); /* If the WIN_INIT bytes after the end of the current data have never been * written, then zero those bytes in order to avoid memory check reports of * the use of uninitialized (or uninitialised as Julian writes) bytes by * the longest match routines. Update the high water mark for the next * time through here. WIN_INIT is set to MAX_MATCH since the longest match * routines allow scanning to strstart + MAX_MATCH, ignoring lookahead. */ if (s->high_water < s->window_size) { ulg curr = s->strstart + (ulg)(s->lookahead); ulg init; if (s->high_water < curr) { /* Previous high water mark below current data -- zero WIN_INIT * bytes or up to end of window, whichever is less. */ init = s->window_size - curr; if (init > WIN_INIT) init = WIN_INIT; zmemzero(s->window + curr, (unsigned)init); s->high_water = curr + init; } else if (s->high_water < (ulg)curr + WIN_INIT) { /* High water mark at or above current data, but below current data * plus WIN_INIT -- zero out to current data plus WIN_INIT, or up * to end of window, whichever is less. */ init = (ulg)curr + WIN_INIT - s->high_water; if (init > s->window_size - s->high_water) init = s->window_size - s->high_water; zmemzero(s->window + s->high_water, (unsigned)init); s->high_water += init; } } Assert((ulg)s->strstart <= s->window_size - MIN_LOOKAHEAD, "not enough room for search"); } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateInit_(z_streamp strm, int level, const char *version, int stream_size) { return deflateInit2_(strm, level, Z_DEFLATED, MAX_WBITS, DEF_MEM_LEVEL, Z_DEFAULT_STRATEGY, version, stream_size); /* To do: ignore strm->next_in if we use it as window */ } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateInit2_(z_streamp strm, int level, int method, int windowBits, int memLevel, int strategy, const char *version, int stream_size) { deflate_state *s; int wrap = 1; static const char my_version[] = ZLIB_VERSION; if (version == Z_NULL || version[0] != my_version[0] || stream_size != sizeof(z_stream)) { return Z_VERSION_ERROR; } if (strm == Z_NULL) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; strm->msg = Z_NULL; if (strm->zalloc == (alloc_func)0) { #ifdef Z_SOLO return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else strm->zalloc = zcalloc; strm->opaque = (voidpf)0; #endif } if (strm->zfree == (free_func)0) #ifdef Z_SOLO return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else strm->zfree = zcfree; #endif #ifdef FASTEST if (level != 0) level = 1; #else if (level == Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION) level = 6; #endif if (windowBits < 0) { /* suppress zlib wrapper */ wrap = 0; if (windowBits < -15) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; windowBits = -windowBits; } #ifdef GZIP else if (windowBits > 15) { wrap = 2; /* write gzip wrapper instead */ windowBits -= 16; } #endif if (memLevel < 1 || memLevel > MAX_MEM_LEVEL || method != Z_DEFLATED || windowBits < 8 || windowBits > 15 || level < 0 || level > 9 || strategy < 0 || strategy > Z_FIXED || (windowBits == 8 && wrap != 1)) { return Z_STREAM_ERROR; } if (windowBits == 8) windowBits = 9; /* until 256-byte window bug fixed */ s = (deflate_state *) ZALLOC(strm, 1, sizeof(deflate_state)); if (s == Z_NULL) return Z_MEM_ERROR; strm->state = (struct internal_state FAR *)s; s->strm = strm; s->status = INIT_STATE; /* to pass state test in deflateReset() */ s->wrap = wrap; s->gzhead = Z_NULL; s->w_bits = (uInt)windowBits; s->w_size = 1 << s->w_bits; s->w_mask = s->w_size - 1; s->hash_bits = (uInt)memLevel + 7; s->hash_size = 1 << s->hash_bits; s->hash_mask = s->hash_size - 1; s->hash_shift = ((s->hash_bits + MIN_MATCH-1) / MIN_MATCH); s->window = (Bytef *) ZALLOC(strm, s->w_size, 2*sizeof(Byte)); s->prev = (Posf *) ZALLOC(strm, s->w_size, sizeof(Pos)); s->head = (Posf *) ZALLOC(strm, s->hash_size, sizeof(Pos)); s->high_water = 0; /* nothing written to s->window yet */ s->lit_bufsize = 1 << (memLevel + 6); /* 16K elements by default */ /* We overlay pending_buf and sym_buf. This works since the average size * for length/distance pairs over any compressed block is assured to be 31 * bits or less. * * Analysis: The longest fixed codes are a length code of 8 bits plus 5 * extra bits, for lengths 131 to 257. The longest fixed distance codes are * 5 bits plus 13 extra bits, for distances 16385 to 32768. The longest * possible fixed-codes length/distance pair is then 31 bits total. * * sym_buf starts one-fourth of the way into pending_buf. So there are * three bytes in sym_buf for every four bytes in pending_buf. Each symbol * in sym_buf is three bytes -- two for the distance and one for the * literal/length. As each symbol is consumed, the pointer to the next * sym_buf value to read moves forward three bytes. From that symbol, up to * 31 bits are written to pending_buf. The closest the written pending_buf * bits gets to the next sym_buf symbol to read is just before the last * code is written. At that time, 31*(n - 2) bits have been written, just * after 24*(n - 2) bits have been consumed from sym_buf. sym_buf starts at * 8*n bits into pending_buf. (Note that the symbol buffer fills when n - 1 * symbols are written.) The closest the writing gets to what is unread is * then n + 14 bits. Here n is lit_bufsize, which is 16384 by default, and * can range from 128 to 32768. * * Therefore, at a minimum, there are 142 bits of space between what is * written and what is read in the overlain buffers, so the symbols cannot * be overwritten by the compressed data. That space is actually 139 bits, * due to the three-bit fixed-code block header. * * That covers the case where either Z_FIXED is specified, forcing fixed * codes, or when the use of fixed codes is chosen, because that choice * results in a smaller compressed block than dynamic codes. That latter * condition then assures that the above analysis also covers all dynamic * blocks. A dynamic-code block will only be chosen to be emitted if it has * fewer bits than a fixed-code block would for the same set of symbols. * Therefore its average symbol length is assured to be less than 31. So * the compressed data for a dynamic block also cannot overwrite the * symbols from which it is being constructed. */ s->pending_buf = (uchf *) ZALLOC(strm, s->lit_bufsize, LIT_BUFS); s->pending_buf_size = (ulg)s->lit_bufsize * 4; if (s->window == Z_NULL || s->prev == Z_NULL || s->head == Z_NULL || s->pending_buf == Z_NULL) { s->status = FINISH_STATE; strm->msg = ERR_MSG(Z_MEM_ERROR); deflateEnd (strm); return Z_MEM_ERROR; } #ifdef LIT_MEM s->d_buf = (ushf *)(s->pending_buf + (s->lit_bufsize << 1)); s->l_buf = s->pending_buf + (s->lit_bufsize << 2); s->sym_end = s->lit_bufsize - 1; #else s->sym_buf = s->pending_buf + s->lit_bufsize; s->sym_end = (s->lit_bufsize - 1) * 3; #endif /* We avoid equality with lit_bufsize*3 because of wraparound at 64K * on 16 bit machines and because stored blocks are restricted to * 64K-1 bytes. */ s->level = level; s->strategy = strategy; s->method = (Byte)method; return deflateReset(strm); } /* ========================================================================= * Check for a valid deflate stream state. Return 0 if ok, 1 if not. */ local int deflateStateCheck(z_streamp strm) { deflate_state *s; if (strm == Z_NULL || strm->zalloc == (alloc_func)0 || strm->zfree == (free_func)0) return 1; s = strm->state; if (s == Z_NULL || s->strm != strm || (s->status != INIT_STATE && #ifdef GZIP s->status != GZIP_STATE && #endif s->status != EXTRA_STATE && s->status != NAME_STATE && s->status != COMMENT_STATE && s->status != HCRC_STATE && s->status != BUSY_STATE && s->status != FINISH_STATE)) return 1; return 0; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateSetDictionary(z_streamp strm, const Bytef *dictionary, uInt dictLength) { deflate_state *s; uInt str, n; int wrap; unsigned avail; z_const unsigned char *next; if (deflateStateCheck(strm) || dictionary == Z_NULL) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; s = strm->state; wrap = s->wrap; if (wrap == 2 || (wrap == 1 && s->status != INIT_STATE) || s->lookahead) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; /* when using zlib wrappers, compute Adler-32 for provided dictionary */ if (wrap == 1) strm->adler = adler32(strm->adler, dictionary, dictLength); s->wrap = 0; /* avoid computing Adler-32 in read_buf */ /* if dictionary would fill window, just replace the history */ if (dictLength >= s->w_size) { if (wrap == 0) { /* already empty otherwise */ CLEAR_HASH(s); s->strstart = 0; s->block_start = 0L; s->insert = 0; } dictionary += dictLength - s->w_size; /* use the tail */ dictLength = s->w_size; } /* insert dictionary into window and hash */ avail = strm->avail_in; next = strm->next_in; strm->avail_in = dictLength; strm->next_in = (z_const Bytef *)dictionary; fill_window(s); while (s->lookahead >= MIN_MATCH) { str = s->strstart; n = s->lookahead - (MIN_MATCH-1); do { UPDATE_HASH(s, s->ins_h, s->window[str + MIN_MATCH-1]); #ifndef FASTEST s->prev[str & s->w_mask] = s->head[s->ins_h]; #endif s->head[s->ins_h] = (Pos)str; str++; } while (--n); s->strstart = str; s->lookahead = MIN_MATCH-1; fill_window(s); } s->strstart += s->lookahead; s->block_start = (long)s->strstart; s->insert = s->lookahead; s->lookahead = 0; s->match_length = s->prev_length = MIN_MATCH-1; s->match_available = 0; strm->next_in = next; strm->avail_in = avail; s->wrap = wrap; return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateGetDictionary(z_streamp strm, Bytef *dictionary, uInt *dictLength) { deflate_state *s; uInt len; if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; s = strm->state; len = s->strstart + s->lookahead; if (len > s->w_size) len = s->w_size; if (dictionary != Z_NULL && len) zmemcpy(dictionary, s->window + s->strstart + s->lookahead - len, len); if (dictLength != Z_NULL) *dictLength = len; return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateResetKeep(z_streamp strm) { deflate_state *s; if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) { return Z_STREAM_ERROR; } strm->total_in = strm->total_out = 0; strm->msg = Z_NULL; /* use zfree if we ever allocate msg dynamically */ strm->data_type = Z_UNKNOWN; s = (deflate_state *)strm->state; s->pending = 0; s->pending_out = s->pending_buf; if (s->wrap < 0) { s->wrap = -s->wrap; /* was made negative by deflate(..., Z_FINISH); */ } s->status = #ifdef GZIP s->wrap == 2 ? GZIP_STATE : #endif INIT_STATE; strm->adler = #ifdef GZIP s->wrap == 2 ? crc32(0L, Z_NULL, 0) : #endif adler32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); s->last_flush = -2; _tr_init(s); return Z_OK; } /* =========================================================================== * Initialize the "longest match" routines for a new zlib stream */ local void lm_init(deflate_state *s) { s->window_size = (ulg)2L*s->w_size; CLEAR_HASH(s); /* Set the default configuration parameters: */ s->max_lazy_match = configuration_table[s->level].max_lazy; s->good_match = configuration_table[s->level].good_length; s->nice_match = configuration_table[s->level].nice_length; s->max_chain_length = configuration_table[s->level].max_chain; s->strstart = 0; s->block_start = 0L; s->lookahead = 0; s->insert = 0; s->match_length = s->prev_length = MIN_MATCH-1; s->match_available = 0; s->ins_h = 0; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateReset(z_streamp strm) { int ret; ret = deflateResetKeep(strm); if (ret == Z_OK) lm_init(strm->state); return ret; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateSetHeader(z_streamp strm, gz_headerp head) { if (deflateStateCheck(strm) || strm->state->wrap != 2) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; strm->state->gzhead = head; return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflatePending(z_streamp strm, unsigned *pending, int *bits) { if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; if (pending != Z_NULL) *pending = strm->state->pending; if (bits != Z_NULL) *bits = strm->state->bi_valid; return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflatePrime(z_streamp strm, int bits, int value) { deflate_state *s; int put; if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; s = strm->state; #ifdef LIT_MEM if (bits < 0 || bits > 16 || (uchf *)s->d_buf < s->pending_out + ((Buf_size + 7) >> 3)) return Z_BUF_ERROR; #else if (bits < 0 || bits > 16 || s->sym_buf < s->pending_out + ((Buf_size + 7) >> 3)) return Z_BUF_ERROR; #endif do { put = Buf_size - s->bi_valid; if (put > bits) put = bits; s->bi_buf |= (ush)((value & ((1 << put) - 1)) << s->bi_valid); s->bi_valid += put; _tr_flush_bits(s); value >>= put; bits -= put; } while (bits); return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateParams(z_streamp strm, int level, int strategy) { deflate_state *s; compress_func func; if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; s = strm->state; #ifdef FASTEST if (level != 0) level = 1; #else if (level == Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION) level = 6; #endif if (level < 0 || level > 9 || strategy < 0 || strategy > Z_FIXED) { return Z_STREAM_ERROR; } func = configuration_table[s->level].func; if ((strategy != s->strategy || func != configuration_table[level].func) && s->last_flush != -2) { /* Flush the last buffer: */ int err = deflate(strm, Z_BLOCK); if (err == Z_STREAM_ERROR) return err; if (strm->avail_in || (s->strstart - s->block_start) + s->lookahead) return Z_BUF_ERROR; } if (s->level != level) { if (s->level == 0 && s->matches != 0) { if (s->matches == 1) slide_hash(s); else CLEAR_HASH(s); s->matches = 0; } s->level = level; s->max_lazy_match = configuration_table[level].max_lazy; s->good_match = configuration_table[level].good_length; s->nice_match = configuration_table[level].nice_length; s->max_chain_length = configuration_table[level].max_chain; } s->strategy = strategy; return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateTune(z_streamp strm, int good_length, int max_lazy, int nice_length, int max_chain) { deflate_state *s; if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; s = strm->state; s->good_match = (uInt)good_length; s->max_lazy_match = (uInt)max_lazy; s->nice_match = nice_length; s->max_chain_length = (uInt)max_chain; return Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= * For the default windowBits of 15 and memLevel of 8, this function returns a * close to exact, as well as small, upper bound on the compressed size. This * is an expansion of ~0.03%, plus a small constant. * * For any setting other than those defaults for windowBits and memLevel, one * of two worst case bounds is returned. This is at most an expansion of ~4% or * ~13%, plus a small constant. * * Both the 0.03% and 4% derive from the overhead of stored blocks. The first * one is for stored blocks of 16383 bytes (memLevel == 8), whereas the second * is for stored blocks of 127 bytes (the worst case memLevel == 1). The * expansion results from five bytes of header for each stored block. * * The larger expansion of 13% results from a window size less than or equal to * the symbols buffer size (windowBits <= memLevel + 7). In that case some of * the data being compressed may have slid out of the sliding window, impeding * a stored block from being emitted. Then the only choice is a fixed or * dynamic block, where a fixed block limits the maximum expansion to 9 bits * per 8-bit byte, plus 10 bits for every block. The smallest block size for * which this can occur is 255 (memLevel == 2). * * Shifts are used to approximate divisions, for speed. */ uLong ZEXPORT deflateBound(z_streamp strm, uLong sourceLen) { deflate_state *s; uLong fixedlen, storelen, wraplen; /* upper bound for fixed blocks with 9-bit literals and length 255 (memLevel == 2, which is the lowest that may not use stored blocks) -- ~13% overhead plus a small constant */ fixedlen = sourceLen + (sourceLen >> 3) + (sourceLen >> 8) + (sourceLen >> 9) + 4; /* upper bound for stored blocks with length 127 (memLevel == 1) -- ~4% overhead plus a small constant */ storelen = sourceLen + (sourceLen >> 5) + (sourceLen >> 7) + (sourceLen >> 11) + 7; /* if can't get parameters, return larger bound plus a zlib wrapper */ if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return (fixedlen > storelen ? fixedlen : storelen) + 6; /* compute wrapper length */ s = strm->state; switch (s->wrap) { case 0: /* raw deflate */ wraplen = 0; break; case 1: /* zlib wrapper */ wraplen = 6 + (s->strstart ? 4 : 0); break; #ifdef GZIP case 2: /* gzip wrapper */ wraplen = 18; if (s->gzhead != Z_NULL) { /* user-supplied gzip header */ Bytef *str; if (s->gzhead->extra != Z_NULL) wraplen += 2 + s->gzhead->extra_len; str = s->gzhead->name; if (str != Z_NULL) do { wraplen++; } while (*str++); str = s->gzhead->comment; if (str != Z_NULL) do { wraplen++; } while (*str++); if (s->gzhead->hcrc) wraplen += 2; } break; #endif default: /* for compiler happiness */ wraplen = 6; } /* if not default parameters, return one of the conservative bounds */ if (s->w_bits != 15 || s->hash_bits != 8 + 7) return (s->w_bits <= s->hash_bits && s->level ? fixedlen : storelen) + wraplen; /* default settings: return tight bound for that case -- ~0.03% overhead plus a small constant */ return sourceLen + (sourceLen >> 12) + (sourceLen >> 14) + (sourceLen >> 25) + 13 - 6 + wraplen; } /* ========================================================================= * Put a short in the pending buffer. The 16-bit value is put in MSB order. * IN assertion: the stream state is correct and there is enough room in * pending_buf. */ local void putShortMSB(deflate_state *s, uInt b) { put_byte(s, (Byte)(b >> 8)); put_byte(s, (Byte)(b & 0xff)); } /* ========================================================================= * Flush as much pending output as possible. All deflate() output, except for * some deflate_stored() output, goes through this function so some * applications may wish to modify it to avoid allocating a large * strm->next_out buffer and copying into it. (See also read_buf()). */ local void flush_pending(z_streamp strm) { unsigned len; deflate_state *s = strm->state; _tr_flush_bits(s); len = s->pending; if (len > strm->avail_out) len = strm->avail_out; if (len == 0) return; zmemcpy(strm->next_out, s->pending_out, len); strm->next_out += len; s->pending_out += len; strm->total_out += len; strm->avail_out -= len; s->pending -= len; if (s->pending == 0) { s->pending_out = s->pending_buf; } } /* =========================================================================== * Update the header CRC with the bytes s->pending_buf[beg..s->pending - 1]. */ #define HCRC_UPDATE(beg) \ do { \ if (s->gzhead->hcrc && s->pending > (beg)) \ strm->adler = crc32(strm->adler, s->pending_buf + (beg), \ s->pending - (beg)); \ } while (0) /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflate(z_streamp strm, int flush) { int old_flush; /* value of flush param for previous deflate call */ deflate_state *s; if (deflateStateCheck(strm) || flush > Z_BLOCK || flush < 0) { return Z_STREAM_ERROR; } s = strm->state; if (strm->next_out == Z_NULL || (strm->avail_in != 0 && strm->next_in == Z_NULL) || (s->status == FINISH_STATE && flush != Z_FINISH)) { ERR_RETURN(strm, Z_STREAM_ERROR); } if (strm->avail_out == 0) ERR_RETURN(strm, Z_BUF_ERROR); old_flush = s->last_flush; s->last_flush = flush; /* Flush as much pending output as possible */ if (s->pending != 0) { flush_pending(strm); if (strm->avail_out == 0) { /* Since avail_out is 0, deflate will be called again with * more output space, but possibly with both pending and * avail_in equal to zero. There won't be anything to do, * but this is not an error situation so make sure we * return OK instead of BUF_ERROR at next call of deflate: */ s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } /* Make sure there is something to do and avoid duplicate consecutive * flushes. For repeated and useless calls with Z_FINISH, we keep * returning Z_STREAM_END instead of Z_BUF_ERROR. */ } else if (strm->avail_in == 0 && RANK(flush) <= RANK(old_flush) && flush != Z_FINISH) { ERR_RETURN(strm, Z_BUF_ERROR); } /* User must not provide more input after the first FINISH: */ if (s->status == FINISH_STATE && strm->avail_in != 0) { ERR_RETURN(strm, Z_BUF_ERROR); } /* Write the header */ if (s->status == INIT_STATE && s->wrap == 0) s->status = BUSY_STATE; if (s->status == INIT_STATE) { /* zlib header */ uInt header = (Z_DEFLATED + ((s->w_bits - 8) << 4)) << 8; uInt level_flags; if (s->strategy >= Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY || s->level < 2) level_flags = 0; else if (s->level < 6) level_flags = 1; else if (s->level == 6) level_flags = 2; else level_flags = 3; header |= (level_flags << 6); if (s->strstart != 0) header |= PRESET_DICT; header += 31 - (header % 31); putShortMSB(s, header); /* Save the adler32 of the preset dictionary: */ if (s->strstart != 0) { putShortMSB(s, (uInt)(strm->adler >> 16)); putShortMSB(s, (uInt)(strm->adler & 0xffff)); } strm->adler = adler32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); s->status = BUSY_STATE; /* Compression must start with an empty pending buffer */ flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } } #ifdef GZIP if (s->status == GZIP_STATE) { /* gzip header */ strm->adler = crc32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); put_byte(s, 31); put_byte(s, 139); put_byte(s, 8); if (s->gzhead == Z_NULL) { put_byte(s, 0); put_byte(s, 0); put_byte(s, 0); put_byte(s, 0); put_byte(s, 0); put_byte(s, s->level == 9 ? 2 : (s->strategy >= Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY || s->level < 2 ? 4 : 0)); put_byte(s, OS_CODE); s->status = BUSY_STATE; /* Compression must start with an empty pending buffer */ flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } } else { put_byte(s, (s->gzhead->text ? 1 : 0) + (s->gzhead->hcrc ? 2 : 0) + (s->gzhead->extra == Z_NULL ? 0 : 4) + (s->gzhead->name == Z_NULL ? 0 : 8) + (s->gzhead->comment == Z_NULL ? 0 : 16) ); put_byte(s, (Byte)(s->gzhead->time & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((s->gzhead->time >> 8) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((s->gzhead->time >> 16) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((s->gzhead->time >> 24) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, s->level == 9 ? 2 : (s->strategy >= Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY || s->level < 2 ? 4 : 0)); put_byte(s, s->gzhead->os & 0xff); if (s->gzhead->extra != Z_NULL) { put_byte(s, s->gzhead->extra_len & 0xff); put_byte(s, (s->gzhead->extra_len >> 8) & 0xff); } if (s->gzhead->hcrc) strm->adler = crc32(strm->adler, s->pending_buf, s->pending); s->gzindex = 0; s->status = EXTRA_STATE; } } if (s->status == EXTRA_STATE) { if (s->gzhead->extra != Z_NULL) { ulg beg = s->pending; /* start of bytes to update crc */ uInt left = (s->gzhead->extra_len & 0xffff) - s->gzindex; while (s->pending + left > s->pending_buf_size) { uInt copy = s->pending_buf_size - s->pending; zmemcpy(s->pending_buf + s->pending, s->gzhead->extra + s->gzindex, copy); s->pending = s->pending_buf_size; HCRC_UPDATE(beg); s->gzindex += copy; flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } beg = 0; left -= copy; } zmemcpy(s->pending_buf + s->pending, s->gzhead->extra + s->gzindex, left); s->pending += left; HCRC_UPDATE(beg); s->gzindex = 0; } s->status = NAME_STATE; } if (s->status == NAME_STATE) { if (s->gzhead->name != Z_NULL) { ulg beg = s->pending; /* start of bytes to update crc */ int val; do { if (s->pending == s->pending_buf_size) { HCRC_UPDATE(beg); flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } beg = 0; } val = s->gzhead->name[s->gzindex++]; put_byte(s, val); } while (val != 0); HCRC_UPDATE(beg); s->gzindex = 0; } s->status = COMMENT_STATE; } if (s->status == COMMENT_STATE) { if (s->gzhead->comment != Z_NULL) { ulg beg = s->pending; /* start of bytes to update crc */ int val; do { if (s->pending == s->pending_buf_size) { HCRC_UPDATE(beg); flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } beg = 0; } val = s->gzhead->comment[s->gzindex++]; put_byte(s, val); } while (val != 0); HCRC_UPDATE(beg); } s->status = HCRC_STATE; } if (s->status == HCRC_STATE) { if (s->gzhead->hcrc) { if (s->pending + 2 > s->pending_buf_size) { flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } } put_byte(s, (Byte)(strm->adler & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->adler >> 8) & 0xff)); strm->adler = crc32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); } s->status = BUSY_STATE; /* Compression must start with an empty pending buffer */ flush_pending(strm); if (s->pending != 0) { s->last_flush = -1; return Z_OK; } } #endif /* Start a new block or continue the current one. */ if (strm->avail_in != 0 || s->lookahead != 0 || (flush != Z_NO_FLUSH && s->status != FINISH_STATE)) { block_state bstate; bstate = s->level == 0 ? deflate_stored(s, flush) : s->strategy == Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY ? deflate_huff(s, flush) : s->strategy == Z_RLE ? deflate_rle(s, flush) : (*(configuration_table[s->level].func))(s, flush); if (bstate == finish_started || bstate == finish_done) { s->status = FINISH_STATE; } if (bstate == need_more || bstate == finish_started) { if (strm->avail_out == 0) { s->last_flush = -1; /* avoid BUF_ERROR next call, see above */ } return Z_OK; /* If flush != Z_NO_FLUSH && avail_out == 0, the next call * of deflate should use the same flush parameter to make sure * that the flush is complete. So we don't have to output an * empty block here, this will be done at next call. This also * ensures that for a very small output buffer, we emit at most * one empty block. */ } if (bstate == block_done) { if (flush == Z_PARTIAL_FLUSH) { _tr_align(s); } else if (flush != Z_BLOCK) { /* FULL_FLUSH or SYNC_FLUSH */ _tr_stored_block(s, (char*)0, 0L, 0); /* For a full flush, this empty block will be recognized * as a special marker by inflate_sync(). */ if (flush == Z_FULL_FLUSH) { CLEAR_HASH(s); /* forget history */ if (s->lookahead == 0) { s->strstart = 0; s->block_start = 0L; s->insert = 0; } } } flush_pending(strm); if (strm->avail_out == 0) { s->last_flush = -1; /* avoid BUF_ERROR at next call, see above */ return Z_OK; } } } if (flush != Z_FINISH) return Z_OK; if (s->wrap <= 0) return Z_STREAM_END; /* Write the trailer */ #ifdef GZIP if (s->wrap == 2) { put_byte(s, (Byte)(strm->adler & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->adler >> 8) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->adler >> 16) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->adler >> 24) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)(strm->total_in & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->total_in >> 8) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->total_in >> 16) & 0xff)); put_byte(s, (Byte)((strm->total_in >> 24) & 0xff)); } else #endif { putShortMSB(s, (uInt)(strm->adler >> 16)); putShortMSB(s, (uInt)(strm->adler & 0xffff)); } flush_pending(strm); /* If avail_out is zero, the application will call deflate again * to flush the rest. */ if (s->wrap > 0) s->wrap = -s->wrap; /* write the trailer only once! */ return s->pending != 0 ? Z_OK : Z_STREAM_END; } /* ========================================================================= */ int ZEXPORT deflateEnd(z_streamp strm) { int status; if (deflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; status = strm->state->status; /* Deallocate in reverse order of allocations: */ TRY_FREE(strm, strm->state->pending_buf); TRY_FREE(strm, strm->state->head); TRY_FREE(strm, strm->state->prev); TRY_FREE(strm, strm->state->window); ZFREE(strm, strm->state); strm->state = Z_NULL; return status == BUSY_STATE ? Z_DATA_ERROR : Z_OK; } /* ========================================================================= * Copy the source state to the destination state. * To simplify the source, this is not supported for 16-bit MSDOS (which * doesn't have enough memory anyway to duplicate compression states). */ int ZEXPORT deflateCopy(z_streamp dest, z_streamp source) { #ifdef MAXSEG_64K (void)dest; (void)source; return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else deflate_state *ds; deflate_state *ss; if (deflateStateCheck(source) || dest == Z_NULL) { return Z_STREAM_ERROR; } ss = source->state; zmemcpy((voidpf)dest, (voidpf)source, sizeof(z_stream)); ds = (deflate_state *) ZALLOC(dest, 1, sizeof(deflate_state)); if (ds == Z_NULL) return Z_MEM_ERROR; dest->state = (struct internal_state FAR *) ds; zmemcpy((voidpf)ds, (voidpf)ss, sizeof(deflate_state)); ds->strm = dest; ds->window = (Bytef *) ZALLOC(dest, ds->w_size, 2*sizeof(Byte)); ds->prev = (Posf *) ZALLOC(dest, ds->w_size, sizeof(Pos)); ds->head = (Posf *) ZALLOC(dest, ds->hash_size, sizeof(Pos)); ds->pending_buf = (uchf *) ZALLOC(dest, ds->lit_bufsize, LIT_BUFS); if (ds->window == Z_NULL || ds->prev == Z_NULL || ds->head == Z_NULL || ds->pending_buf == Z_NULL) { deflateEnd (dest); return Z_MEM_ERROR; } /* following zmemcpy do not work for 16-bit MSDOS */ zmemcpy(ds->window, ss->window, ds->w_size * 2 * sizeof(Byte)); zmemcpy((voidpf)ds->prev, (voidpf)ss->prev, ds->w_size * sizeof(Pos)); zmemcpy((voidpf)ds->head, (voidpf)ss->head, ds->hash_size * sizeof(Pos)); zmemcpy(ds->pending_buf, ss->pending_buf, ds->lit_bufsize * LIT_BUFS); ds->pending_out = ds->pending_buf + (ss->pending_out - ss->pending_buf); #ifdef LIT_MEM ds->d_buf = (ushf *)(ds->pending_buf + (ds->lit_bufsize << 1)); ds->l_buf = ds->pending_buf + (ds->lit_bufsize << 2); #else ds->sym_buf = ds->pending_buf + ds->lit_bufsize; #endif ds->l_desc.dyn_tree = ds->dyn_ltree; ds->d_desc.dyn_tree = ds->dyn_dtree; ds->bl_desc.dyn_tree = ds->bl_tree; return Z_OK; #endif /* MAXSEG_64K */ } #ifndef FASTEST /* =========================================================================== * Set match_start to the longest match starting at the given string and * return its length. Matches shorter or equal to prev_length are discarded, * in which case the result is equal to prev_length and match_start is * garbage. * IN assertions: cur_match is the head of the hash chain for the current * string (strstart) and its distance is <= MAX_DIST, and prev_length >= 1 * OUT assertion: the match length is not greater than s->lookahead. */ local uInt longest_match(deflate_state *s, IPos cur_match) { unsigned chain_length = s->max_chain_length;/* max hash chain length */ register Bytef *scan = s->window + s->strstart; /* current string */ register Bytef *match; /* matched string */ register int len; /* length of current match */ int best_len = (int)s->prev_length; /* best match length so far */ int nice_match = s->nice_match; /* stop if match long enough */ IPos limit = s->strstart > (IPos)MAX_DIST(s) ? s->strstart - (IPos)MAX_DIST(s) : NIL; /* Stop when cur_match becomes <= limit. To simplify the code, * we prevent matches with the string of window index 0. */ Posf *prev = s->prev; uInt wmask = s->w_mask; #ifdef UNALIGNED_OK /* Compare two bytes at a time. Note: this is not always beneficial. * Try with and without -DUNALIGNED_OK to check. */ register Bytef *strend = s->window + s->strstart + MAX_MATCH - 1; register ush scan_start = *(ushf*)scan; register ush scan_end = *(ushf*)(scan + best_len - 1); #else register Bytef *strend = s->window + s->strstart + MAX_MATCH; register Byte scan_end1 = scan[best_len - 1]; register Byte scan_end = scan[best_len]; #endif /* The code is optimized for HASH_BITS >= 8 and MAX_MATCH-2 multiple of 16. * It is easy to get rid of this optimization if necessary. */ Assert(s->hash_bits >= 8 && MAX_MATCH == 258, "Code too clever"); /* Do not waste too much time if we already have a good match: */ if (s->prev_length >= s->good_match) { chain_length >>= 2; } /* Do not look for matches beyond the end of the input. This is necessary * to make deflate deterministic. */ if ((uInt)nice_match > s->lookahead) nice_match = (int)s->lookahead; Assert((ulg)s->strstart <= s->window_size - MIN_LOOKAHEAD, "need lookahead"); do { Assert(cur_match < s->strstart, "no future"); match = s->window + cur_match; /* Skip to next match if the match length cannot increase * or if the match length is less than 2. Note that the checks below * for insufficient lookahead only occur occasionally for performance * reasons. Therefore uninitialized memory will be accessed, and * conditional jumps will be made that depend on those values. * However the length of the match is limited to the lookahead, so * the output of deflate is not affected by the uninitialized values. */ #if (defined(UNALIGNED_OK) && MAX_MATCH == 258) /* This code assumes sizeof(unsigned short) == 2. Do not use * UNALIGNED_OK if your compiler uses a different size. */ if (*(ushf*)(match + best_len - 1) != scan_end || *(ushf*)match != scan_start) continue; /* It is not necessary to compare scan[2] and match[2] since they are * always equal when the other bytes match, given that the hash keys * are equal and that HASH_BITS >= 8. Compare 2 bytes at a time at * strstart + 3, + 5, up to strstart + 257. We check for insufficient * lookahead only every 4th comparison; the 128th check will be made * at strstart + 257. If MAX_MATCH-2 is not a multiple of 8, it is * necessary to put more guard bytes at the end of the window, or * to check more often for insufficient lookahead. */ Assert(scan[2] == match[2], "scan[2]?"); scan++, match++; do { } while (*(ushf*)(scan += 2) == *(ushf*)(match += 2) && *(ushf*)(scan += 2) == *(ushf*)(match += 2) && *(ushf*)(scan += 2) == *(ushf*)(match += 2) && *(ushf*)(scan += 2) == *(ushf*)(match += 2) && scan < strend); /* The funny "do {}" generates better code on most compilers */ /* Here, scan <= window + strstart + 257 */ Assert(scan <= s->window + (unsigned)(s->window_size - 1), "wild scan"); if (*scan == *match) scan++; len = (MAX_MATCH - 1) - (int)(strend - scan); scan = strend - (MAX_MATCH-1); #else /* UNALIGNED_OK */ if (match[best_len] != scan_end || match[best_len - 1] != scan_end1 || *match != *scan || *++match != scan[1]) continue; /* The check at best_len - 1 can be removed because it will be made * again later. (This heuristic is not always a win.) * It is not necessary to compare scan[2] and match[2] since they * are always equal when the other bytes match, given that * the hash keys are equal and that HASH_BITS >= 8. */ scan += 2, match++; Assert(*scan == *match, "match[2]?"); /* We check for insufficient lookahead only every 8th comparison; * the 256th check will be made at strstart + 258. */ do { } while (*++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && scan < strend); Assert(scan <= s->window + (unsigned)(s->window_size - 1), "wild scan"); len = MAX_MATCH - (int)(strend - scan); scan = strend - MAX_MATCH; #endif /* UNALIGNED_OK */ if (len > best_len) { s->match_start = cur_match; best_len = len; if (len >= nice_match) break; #ifdef UNALIGNED_OK scan_end = *(ushf*)(scan + best_len - 1); #else scan_end1 = scan[best_len - 1]; scan_end = scan[best_len]; #endif } } while ((cur_match = prev[cur_match & wmask]) > limit && --chain_length != 0); if ((uInt)best_len <= s->lookahead) return (uInt)best_len; return s->lookahead; } #else /* FASTEST */ /* --------------------------------------------------------------------------- * Optimized version for FASTEST only */ local uInt longest_match(deflate_state *s, IPos cur_match) { register Bytef *scan = s->window + s->strstart; /* current string */ register Bytef *match; /* matched string */ register int len; /* length of current match */ register Bytef *strend = s->window + s->strstart + MAX_MATCH; /* The code is optimized for HASH_BITS >= 8 and MAX_MATCH-2 multiple of 16. * It is easy to get rid of this optimization if necessary. */ Assert(s->hash_bits >= 8 && MAX_MATCH == 258, "Code too clever"); Assert((ulg)s->strstart <= s->window_size - MIN_LOOKAHEAD, "need lookahead"); Assert(cur_match < s->strstart, "no future"); match = s->window + cur_match; /* Return failure if the match length is less than 2: */ if (match[0] != scan[0] || match[1] != scan[1]) return MIN_MATCH-1; /* The check at best_len - 1 can be removed because it will be made * again later. (This heuristic is not always a win.) * It is not necessary to compare scan[2] and match[2] since they * are always equal when the other bytes match, given that * the hash keys are equal and that HASH_BITS >= 8. */ scan += 2, match += 2; Assert(*scan == *match, "match[2]?"); /* We check for insufficient lookahead only every 8th comparison; * the 256th check will be made at strstart + 258. */ do { } while (*++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && *++scan == *++match && scan < strend); Assert(scan <= s->window + (unsigned)(s->window_size - 1), "wild scan"); len = MAX_MATCH - (int)(strend - scan); if (len < MIN_MATCH) return MIN_MATCH - 1; s->match_start = cur_match; return (uInt)len <= s->lookahead ? (uInt)len : s->lookahead; } #endif /* FASTEST */ #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG #define EQUAL 0 /* result of memcmp for equal strings */ /* =========================================================================== * Check that the match at match_start is indeed a match. */ local void check_match(deflate_state *s, IPos start, IPos match, int length) { /* check that the match is indeed a match */ Bytef *back = s->window + (int)match, *here = s->window + start; IPos len = length; if (match == (IPos)-1) { /* match starts one byte before the current window -- just compare the subsequent length-1 bytes */ back++; here++; len--; } if (zmemcmp(back, here, len) != EQUAL) { fprintf(stderr, " start %u, match %d, length %d\n", start, (int)match, length); do { fprintf(stderr, "(%02x %02x)", *back++, *here++); } while (--len != 0); z_error("invalid match"); } if (z_verbose > 1) { fprintf(stderr,"\\[%d,%d]", start - match, length); do { putc(s->window[start++], stderr); } while (--length != 0); } } #else # define check_match(s, start, match, length) #endif /* ZLIB_DEBUG */ /* =========================================================================== * Flush the current block, with given end-of-file flag. * IN assertion: strstart is set to the end of the current match. */ #define FLUSH_BLOCK_ONLY(s, last) { \ _tr_flush_block(s, (s->block_start >= 0L ? \ (charf *)&s->window[(unsigned)s->block_start] : \ (charf *)Z_NULL), \ (ulg)((long)s->strstart - s->block_start), \ (last)); \ s->block_start = s->strstart; \ flush_pending(s->strm); \ Tracev((stderr,"[FLUSH]")); \ } /* Same but force premature exit if necessary. */ #define FLUSH_BLOCK(s, last) { \ FLUSH_BLOCK_ONLY(s, last); \ if (s->strm->avail_out == 0) return (last) ? finish_started : need_more; \ } /* Maximum stored block length in deflate format (not including header). */ #define MAX_STORED 65535 /* Minimum of a and b. */ #define MIN(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a)) /* =========================================================================== * Copy without compression as much as possible from the input stream, return * the current block state. * * In case deflateParams() is used to later switch to a non-zero compression * level, s->matches (otherwise unused when storing) keeps track of the number * of hash table slides to perform. If s->matches is 1, then one hash table * slide will be done when switching. If s->matches is 2, the maximum value * allowed here, then the hash table will be cleared, since two or more slides * is the same as a clear. * * deflate_stored() is written to minimize the number of times an input byte is * copied. It is most efficient with large input and output buffers, which * maximizes the opportunities to have a single copy from next_in to next_out. */ local block_state deflate_stored(deflate_state *s, int flush) { /* Smallest worthy block size when not flushing or finishing. By default * this is 32K. This can be as small as 507 bytes for memLevel == 1. For * large input and output buffers, the stored block size will be larger. */ unsigned min_block = MIN(s->pending_buf_size - 5, s->w_size); /* Copy as many min_block or larger stored blocks directly to next_out as * possible. If flushing, copy the remaining available input to next_out as * stored blocks, if there is enough space. */ unsigned len, left, have, last = 0; unsigned used = s->strm->avail_in; do { /* Set len to the maximum size block that we can copy directly with the * available input data and output space. Set left to how much of that * would be copied from what's left in the window. */ len = MAX_STORED; /* maximum deflate stored block length */ have = (s->bi_valid + 42) >> 3; /* number of header bytes */ if (s->strm->avail_out < have) /* need room for header */ break; /* maximum stored block length that will fit in avail_out: */ have = s->strm->avail_out - have; left = s->strstart - s->block_start; /* bytes left in window */ if (len > (ulg)left + s->strm->avail_in) len = left + s->strm->avail_in; /* limit len to the input */ if (len > have) len = have; /* limit len to the output */ /* If the stored block would be less than min_block in length, or if * unable to copy all of the available input when flushing, then try * copying to the window and the pending buffer instead. Also don't * write an empty block when flushing -- deflate() does that. */ if (len < min_block && ((len == 0 && flush != Z_FINISH) || flush == Z_NO_FLUSH || len != left + s->strm->avail_in)) break; /* Make a dummy stored block in pending to get the header bytes, * including any pending bits. This also updates the debugging counts. */ last = flush == Z_FINISH && len == left + s->strm->avail_in ? 1 : 0; _tr_stored_block(s, (char *)0, 0L, last); /* Replace the lengths in the dummy stored block with len. */ s->pending_buf[s->pending - 4] = len; s->pending_buf[s->pending - 3] = len >> 8; s->pending_buf[s->pending - 2] = ~len; s->pending_buf[s->pending - 1] = ~len >> 8; /* Write the stored block header bytes. */ flush_pending(s->strm); #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG /* Update debugging counts for the data about to be copied. */ s->compressed_len += len << 3; s->bits_sent += len << 3; #endif /* Copy uncompressed bytes from the window to next_out. */ if (left) { if (left > len) left = len; zmemcpy(s->strm->next_out, s->window + s->block_start, left); s->strm->next_out += left; s->strm->avail_out -= left; s->strm->total_out += left; s->block_start += left; len -= left; } /* Copy uncompressed bytes directly from next_in to next_out, updating * the check value. */ if (len) { read_buf(s->strm, s->strm->next_out, len); s->strm->next_out += len; s->strm->avail_out -= len; s->strm->total_out += len; } } while (last == 0); /* Update the sliding window with the last s->w_size bytes of the copied * data, or append all of the copied data to the existing window if less * than s->w_size bytes were copied. Also update the number of bytes to * insert in the hash tables, in the event that deflateParams() switches to * a non-zero compression level. */ used -= s->strm->avail_in; /* number of input bytes directly copied */ if (used) { /* If any input was used, then no unused input remains in the window, * therefore s->block_start == s->strstart. */ if (used >= s->w_size) { /* supplant the previous history */ s->matches = 2; /* clear hash */ zmemcpy(s->window, s->strm->next_in - s->w_size, s->w_size); s->strstart = s->w_size; s->insert = s->strstart; } else { if (s->window_size - s->strstart <= used) { /* Slide the window down. */ s->strstart -= s->w_size; zmemcpy(s->window, s->window + s->w_size, s->strstart); if (s->matches < 2) s->matches++; /* add a pending slide_hash() */ if (s->insert > s->strstart) s->insert = s->strstart; } zmemcpy(s->window + s->strstart, s->strm->next_in - used, used); s->strstart += used; s->insert += MIN(used, s->w_size - s->insert); } s->block_start = s->strstart; } if (s->high_water < s->strstart) s->high_water = s->strstart; /* If the last block was written to next_out, then done. */ if (last) return finish_done; /* If flushing and all input has been consumed, then done. */ if (flush != Z_NO_FLUSH && flush != Z_FINISH && s->strm->avail_in == 0 && (long)s->strstart == s->block_start) return block_done; /* Fill the window with any remaining input. */ have = s->window_size - s->strstart; if (s->strm->avail_in > have && s->block_start >= (long)s->w_size) { /* Slide the window down. */ s->block_start -= s->w_size; s->strstart -= s->w_size; zmemcpy(s->window, s->window + s->w_size, s->strstart); if (s->matches < 2) s->matches++; /* add a pending slide_hash() */ have += s->w_size; /* more space now */ if (s->insert > s->strstart) s->insert = s->strstart; } if (have > s->strm->avail_in) have = s->strm->avail_in; if (have) { read_buf(s->strm, s->window + s->strstart, have); s->strstart += have; s->insert += MIN(have, s->w_size - s->insert); } if (s->high_water < s->strstart) s->high_water = s->strstart; /* There was not enough avail_out to write a complete worthy or flushed * stored block to next_out. Write a stored block to pending instead, if we * have enough input for a worthy block, or if flushing and there is enough * room for the remaining input as a stored block in the pending buffer. */ have = (s->bi_valid + 42) >> 3; /* number of header bytes */ /* maximum stored block length that will fit in pending: */ have = MIN(s->pending_buf_size - have, MAX_STORED); min_block = MIN(have, s->w_size); left = s->strstart - s->block_start; if (left >= min_block || ((left || flush == Z_FINISH) && flush != Z_NO_FLUSH && s->strm->avail_in == 0 && left <= have)) { len = MIN(left, have); last = flush == Z_FINISH && s->strm->avail_in == 0 && len == left ? 1 : 0; _tr_stored_block(s, (charf *)s->window + s->block_start, len, last); s->block_start += len; flush_pending(s->strm); } /* We've done all we can with the available input and output. */ return last ? finish_started : need_more; } /* =========================================================================== * Compress as much as possible from the input stream, return the current * block state. * This function does not perform lazy evaluation of matches and inserts * new strings in the dictionary only for unmatched strings or for short * matches. It is used only for the fast compression options. */ local block_state deflate_fast(deflate_state *s, int flush) { IPos hash_head; /* head of the hash chain */ int bflush; /* set if current block must be flushed */ for (;;) { /* Make sure that we always have enough lookahead, except * at the end of the input file. We need MAX_MATCH bytes * for the next match, plus MIN_MATCH bytes to insert the * string following the next match. */ if (s->lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD) { fill_window(s); if (s->lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD && flush == Z_NO_FLUSH) { return need_more; } if (s->lookahead == 0) break; /* flush the current block */ } /* Insert the string window[strstart .. strstart + 2] in the * dictionary, and set hash_head to the head of the hash chain: */ hash_head = NIL; if (s->lookahead >= MIN_MATCH) { INSERT_STRING(s, s->strstart, hash_head); } /* Find the longest match, discarding those <= prev_length. * At this point we have always match_length < MIN_MATCH */ if (hash_head != NIL && s->strstart - hash_head <= MAX_DIST(s)) { /* To simplify the code, we prevent matches with the string * of window index 0 (in particular we have to avoid a match * of the string with itself at the start of the input file). */ s->match_length = longest_match (s, hash_head); /* longest_match() sets match_start */ } if (s->match_length >= MIN_MATCH) { check_match(s, s->strstart, s->match_start, s->match_length); _tr_tally_dist(s, s->strstart - s->match_start, s->match_length - MIN_MATCH, bflush); s->lookahead -= s->match_length; /* Insert new strings in the hash table only if the match length * is not too large. This saves time but degrades compression. */ #ifndef FASTEST if (s->match_length <= s->max_insert_length && s->lookahead >= MIN_MATCH) { s->match_length--; /* string at strstart already in table */ do { s->strstart++; INSERT_STRING(s, s->strstart, hash_head); /* strstart never exceeds WSIZE-MAX_MATCH, so there are * always MIN_MATCH bytes ahead. */ } while (--s->match_length != 0); s->strstart++; } else #endif { s->strstart += s->match_length; s->match_length = 0; s->ins_h = s->window[s->strstart]; UPDATE_HASH(s, s->ins_h, s->window[s->strstart + 1]); #if MIN_MATCH != 3 Call UPDATE_HASH() MIN_MATCH-3 more times #endif /* If lookahead < MIN_MATCH, ins_h is garbage, but it does not * matter since it will be recomputed at next deflate call. */ } } else { /* No match, output a literal byte */ Tracevv((stderr,"%c", s->window[s->strstart])); _tr_tally_lit(s, s->window[s->strstart], bflush); s->lookahead--; s->strstart++; } if (bflush) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); } s->insert = s->strstart < MIN_MATCH-1 ? s->strstart : MIN_MATCH-1; if (flush == Z_FINISH) { FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 1); return finish_done; } if (s->sym_next) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); return block_done; } #ifndef FASTEST /* =========================================================================== * Same as above, but achieves better compression. We use a lazy * evaluation for matches: a match is finally adopted only if there is * no better match at the next window position. */ local block_state deflate_slow(deflate_state *s, int flush) { IPos hash_head; /* head of hash chain */ int bflush; /* set if current block must be flushed */ /* Process the input block. */ for (;;) { /* Make sure that we always have enough lookahead, except * at the end of the input file. We need MAX_MATCH bytes * for the next match, plus MIN_MATCH bytes to insert the * string following the next match. */ if (s->lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD) { fill_window(s); if (s->lookahead < MIN_LOOKAHEAD && flush == Z_NO_FLUSH) { return need_more; } if (s->lookahead == 0) break; /* flush the current block */ } /* Insert the string window[strstart .. strstart + 2] in the * dictionary, and set hash_head to the head of the hash chain: */ hash_head = NIL; if (s->lookahead >= MIN_MATCH) { INSERT_STRING(s, s->strstart, hash_head); } /* Find the longest match, discarding those <= prev_length. */ s->prev_length = s->match_length, s->prev_match = s->match_start; s->match_length = MIN_MATCH-1; if (hash_head != NIL && s->prev_length < s->max_lazy_match && s->strstart - hash_head <= MAX_DIST(s)) { /* To simplify the code, we prevent matches with the string * of window index 0 (in particular we have to avoid a match * of the string with itself at the start of the input file). */ s->match_length = longest_match (s, hash_head); /* longest_match() sets match_start */ if (s->match_length <= 5 && (s->strategy == Z_FILTERED #if TOO_FAR <= 32767 || (s->match_length == MIN_MATCH && s->strstart - s->match_start > TOO_FAR) #endif )) { /* If prev_match is also MIN_MATCH, match_start is garbage * but we will ignore the current match anyway. */ s->match_length = MIN_MATCH-1; } } /* If there was a match at the previous step and the current * match is not better, output the previous match: */ if (s->prev_length >= MIN_MATCH && s->match_length <= s->prev_length) { uInt max_insert = s->strstart + s->lookahead - MIN_MATCH; /* Do not insert strings in hash table beyond this. */ check_match(s, s->strstart - 1, s->prev_match, s->prev_length); _tr_tally_dist(s, s->strstart - 1 - s->prev_match, s->prev_length - MIN_MATCH, bflush); /* Insert in hash table all strings up to the end of the match. * strstart - 1 and strstart are already inserted. If there is not * enough lookahead, the last two strings are not inserted in * the hash table. */ s->lookahead -= s->prev_length - 1; s->prev_length -= 2; do { if (++s->strstart <= max_insert) { INSERT_STRING(s, s->strstart, hash_head); } } while (--s->prev_length != 0); s->match_available = 0; s->match_length = MIN_MATCH-1; s->strstart++; if (bflush) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); } else if (s->match_available) { /* If there was no match at the previous position, output a * single literal. If there was a match but the current match * is longer, truncate the previous match to a single literal. */ Tracevv((stderr,"%c", s->window[s->strstart - 1])); _tr_tally_lit(s, s->window[s->strstart - 1], bflush); if (bflush) { FLUSH_BLOCK_ONLY(s, 0); } s->strstart++; s->lookahead--; if (s->strm->avail_out == 0) return need_more; } else { /* There is no previous match to compare with, wait for * the next step to decide. */ s->match_available = 1; s->strstart++; s->lookahead--; } } Assert (flush != Z_NO_FLUSH, "no flush?"); if (s->match_available) { Tracevv((stderr,"%c", s->window[s->strstart - 1])); _tr_tally_lit(s, s->window[s->strstart - 1], bflush); s->match_available = 0; } s->insert = s->strstart < MIN_MATCH-1 ? s->strstart : MIN_MATCH-1; if (flush == Z_FINISH) { FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 1); return finish_done; } if (s->sym_next) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); return block_done; } #endif /* FASTEST */ /* =========================================================================== * For Z_RLE, simply look for runs of bytes, generate matches only of distance * one. Do not maintain a hash table. (It will be regenerated if this run of * deflate switches away from Z_RLE.) */ local block_state deflate_rle(deflate_state *s, int flush) { int bflush; /* set if current block must be flushed */ uInt prev; /* byte at distance one to match */ Bytef *scan, *strend; /* scan goes up to strend for length of run */ for (;;) { /* Make sure that we always have enough lookahead, except * at the end of the input file. We need MAX_MATCH bytes * for the longest run, plus one for the unrolled loop. */ if (s->lookahead <= MAX_MATCH) { fill_window(s); if (s->lookahead <= MAX_MATCH && flush == Z_NO_FLUSH) { return need_more; } if (s->lookahead == 0) break; /* flush the current block */ } /* See how many times the previous byte repeats */ s->match_length = 0; if (s->lookahead >= MIN_MATCH && s->strstart > 0) { scan = s->window + s->strstart - 1; prev = *scan; if (prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan) { strend = s->window + s->strstart + MAX_MATCH; do { } while (prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && prev == *++scan && scan < strend); s->match_length = MAX_MATCH - (uInt)(strend - scan); if (s->match_length > s->lookahead) s->match_length = s->lookahead; } Assert(scan <= s->window + (uInt)(s->window_size - 1), "wild scan"); } /* Emit match if have run of MIN_MATCH or longer, else emit literal */ if (s->match_length >= MIN_MATCH) { check_match(s, s->strstart, s->strstart - 1, s->match_length); _tr_tally_dist(s, 1, s->match_length - MIN_MATCH, bflush); s->lookahead -= s->match_length; s->strstart += s->match_length; s->match_length = 0; } else { /* No match, output a literal byte */ Tracevv((stderr,"%c", s->window[s->strstart])); _tr_tally_lit(s, s->window[s->strstart], bflush); s->lookahead--; s->strstart++; } if (bflush) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); } s->insert = 0; if (flush == Z_FINISH) { FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 1); return finish_done; } if (s->sym_next) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); return block_done; } /* =========================================================================== * For Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY, do not look for matches. Do not maintain a hash table. * (It will be regenerated if this run of deflate switches away from Huffman.) */ local block_state deflate_huff(deflate_state *s, int flush) { int bflush; /* set if current block must be flushed */ for (;;) { /* Make sure that we have a literal to write. */ if (s->lookahead == 0) { fill_window(s); if (s->lookahead == 0) { if (flush == Z_NO_FLUSH) return need_more; break; /* flush the current block */ } } /* Output a literal byte */ s->match_length = 0; Tracevv((stderr,"%c", s->window[s->strstart])); _tr_tally_lit(s, s->window[s->strstart], bflush); s->lookahead--; s->strstart++; if (bflush) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); } s->insert = 0; if (flush == Z_FINISH) { FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 1); return finish_done; } if (s->sym_next) FLUSH_BLOCK(s, 0); return block_done; }
• inflateBackInit_ • fixedtables • inflateBack • inflateBackEnd
/* infback.c -- inflate using a call-back interface * Copyright (C) 1995-2022 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* This code is largely copied from inflate.c. Normally either infback.o or inflate.o would be linked into an application--not both. The interface with inffast.c is retained so that optimized assembler-coded versions of inflate_fast() can be used with either inflate.c or infback.c. */ #include "zutil.h" #include "inftrees.h" #include "inflate.h" #include "inffast.h" /* strm provides memory allocation functions in zalloc and zfree, or Z_NULL to use the library memory allocation functions. windowBits is in the range 8..15, and window is a user-supplied window and output buffer that is 2**windowBits bytes. */ int ZEXPORT inflateBackInit_(z_streamp strm, int windowBits, unsigned char FAR *window, const char *version, int stream_size) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (version == Z_NULL || version[0] != ZLIB_VERSION[0] || stream_size != (int)(sizeof(z_stream))) return Z_VERSION_ERROR; if (strm == Z_NULL || window == Z_NULL || windowBits < 8 || windowBits > 15) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; strm->msg = Z_NULL; /* in case we return an error */ if (strm->zalloc == (alloc_func)0) { #ifdef Z_SOLO return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else strm->zalloc = zcalloc; strm->opaque = (voidpf)0; #endif } if (strm->zfree == (free_func)0) #ifdef Z_SOLO return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else strm->zfree = zcfree; #endif state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)ZALLOC(strm, 1, sizeof(struct inflate_state)); if (state == Z_NULL) return Z_MEM_ERROR; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: allocated\n")); strm->state = (struct internal_state FAR *)state; state->dmax = 32768U; state->wbits = (uInt)windowBits; state->wsize = 1U << windowBits; state->window = window; state->wnext = 0; state->whave = 0; state->sane = 1; return Z_OK; } /* Return state with length and distance decoding tables and index sizes set to fixed code decoding. Normally this returns fixed tables from inffixed.h. If BUILDFIXED is defined, then instead this routine builds the tables the first time it's called, and returns those tables the first time and thereafter. This reduces the size of the code by about 2K bytes, in exchange for a little execution time. However, BUILDFIXED should not be used for threaded applications, since the rewriting of the tables and virgin may not be thread-safe. */ local void fixedtables(struct inflate_state FAR *state) { #ifdef BUILDFIXED static int virgin = 1; static code *lenfix, *distfix; static code fixed[544]; /* build fixed huffman tables if first call (may not be thread safe) */ if (virgin) { unsigned sym, bits; static code *next; /* literal/length table */ sym = 0; while (sym < 144) state->lens[sym++] = 8; while (sym < 256) state->lens[sym++] = 9; while (sym < 280) state->lens[sym++] = 7; while (sym < 288) state->lens[sym++] = 8; next = fixed; lenfix = next; bits = 9; inflate_table(LENS, state->lens, 288, &(next), &(bits), state->work); /* distance table */ sym = 0; while (sym < 32) state->lens[sym++] = 5; distfix = next; bits = 5; inflate_table(DISTS, state->lens, 32, &(next), &(bits), state->work); /* do this just once */ virgin = 0; } #else /* !BUILDFIXED */ # include "inffixed.h" #endif /* BUILDFIXED */ state->lencode = lenfix; state->lenbits = 9; state->distcode = distfix; state->distbits = 5; } /* Macros for inflateBack(): */ /* Load returned state from inflate_fast() */ #define LOAD() \ do { \ put = strm->next_out; \ left = strm->avail_out; \ next = strm->next_in; \ have = strm->avail_in; \ hold = state->hold; \ bits = state->bits; \ } while (0) /* Set state from registers for inflate_fast() */ #define RESTORE() \ do { \ strm->next_out = put; \ strm->avail_out = left; \ strm->next_in = next; \ strm->avail_in = have; \ state->hold = hold; \ state->bits = bits; \ } while (0) /* Clear the input bit accumulator */ #define INITBITS() \ do { \ hold = 0; \ bits = 0; \ } while (0) /* Assure that some input is available. If input is requested, but denied, then return a Z_BUF_ERROR from inflateBack(). */ #define PULL() \ do { \ if (have == 0) { \ have = in(in_desc, &next); \ if (have == 0) { \ next = Z_NULL; \ ret = Z_BUF_ERROR; \ goto inf_leave; \ } \ } \ } while (0) /* Get a byte of input into the bit accumulator, or return from inflateBack() with an error if there is no input available. */ #define PULLBYTE() \ do { \ PULL(); \ have--; \ hold += (unsigned long)(*next++) << bits; \ bits += 8; \ } while (0) /* Assure that there are at least n bits in the bit accumulator. If there is not enough available input to do that, then return from inflateBack() with an error. */ #define NEEDBITS(n) \ do { \ while (bits < (unsigned)(n)) \ PULLBYTE(); \ } while (0) /* Return the low n bits of the bit accumulator (n < 16) */ #define BITS(n) \ ((unsigned)hold & ((1U << (n)) - 1)) /* Remove n bits from the bit accumulator */ #define DROPBITS(n) \ do { \ hold >>= (n); \ bits -= (unsigned)(n); \ } while (0) /* Remove zero to seven bits as needed to go to a byte boundary */ #define BYTEBITS() \ do { \ hold >>= bits & 7; \ bits -= bits & 7; \ } while (0) /* Assure that some output space is available, by writing out the window if it's full. If the write fails, return from inflateBack() with a Z_BUF_ERROR. */ #define ROOM() \ do { \ if (left == 0) { \ put = state->window; \ left = state->wsize; \ state->whave = left; \ if (out(out_desc, put, left)) { \ ret = Z_BUF_ERROR; \ goto inf_leave; \ } \ } \ } while (0) /* strm provides the memory allocation functions and window buffer on input, and provides information on the unused input on return. For Z_DATA_ERROR returns, strm will also provide an error message. in() and out() are the call-back input and output functions. When inflateBack() needs more input, it calls in(). When inflateBack() has filled the window with output, or when it completes with data in the window, it calls out() to write out the data. The application must not change the provided input until in() is called again or inflateBack() returns. The application must not change the window/output buffer until inflateBack() returns. in() and out() are called with a descriptor parameter provided in the inflateBack() call. This parameter can be a structure that provides the information required to do the read or write, as well as accumulated information on the input and output such as totals and check values. in() should return zero on failure. out() should return non-zero on failure. If either in() or out() fails, than inflateBack() returns a Z_BUF_ERROR. strm->next_in can be checked for Z_NULL to see whether it was in() or out() that caused in the error. Otherwise, inflateBack() returns Z_STREAM_END on success, Z_DATA_ERROR for an deflate format error, or Z_MEM_ERROR if it could not allocate memory for the state. inflateBack() can also return Z_STREAM_ERROR if the input parameters are not correct, i.e. strm is Z_NULL or the state was not initialized. */ int ZEXPORT inflateBack(z_streamp strm, in_func in, void FAR *in_desc, out_func out, void FAR *out_desc) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; z_const unsigned char FAR *next; /* next input */ unsigned char FAR *put; /* next output */ unsigned have, left; /* available input and output */ unsigned long hold; /* bit buffer */ unsigned bits; /* bits in bit buffer */ unsigned copy; /* number of stored or match bytes to copy */ unsigned char FAR *from; /* where to copy match bytes from */ code here; /* current decoding table entry */ code last; /* parent table entry */ unsigned len; /* length to copy for repeats, bits to drop */ int ret; /* return code */ static const unsigned short order[19] = /* permutation of code lengths */ {16, 17, 18, 0, 8, 7, 9, 6, 10, 5, 11, 4, 12, 3, 13, 2, 14, 1, 15}; /* Check that the strm exists and that the state was initialized */ if (strm == Z_NULL || strm->state == Z_NULL) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; /* Reset the state */ strm->msg = Z_NULL; state->mode = TYPE; state->last = 0; state->whave = 0; next = strm->next_in; have = next != Z_NULL ? strm->avail_in : 0; hold = 0; bits = 0; put = state->window; left = state->wsize; /* Inflate until end of block marked as last */ for (;;) switch (state->mode) { case TYPE: /* determine and dispatch block type */ if (state->last) { BYTEBITS(); state->mode = DONE; break; } NEEDBITS(3); state->last = BITS(1); DROPBITS(1); switch (BITS(2)) { case 0: /* stored block */ Tracev((stderr, "inflate: stored block%s\n", state->last ? " (last)" : "")); state->mode = STORED; break; case 1: /* fixed block */ fixedtables(state); Tracev((stderr, "inflate: fixed codes block%s\n", state->last ? " (last)" : "")); state->mode = LEN; /* decode codes */ break; case 2: /* dynamic block */ Tracev((stderr, "inflate: dynamic codes block%s\n", state->last ? " (last)" : "")); state->mode = TABLE; break; case 3: strm->msg = (char *)"invalid block type"; state->mode = BAD; } DROPBITS(2); break; case STORED: /* get and verify stored block length */ BYTEBITS(); /* go to byte boundary */ NEEDBITS(32); if ((hold & 0xffff) != ((hold >> 16) ^ 0xffff)) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid stored block lengths"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->length = (unsigned)hold & 0xffff; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: stored length %u\n", state->length)); INITBITS(); /* copy stored block from input to output */ while (state->length != 0) { copy = state->length; PULL(); ROOM(); if (copy > have) copy = have; if (copy > left) copy = left; zmemcpy(put, next, copy); have -= copy; next += copy; left -= copy; put += copy; state->length -= copy; } Tracev((stderr, "inflate: stored end\n")); state->mode = TYPE; break; case TABLE: /* get dynamic table entries descriptor */ NEEDBITS(14); state->nlen = BITS(5) + 257; DROPBITS(5); state->ndist = BITS(5) + 1; DROPBITS(5); state->ncode = BITS(4) + 4; DROPBITS(4); #ifndef PKZIP_BUG_WORKAROUND if (state->nlen > 286 || state->ndist > 30) { strm->msg = (char *)"too many length or distance symbols"; state->mode = BAD; break; } #endif Tracev((stderr, "inflate: table sizes ok\n")); /* get code length code lengths (not a typo) */ state->have = 0; while (state->have < state->ncode) { NEEDBITS(3); state->lens[order[state->have++]] = (unsigned short)BITS(3); DROPBITS(3); } while (state->have < 19) state->lens[order[state->have++]] = 0; state->next = state->codes; state->lencode = (code const FAR *)(state->next); state->lenbits = 7; ret = inflate_table(CODES, state->lens, 19, &(state->next), &(state->lenbits), state->work); if (ret) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid code lengths set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } Tracev((stderr, "inflate: code lengths ok\n")); /* get length and distance code code lengths */ state->have = 0; while (state->have < state->nlen + state->ndist) { for (;;) { here = state->lencode[BITS(state->lenbits)]; if ((unsigned)(here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } if (here.val < 16) { DROPBITS(here.bits); state->lens[state->have++] = here.val; } else { if (here.val == 16) { NEEDBITS(here.bits + 2); DROPBITS(here.bits); if (state->have == 0) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid bit length repeat"; state->mode = BAD; break; } len = (unsigned)(state->lens[state->have - 1]); copy = 3 + BITS(2); DROPBITS(2); } else if (here.val == 17) { NEEDBITS(here.bits + 3); DROPBITS(here.bits); len = 0; copy = 3 + BITS(3); DROPBITS(3); } else { NEEDBITS(here.bits + 7); DROPBITS(here.bits); len = 0; copy = 11 + BITS(7); DROPBITS(7); } if (state->have + copy > state->nlen + state->ndist) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid bit length repeat"; state->mode = BAD; break; } while (copy--) state->lens[state->have++] = (unsigned short)len; } } /* handle error breaks in while */ if (state->mode == BAD) break; /* check for end-of-block code (better have one) */ if (state->lens[256] == 0) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid code -- missing end-of-block"; state->mode = BAD; break; } /* build code tables -- note: do not change the lenbits or distbits values here (9 and 6) without reading the comments in inftrees.h concerning the ENOUGH constants, which depend on those values */ state->next = state->codes; state->lencode = (code const FAR *)(state->next); state->lenbits = 9; ret = inflate_table(LENS, state->lens, state->nlen, &(state->next), &(state->lenbits), state->work); if (ret) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid literal/lengths set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->distcode = (code const FAR *)(state->next); state->distbits = 6; ret = inflate_table(DISTS, state->lens + state->nlen, state->ndist, &(state->next), &(state->distbits), state->work); if (ret) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distances set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } Tracev((stderr, "inflate: codes ok\n")); state->mode = LEN; /* fallthrough */ case LEN: /* use inflate_fast() if we have enough input and output */ if (have >= 6 && left >= 258) { RESTORE(); if (state->whave < state->wsize) state->whave = state->wsize - left; inflate_fast(strm, state->wsize); LOAD(); break; } /* get a literal, length, or end-of-block code */ for (;;) { here = state->lencode[BITS(state->lenbits)]; if ((unsigned)(here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } if (here.op && (here.op & 0xf0) == 0) { last = here; for (;;) { here = state->lencode[last.val + (BITS(last.bits + last.op) >> last.bits)]; if ((unsigned)(last.bits + here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } DROPBITS(last.bits); } DROPBITS(here.bits); state->length = (unsigned)here.val; /* process literal */ if (here.op == 0) { Tracevv((stderr, here.val >= 0x20 && here.val < 0x7f ? "inflate: literal '%c'\n" : "inflate: literal 0x%02x\n", here.val)); ROOM(); *put++ = (unsigned char)(state->length); left--; state->mode = LEN; break; } /* process end of block */ if (here.op & 32) { Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: end of block\n")); state->mode = TYPE; break; } /* invalid code */ if (here.op & 64) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid literal/length code"; state->mode = BAD; break; } /* length code -- get extra bits, if any */ state->extra = (unsigned)(here.op) & 15; if (state->extra != 0) { NEEDBITS(state->extra); state->length += BITS(state->extra); DROPBITS(state->extra); } Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: length %u\n", state->length)); /* get distance code */ for (;;) { here = state->distcode[BITS(state->distbits)]; if ((unsigned)(here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } if ((here.op & 0xf0) == 0) { last = here; for (;;) { here = state->distcode[last.val + (BITS(last.bits + last.op) >> last.bits)]; if ((unsigned)(last.bits + here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } DROPBITS(last.bits); } DROPBITS(here.bits); if (here.op & 64) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance code"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->offset = (unsigned)here.val; /* get distance extra bits, if any */ state->extra = (unsigned)(here.op) & 15; if (state->extra != 0) { NEEDBITS(state->extra); state->offset += BITS(state->extra); DROPBITS(state->extra); } if (state->offset > state->wsize - (state->whave < state->wsize ? left : 0)) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance too far back"; state->mode = BAD; break; } Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: distance %u\n", state->offset)); /* copy match from window to output */ do { ROOM(); copy = state->wsize - state->offset; if (copy < left) { from = put + copy; copy = left - copy; } else { from = put - state->offset; copy = left; } if (copy > state->length) copy = state->length; state->length -= copy; left -= copy; do { *put++ = *from++; } while (--copy); } while (state->length != 0); break; case DONE: /* inflate stream terminated properly */ ret = Z_STREAM_END; goto inf_leave; case BAD: ret = Z_DATA_ERROR; goto inf_leave; default: /* can't happen, but makes compilers happy */ ret = Z_STREAM_ERROR; goto inf_leave; } /* Write leftover output and return unused input */ inf_leave: if (left < state->wsize) { if (out(out_desc, state->window, state->wsize - left) && ret == Z_STREAM_END) ret = Z_BUF_ERROR; } strm->next_in = next; strm->avail_in = have; return ret; } int ZEXPORT inflateBackEnd(z_streamp strm) { if (strm == Z_NULL || strm->state == Z_NULL || strm->zfree == (free_func)0) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; ZFREE(strm, strm->state); strm->state = Z_NULL; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: end\n")); return Z_OK; }
/* inffast.c -- fast decoding * Copyright (C) 1995-2017 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ #include "zutil.h" #include "inftrees.h" #include "inflate.h" #include "inffast.h" #ifdef ASMINF # pragma message("Assembler code may have bugs -- use at your own risk") #else /* Decode literal, length, and distance codes and write out the resulting literal and match bytes until either not enough input or output is available, an end-of-block is encountered, or a data error is encountered. When large enough input and output buffers are supplied to inflate(), for example, a 16K input buffer and a 64K output buffer, more than 95% of the inflate execution time is spent in this routine. Entry assumptions: state->mode == LEN strm->avail_in >= 6 strm->avail_out >= 258 start >= strm->avail_out state->bits < 8 On return, state->mode is one of: LEN -- ran out of enough output space or enough available input TYPE -- reached end of block code, inflate() to interpret next block BAD -- error in block data Notes: - The maximum input bits used by a length/distance pair is 15 bits for the length code, 5 bits for the length extra, 15 bits for the distance code, and 13 bits for the distance extra. This totals 48 bits, or six bytes. Therefore if strm->avail_in >= 6, then there is enough input to avoid checking for available input while decoding. - The maximum bytes that a single length/distance pair can output is 258 bytes, which is the maximum length that can be coded. inflate_fast() requires strm->avail_out >= 258 for each loop to avoid checking for output space. */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL inflate_fast(z_streamp strm, unsigned start) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; z_const unsigned char FAR *in; /* local strm->next_in */ z_const unsigned char FAR *last; /* have enough input while in < last */ unsigned char FAR *out; /* local strm->next_out */ unsigned char FAR *beg; /* inflate()'s initial strm->next_out */ unsigned char FAR *end; /* while out < end, enough space available */ #ifdef INFLATE_STRICT unsigned dmax; /* maximum distance from zlib header */ #endif unsigned wsize; /* window size or zero if not using window */ unsigned whave; /* valid bytes in the window */ unsigned wnext; /* window write index */ unsigned char FAR *window; /* allocated sliding window, if wsize != 0 */ unsigned long hold; /* local strm->hold */ unsigned bits; /* local strm->bits */ code const FAR *lcode; /* local strm->lencode */ code const FAR *dcode; /* local strm->distcode */ unsigned lmask; /* mask for first level of length codes */ unsigned dmask; /* mask for first level of distance codes */ code const *here; /* retrieved table entry */ unsigned op; /* code bits, operation, extra bits, or */ /* window position, window bytes to copy */ unsigned len; /* match length, unused bytes */ unsigned dist; /* match distance */ unsigned char FAR *from; /* where to copy match from */ /* copy state to local variables */ state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; in = strm->next_in; last = in + (strm->avail_in - 5); out = strm->next_out; beg = out - (start - strm->avail_out); end = out + (strm->avail_out - 257); #ifdef INFLATE_STRICT dmax = state->dmax; #endif wsize = state->wsize; whave = state->whave; wnext = state->wnext; window = state->window; hold = state->hold; bits = state->bits; lcode = state->lencode; dcode = state->distcode; lmask = (1U << state->lenbits) - 1; dmask = (1U << state->distbits) - 1; /* decode literals and length/distances until end-of-block or not enough input data or output space */ do { if (bits < 15) { hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; } here = lcode + (hold & lmask); dolen: op = (unsigned)(here->bits); hold >>= op; bits -= op; op = (unsigned)(here->op); if (op == 0) { /* literal */ Tracevv((stderr, here->val >= 0x20 && here->val < 0x7f ? "inflate: literal '%c'\n" : "inflate: literal 0x%02x\n", here->val)); *out++ = (unsigned char)(here->val); } else if (op & 16) { /* length base */ len = (unsigned)(here->val); op &= 15; /* number of extra bits */ if (op) { if (bits < op) { hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; } len += (unsigned)hold & ((1U << op) - 1); hold >>= op; bits -= op; } Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: length %u\n", len)); if (bits < 15) { hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; } here = dcode + (hold & dmask); dodist: op = (unsigned)(here->bits); hold >>= op; bits -= op; op = (unsigned)(here->op); if (op & 16) { /* distance base */ dist = (unsigned)(here->val); op &= 15; /* number of extra bits */ if (bits < op) { hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; if (bits < op) { hold += (unsigned long)(*in++) << bits; bits += 8; } } dist += (unsigned)hold & ((1U << op) - 1); #ifdef INFLATE_STRICT if (dist > dmax) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance too far back"; state->mode = BAD; break; } #endif hold >>= op; bits -= op; Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: distance %u\n", dist)); op = (unsigned)(out - beg); /* max distance in output */ if (dist > op) { /* see if copy from window */ op = dist - op; /* distance back in window */ if (op > whave) { if (state->sane) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance too far back"; state->mode = BAD; break; } #ifdef INFLATE_ALLOW_INVALID_DISTANCE_TOOFAR_ARRR if (len <= op - whave) { do { *out++ = 0; } while (--len); continue; } len -= op - whave; do { *out++ = 0; } while (--op > whave); if (op == 0) { from = out - dist; do { *out++ = *from++; } while (--len); continue; } #endif } from = window; if (wnext == 0) { /* very common case */ from += wsize - op; if (op < len) { /* some from window */ len -= op; do { *out++ = *from++; } while (--op); from = out - dist; /* rest from output */ } } else if (wnext < op) { /* wrap around window */ from += wsize + wnext - op; op -= wnext; if (op < len) { /* some from end of window */ len -= op; do { *out++ = *from++; } while (--op); from = window; if (wnext < len) { /* some from start of window */ op = wnext; len -= op; do { *out++ = *from++; } while (--op); from = out - dist; /* rest from output */ } } } else { /* contiguous in window */ from += wnext - op; if (op < len) { /* some from window */ len -= op; do { *out++ = *from++; } while (--op); from = out - dist; /* rest from output */ } } while (len > 2) { *out++ = *from++; *out++ = *from++; *out++ = *from++; len -= 3; } if (len) { *out++ = *from++; if (len > 1) *out++ = *from++; } } else { from = out - dist; /* copy direct from output */ do { /* minimum length is three */ *out++ = *from++; *out++ = *from++; *out++ = *from++; len -= 3; } while (len > 2); if (len) { *out++ = *from++; if (len > 1) *out++ = *from++; } } } else if ((op & 64) == 0) { /* 2nd level distance code */ here = dcode + here->val + (hold & ((1U << op) - 1)); goto dodist; } else { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance code"; state->mode = BAD; break; } } else if ((op & 64) == 0) { /* 2nd level length code */ here = lcode + here->val + (hold & ((1U << op) - 1)); goto dolen; } else if (op & 32) { /* end-of-block */ Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: end of block\n")); state->mode = TYPE; break; } else { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid literal/length code"; state->mode = BAD; break; } } while (in < last && out < end); /* return unused bytes (on entry, bits < 8, so in won't go too far back) */ len = bits >> 3; in -= len; bits -= len << 3; hold &= (1U << bits) - 1; /* update state and return */ strm->next_in = in; strm->next_out = out; strm->avail_in = (unsigned)(in < last ? 5 + (last - in) : 5 - (in - last)); strm->avail_out = (unsigned)(out < end ? 257 + (end - out) : 257 - (out - end)); state->hold = hold; state->bits = bits; return; } /* inflate_fast() speedups that turned out slower (on a PowerPC G3 750CXe): - Using bit fields for code structure - Different op definition to avoid & for extra bits (do & for table bits) - Three separate decoding do-loops for direct, window, and wnext == 0 - Special case for distance > 1 copies to do overlapped load and store copy - Explicit branch predictions (based on measured branch probabilities) - Deferring match copy and interspersed it with decoding subsequent codes - Swapping literal/length else - Swapping window/direct else - Larger unrolled copy loops (three is about right) - Moving len -= 3 statement into middle of loop */ #endif /* !ASMINF */
• inflateStateCheck • inflateResetKeep • inflateReset • inflateReset2 • inflateInit2_ • inflateInit_ • inflatePrime • fixedtables • makefixed • updatewindow • inflate • inflateEnd • inflateGetDictionary • inflateSetDictionary • inflateGetHeader • syncsearch • inflateSync • inflateSyncPoint • inflateCopy • inflateUndermine • inflateValidate • inflateMark • inflateCodesUsed
/* inflate.c -- zlib decompression * Copyright (C) 1995-2022 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* * Change history: * * 1.2.beta0 24 Nov 2002 * - First version -- complete rewrite of inflate to simplify code, avoid * creation of window when not needed, minimize use of window when it is * needed, make inffast.c even faster, implement gzip decoding, and to * improve code readability and style over the previous zlib inflate code * * 1.2.beta1 25 Nov 2002 * - Use pointers for available input and output checking in inffast.c * - Remove input and output counters in inffast.c * - Change inffast.c entry and loop from avail_in >= 7 to >= 6 * - Remove unnecessary second byte pull from length extra in inffast.c * - Unroll direct copy to three copies per loop in inffast.c * * 1.2.beta2 4 Dec 2002 * - Change external routine names to reduce potential conflicts * - Correct filename to inffixed.h for fixed tables in inflate.c * - Make hbuf[] unsigned char to match parameter type in inflate.c * - Change strm->next_out[-state->offset] to *(strm->next_out - state->offset) * to avoid negation problem on Alphas (64 bit) in inflate.c * * 1.2.beta3 22 Dec 2002 * - Add comments on state->bits assertion in inffast.c * - Add comments on op field in inftrees.h * - Fix bug in reuse of allocated window after inflateReset() * - Remove bit fields--back to byte structure for speed * - Remove distance extra == 0 check in inflate_fast()--only helps for lengths * - Change post-increments to pre-increments in inflate_fast(), PPC biased? * - Add compile time option, POSTINC, to use post-increments instead (Intel?) * - Make MATCH copy in inflate() much faster for when inflate_fast() not used * - Use local copies of stream next and avail values, as well as local bit * buffer and bit count in inflate()--for speed when inflate_fast() not used * * 1.2.beta4 1 Jan 2003 * - Split ptr - 257 statements in inflate_table() to avoid compiler warnings * - Move a comment on output buffer sizes from inffast.c to inflate.c * - Add comments in inffast.c to introduce the inflate_fast() routine * - Rearrange window copies in inflate_fast() for speed and simplification * - Unroll last copy for window match in inflate_fast() * - Use local copies of window variables in inflate_fast() for speed * - Pull out common wnext == 0 case for speed in inflate_fast() * - Make op and len in inflate_fast() unsigned for consistency * - Add FAR to lcode and dcode declarations in inflate_fast() * - Simplified bad distance check in inflate_fast() * - Added inflateBackInit(), inflateBack(), and inflateBackEnd() in new * source file infback.c to provide a call-back interface to inflate for * programs like gzip and unzip -- uses window as output buffer to avoid * window copying * * 1.2.beta5 1 Jan 2003 * - Improved inflateBack() interface to allow the caller to provide initial * input in strm. * - Fixed stored blocks bug in inflateBack() * * 1.2.beta6 4 Jan 2003 * - Added comments in inffast.c on effectiveness of POSTINC * - Typecasting all around to reduce compiler warnings * - Changed loops from while (1) or do {} while (1) to for (;;), again to * make compilers happy * - Changed type of window in inflateBackInit() to unsigned char * * * 1.2.beta7 27 Jan 2003 * - Changed many types to unsigned or unsigned short to avoid warnings * - Added inflateCopy() function * * 1.2.0 9 Mar 2003 * - Changed inflateBack() interface to provide separate opaque descriptors * for the in() and out() functions * - Changed inflateBack() argument and in_func typedef to swap the length * and buffer address return values for the input function * - Check next_in and next_out for Z_NULL on entry to inflate() * * The history for versions after 1.2.0 are in ChangeLog in zlib distribution. */ #include "zutil.h" #include "inftrees.h" #include "inflate.h" #include "inffast.h" #ifdef MAKEFIXED # ifndef BUILDFIXED # define BUILDFIXED # endif #endif local int inflateStateCheck(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (strm == Z_NULL || strm->zalloc == (alloc_func)0 || strm->zfree == (free_func)0) return 1; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (state == Z_NULL || state->strm != strm || state->mode < HEAD || state->mode > SYNC) return 1; return 0; } int ZEXPORT inflateResetKeep(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; strm->total_in = strm->total_out = state->total = 0; strm->msg = Z_NULL; if (state->wrap) /* to support ill-conceived Java test suite */ strm->adler = state->wrap & 1; state->mode = HEAD; state->last = 0; state->havedict = 0; state->flags = -1; state->dmax = 32768U; state->head = Z_NULL; state->hold = 0; state->bits = 0; state->lencode = state->distcode = state->next = state->codes; state->sane = 1; state->back = -1; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: reset\n")); return Z_OK; } int ZEXPORT inflateReset(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; state->wsize = 0; state->whave = 0; state->wnext = 0; return inflateResetKeep(strm); } int ZEXPORT inflateReset2(z_streamp strm, int windowBits) { int wrap; struct inflate_state FAR *state; /* get the state */ if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; /* extract wrap request from windowBits parameter */ if (windowBits < 0) { if (windowBits < -15) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; wrap = 0; windowBits = -windowBits; } else { wrap = (windowBits >> 4) + 5; #ifdef GUNZIP if (windowBits < 48) windowBits &= 15; #endif } /* set number of window bits, free window if different */ if (windowBits && (windowBits < 8 || windowBits > 15)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; if (state->window != Z_NULL && state->wbits != (unsigned)windowBits) { ZFREE(strm, state->window); state->window = Z_NULL; } /* update state and reset the rest of it */ state->wrap = wrap; state->wbits = (unsigned)windowBits; return inflateReset(strm); } int ZEXPORT inflateInit2_(z_streamp strm, int windowBits, const char *version, int stream_size) { int ret; struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (version == Z_NULL || version[0] != ZLIB_VERSION[0] || stream_size != (int)(sizeof(z_stream))) return Z_VERSION_ERROR; if (strm == Z_NULL) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; strm->msg = Z_NULL; /* in case we return an error */ if (strm->zalloc == (alloc_func)0) { #ifdef Z_SOLO return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else strm->zalloc = zcalloc; strm->opaque = (voidpf)0; #endif } if (strm->zfree == (free_func)0) #ifdef Z_SOLO return Z_STREAM_ERROR; #else strm->zfree = zcfree; #endif state = (struct inflate_state FAR *) ZALLOC(strm, 1, sizeof(struct inflate_state)); if (state == Z_NULL) return Z_MEM_ERROR; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: allocated\n")); strm->state = (struct internal_state FAR *)state; state->strm = strm; state->window = Z_NULL; state->mode = HEAD; /* to pass state test in inflateReset2() */ ret = inflateReset2(strm, windowBits); if (ret != Z_OK) { ZFREE(strm, state); strm->state = Z_NULL; } return ret; } int ZEXPORT inflateInit_(z_streamp strm, const char *version, int stream_size) { return inflateInit2_(strm, DEF_WBITS, version, stream_size); } int ZEXPORT inflatePrime(z_streamp strm, int bits, int value) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; if (bits == 0) return Z_OK; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (bits < 0) { state->hold = 0; state->bits = 0; return Z_OK; } if (bits > 16 || state->bits + (uInt)bits > 32) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; value &= (1L << bits) - 1; state->hold += (unsigned)value << state->bits; state->bits += (uInt)bits; return Z_OK; } /* Return state with length and distance decoding tables and index sizes set to fixed code decoding. Normally this returns fixed tables from inffixed.h. If BUILDFIXED is defined, then instead this routine builds the tables the first time it's called, and returns those tables the first time and thereafter. This reduces the size of the code by about 2K bytes, in exchange for a little execution time. However, BUILDFIXED should not be used for threaded applications, since the rewriting of the tables and virgin may not be thread-safe. */ local void fixedtables(struct inflate_state FAR *state) { #ifdef BUILDFIXED static int virgin = 1; static code *lenfix, *distfix; static code fixed[544]; /* build fixed huffman tables if first call (may not be thread safe) */ if (virgin) { unsigned sym, bits; static code *next; /* literal/length table */ sym = 0; while (sym < 144) state->lens[sym++] = 8; while (sym < 256) state->lens[sym++] = 9; while (sym < 280) state->lens[sym++] = 7; while (sym < 288) state->lens[sym++] = 8; next = fixed; lenfix = next; bits = 9; inflate_table(LENS, state->lens, 288, &(next), &(bits), state->work); /* distance table */ sym = 0; while (sym < 32) state->lens[sym++] = 5; distfix = next; bits = 5; inflate_table(DISTS, state->lens, 32, &(next), &(bits), state->work); /* do this just once */ virgin = 0; } #else /* !BUILDFIXED */ # include "inffixed.h" #endif /* BUILDFIXED */ state->lencode = lenfix; state->lenbits = 9; state->distcode = distfix; state->distbits = 5; } #ifdef MAKEFIXED #include <stdio.h> /* Write out the inffixed.h that is #include'd above. Defining MAKEFIXED also defines BUILDFIXED, so the tables are built on the fly. makefixed() writes those tables to stdout, which would be piped to inffixed.h. A small program can simply call makefixed to do this: void makefixed(void); int main(void) { makefixed(); return 0; } Then that can be linked with zlib built with MAKEFIXED defined and run: a.out > inffixed.h */ void makefixed(void) { unsigned low, size; struct inflate_state state; fixedtables(&state); puts(" /* inffixed.h -- table for decoding fixed codes"); puts(" * Generated automatically by makefixed()."); puts(" */"); puts(""); puts(" /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications."); puts(" It is part of the implementation of this library and is"); puts(" subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h."); puts(" */"); puts(""); size = 1U << 9; printf(" static const code lenfix[%u] = {", size); low = 0; for (;;) { if ((low % 7) == 0) printf("\n "); printf("{%u,%u,%d}", (low & 127) == 99 ? 64 : state.lencode[low].op, state.lencode[low].bits, state.lencode[low].val); if (++low == size) break; putchar(','); } puts("\n };"); size = 1U << 5; printf("\n static const code distfix[%u] = {", size); low = 0; for (;;) { if ((low % 6) == 0) printf("\n "); printf("{%u,%u,%d}", state.distcode[low].op, state.distcode[low].bits, state.distcode[low].val); if (++low == size) break; putchar(','); } puts("\n };"); } #endif /* MAKEFIXED */ /* Update the window with the last wsize (normally 32K) bytes written before returning. If window does not exist yet, create it. This is only called when a window is already in use, or when output has been written during this inflate call, but the end of the deflate stream has not been reached yet. It is also called to create a window for dictionary data when a dictionary is loaded. Providing output buffers larger than 32K to inflate() should provide a speed advantage, since only the last 32K of output is copied to the sliding window upon return from inflate(), and since all distances after the first 32K of output will fall in the output data, making match copies simpler and faster. The advantage may be dependent on the size of the processor's data caches. */ local int updatewindow(z_streamp strm, const Bytef *end, unsigned copy) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; unsigned dist; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; /* if it hasn't been done already, allocate space for the window */ if (state->window == Z_NULL) { state->window = (unsigned char FAR *) ZALLOC(strm, 1U << state->wbits, sizeof(unsigned char)); if (state->window == Z_NULL) return 1; } /* if window not in use yet, initialize */ if (state->wsize == 0) { state->wsize = 1U << state->wbits; state->wnext = 0; state->whave = 0; } /* copy state->wsize or less output bytes into the circular window */ if (copy >= state->wsize) { zmemcpy(state->window, end - state->wsize, state->wsize); state->wnext = 0; state->whave = state->wsize; } else { dist = state->wsize - state->wnext; if (dist > copy) dist = copy; zmemcpy(state->window + state->wnext, end - copy, dist); copy -= dist; if (copy) { zmemcpy(state->window, end - copy, copy); state->wnext = copy; state->whave = state->wsize; } else { state->wnext += dist; if (state->wnext == state->wsize) state->wnext = 0; if (state->whave < state->wsize) state->whave += dist; } } return 0; } /* Macros for inflate(): */ /* check function to use adler32() for zlib or crc32() for gzip */ #ifdef GUNZIP # define UPDATE_CHECK(check, buf, len) \ (state->flags ? crc32(check, buf, len) : adler32(check, buf, len)) #else # define UPDATE_CHECK(check, buf, len) adler32(check, buf, len) #endif /* check macros for header crc */ #ifdef GUNZIP # define CRC2(check, word) \ do { \ hbuf[0] = (unsigned char)(word); \ hbuf[1] = (unsigned char)((word) >> 8); \ check = crc32(check, hbuf, 2); \ } while (0) # define CRC4(check, word) \ do { \ hbuf[0] = (unsigned char)(word); \ hbuf[1] = (unsigned char)((word) >> 8); \ hbuf[2] = (unsigned char)((word) >> 16); \ hbuf[3] = (unsigned char)((word) >> 24); \ check = crc32(check, hbuf, 4); \ } while (0) #endif /* Load registers with state in inflate() for speed */ #define LOAD() \ do { \ put = strm->next_out; \ left = strm->avail_out; \ next = strm->next_in; \ have = strm->avail_in; \ hold = state->hold; \ bits = state->bits; \ } while (0) /* Restore state from registers in inflate() */ #define RESTORE() \ do { \ strm->next_out = put; \ strm->avail_out = left; \ strm->next_in = next; \ strm->avail_in = have; \ state->hold = hold; \ state->bits = bits; \ } while (0) /* Clear the input bit accumulator */ #define INITBITS() \ do { \ hold = 0; \ bits = 0; \ } while (0) /* Get a byte of input into the bit accumulator, or return from inflate() if there is no input available. */ #define PULLBYTE() \ do { \ if (have == 0) goto inf_leave; \ have--; \ hold += (unsigned long)(*next++) << bits; \ bits += 8; \ } while (0) /* Assure that there are at least n bits in the bit accumulator. If there is not enough available input to do that, then return from inflate(). */ #define NEEDBITS(n) \ do { \ while (bits < (unsigned)(n)) \ PULLBYTE(); \ } while (0) /* Return the low n bits of the bit accumulator (n < 16) */ #define BITS(n) \ ((unsigned)hold & ((1U << (n)) - 1)) /* Remove n bits from the bit accumulator */ #define DROPBITS(n) \ do { \ hold >>= (n); \ bits -= (unsigned)(n); \ } while (0) /* Remove zero to seven bits as needed to go to a byte boundary */ #define BYTEBITS() \ do { \ hold >>= bits & 7; \ bits -= bits & 7; \ } while (0) /* inflate() uses a state machine to process as much input data and generate as much output data as possible before returning. The state machine is structured roughly as follows: for (;;) switch (state) { ... case STATEn: if (not enough input data or output space to make progress) return; ... make progress ... state = STATEm; break; ... } so when inflate() is called again, the same case is attempted again, and if the appropriate resources are provided, the machine proceeds to the next state. The NEEDBITS() macro is usually the way the state evaluates whether it can proceed or should return. NEEDBITS() does the return if the requested bits are not available. The typical use of the BITS macros is: NEEDBITS(n); ... do something with BITS(n) ... DROPBITS(n); where NEEDBITS(n) either returns from inflate() if there isn't enough input left to load n bits into the accumulator, or it continues. BITS(n) gives the low n bits in the accumulator. When done, DROPBITS(n) drops the low n bits off the accumulator. INITBITS() clears the accumulator and sets the number of available bits to zero. BYTEBITS() discards just enough bits to put the accumulator on a byte boundary. After BYTEBITS() and a NEEDBITS(8), then BITS(8) would return the next byte in the stream. NEEDBITS(n) uses PULLBYTE() to get an available byte of input, or to return if there is no input available. The decoding of variable length codes uses PULLBYTE() directly in order to pull just enough bytes to decode the next code, and no more. Some states loop until they get enough input, making sure that enough state information is maintained to continue the loop where it left off if NEEDBITS() returns in the loop. For example, want, need, and keep would all have to actually be part of the saved state in case NEEDBITS() returns: case STATEw: while (want < need) { NEEDBITS(n); keep[want++] = BITS(n); DROPBITS(n); } state = STATEx; case STATEx: As shown above, if the next state is also the next case, then the break is omitted. A state may also return if there is not enough output space available to complete that state. Those states are copying stored data, writing a literal byte, and copying a matching string. When returning, a "goto inf_leave" is used to update the total counters, update the check value, and determine whether any progress has been made during that inflate() call in order to return the proper return code. Progress is defined as a change in either strm->avail_in or strm->avail_out. When there is a window, goto inf_leave will update the window with the last output written. If a goto inf_leave occurs in the middle of decompression and there is no window currently, goto inf_leave will create one and copy output to the window for the next call of inflate(). In this implementation, the flush parameter of inflate() only affects the return code (per zlib.h). inflate() always writes as much as possible to strm->next_out, given the space available and the provided input--the effect documented in zlib.h of Z_SYNC_FLUSH. Furthermore, inflate() always defers the allocation of and copying into a sliding window until necessary, which provides the effect documented in zlib.h for Z_FINISH when the entire input stream available. So the only thing the flush parameter actually does is: when flush is set to Z_FINISH, inflate() cannot return Z_OK. Instead it will return Z_BUF_ERROR if it has not reached the end of the stream. */ int ZEXPORT inflate(z_streamp strm, int flush) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; z_const unsigned char FAR *next; /* next input */ unsigned char FAR *put; /* next output */ unsigned have, left; /* available input and output */ unsigned long hold; /* bit buffer */ unsigned bits; /* bits in bit buffer */ unsigned in, out; /* save starting available input and output */ unsigned copy; /* number of stored or match bytes to copy */ unsigned char FAR *from; /* where to copy match bytes from */ code here; /* current decoding table entry */ code last; /* parent table entry */ unsigned len; /* length to copy for repeats, bits to drop */ int ret; /* return code */ #ifdef GUNZIP unsigned char hbuf[4]; /* buffer for gzip header crc calculation */ #endif static const unsigned short order[19] = /* permutation of code lengths */ {16, 17, 18, 0, 8, 7, 9, 6, 10, 5, 11, 4, 12, 3, 13, 2, 14, 1, 15}; if (inflateStateCheck(strm) || strm->next_out == Z_NULL || (strm->next_in == Z_NULL && strm->avail_in != 0)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (state->mode == TYPE) state->mode = TYPEDO; /* skip check */ LOAD(); in = have; out = left; ret = Z_OK; for (;;) switch (state->mode) { case HEAD: if (state->wrap == 0) { state->mode = TYPEDO; break; } NEEDBITS(16); #ifdef GUNZIP if ((state->wrap & 2) && hold == 0x8b1f) { /* gzip header */ if (state->wbits == 0) state->wbits = 15; state->check = crc32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); CRC2(state->check, hold); INITBITS(); state->mode = FLAGS; break; } if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->done = -1; if (!(state->wrap & 1) || /* check if zlib header allowed */ #else if ( #endif ((BITS(8) << 8) + (hold >> 8)) % 31) { strm->msg = (char *)"incorrect header check"; state->mode = BAD; break; } if (BITS(4) != Z_DEFLATED) { strm->msg = (char *)"unknown compression method"; state->mode = BAD; break; } DROPBITS(4); len = BITS(4) + 8; if (state->wbits == 0) state->wbits = len; if (len > 15 || len > state->wbits) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid window size"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->dmax = 1U << len; state->flags = 0; /* indicate zlib header */ Tracev((stderr, "inflate: zlib header ok\n")); strm->adler = state->check = adler32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); state->mode = hold & 0x200 ? DICTID : TYPE; INITBITS(); break; #ifdef GUNZIP case FLAGS: NEEDBITS(16); state->flags = (int)(hold); if ((state->flags & 0xff) != Z_DEFLATED) { strm->msg = (char *)"unknown compression method"; state->mode = BAD; break; } if (state->flags & 0xe000) { strm->msg = (char *)"unknown header flags set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->text = (int)((hold >> 8) & 1); if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) CRC2(state->check, hold); INITBITS(); state->mode = TIME; /* fallthrough */ case TIME: NEEDBITS(32); if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->time = hold; if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) CRC4(state->check, hold); INITBITS(); state->mode = OS; /* fallthrough */ case OS: NEEDBITS(16); if (state->head != Z_NULL) { state->head->xflags = (int)(hold & 0xff); state->head->os = (int)(hold >> 8); } if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) CRC2(state->check, hold); INITBITS(); state->mode = EXLEN; /* fallthrough */ case EXLEN: if (state->flags & 0x0400) { NEEDBITS(16); state->length = (unsigned)(hold); if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->extra_len = (unsigned)hold; if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) CRC2(state->check, hold); INITBITS(); } else if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->extra = Z_NULL; state->mode = EXTRA; /* fallthrough */ case EXTRA: if (state->flags & 0x0400) { copy = state->length; if (copy > have) copy = have; if (copy) { if (state->head != Z_NULL && state->head->extra != Z_NULL && (len = state->head->extra_len - state->length) < state->head->extra_max) { zmemcpy(state->head->extra + len, next, len + copy > state->head->extra_max ? state->head->extra_max - len : copy); } if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) state->check = crc32(state->check, next, copy); have -= copy; next += copy; state->length -= copy; } if (state->length) goto inf_leave; } state->length = 0; state->mode = NAME; /* fallthrough */ case NAME: if (state->flags & 0x0800) { if (have == 0) goto inf_leave; copy = 0; do { len = (unsigned)(next[copy++]); if (state->head != Z_NULL && state->head->name != Z_NULL && state->length < state->head->name_max) state->head->name[state->length++] = (Bytef)len; } while (len && copy < have); if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) state->check = crc32(state->check, next, copy); have -= copy; next += copy; if (len) goto inf_leave; } else if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->name = Z_NULL; state->length = 0; state->mode = COMMENT; /* fallthrough */ case COMMENT: if (state->flags & 0x1000) { if (have == 0) goto inf_leave; copy = 0; do { len = (unsigned)(next[copy++]); if (state->head != Z_NULL && state->head->comment != Z_NULL && state->length < state->head->comm_max) state->head->comment[state->length++] = (Bytef)len; } while (len && copy < have); if ((state->flags & 0x0200) && (state->wrap & 4)) state->check = crc32(state->check, next, copy); have -= copy; next += copy; if (len) goto inf_leave; } else if (state->head != Z_NULL) state->head->comment = Z_NULL; state->mode = HCRC; /* fallthrough */ case HCRC: if (state->flags & 0x0200) { NEEDBITS(16); if ((state->wrap & 4) && hold != (state->check & 0xffff)) { strm->msg = (char *)"header crc mismatch"; state->mode = BAD; break; } INITBITS(); } if (state->head != Z_NULL) { state->head->hcrc = (int)((state->flags >> 9) & 1); state->head->done = 1; } strm->adler = state->check = crc32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); state->mode = TYPE; break; #endif case DICTID: NEEDBITS(32); strm->adler = state->check = ZSWAP32(hold); INITBITS(); state->mode = DICT; /* fallthrough */ case DICT: if (state->havedict == 0) { RESTORE(); return Z_NEED_DICT; } strm->adler = state->check = adler32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); state->mode = TYPE; /* fallthrough */ case TYPE: if (flush == Z_BLOCK || flush == Z_TREES) goto inf_leave; /* fallthrough */ case TYPEDO: if (state->last) { BYTEBITS(); state->mode = CHECK; break; } NEEDBITS(3); state->last = BITS(1); DROPBITS(1); switch (BITS(2)) { case 0: /* stored block */ Tracev((stderr, "inflate: stored block%s\n", state->last ? " (last)" : "")); state->mode = STORED; break; case 1: /* fixed block */ fixedtables(state); Tracev((stderr, "inflate: fixed codes block%s\n", state->last ? " (last)" : "")); state->mode = LEN_; /* decode codes */ if (flush == Z_TREES) { DROPBITS(2); goto inf_leave; } break; case 2: /* dynamic block */ Tracev((stderr, "inflate: dynamic codes block%s\n", state->last ? " (last)" : "")); state->mode = TABLE; break; case 3: strm->msg = (char *)"invalid block type"; state->mode = BAD; } DROPBITS(2); break; case STORED: BYTEBITS(); /* go to byte boundary */ NEEDBITS(32); if ((hold & 0xffff) != ((hold >> 16) ^ 0xffff)) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid stored block lengths"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->length = (unsigned)hold & 0xffff; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: stored length %u\n", state->length)); INITBITS(); state->mode = COPY_; if (flush == Z_TREES) goto inf_leave; /* fallthrough */ case COPY_: state->mode = COPY; /* fallthrough */ case COPY: copy = state->length; if (copy) { if (copy > have) copy = have; if (copy > left) copy = left; if (copy == 0) goto inf_leave; zmemcpy(put, next, copy); have -= copy; next += copy; left -= copy; put += copy; state->length -= copy; break; } Tracev((stderr, "inflate: stored end\n")); state->mode = TYPE; break; case TABLE: NEEDBITS(14); state->nlen = BITS(5) + 257; DROPBITS(5); state->ndist = BITS(5) + 1; DROPBITS(5); state->ncode = BITS(4) + 4; DROPBITS(4); #ifndef PKZIP_BUG_WORKAROUND if (state->nlen > 286 || state->ndist > 30) { strm->msg = (char *)"too many length or distance symbols"; state->mode = BAD; break; } #endif Tracev((stderr, "inflate: table sizes ok\n")); state->have = 0; state->mode = LENLENS; /* fallthrough */ case LENLENS: while (state->have < state->ncode) { NEEDBITS(3); state->lens[order[state->have++]] = (unsigned short)BITS(3); DROPBITS(3); } while (state->have < 19) state->lens[order[state->have++]] = 0; state->next = state->codes; state->lencode = (const code FAR *)(state->next); state->lenbits = 7; ret = inflate_table(CODES, state->lens, 19, &(state->next), &(state->lenbits), state->work); if (ret) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid code lengths set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } Tracev((stderr, "inflate: code lengths ok\n")); state->have = 0; state->mode = CODELENS; /* fallthrough */ case CODELENS: while (state->have < state->nlen + state->ndist) { for (;;) { here = state->lencode[BITS(state->lenbits)]; if ((unsigned)(here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } if (here.val < 16) { DROPBITS(here.bits); state->lens[state->have++] = here.val; } else { if (here.val == 16) { NEEDBITS(here.bits + 2); DROPBITS(here.bits); if (state->have == 0) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid bit length repeat"; state->mode = BAD; break; } len = state->lens[state->have - 1]; copy = 3 + BITS(2); DROPBITS(2); } else if (here.val == 17) { NEEDBITS(here.bits + 3); DROPBITS(here.bits); len = 0; copy = 3 + BITS(3); DROPBITS(3); } else { NEEDBITS(here.bits + 7); DROPBITS(here.bits); len = 0; copy = 11 + BITS(7); DROPBITS(7); } if (state->have + copy > state->nlen + state->ndist) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid bit length repeat"; state->mode = BAD; break; } while (copy--) state->lens[state->have++] = (unsigned short)len; } } /* handle error breaks in while */ if (state->mode == BAD) break; /* check for end-of-block code (better have one) */ if (state->lens[256] == 0) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid code -- missing end-of-block"; state->mode = BAD; break; } /* build code tables -- note: do not change the lenbits or distbits values here (9 and 6) without reading the comments in inftrees.h concerning the ENOUGH constants, which depend on those values */ state->next = state->codes; state->lencode = (const code FAR *)(state->next); state->lenbits = 9; ret = inflate_table(LENS, state->lens, state->nlen, &(state->next), &(state->lenbits), state->work); if (ret) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid literal/lengths set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->distcode = (const code FAR *)(state->next); state->distbits = 6; ret = inflate_table(DISTS, state->lens + state->nlen, state->ndist, &(state->next), &(state->distbits), state->work); if (ret) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distances set"; state->mode = BAD; break; } Tracev((stderr, "inflate: codes ok\n")); state->mode = LEN_; if (flush == Z_TREES) goto inf_leave; /* fallthrough */ case LEN_: state->mode = LEN; /* fallthrough */ case LEN: if (have >= 6 && left >= 258) { RESTORE(); inflate_fast(strm, out); LOAD(); if (state->mode == TYPE) state->back = -1; break; } state->back = 0; for (;;) { here = state->lencode[BITS(state->lenbits)]; if ((unsigned)(here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } if (here.op && (here.op & 0xf0) == 0) { last = here; for (;;) { here = state->lencode[last.val + (BITS(last.bits + last.op) >> last.bits)]; if ((unsigned)(last.bits + here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } DROPBITS(last.bits); state->back += last.bits; } DROPBITS(here.bits); state->back += here.bits; state->length = (unsigned)here.val; if ((int)(here.op) == 0) { Tracevv((stderr, here.val >= 0x20 && here.val < 0x7f ? "inflate: literal '%c'\n" : "inflate: literal 0x%02x\n", here.val)); state->mode = LIT; break; } if (here.op & 32) { Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: end of block\n")); state->back = -1; state->mode = TYPE; break; } if (here.op & 64) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid literal/length code"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->extra = (unsigned)(here.op) & 15; state->mode = LENEXT; /* fallthrough */ case LENEXT: if (state->extra) { NEEDBITS(state->extra); state->length += BITS(state->extra); DROPBITS(state->extra); state->back += state->extra; } Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: length %u\n", state->length)); state->was = state->length; state->mode = DIST; /* fallthrough */ case DIST: for (;;) { here = state->distcode[BITS(state->distbits)]; if ((unsigned)(here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } if ((here.op & 0xf0) == 0) { last = here; for (;;) { here = state->distcode[last.val + (BITS(last.bits + last.op) >> last.bits)]; if ((unsigned)(last.bits + here.bits) <= bits) break; PULLBYTE(); } DROPBITS(last.bits); state->back += last.bits; } DROPBITS(here.bits); state->back += here.bits; if (here.op & 64) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance code"; state->mode = BAD; break; } state->offset = (unsigned)here.val; state->extra = (unsigned)(here.op) & 15; state->mode = DISTEXT; /* fallthrough */ case DISTEXT: if (state->extra) { NEEDBITS(state->extra); state->offset += BITS(state->extra); DROPBITS(state->extra); state->back += state->extra; } #ifdef INFLATE_STRICT if (state->offset > state->dmax) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance too far back"; state->mode = BAD; break; } #endif Tracevv((stderr, "inflate: distance %u\n", state->offset)); state->mode = MATCH; /* fallthrough */ case MATCH: if (left == 0) goto inf_leave; copy = out - left; if (state->offset > copy) { /* copy from window */ copy = state->offset - copy; if (copy > state->whave) { if (state->sane) { strm->msg = (char *)"invalid distance too far back"; state->mode = BAD; break; } #ifdef INFLATE_ALLOW_INVALID_DISTANCE_TOOFAR_ARRR Trace((stderr, "inflate.c too far\n")); copy -= state->whave; if (copy > state->length) copy = state->length; if (copy > left) copy = left; left -= copy; state->length -= copy; do { *put++ = 0; } while (--copy); if (state->length == 0) state->mode = LEN; break; #endif } if (copy > state->wnext) { copy -= state->wnext; from = state->window + (state->wsize - copy); } else from = state->window + (state->wnext - copy); if (copy > state->length) copy = state->length; } else { /* copy from output */ from = put - state->offset; copy = state->length; } if (copy > left) copy = left; left -= copy; state->length -= copy; do { *put++ = *from++; } while (--copy); if (state->length == 0) state->mode = LEN; break; case LIT: if (left == 0) goto inf_leave; *put++ = (unsigned char)(state->length); left--; state->mode = LEN; break; case CHECK: if (state->wrap) { NEEDBITS(32); out -= left; strm->total_out += out; state->total += out; if ((state->wrap & 4) && out) strm->adler = state->check = UPDATE_CHECK(state->check, put - out, out); out = left; if ((state->wrap & 4) && ( #ifdef GUNZIP state->flags ? hold : #endif ZSWAP32(hold)) != state->check) { strm->msg = (char *)"incorrect data check"; state->mode = BAD; break; } INITBITS(); Tracev((stderr, "inflate: check matches trailer\n")); } #ifdef GUNZIP state->mode = LENGTH; /* fallthrough */ case LENGTH: if (state->wrap && state->flags) { NEEDBITS(32); if ((state->wrap & 4) && hold != (state->total & 0xffffffff)) { strm->msg = (char *)"incorrect length check"; state->mode = BAD; break; } INITBITS(); Tracev((stderr, "inflate: length matches trailer\n")); } #endif state->mode = DONE; /* fallthrough */ case DONE: ret = Z_STREAM_END; goto inf_leave; case BAD: ret = Z_DATA_ERROR; goto inf_leave; case MEM: return Z_MEM_ERROR; case SYNC: /* fallthrough */ default: return Z_STREAM_ERROR; } /* Return from inflate(), updating the total counts and the check value. If there was no progress during the inflate() call, return a buffer error. Call updatewindow() to create and/or update the window state. Note: a memory error from inflate() is non-recoverable. */ inf_leave: RESTORE(); if (state->wsize || (out != strm->avail_out && state->mode < BAD && (state->mode < CHECK || flush != Z_FINISH))) if (updatewindow(strm, strm->next_out, out - strm->avail_out)) { state->mode = MEM; return Z_MEM_ERROR; } in -= strm->avail_in; out -= strm->avail_out; strm->total_in += in; strm->total_out += out; state->total += out; if ((state->wrap & 4) && out) strm->adler = state->check = UPDATE_CHECK(state->check, strm->next_out - out, out); strm->data_type = (int)state->bits + (state->last ? 64 : 0) + (state->mode == TYPE ? 128 : 0) + (state->mode == LEN_ || state->mode == COPY_ ? 256 : 0); if (((in == 0 && out == 0) || flush == Z_FINISH) && ret == Z_OK) ret = Z_BUF_ERROR; return ret; } int ZEXPORT inflateEnd(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (state->window != Z_NULL) ZFREE(strm, state->window); ZFREE(strm, strm->state); strm->state = Z_NULL; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: end\n")); return Z_OK; } int ZEXPORT inflateGetDictionary(z_streamp strm, Bytef *dictionary, uInt *dictLength) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; /* check state */ if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; /* copy dictionary */ if (state->whave && dictionary != Z_NULL) { zmemcpy(dictionary, state->window + state->wnext, state->whave - state->wnext); zmemcpy(dictionary + state->whave - state->wnext, state->window, state->wnext); } if (dictLength != Z_NULL) *dictLength = state->whave; return Z_OK; } int ZEXPORT inflateSetDictionary(z_streamp strm, const Bytef *dictionary, uInt dictLength) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; unsigned long dictid; int ret; /* check state */ if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (state->wrap != 0 && state->mode != DICT) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; /* check for correct dictionary identifier */ if (state->mode == DICT) { dictid = adler32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); dictid = adler32(dictid, dictionary, dictLength); if (dictid != state->check) return Z_DATA_ERROR; } /* copy dictionary to window using updatewindow(), which will amend the existing dictionary if appropriate */ ret = updatewindow(strm, dictionary + dictLength, dictLength); if (ret) { state->mode = MEM; return Z_MEM_ERROR; } state->havedict = 1; Tracev((stderr, "inflate: dictionary set\n")); return Z_OK; } int ZEXPORT inflateGetHeader(z_streamp strm, gz_headerp head) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; /* check state */ if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if ((state->wrap & 2) == 0) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; /* save header structure */ state->head = head; head->done = 0; return Z_OK; } /* Search buf[0..len-1] for the pattern: 0, 0, 0xff, 0xff. Return when found or when out of input. When called, *have is the number of pattern bytes found in order so far, in 0..3. On return *have is updated to the new state. If on return *have equals four, then the pattern was found and the return value is how many bytes were read including the last byte of the pattern. If *have is less than four, then the pattern has not been found yet and the return value is len. In the latter case, syncsearch() can be called again with more data and the *have state. *have is initialized to zero for the first call. */ local unsigned syncsearch(unsigned FAR *have, const unsigned char FAR *buf, unsigned len) { unsigned got; unsigned next; got = *have; next = 0; while (next < len && got < 4) { if ((int)(buf[next]) == (got < 2 ? 0 : 0xff)) got++; else if (buf[next]) got = 0; else got = 4 - got; next++; } *have = got; return next; } int ZEXPORT inflateSync(z_streamp strm) { unsigned len; /* number of bytes to look at or looked at */ int flags; /* temporary to save header status */ unsigned long in, out; /* temporary to save total_in and total_out */ unsigned char buf[4]; /* to restore bit buffer to byte string */ struct inflate_state FAR *state; /* check parameters */ if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (strm->avail_in == 0 && state->bits < 8) return Z_BUF_ERROR; /* if first time, start search in bit buffer */ if (state->mode != SYNC) { state->mode = SYNC; state->hold >>= state->bits & 7; state->bits -= state->bits & 7; len = 0; while (state->bits >= 8) { buf[len++] = (unsigned char)(state->hold); state->hold >>= 8; state->bits -= 8; } state->have = 0; syncsearch(&(state->have), buf, len); } /* search available input */ len = syncsearch(&(state->have), strm->next_in, strm->avail_in); strm->avail_in -= len; strm->next_in += len; strm->total_in += len; /* return no joy or set up to restart inflate() on a new block */ if (state->have != 4) return Z_DATA_ERROR; if (state->flags == -1) state->wrap = 0; /* if no header yet, treat as raw */ else state->wrap &= ~4; /* no point in computing a check value now */ flags = state->flags; in = strm->total_in; out = strm->total_out; inflateReset(strm); strm->total_in = in; strm->total_out = out; state->flags = flags; state->mode = TYPE; return Z_OK; } /* Returns true if inflate is currently at the end of a block generated by Z_SYNC_FLUSH or Z_FULL_FLUSH. This function is used by one PPP implementation to provide an additional safety check. PPP uses Z_SYNC_FLUSH but removes the length bytes of the resulting empty stored block. When decompressing, PPP checks that at the end of input packet, inflate is waiting for these length bytes. */ int ZEXPORT inflateSyncPoint(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; return state->mode == STORED && state->bits == 0; } int ZEXPORT inflateCopy(z_streamp dest, z_streamp source) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; struct inflate_state FAR *copy; unsigned char FAR *window; unsigned wsize; /* check input */ if (inflateStateCheck(source) || dest == Z_NULL) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)source->state; /* allocate space */ copy = (struct inflate_state FAR *) ZALLOC(source, 1, sizeof(struct inflate_state)); if (copy == Z_NULL) return Z_MEM_ERROR; window = Z_NULL; if (state->window != Z_NULL) { window = (unsigned char FAR *) ZALLOC(source, 1U << state->wbits, sizeof(unsigned char)); if (window == Z_NULL) { ZFREE(source, copy); return Z_MEM_ERROR; } } /* copy state */ zmemcpy((voidpf)dest, (voidpf)source, sizeof(z_stream)); zmemcpy((voidpf)copy, (voidpf)state, sizeof(struct inflate_state)); copy->strm = dest; if (state->lencode >= state->codes && state->lencode <= state->codes + ENOUGH - 1) { copy->lencode = copy->codes + (state->lencode - state->codes); copy->distcode = copy->codes + (state->distcode - state->codes); } copy->next = copy->codes + (state->next - state->codes); if (window != Z_NULL) { wsize = 1U << state->wbits; zmemcpy(window, state->window, wsize); } copy->window = window; dest->state = (struct internal_state FAR *)copy; return Z_OK; } int ZEXPORT inflateUndermine(z_streamp strm, int subvert) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; #ifdef INFLATE_ALLOW_INVALID_DISTANCE_TOOFAR_ARRR state->sane = !subvert; return Z_OK; #else (void)subvert; state->sane = 1; return Z_DATA_ERROR; #endif } int ZEXPORT inflateValidate(z_streamp strm, int check) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return Z_STREAM_ERROR; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; if (check && state->wrap) state->wrap |= 4; else state->wrap &= ~4; return Z_OK; } long ZEXPORT inflateMark(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return -(1L << 16); state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; return (long)(((unsigned long)((long)state->back)) << 16) + (state->mode == COPY ? state->length : (state->mode == MATCH ? state->was - state->length : 0)); } unsigned long ZEXPORT inflateCodesUsed(z_streamp strm) { struct inflate_state FAR *state; if (inflateStateCheck(strm)) return (unsigned long)-1; state = (struct inflate_state FAR *)strm->state; return (unsigned long)(state->next - state->codes); }
/* inftrees.c -- generate Huffman trees for efficient decoding * Copyright (C) 1995-2024 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ #include "zutil.h" #include "inftrees.h" #define MAXBITS 15 const char inflate_copyright[] = " inflate 1.3.1 Copyright 1995-2024 Mark Adler "; /* If you use the zlib library in a product, an acknowledgment is welcome in the documentation of your product. If for some reason you cannot include such an acknowledgment, I would appreciate that you keep this copyright string in the executable of your product. */ /* Build a set of tables to decode the provided canonical Huffman code. The code lengths are lens[0..codes-1]. The result starts at *table, whose indices are 0..2^bits-1. work is a writable array of at least lens shorts, which is used as a work area. type is the type of code to be generated, CODES, LENS, or DISTS. On return, zero is success, -1 is an invalid code, and +1 means that ENOUGH isn't enough. table on return points to the next available entry's address. bits is the requested root table index bits, and on return it is the actual root table index bits. It will differ if the request is greater than the longest code or if it is less than the shortest code. */ int ZLIB_INTERNAL inflate_table(codetype type, unsigned short FAR *lens, unsigned codes, code FAR * FAR *table, unsigned FAR *bits, unsigned short FAR *work) { unsigned len; /* a code's length in bits */ unsigned sym; /* index of code symbols */ unsigned min, max; /* minimum and maximum code lengths */ unsigned root; /* number of index bits for root table */ unsigned curr; /* number of index bits for current table */ unsigned drop; /* code bits to drop for sub-table */ int left; /* number of prefix codes available */ unsigned used; /* code entries in table used */ unsigned huff; /* Huffman code */ unsigned incr; /* for incrementing code, index */ unsigned fill; /* index for replicating entries */ unsigned low; /* low bits for current root entry */ unsigned mask; /* mask for low root bits */ code here; /* table entry for duplication */ code FAR *next; /* next available space in table */ const unsigned short FAR *base; /* base value table to use */ const unsigned short FAR *extra; /* extra bits table to use */ unsigned match; /* use base and extra for symbol >= match */ unsigned short count[MAXBITS+1]; /* number of codes of each length */ unsigned short offs[MAXBITS+1]; /* offsets in table for each length */ static const unsigned short lbase[31] = { /* Length codes 257..285 base */ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 23, 27, 31, 35, 43, 51, 59, 67, 83, 99, 115, 131, 163, 195, 227, 258, 0, 0}; static const unsigned short lext[31] = { /* Length codes 257..285 extra */ 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 17, 17, 17, 17, 18, 18, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 19, 20, 20, 20, 20, 21, 21, 21, 21, 16, 203, 77}; static const unsigned short dbase[32] = { /* Distance codes 0..29 base */ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 13, 17, 25, 33, 49, 65, 97, 129, 193, 257, 385, 513, 769, 1025, 1537, 2049, 3073, 4097, 6145, 8193, 12289, 16385, 24577, 0, 0}; static const unsigned short dext[32] = { /* Distance codes 0..29 extra */ 16, 16, 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 21, 21, 22, 22, 23, 23, 24, 24, 25, 25, 26, 26, 27, 27, 28, 28, 29, 29, 64, 64}; /* Process a set of code lengths to create a canonical Huffman code. The code lengths are lens[0..codes-1]. Each length corresponds to the symbols 0..codes-1. The Huffman code is generated by first sorting the symbols by length from short to long, and retaining the symbol order for codes with equal lengths. Then the code starts with all zero bits for the first code of the shortest length, and the codes are integer increments for the same length, and zeros are appended as the length increases. For the deflate format, these bits are stored backwards from their more natural integer increment ordering, and so when the decoding tables are built in the large loop below, the integer codes are incremented backwards. This routine assumes, but does not check, that all of the entries in lens[] are in the range 0..MAXBITS. The caller must assure this. 1..MAXBITS is interpreted as that code length. zero means that that symbol does not occur in this code. The codes are sorted by computing a count of codes for each length, creating from that a table of starting indices for each length in the sorted table, and then entering the symbols in order in the sorted table. The sorted table is work[], with that space being provided by the caller. The length counts are used for other purposes as well, i.e. finding the minimum and maximum length codes, determining if there are any codes at all, checking for a valid set of lengths, and looking ahead at length counts to determine sub-table sizes when building the decoding tables. */ /* accumulate lengths for codes (assumes lens[] all in 0..MAXBITS) */ for (len = 0; len <= MAXBITS; len++) count[len] = 0; for (sym = 0; sym < codes; sym++) count[lens[sym]]++; /* bound code lengths, force root to be within code lengths */ root = *bits; for (max = MAXBITS; max >= 1; max--) if (count[max] != 0) break; if (root > max) root = max; if (max == 0) { /* no symbols to code at all */ here.op = (unsigned char)64; /* invalid code marker */ here.bits = (unsigned char)1; here.val = (unsigned short)0; *(*table)++ = here; /* make a table to force an error */ *(*table)++ = here; *bits = 1; return 0; /* no symbols, but wait for decoding to report error */ } for (min = 1; min < max; min++) if (count[min] != 0) break; if (root < min) root = min; /* check for an over-subscribed or incomplete set of lengths */ left = 1; for (len = 1; len <= MAXBITS; len++) { left <<= 1; left -= count[len]; if (left < 0) return -1; /* over-subscribed */ } if (left > 0 && (type == CODES || max != 1)) return -1; /* incomplete set */ /* generate offsets into symbol table for each length for sorting */ offs[1] = 0; for (len = 1; len < MAXBITS; len++) offs[len + 1] = offs[len] + count[len]; /* sort symbols by length, by symbol order within each length */ for (sym = 0; sym < codes; sym++) if (lens[sym] != 0) work[offs[lens[sym]]++] = (unsigned short)sym; /* Create and fill in decoding tables. In this loop, the table being filled is at next and has curr index bits. The code being used is huff with length len. That code is converted to an index by dropping drop bits off of the bottom. For codes where len is less than drop + curr, those top drop + curr - len bits are incremented through all values to fill the table with replicated entries. root is the number of index bits for the root table. When len exceeds root, sub-tables are created pointed to by the root entry with an index of the low root bits of huff. This is saved in low to check for when a new sub-table should be started. drop is zero when the root table is being filled, and drop is root when sub-tables are being filled. When a new sub-table is needed, it is necessary to look ahead in the code lengths to determine what size sub-table is needed. The length counts are used for this, and so count[] is decremented as codes are entered in the tables. used keeps track of how many table entries have been allocated from the provided *table space. It is checked for LENS and DIST tables against the constants ENOUGH_LENS and ENOUGH_DISTS to guard against changes in the initial root table size constants. See the comments in inftrees.h for more information. sym increments through all symbols, and the loop terminates when all codes of length max, i.e. all codes, have been processed. This routine permits incomplete codes, so another loop after this one fills in the rest of the decoding tables with invalid code markers. */ /* set up for code type */ switch (type) { case CODES: base = extra = work; /* dummy value--not used */ match = 20; break; case LENS: base = lbase; extra = lext; match = 257; break; default: /* DISTS */ base = dbase; extra = dext; match = 0; } /* initialize state for loop */ huff = 0; /* starting code */ sym = 0; /* starting code symbol */ len = min; /* starting code length */ next = *table; /* current table to fill in */ curr = root; /* current table index bits */ drop = 0; /* current bits to drop from code for index */ low = (unsigned)(-1); /* trigger new sub-table when len > root */ used = 1U << root; /* use root table entries */ mask = used - 1; /* mask for comparing low */ /* check available table space */ if ((type == LENS && used > ENOUGH_LENS) || (type == DISTS && used > ENOUGH_DISTS)) return 1; /* process all codes and make table entries */ for (;;) { /* create table entry */ here.bits = (unsigned char)(len - drop); if (work[sym] + 1U < match) { here.op = (unsigned char)0; here.val = work[sym]; } else if (work[sym] >= match) { here.op = (unsigned char)(extra[work[sym] - match]); here.val = base[work[sym] - match]; } else { here.op = (unsigned char)(32 + 64); /* end of block */ here.val = 0; } /* replicate for those indices with low len bits equal to huff */ incr = 1U << (len - drop); fill = 1U << curr; min = fill; /* save offset to next table */ do { fill -= incr; next[(huff >> drop) + fill] = here; } while (fill != 0); /* backwards increment the len-bit code huff */ incr = 1U << (len - 1); while (huff & incr) incr >>= 1; if (incr != 0) { huff &= incr - 1; huff += incr; } else huff = 0; /* go to next symbol, update count, len */ sym++; if (--(count[len]) == 0) { if (len == max) break; len = lens[work[sym]]; } /* create new sub-table if needed */ if (len > root && (huff & mask) != low) { /* if first time, transition to sub-tables */ if (drop == 0) drop = root; /* increment past last table */ next += min; /* here min is 1 << curr */ /* determine length of next table */ curr = len - drop; left = (int)(1 << curr); while (curr + drop < max) { left -= count[curr + drop]; if (left <= 0) break; curr++; left <<= 1; } /* check for enough space */ used += 1U << curr; if ((type == LENS && used > ENOUGH_LENS) || (type == DISTS && used > ENOUGH_DISTS)) return 1; /* point entry in root table to sub-table */ low = huff & mask; (*table)[low].op = (unsigned char)curr; (*table)[low].bits = (unsigned char)root; (*table)[low].val = (unsigned short)(next - *table); } } /* fill in remaining table entry if code is incomplete (guaranteed to have at most one remaining entry, since if the code is incomplete, the maximum code length that was allowed to get this far is one bit) */ if (huff != 0) { here.op = (unsigned char)64; /* invalid code marker */ here.bits = (unsigned char)(len - drop); here.val = (unsigned short)0; next[huff] = here; } /* set return parameters */ *table += used; *bits = root; return 0; }
• put_short • bi_reverse • bi_flush • bi_windup • gen_codes • send_bits • tr_static_init • gen_trees_header • init_block • _tr_init • pqdownheap • gen_bitlen • build_tree • scan_tree • send_tree • build_bl_tree • send_all_trees • _tr_stored_block • _tr_flush_bits • _tr_align • compress_block • detect_data_type • _tr_flush_block • _tr_tally
/* trees.c -- output deflated data using Huffman coding * Copyright (C) 1995-2024 Jean-loup Gailly * detect_data_type() function provided freely by Cosmin Truta, 2006 * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* * ALGORITHM * * The "deflation" process uses several Huffman trees. The more * common source values are represented by shorter bit sequences. * * Each code tree is stored in a compressed form which is itself * a Huffman encoding of the lengths of all the code strings (in * ascending order by source values). The actual code strings are * reconstructed from the lengths in the inflate process, as described * in the deflate specification. * * REFERENCES * * Deutsch, L.P.,"'Deflate' Compressed Data Format Specification". * Available in ftp.uu.net:/pub/archiving/zip/doc/deflate-1.1.doc * * Storer, James A. * Data Compression: Methods and Theory, pp. 49-50. * Computer Science Press, 1988. ISBN 0-7167-8156-5. * * Sedgewick, R. * Algorithms, p290. * Addison-Wesley, 1983. ISBN 0-201-06672-6. */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ /* #define GEN_TREES_H */ #include "deflate.h" #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG # include <ctype.h> #endif /* =========================================================================== * Constants */ #define MAX_BL_BITS 7 /* Bit length codes must not exceed MAX_BL_BITS bits */ #define END_BLOCK 256 /* end of block literal code */ #define REP_3_6 16 /* repeat previous bit length 3-6 times (2 bits of repeat count) */ #define REPZ_3_10 17 /* repeat a zero length 3-10 times (3 bits of repeat count) */ #define REPZ_11_138 18 /* repeat a zero length 11-138 times (7 bits of repeat count) */ local const int extra_lbits[LENGTH_CODES] /* extra bits for each length code */ = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,5,5,5,5,0}; local const int extra_dbits[D_CODES] /* extra bits for each distance code */ = {0,0,0,0,1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,9,9,10,10,11,11,12,12,13,13}; local const int extra_blbits[BL_CODES]/* extra bits for each bit length code */ = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,2,3,7}; local const uch bl_order[BL_CODES] = {16,17,18,0,8,7,9,6,10,5,11,4,12,3,13,2,14,1,15}; /* The lengths of the bit length codes are sent in order of decreasing * probability, to avoid transmitting the lengths for unused bit length codes. */ /* =========================================================================== * Local data. These are initialized only once. */ #define DIST_CODE_LEN 512 /* see definition of array dist_code below */ #if defined(GEN_TREES_H) || !defined(STDC) /* non ANSI compilers may not accept trees.h */ local ct_data static_ltree[L_CODES+2]; /* The static literal tree. Since the bit lengths are imposed, there is no * need for the L_CODES extra codes used during heap construction. However * The codes 286 and 287 are needed to build a canonical tree (see _tr_init * below). */ local ct_data static_dtree[D_CODES]; /* The static distance tree. (Actually a trivial tree since all codes use * 5 bits.) */ uch _dist_code[DIST_CODE_LEN]; /* Distance codes. The first 256 values correspond to the distances * 3 .. 258, the last 256 values correspond to the top 8 bits of * the 15 bit distances. */ uch _length_code[MAX_MATCH-MIN_MATCH+1]; /* length code for each normalized match length (0 == MIN_MATCH) */ local int base_length[LENGTH_CODES]; /* First normalized length for each code (0 = MIN_MATCH) */ local int base_dist[D_CODES]; /* First normalized distance for each code (0 = distance of 1) */ #else # include "trees.h" #endif /* GEN_TREES_H */ struct static_tree_desc_s { const ct_data *static_tree; /* static tree or NULL */ const intf *extra_bits; /* extra bits for each code or NULL */ int extra_base; /* base index for extra_bits */ int elems; /* max number of elements in the tree */ int max_length; /* max bit length for the codes */ }; #ifdef NO_INIT_GLOBAL_POINTERS # define TCONST #else # define TCONST const #endif local TCONST static_tree_desc static_l_desc = {static_ltree, extra_lbits, LITERALS+1, L_CODES, MAX_BITS}; local TCONST static_tree_desc static_d_desc = {static_dtree, extra_dbits, 0, D_CODES, MAX_BITS}; local TCONST static_tree_desc static_bl_desc = {(const ct_data *)0, extra_blbits, 0, BL_CODES, MAX_BL_BITS}; /* =========================================================================== * Output a short LSB first on the stream. * IN assertion: there is enough room in pendingBuf. */ #define put_short(s, w) { \ put_byte(s, (uch)((w) & 0xff)); \ put_byte(s, (uch)((ush)(w) >> 8)); \ } /* =========================================================================== * Reverse the first len bits of a code, using straightforward code (a faster * method would use a table) * IN assertion: 1 <= len <= 15 */ local unsigned bi_reverse(unsigned code, int len) { register unsigned res = 0; do { res |= code & 1; code >>= 1, res <<= 1; } while (--len > 0); return res >> 1; } /* =========================================================================== * Flush the bit buffer, keeping at most 7 bits in it. */ local void bi_flush(deflate_state *s) { if (s->bi_valid == 16) { put_short(s, s->bi_buf); s->bi_buf = 0; s->bi_valid = 0; } else if (s->bi_valid >= 8) { put_byte(s, (Byte)s->bi_buf); s->bi_buf >>= 8; s->bi_valid -= 8; } } /* =========================================================================== * Flush the bit buffer and align the output on a byte boundary */ local void bi_windup(deflate_state *s) { if (s->bi_valid > 8) { put_short(s, s->bi_buf); } else if (s->bi_valid > 0) { put_byte(s, (Byte)s->bi_buf); } s->bi_buf = 0; s->bi_valid = 0; #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->bits_sent = (s->bits_sent + 7) & ~7; #endif } /* =========================================================================== * Generate the codes for a given tree and bit counts (which need not be * optimal). * IN assertion: the array bl_count contains the bit length statistics for * the given tree and the field len is set for all tree elements. * OUT assertion: the field code is set for all tree elements of non * zero code length. */ local void gen_codes(ct_data *tree, int max_code, ushf *bl_count) { ush next_code[MAX_BITS+1]; /* next code value for each bit length */ unsigned code = 0; /* running code value */ int bits; /* bit index */ int n; /* code index */ /* The distribution counts are first used to generate the code values * without bit reversal. */ for (bits = 1; bits <= MAX_BITS; bits++) { code = (code + bl_count[bits - 1]) << 1; next_code[bits] = (ush)code; } /* Check that the bit counts in bl_count are consistent. The last code * must be all ones. */ Assert (code + bl_count[MAX_BITS] - 1 == (1 << MAX_BITS) - 1, "inconsistent bit counts"); Tracev((stderr,"\ngen_codes: max_code %d ", max_code)); for (n = 0; n <= max_code; n++) { int len = tree[n].Len; if (len == 0) continue; /* Now reverse the bits */ tree[n].Code = (ush)bi_reverse(next_code[len]++, len); Tracecv(tree != static_ltree, (stderr,"\nn %3d %c l %2d c %4x (%x) ", n, (isgraph(n) ? n : ' '), len, tree[n].Code, next_code[len] - 1)); } } #ifdef GEN_TREES_H local void gen_trees_header(void); #endif #ifndef ZLIB_DEBUG # define send_code(s, c, tree) send_bits(s, tree[c].Code, tree[c].Len) /* Send a code of the given tree. c and tree must not have side effects */ #else /* !ZLIB_DEBUG */ # define send_code(s, c, tree) \ { if (z_verbose>2) fprintf(stderr,"\ncd %3d ",(c)); \ send_bits(s, tree[c].Code, tree[c].Len); } #endif /* =========================================================================== * Send a value on a given number of bits. * IN assertion: length <= 16 and value fits in length bits. */ #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG local void send_bits(deflate_state *s, int value, int length) { Tracevv((stderr," l %2d v %4x ", length, value)); Assert(length > 0 && length <= 15, "invalid length"); s->bits_sent += (ulg)length; /* If not enough room in bi_buf, use (valid) bits from bi_buf and * (16 - bi_valid) bits from value, leaving (width - (16 - bi_valid)) * unused bits in value. */ if (s->bi_valid > (int)Buf_size - length) { s->bi_buf |= (ush)value << s->bi_valid; put_short(s, s->bi_buf); s->bi_buf = (ush)value >> (Buf_size - s->bi_valid); s->bi_valid += length - Buf_size; } else { s->bi_buf |= (ush)value << s->bi_valid; s->bi_valid += length; } } #else /* !ZLIB_DEBUG */ #define send_bits(s, value, length) \ { int len = length;\ if (s->bi_valid > (int)Buf_size - len) {\ int val = (int)value;\ s->bi_buf |= (ush)val << s->bi_valid;\ put_short(s, s->bi_buf);\ s->bi_buf = (ush)val >> (Buf_size - s->bi_valid);\ s->bi_valid += len - Buf_size;\ } else {\ s->bi_buf |= (ush)(value) << s->bi_valid;\ s->bi_valid += len;\ }\ } #endif /* ZLIB_DEBUG */ /* the arguments must not have side effects */ /* =========================================================================== * Initialize the various 'constant' tables. */ local void tr_static_init(void) { #if defined(GEN_TREES_H) || !defined(STDC) static int static_init_done = 0; int n; /* iterates over tree elements */ int bits; /* bit counter */ int length; /* length value */ int code; /* code value */ int dist; /* distance index */ ush bl_count[MAX_BITS+1]; /* number of codes at each bit length for an optimal tree */ if (static_init_done) return; /* For some embedded targets, global variables are not initialized: */ #ifdef NO_INIT_GLOBAL_POINTERS static_l_desc.static_tree = static_ltree; static_l_desc.extra_bits = extra_lbits; static_d_desc.static_tree = static_dtree; static_d_desc.extra_bits = extra_dbits; static_bl_desc.extra_bits = extra_blbits; #endif /* Initialize the mapping length (0..255) -> length code (0..28) */ length = 0; for (code = 0; code < LENGTH_CODES-1; code++) { base_length[code] = length; for (n = 0; n < (1 << extra_lbits[code]); n++) { _length_code[length++] = (uch)code; } } Assert (length == 256, "tr_static_init: length != 256"); /* Note that the length 255 (match length 258) can be represented * in two different ways: code 284 + 5 bits or code 285, so we * overwrite length_code[255] to use the best encoding: */ _length_code[length - 1] = (uch)code; /* Initialize the mapping dist (0..32K) -> dist code (0..29) */ dist = 0; for (code = 0 ; code < 16; code++) { base_dist[code] = dist; for (n = 0; n < (1 << extra_dbits[code]); n++) { _dist_code[dist++] = (uch)code; } } Assert (dist == 256, "tr_static_init: dist != 256"); dist >>= 7; /* from now on, all distances are divided by 128 */ for ( ; code < D_CODES; code++) { base_dist[code] = dist << 7; for (n = 0; n < (1 << (extra_dbits[code] - 7)); n++) { _dist_code[256 + dist++] = (uch)code; } } Assert (dist == 256, "tr_static_init: 256 + dist != 512"); /* Construct the codes of the static literal tree */ for (bits = 0; bits <= MAX_BITS; bits++) bl_count[bits] = 0; n = 0; while (n <= 143) static_ltree[n++].Len = 8, bl_count[8]++; while (n <= 255) static_ltree[n++].Len = 9, bl_count[9]++; while (n <= 279) static_ltree[n++].Len = 7, bl_count[7]++; while (n <= 287) static_ltree[n++].Len = 8, bl_count[8]++; /* Codes 286 and 287 do not exist, but we must include them in the * tree construction to get a canonical Huffman tree (longest code * all ones) */ gen_codes((ct_data *)static_ltree, L_CODES+1, bl_count); /* The static distance tree is trivial: */ for (n = 0; n < D_CODES; n++) { static_dtree[n].Len = 5; static_dtree[n].Code = bi_reverse((unsigned)n, 5); } static_init_done = 1; # ifdef GEN_TREES_H gen_trees_header(); # endif #endif /* defined(GEN_TREES_H) || !defined(STDC) */ } /* =========================================================================== * Generate the file trees.h describing the static trees. */ #ifdef GEN_TREES_H # ifndef ZLIB_DEBUG # include <stdio.h> # endif # define SEPARATOR(i, last, width) \ ((i) == (last)? "\n};\n\n" : \ ((i) % (width) == (width) - 1 ? ",\n" : ", ")) void gen_trees_header(void) { FILE *header = fopen("trees.h", "w"); int i; Assert (header != NULL, "Can't open trees.h"); fprintf(header, "/* header created automatically with -DGEN_TREES_H */\n\n"); fprintf(header, "local const ct_data static_ltree[L_CODES+2] = {\n"); for (i = 0; i < L_CODES+2; i++) { fprintf(header, "{{%3u},{%3u}}%s", static_ltree[i].Code, static_ltree[i].Len, SEPARATOR(i, L_CODES+1, 5)); } fprintf(header, "local const ct_data static_dtree[D_CODES] = {\n"); for (i = 0; i < D_CODES; i++) { fprintf(header, "{{%2u},{%2u}}%s", static_dtree[i].Code, static_dtree[i].Len, SEPARATOR(i, D_CODES-1, 5)); } fprintf(header, "const uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _dist_code[DIST_CODE_LEN] = {\n"); for (i = 0; i < DIST_CODE_LEN; i++) { fprintf(header, "%2u%s", _dist_code[i], SEPARATOR(i, DIST_CODE_LEN-1, 20)); } fprintf(header, "const uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _length_code[MAX_MATCH-MIN_MATCH+1]= {\n"); for (i = 0; i < MAX_MATCH-MIN_MATCH+1; i++) { fprintf(header, "%2u%s", _length_code[i], SEPARATOR(i, MAX_MATCH-MIN_MATCH, 20)); } fprintf(header, "local const int base_length[LENGTH_CODES] = {\n"); for (i = 0; i < LENGTH_CODES; i++) { fprintf(header, "%1u%s", base_length[i], SEPARATOR(i, LENGTH_CODES-1, 20)); } fprintf(header, "local const int base_dist[D_CODES] = {\n"); for (i = 0; i < D_CODES; i++) { fprintf(header, "%5u%s", base_dist[i], SEPARATOR(i, D_CODES-1, 10)); } fclose(header); } #endif /* GEN_TREES_H */ /* =========================================================================== * Initialize a new block. */ local void init_block(deflate_state *s) { int n; /* iterates over tree elements */ /* Initialize the trees. */ for (n = 0; n < L_CODES; n++) s->dyn_ltree[n].Freq = 0; for (n = 0; n < D_CODES; n++) s->dyn_dtree[n].Freq = 0; for (n = 0; n < BL_CODES; n++) s->bl_tree[n].Freq = 0; s->dyn_ltree[END_BLOCK].Freq = 1; s->opt_len = s->static_len = 0L; s->sym_next = s->matches = 0; } /* =========================================================================== * Initialize the tree data structures for a new zlib stream. */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_init(deflate_state *s) { tr_static_init(); s->l_desc.dyn_tree = s->dyn_ltree; s->l_desc.stat_desc = &static_l_desc; s->d_desc.dyn_tree = s->dyn_dtree; s->d_desc.stat_desc = &static_d_desc; s->bl_desc.dyn_tree = s->bl_tree; s->bl_desc.stat_desc = &static_bl_desc; s->bi_buf = 0; s->bi_valid = 0; #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->compressed_len = 0L; s->bits_sent = 0L; #endif /* Initialize the first block of the first file: */ init_block(s); } #define SMALLEST 1 /* Index within the heap array of least frequent node in the Huffman tree */ /* =========================================================================== * Remove the smallest element from the heap and recreate the heap with * one less element. Updates heap and heap_len. */ #define pqremove(s, tree, top) \ {\ top = s->heap[SMALLEST]; \ s->heap[SMALLEST] = s->heap[s->heap_len--]; \ pqdownheap(s, tree, SMALLEST); \ } /* =========================================================================== * Compares to subtrees, using the tree depth as tie breaker when * the subtrees have equal frequency. This minimizes the worst case length. */ #define smaller(tree, n, m, depth) \ (tree[n].Freq < tree[m].Freq || \ (tree[n].Freq == tree[m].Freq && depth[n] <= depth[m])) /* =========================================================================== * Restore the heap property by moving down the tree starting at node k, * exchanging a node with the smallest of its two sons if necessary, stopping * when the heap property is re-established (each father smaller than its * two sons). */ local void pqdownheap(deflate_state *s, ct_data *tree, int k) { int v = s->heap[k]; int j = k << 1; /* left son of k */ while (j <= s->heap_len) { /* Set j to the smallest of the two sons: */ if (j < s->heap_len && smaller(tree, s->heap[j + 1], s->heap[j], s->depth)) { j++; } /* Exit if v is smaller than both sons */ if (smaller(tree, v, s->heap[j], s->depth)) break; /* Exchange v with the smallest son */ s->heap[k] = s->heap[j]; k = j; /* And continue down the tree, setting j to the left son of k */ j <<= 1; } s->heap[k] = v; } /* =========================================================================== * Compute the optimal bit lengths for a tree and update the total bit length * for the current block. * IN assertion: the fields freq and dad are set, heap[heap_max] and * above are the tree nodes sorted by increasing frequency. * OUT assertions: the field len is set to the optimal bit length, the * array bl_count contains the frequencies for each bit length. * The length opt_len is updated; static_len is also updated if stree is * not null. */ local void gen_bitlen(deflate_state *s, tree_desc *desc) { ct_data *tree = desc->dyn_tree; int max_code = desc->max_code; const ct_data *stree = desc->stat_desc->static_tree; const intf *extra = desc->stat_desc->extra_bits; int base = desc->stat_desc->extra_base; int max_length = desc->stat_desc->max_length; int h; /* heap index */ int n, m; /* iterate over the tree elements */ int bits; /* bit length */ int xbits; /* extra bits */ ush f; /* frequency */ int overflow = 0; /* number of elements with bit length too large */ for (bits = 0; bits <= MAX_BITS; bits++) s->bl_count[bits] = 0; /* In a first pass, compute the optimal bit lengths (which may * overflow in the case of the bit length tree). */ tree[s->heap[s->heap_max]].Len = 0; /* root of the heap */ for (h = s->heap_max + 1; h < HEAP_SIZE; h++) { n = s->heap[h]; bits = tree[tree[n].Dad].Len + 1; if (bits > max_length) bits = max_length, overflow++; tree[n].Len = (ush)bits; /* We overwrite tree[n].Dad which is no longer needed */ if (n > max_code) continue; /* not a leaf node */ s->bl_count[bits]++; xbits = 0; if (n >= base) xbits = extra[n - base]; f = tree[n].Freq; s->opt_len += (ulg)f * (unsigned)(bits + xbits); if (stree) s->static_len += (ulg)f * (unsigned)(stree[n].Len + xbits); } if (overflow == 0) return; Tracev((stderr,"\nbit length overflow\n")); /* This happens for example on obj2 and pic of the Calgary corpus */ /* Find the first bit length which could increase: */ do { bits = max_length - 1; while (s->bl_count[bits] == 0) bits--; s->bl_count[bits]--; /* move one leaf down the tree */ s->bl_count[bits + 1] += 2; /* move one overflow item as its brother */ s->bl_count[max_length]--; /* The brother of the overflow item also moves one step up, * but this does not affect bl_count[max_length] */ overflow -= 2; } while (overflow > 0); /* Now recompute all bit lengths, scanning in increasing frequency. * h is still equal to HEAP_SIZE. (It is simpler to reconstruct all * lengths instead of fixing only the wrong ones. This idea is taken * from 'ar' written by Haruhiko Okumura.) */ for (bits = max_length; bits != 0; bits--) { n = s->bl_count[bits]; while (n != 0) { m = s->heap[--h]; if (m > max_code) continue; if ((unsigned) tree[m].Len != (unsigned) bits) { Tracev((stderr,"code %d bits %d->%d\n", m, tree[m].Len, bits)); s->opt_len += ((ulg)bits - tree[m].Len) * tree[m].Freq; tree[m].Len = (ush)bits; } n--; } } } #ifdef DUMP_BL_TREE # include <stdio.h> #endif /* =========================================================================== * Construct one Huffman tree and assigns the code bit strings and lengths. * Update the total bit length for the current block. * IN assertion: the field freq is set for all tree elements. * OUT assertions: the fields len and code are set to the optimal bit length * and corresponding code. The length opt_len is updated; static_len is * also updated if stree is not null. The field max_code is set. */ local void build_tree(deflate_state *s, tree_desc *desc) { ct_data *tree = desc->dyn_tree; const ct_data *stree = desc->stat_desc->static_tree; int elems = desc->stat_desc->elems; int n, m; /* iterate over heap elements */ int max_code = -1; /* largest code with non zero frequency */ int node; /* new node being created */ /* Construct the initial heap, with least frequent element in * heap[SMALLEST]. The sons of heap[n] are heap[2*n] and heap[2*n + 1]. * heap[0] is not used. */ s->heap_len = 0, s->heap_max = HEAP_SIZE; for (n = 0; n < elems; n++) { if (tree[n].Freq != 0) { s->heap[++(s->heap_len)] = max_code = n; s->depth[n] = 0; } else { tree[n].Len = 0; } } /* The pkzip format requires that at least one distance code exists, * and that at least one bit should be sent even if there is only one * possible code. So to avoid special checks later on we force at least * two codes of non zero frequency. */ while (s->heap_len < 2) { node = s->heap[++(s->heap_len)] = (max_code < 2 ? ++max_code : 0); tree[node].Freq = 1; s->depth[node] = 0; s->opt_len--; if (stree) s->static_len -= stree[node].Len; /* node is 0 or 1 so it does not have extra bits */ } desc->max_code = max_code; /* The elements heap[heap_len/2 + 1 .. heap_len] are leaves of the tree, * establish sub-heaps of increasing lengths: */ for (n = s->heap_len/2; n >= 1; n--) pqdownheap(s, tree, n); /* Construct the Huffman tree by repeatedly combining the least two * frequent nodes. */ node = elems; /* next internal node of the tree */ do { pqremove(s, tree, n); /* n = node of least frequency */ m = s->heap[SMALLEST]; /* m = node of next least frequency */ s->heap[--(s->heap_max)] = n; /* keep the nodes sorted by frequency */ s->heap[--(s->heap_max)] = m; /* Create a new node father of n and m */ tree[node].Freq = tree[n].Freq + tree[m].Freq; s->depth[node] = (uch)((s->depth[n] >= s->depth[m] ? s->depth[n] : s->depth[m]) + 1); tree[n].Dad = tree[m].Dad = (ush)node; #ifdef DUMP_BL_TREE if (tree == s->bl_tree) { fprintf(stderr,"\nnode %d(%d), sons %d(%d) %d(%d)", node, tree[node].Freq, n, tree[n].Freq, m, tree[m].Freq); } #endif /* and insert the new node in the heap */ s->heap[SMALLEST] = node++; pqdownheap(s, tree, SMALLEST); } while (s->heap_len >= 2); s->heap[--(s->heap_max)] = s->heap[SMALLEST]; /* At this point, the fields freq and dad are set. We can now * generate the bit lengths. */ gen_bitlen(s, (tree_desc *)desc); /* The field len is now set, we can generate the bit codes */ gen_codes ((ct_data *)tree, max_code, s->bl_count); } /* =========================================================================== * Scan a literal or distance tree to determine the frequencies of the codes * in the bit length tree. */ local void scan_tree(deflate_state *s, ct_data *tree, int max_code) { int n; /* iterates over all tree elements */ int prevlen = -1; /* last emitted length */ int curlen; /* length of current code */ int nextlen = tree[0].Len; /* length of next code */ int count = 0; /* repeat count of the current code */ int max_count = 7; /* max repeat count */ int min_count = 4; /* min repeat count */ if (nextlen == 0) max_count = 138, min_count = 3; tree[max_code + 1].Len = (ush)0xffff; /* guard */ for (n = 0; n <= max_code; n++) { curlen = nextlen; nextlen = tree[n + 1].Len; if (++count < max_count && curlen == nextlen) { continue; } else if (count < min_count) { s->bl_tree[curlen].Freq += count; } else if (curlen != 0) { if (curlen != prevlen) s->bl_tree[curlen].Freq++; s->bl_tree[REP_3_6].Freq++; } else if (count <= 10) { s->bl_tree[REPZ_3_10].Freq++; } else { s->bl_tree[REPZ_11_138].Freq++; } count = 0; prevlen = curlen; if (nextlen == 0) { max_count = 138, min_count = 3; } else if (curlen == nextlen) { max_count = 6, min_count = 3; } else { max_count = 7, min_count = 4; } } } /* =========================================================================== * Send a literal or distance tree in compressed form, using the codes in * bl_tree. */ local void send_tree(deflate_state *s, ct_data *tree, int max_code) { int n; /* iterates over all tree elements */ int prevlen = -1; /* last emitted length */ int curlen; /* length of current code */ int nextlen = tree[0].Len; /* length of next code */ int count = 0; /* repeat count of the current code */ int max_count = 7; /* max repeat count */ int min_count = 4; /* min repeat count */ /* tree[max_code + 1].Len = -1; */ /* guard already set */ if (nextlen == 0) max_count = 138, min_count = 3; for (n = 0; n <= max_code; n++) { curlen = nextlen; nextlen = tree[n + 1].Len; if (++count < max_count && curlen == nextlen) { continue; } else if (count < min_count) { do { send_code(s, curlen, s->bl_tree); } while (--count != 0); } else if (curlen != 0) { if (curlen != prevlen) { send_code(s, curlen, s->bl_tree); count--; } Assert(count >= 3 && count <= 6, " 3_6?"); send_code(s, REP_3_6, s->bl_tree); send_bits(s, count - 3, 2); } else if (count <= 10) { send_code(s, REPZ_3_10, s->bl_tree); send_bits(s, count - 3, 3); } else { send_code(s, REPZ_11_138, s->bl_tree); send_bits(s, count - 11, 7); } count = 0; prevlen = curlen; if (nextlen == 0) { max_count = 138, min_count = 3; } else if (curlen == nextlen) { max_count = 6, min_count = 3; } else { max_count = 7, min_count = 4; } } } /* =========================================================================== * Construct the Huffman tree for the bit lengths and return the index in * bl_order of the last bit length code to send. */ local int build_bl_tree(deflate_state *s) { int max_blindex; /* index of last bit length code of non zero freq */ /* Determine the bit length frequencies for literal and distance trees */ scan_tree(s, (ct_data *)s->dyn_ltree, s->l_desc.max_code); scan_tree(s, (ct_data *)s->dyn_dtree, s->d_desc.max_code); /* Build the bit length tree: */ build_tree(s, (tree_desc *)(&(s->bl_desc))); /* opt_len now includes the length of the tree representations, except the * lengths of the bit lengths codes and the 5 + 5 + 4 bits for the counts. */ /* Determine the number of bit length codes to send. The pkzip format * requires that at least 4 bit length codes be sent. (appnote.txt says * 3 but the actual value used is 4.) */ for (max_blindex = BL_CODES-1; max_blindex >= 3; max_blindex--) { if (s->bl_tree[bl_order[max_blindex]].Len != 0) break; } /* Update opt_len to include the bit length tree and counts */ s->opt_len += 3*((ulg)max_blindex + 1) + 5 + 5 + 4; Tracev((stderr, "\ndyn trees: dyn %ld, stat %ld", s->opt_len, s->static_len)); return max_blindex; } /* =========================================================================== * Send the header for a block using dynamic Huffman trees: the counts, the * lengths of the bit length codes, the literal tree and the distance tree. * IN assertion: lcodes >= 257, dcodes >= 1, blcodes >= 4. */ local void send_all_trees(deflate_state *s, int lcodes, int dcodes, int blcodes) { int rank; /* index in bl_order */ Assert (lcodes >= 257 && dcodes >= 1 && blcodes >= 4, "not enough codes"); Assert (lcodes <= L_CODES && dcodes <= D_CODES && blcodes <= BL_CODES, "too many codes"); Tracev((stderr, "\nbl counts: ")); send_bits(s, lcodes - 257, 5); /* not +255 as stated in appnote.txt */ send_bits(s, dcodes - 1, 5); send_bits(s, blcodes - 4, 4); /* not -3 as stated in appnote.txt */ for (rank = 0; rank < blcodes; rank++) { Tracev((stderr, "\nbl code %2d ", bl_order[rank])); send_bits(s, s->bl_tree[bl_order[rank]].Len, 3); } Tracev((stderr, "\nbl tree: sent %ld", s->bits_sent)); send_tree(s, (ct_data *)s->dyn_ltree, lcodes - 1); /* literal tree */ Tracev((stderr, "\nlit tree: sent %ld", s->bits_sent)); send_tree(s, (ct_data *)s->dyn_dtree, dcodes - 1); /* distance tree */ Tracev((stderr, "\ndist tree: sent %ld", s->bits_sent)); } /* =========================================================================== * Send a stored block */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_stored_block(deflate_state *s, charf *buf, ulg stored_len, int last) { send_bits(s, (STORED_BLOCK<<1) + last, 3); /* send block type */ bi_windup(s); /* align on byte boundary */ put_short(s, (ush)stored_len); put_short(s, (ush)~stored_len); if (stored_len) zmemcpy(s->pending_buf + s->pending, (Bytef *)buf, stored_len); s->pending += stored_len; #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->compressed_len = (s->compressed_len + 3 + 7) & (ulg)~7L; s->compressed_len += (stored_len + 4) << 3; s->bits_sent += 2*16; s->bits_sent += stored_len << 3; #endif } /* =========================================================================== * Flush the bits in the bit buffer to pending output (leaves at most 7 bits) */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_flush_bits(deflate_state *s) { bi_flush(s); } /* =========================================================================== * Send one empty static block to give enough lookahead for inflate. * This takes 10 bits, of which 7 may remain in the bit buffer. */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_align(deflate_state *s) { send_bits(s, STATIC_TREES<<1, 3); send_code(s, END_BLOCK, static_ltree); #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->compressed_len += 10L; /* 3 for block type, 7 for EOB */ #endif bi_flush(s); } /* =========================================================================== * Send the block data compressed using the given Huffman trees */ local void compress_block(deflate_state *s, const ct_data *ltree, const ct_data *dtree) { unsigned dist; /* distance of matched string */ int lc; /* match length or unmatched char (if dist == 0) */ unsigned sx = 0; /* running index in symbol buffers */ unsigned code; /* the code to send */ int extra; /* number of extra bits to send */ if (s->sym_next != 0) do { #ifdef LIT_MEM dist = s->d_buf[sx]; lc = s->l_buf[sx++]; #else dist = s->sym_buf[sx++] & 0xff; dist += (unsigned)(s->sym_buf[sx++] & 0xff) << 8; lc = s->sym_buf[sx++]; #endif if (dist == 0) { send_code(s, lc, ltree); /* send a literal byte */ Tracecv(isgraph(lc), (stderr," '%c' ", lc)); } else { /* Here, lc is the match length - MIN_MATCH */ code = _length_code[lc]; send_code(s, code + LITERALS + 1, ltree); /* send length code */ extra = extra_lbits[code]; if (extra != 0) { lc -= base_length[code]; send_bits(s, lc, extra); /* send the extra length bits */ } dist--; /* dist is now the match distance - 1 */ code = d_code(dist); Assert (code < D_CODES, "bad d_code"); send_code(s, code, dtree); /* send the distance code */ extra = extra_dbits[code]; if (extra != 0) { dist -= (unsigned)base_dist[code]; send_bits(s, dist, extra); /* send the extra distance bits */ } } /* literal or match pair ? */ /* Check for no overlay of pending_buf on needed symbols */ #ifdef LIT_MEM Assert(s->pending < 2 * (s->lit_bufsize + sx), "pendingBuf overflow"); #else Assert(s->pending < s->lit_bufsize + sx, "pendingBuf overflow"); #endif } while (sx < s->sym_next); send_code(s, END_BLOCK, ltree); } /* =========================================================================== * Check if the data type is TEXT or BINARY, using the following algorithm: * - TEXT if the two conditions below are satisfied: * a) There are no non-portable control characters belonging to the * "block list" (0..6, 14..25, 28..31). * b) There is at least one printable character belonging to the * "allow list" (9 {TAB}, 10 {LF}, 13 {CR}, 32..255). * - BINARY otherwise. * - The following partially-portable control characters form a * "gray list" that is ignored in this detection algorithm: * (7 {BEL}, 8 {BS}, 11 {VT}, 12 {FF}, 26 {SUB}, 27 {ESC}). * IN assertion: the fields Freq of dyn_ltree are set. */ local int detect_data_type(deflate_state *s) { /* block_mask is the bit mask of block-listed bytes * set bits 0..6, 14..25, and 28..31 * 0xf3ffc07f = binary 11110011111111111100000001111111 */ unsigned long block_mask = 0xf3ffc07fUL; int n; /* Check for non-textual ("block-listed") bytes. */ for (n = 0; n <= 31; n++, block_mask >>= 1) if ((block_mask & 1) && (s->dyn_ltree[n].Freq != 0)) return Z_BINARY; /* Check for textual ("allow-listed") bytes. */ if (s->dyn_ltree[9].Freq != 0 || s->dyn_ltree[10].Freq != 0 || s->dyn_ltree[13].Freq != 0) return Z_TEXT; for (n = 32; n < LITERALS; n++) if (s->dyn_ltree[n].Freq != 0) return Z_TEXT; /* There are no "block-listed" or "allow-listed" bytes: * this stream either is empty or has tolerated ("gray-listed") bytes only. */ return Z_BINARY; } /* =========================================================================== * Determine the best encoding for the current block: dynamic trees, static * trees or store, and write out the encoded block. */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_flush_block(deflate_state *s, charf *buf, ulg stored_len, int last) { ulg opt_lenb, static_lenb; /* opt_len and static_len in bytes */ int max_blindex = 0; /* index of last bit length code of non zero freq */ /* Build the Huffman trees unless a stored block is forced */ if (s->level > 0) { /* Check if the file is binary or text */ if (s->strm->data_type == Z_UNKNOWN) s->strm->data_type = detect_data_type(s); /* Construct the literal and distance trees */ build_tree(s, (tree_desc *)(&(s->l_desc))); Tracev((stderr, "\nlit data: dyn %ld, stat %ld", s->opt_len, s->static_len)); build_tree(s, (tree_desc *)(&(s->d_desc))); Tracev((stderr, "\ndist data: dyn %ld, stat %ld", s->opt_len, s->static_len)); /* At this point, opt_len and static_len are the total bit lengths of * the compressed block data, excluding the tree representations. */ /* Build the bit length tree for the above two trees, and get the index * in bl_order of the last bit length code to send. */ max_blindex = build_bl_tree(s); /* Determine the best encoding. Compute the block lengths in bytes. */ opt_lenb = (s->opt_len + 3 + 7) >> 3; static_lenb = (s->static_len + 3 + 7) >> 3; Tracev((stderr, "\nopt %lu(%lu) stat %lu(%lu) stored %lu lit %u ", opt_lenb, s->opt_len, static_lenb, s->static_len, stored_len, s->sym_next / 3)); #ifndef FORCE_STATIC if (static_lenb <= opt_lenb || s->strategy == Z_FIXED) #endif opt_lenb = static_lenb; } else { Assert(buf != (char*)0, "lost buf"); opt_lenb = static_lenb = stored_len + 5; /* force a stored block */ } #ifdef FORCE_STORED if (buf != (char*)0) { /* force stored block */ #else if (stored_len + 4 <= opt_lenb && buf != (char*)0) { /* 4: two words for the lengths */ #endif /* The test buf != NULL is only necessary if LIT_BUFSIZE > WSIZE. * Otherwise we can't have processed more than WSIZE input bytes since * the last block flush, because compression would have been * successful. If LIT_BUFSIZE <= WSIZE, it is never too late to * transform a block into a stored block. */ _tr_stored_block(s, buf, stored_len, last); } else if (static_lenb == opt_lenb) { send_bits(s, (STATIC_TREES<<1) + last, 3); compress_block(s, (const ct_data *)static_ltree, (const ct_data *)static_dtree); #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->compressed_len += 3 + s->static_len; #endif } else { send_bits(s, (DYN_TREES<<1) + last, 3); send_all_trees(s, s->l_desc.max_code + 1, s->d_desc.max_code + 1, max_blindex + 1); compress_block(s, (const ct_data *)s->dyn_ltree, (const ct_data *)s->dyn_dtree); #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->compressed_len += 3 + s->opt_len; #endif } Assert (s->compressed_len == s->bits_sent, "bad compressed size"); /* The above check is made mod 2^32, for files larger than 512 MB * and uLong implemented on 32 bits. */ init_block(s); if (last) { bi_windup(s); #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG s->compressed_len += 7; /* align on byte boundary */ #endif } Tracev((stderr,"\ncomprlen %lu(%lu) ", s->compressed_len >> 3, s->compressed_len - 7*last)); } /* =========================================================================== * Save the match info and tally the frequency counts. Return true if * the current block must be flushed. */ int ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_tally(deflate_state *s, unsigned dist, unsigned lc) { #ifdef LIT_MEM s->d_buf[s->sym_next] = (ush)dist; s->l_buf[s->sym_next++] = (uch)lc; #else s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = (uch)dist; s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = (uch)(dist >> 8); s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = (uch)lc; #endif if (dist == 0) { /* lc is the unmatched char */ s->dyn_ltree[lc].Freq++; } else { s->matches++; /* Here, lc is the match length - MIN_MATCH */ dist--; /* dist = match distance - 1 */ Assert((ush)dist < (ush)MAX_DIST(s) && (ush)lc <= (ush)(MAX_MATCH-MIN_MATCH) && (ush)d_code(dist) < (ush)D_CODES, "_tr_tally: bad match"); s->dyn_ltree[_length_code[lc] + LITERALS + 1].Freq++; s->dyn_dtree[d_code(dist)].Freq++; } return (s->sym_next == s->sym_end); }
/* uncompr.c -- decompress a memory buffer * Copyright (C) 1995-2003, 2010, 2014, 2016 Jean-loup Gailly, Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #define ZLIB_INTERNAL #include "zlib.h" /* =========================================================================== Decompresses the source buffer into the destination buffer. *sourceLen is the byte length of the source buffer. Upon entry, *destLen is the total size of the destination buffer, which must be large enough to hold the entire uncompressed data. (The size of the uncompressed data must have been saved previously by the compressor and transmitted to the decompressor by some mechanism outside the scope of this compression library.) Upon exit, *destLen is the size of the decompressed data and *sourceLen is the number of source bytes consumed. Upon return, source + *sourceLen points to the first unused input byte. uncompress returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough room in the output buffer, or Z_DATA_ERROR if the input data was corrupted, including if the input data is an incomplete zlib stream. */ int ZEXPORT uncompress2(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong *sourceLen) { z_stream stream; int err; const uInt max = (uInt)-1; uLong len, left; Byte buf[1]; /* for detection of incomplete stream when *destLen == 0 */ len = *sourceLen; if (*destLen) { left = *destLen; *destLen = 0; } else { left = 1; dest = buf; } stream.next_in = (z_const Bytef *)source; stream.avail_in = 0; stream.zalloc = (alloc_func)0; stream.zfree = (free_func)0; stream.opaque = (voidpf)0; err = inflateInit(&stream); if (err != Z_OK) return err; stream.next_out = dest; stream.avail_out = 0; do { if (stream.avail_out == 0) { stream.avail_out = left > (uLong)max ? max : (uInt)left; left -= stream.avail_out; } if (stream.avail_in == 0) { stream.avail_in = len > (uLong)max ? max : (uInt)len; len -= stream.avail_in; } err = inflate(&stream, Z_NO_FLUSH); } while (err == Z_OK); *sourceLen -= len + stream.avail_in; if (dest != buf) *destLen = stream.total_out; else if (stream.total_out && err == Z_BUF_ERROR) left = 1; inflateEnd(&stream); return err == Z_STREAM_END ? Z_OK : err == Z_NEED_DICT ? Z_DATA_ERROR : err == Z_BUF_ERROR && left + stream.avail_out ? Z_DATA_ERROR : err; } int ZEXPORT uncompress(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen) { return uncompress2(dest, destLen, source, &sourceLen); }
• zlibVersion • zlibCompileFlags • z_error • zError • zmemcpy • zmemcmp • zmemzero • zcalloc • zcfree
/* zutil.c -- target dependent utility functions for the compression library * Copyright (C) 1995-2017 Jean-loup Gailly * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #include "zutil.h" #ifndef Z_SOLO # include "gzguts.h" #endif z_const char * const z_errmsg[10] = { (z_const char *)"need dictionary", /* Z_NEED_DICT 2 */ (z_const char *)"stream end", /* Z_STREAM_END 1 */ (z_const char *)"", /* Z_OK 0 */ (z_const char *)"file error", /* Z_ERRNO (-1) */ (z_const char *)"stream error", /* Z_STREAM_ERROR (-2) */ (z_const char *)"data error", /* Z_DATA_ERROR (-3) */ (z_const char *)"insufficient memory", /* Z_MEM_ERROR (-4) */ (z_const char *)"buffer error", /* Z_BUF_ERROR (-5) */ (z_const char *)"incompatible version",/* Z_VERSION_ERROR (-6) */ (z_const char *)"" }; const char * ZEXPORT zlibVersion(void) { return ZLIB_VERSION; } uLong ZEXPORT zlibCompileFlags(void) { uLong flags; flags = 0; switch ((int)(sizeof(uInt))) { case 2: break; case 4: flags += 1; break; case 8: flags += 2; break; default: flags += 3; } switch ((int)(sizeof(uLong))) { case 2: break; case 4: flags += 1 << 2; break; case 8: flags += 2 << 2; break; default: flags += 3 << 2; } switch ((int)(sizeof(voidpf))) { case 2: break; case 4: flags += 1 << 4; break; case 8: flags += 2 << 4; break; default: flags += 3 << 4; } switch ((int)(sizeof(z_off_t))) { case 2: break; case 4: flags += 1 << 6; break; case 8: flags += 2 << 6; break; default: flags += 3 << 6; } #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG flags += 1 << 8; #endif /* #if defined(ASMV) || defined(ASMINF) flags += 1 << 9; #endif */ #ifdef ZLIB_WINAPI flags += 1 << 10; #endif #ifdef BUILDFIXED flags += 1 << 12; #endif #ifdef DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE flags += 1 << 13; #endif #ifdef NO_GZCOMPRESS flags += 1L << 16; #endif #ifdef NO_GZIP flags += 1L << 17; #endif #ifdef PKZIP_BUG_WORKAROUND flags += 1L << 20; #endif #ifdef FASTEST flags += 1L << 21; #endif #if defined(STDC) || defined(Z_HAVE_STDARG_H) # ifdef NO_vsnprintf flags += 1L << 25; # ifdef HAS_vsprintf_void flags += 1L << 26; # endif # else # ifdef HAS_vsnprintf_void flags += 1L << 26; # endif # endif #else flags += 1L << 24; # ifdef NO_snprintf flags += 1L << 25; # ifdef HAS_sprintf_void flags += 1L << 26; # endif # else # ifdef HAS_snprintf_void flags += 1L << 26; # endif # endif #endif return flags; } #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG #include <stdlib.h> # ifndef verbose # define verbose 0 # endif int ZLIB_INTERNAL z_verbose = verbose; void ZLIB_INTERNAL z_error(char *m) { fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", m); exit(1); } #endif /* exported to allow conversion of error code to string for compress() and * uncompress() */ const char * ZEXPORT zError(int err) { return ERR_MSG(err); } #if defined(_WIN32_WCE) && _WIN32_WCE < 0x800 /* The older Microsoft C Run-Time Library for Windows CE doesn't have * errno. We define it as a global variable to simplify porting. * Its value is always 0 and should not be used. */ int errno = 0; #endif #ifndef HAVE_MEMCPY void ZLIB_INTERNAL zmemcpy(Bytef* dest, const Bytef* source, uInt len) { if (len == 0) return; do { *dest++ = *source++; /* ??? to be unrolled */ } while (--len != 0); } int ZLIB_INTERNAL zmemcmp(const Bytef* s1, const Bytef* s2, uInt len) { uInt j; for (j = 0; j < len; j++) { if (s1[j] != s2[j]) return 2*(s1[j] > s2[j])-1; } return 0; } void ZLIB_INTERNAL zmemzero(Bytef* dest, uInt len) { if (len == 0) return; do { *dest++ = 0; /* ??? to be unrolled */ } while (--len != 0); } #endif #ifndef Z_SOLO #ifdef SYS16BIT #ifdef __TURBOC__ /* Turbo C in 16-bit mode */ # define MY_ZCALLOC /* Turbo C malloc() does not allow dynamic allocation of 64K bytes * and farmalloc(64K) returns a pointer with an offset of 8, so we * must fix the pointer. Warning: the pointer must be put back to its * original form in order to free it, use zcfree(). */ #define MAX_PTR 10 /* 10*64K = 640K */ local int next_ptr = 0; typedef struct ptr_table_s { voidpf org_ptr; voidpf new_ptr; } ptr_table; local ptr_table table[MAX_PTR]; /* This table is used to remember the original form of pointers * to large buffers (64K). Such pointers are normalized with a zero offset. * Since MSDOS is not a preemptive multitasking OS, this table is not * protected from concurrent access. This hack doesn't work anyway on * a protected system like OS/2. Use Microsoft C instead. */ voidpf ZLIB_INTERNAL zcalloc(voidpf opaque, unsigned items, unsigned size) { voidpf buf; ulg bsize = (ulg)items*size; (void)opaque; /* If we allocate less than 65520 bytes, we assume that farmalloc * will return a usable pointer which doesn't have to be normalized. */ if (bsize < 65520L) { buf = farmalloc(bsize); if (*(ush*)&buf != 0) return buf; } else { buf = farmalloc(bsize + 16L); } if (buf == NULL || next_ptr >= MAX_PTR) return NULL; table[next_ptr].org_ptr = buf; /* Normalize the pointer to seg:0 */ *((ush*)&buf+1) += ((ush)((uch*)buf-0) + 15) >> 4; *(ush*)&buf = 0; table[next_ptr++].new_ptr = buf; return buf; } void ZLIB_INTERNAL zcfree(voidpf opaque, voidpf ptr) { int n; (void)opaque; if (*(ush*)&ptr != 0) { /* object < 64K */ farfree(ptr); return; } /* Find the original pointer */ for (n = 0; n < next_ptr; n++) { if (ptr != table[n].new_ptr) continue; farfree(table[n].org_ptr); while (++n < next_ptr) { table[n-1] = table[n]; } next_ptr--; return; } Assert(0, "zcfree: ptr not found"); } #endif /* __TURBOC__ */ #ifdef M_I86 /* Microsoft C in 16-bit mode */ # define MY_ZCALLOC #if (!defined(_MSC_VER) || (_MSC_VER <= 600)) # define _halloc halloc # define _hfree hfree #endif voidpf ZLIB_INTERNAL zcalloc(voidpf opaque, uInt items, uInt size) { (void)opaque; return _halloc((long)items, size); } void ZLIB_INTERNAL zcfree(voidpf opaque, voidpf ptr) { (void)opaque; _hfree(ptr); } #endif /* M_I86 */ #endif /* SYS16BIT */ #ifndef MY_ZCALLOC /* Any system without a special alloc function */ #ifndef STDC extern voidp malloc(uInt size); extern voidp calloc(uInt items, uInt size); extern void free(voidpf ptr); #endif voidpf ZLIB_INTERNAL zcalloc(voidpf opaque, unsigned items, unsigned size) { (void)opaque; return sizeof(uInt) > 2 ? (voidpf)malloc(items * size) : (voidpf)calloc(items, size); } void ZLIB_INTERNAL zcfree(voidpf opaque, voidpf ptr) { (void)opaque; free(ptr); } #endif /* MY_ZCALLOC */ #endif /* !Z_SOLO */
• Assert • Trace • Tracev • Tracevv • Tracec • Tracecv • TRY_FREE
/* zutil.h -- internal interface and configuration of the compression library * Copyright (C) 1995-2024 Jean-loup Gailly, Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications. It is part of the implementation of the compression library and is subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h. */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #ifndef ZUTIL_H #define ZUTIL_H #ifdef HAVE_HIDDEN # define ZLIB_INTERNAL __attribute__((visibility ("hidden"))) #else # define ZLIB_INTERNAL #endif #include "zlib.h" #if defined(STDC) && !defined(Z_SOLO) # if !(defined(_WIN32_WCE) && defined(_MSC_VER)) # include <stddef.h> # endif # include <string.h> # include <stdlib.h> #endif #ifndef local # define local static #endif /* since "static" is used to mean two completely different things in C, we define "local" for the non-static meaning of "static", for readability (compile with -Dlocal if your debugger can't find static symbols) */ typedef unsigned char uch; typedef uch FAR uchf; typedef unsigned short ush; typedef ush FAR ushf; typedef unsigned long ulg; #if !defined(Z_U8) && !defined(Z_SOLO) && defined(STDC) # include <limits.h> # if (ULONG_MAX == 0xffffffffffffffff) # define Z_U8 unsigned long # elif (ULLONG_MAX == 0xffffffffffffffff) # define Z_U8 unsigned long long # elif (UINT_MAX == 0xffffffffffffffff) # define Z_U8 unsigned # endif #endif extern z_const char * const z_errmsg[10]; /* indexed by 2-zlib_error */ /* (size given to avoid silly warnings with Visual C++) */ #define ERR_MSG(err) z_errmsg[(err) < -6 || (err) > 2 ? 9 : 2 - (err)] #define ERR_RETURN(strm,err) \ return (strm->msg = ERR_MSG(err), (err)) /* To be used only when the state is known to be valid */ /* common constants */ #ifndef DEF_WBITS # define DEF_WBITS MAX_WBITS #endif /* default windowBits for decompression. MAX_WBITS is for compression only */ #if MAX_MEM_LEVEL >= 8 # define DEF_MEM_LEVEL 8 #else # define DEF_MEM_LEVEL MAX_MEM_LEVEL #endif /* default memLevel */ #define STORED_BLOCK 0 #define STATIC_TREES 1 #define DYN_TREES 2 /* The three kinds of block type */ #define MIN_MATCH 3 #define MAX_MATCH 258 /* The minimum and maximum match lengths */ #define PRESET_DICT 0x20 /* preset dictionary flag in zlib header */ /* target dependencies */ #if defined(MSDOS) || (defined(WINDOWS) && !defined(WIN32)) # define OS_CODE 0x00 # ifndef Z_SOLO # if defined(__TURBOC__) || defined(__BORLANDC__) # if (__STDC__ == 1) && (defined(__LARGE__) || defined(__COMPACT__)) /* Allow compilation with ANSI keywords only enabled */ void _Cdecl farfree( void *block ); void *_Cdecl farmalloc( unsigned long nbytes ); # else # include <alloc.h> # endif # else /* MSC or DJGPP */ # include <malloc.h> # endif # endif #endif #ifdef AMIGA # define OS_CODE 1 #endif #if defined(VAXC) || defined(VMS) # define OS_CODE 2 # define F_OPEN(name, mode) \ fopen((name), (mode), "mbc=60", "ctx=stm", "rfm=fix", "mrs=512") #endif #ifdef __370__ # if __TARGET_LIB__ < 0x20000000 # define OS_CODE 4 # elif __TARGET_LIB__ < 0x40000000 # define OS_CODE 11 # else # define OS_CODE 8 # endif #endif #if defined(ATARI) || defined(atarist) # define OS_CODE 5 #endif #ifdef OS2 # define OS_CODE 6 # if defined(M_I86) && !defined(Z_SOLO) # include <malloc.h> # endif #endif #if defined(MACOS) # define OS_CODE 7 #endif #ifdef __acorn # define OS_CODE 13 #endif #if defined(WIN32) && !defined(__CYGWIN__) # define OS_CODE 10 #endif #ifdef _BEOS_ # define OS_CODE 16 #endif #ifdef __TOS_OS400__ # define OS_CODE 18 #endif #ifdef __APPLE__ # define OS_CODE 19 #endif #if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(MSDOS) #pragma warn -8004 #pragma warn -8008 #pragma warn -8066 #endif /* provide prototypes for these when building zlib without LFS */ #if !defined(_WIN32) && \ (!defined(_LARGEFILE64_SOURCE) || _LFS64_LARGEFILE-0 == 0) ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine64(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine64(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen64(z_off_t); #endif /* common defaults */ #ifndef OS_CODE # define OS_CODE 3 /* assume Unix */ #endif #ifndef F_OPEN # define F_OPEN(name, mode) fopen((name), (mode)) #endif /* functions */ #if defined(pyr) || defined(Z_SOLO) # define NO_MEMCPY #endif #if defined(SMALL_MEDIUM) && !defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(__SC__) /* Use our own functions for small and medium model with MSC <= 5.0. * You may have to use the same strategy for Borland C (untested). * The __SC__ check is for Symantec. */ # define NO_MEMCPY #endif #if defined(STDC) && !defined(HAVE_MEMCPY) && !defined(NO_MEMCPY) # define HAVE_MEMCPY #endif #ifdef HAVE_MEMCPY # ifdef SMALL_MEDIUM /* MSDOS small or medium model */ # define zmemcpy _fmemcpy # define zmemcmp _fmemcmp # define zmemzero(dest, len) _fmemset(dest, 0, len) # else # define zmemcpy memcpy # define zmemcmp memcmp # define zmemzero(dest, len) memset(dest, 0, len) # endif #else void ZLIB_INTERNAL zmemcpy(Bytef* dest, const Bytef* source, uInt len); int ZLIB_INTERNAL zmemcmp(const Bytef* s1, const Bytef* s2, uInt len); void ZLIB_INTERNAL zmemzero(Bytef* dest, uInt len); #endif /* Diagnostic functions */ #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG # include <stdio.h> extern int ZLIB_INTERNAL z_verbose; extern void ZLIB_INTERNAL z_error(char *m); # define Assert(cond,msg) {if(!(cond)) z_error(msg);} # define Trace(x) {if (z_verbose>=0) fprintf x ;} # define Tracev(x) {if (z_verbose>0) fprintf x ;} # define Tracevv(x) {if (z_verbose>1) fprintf x ;} # define Tracec(c,x) {if (z_verbose>0 && (c)) fprintf x ;} # define Tracecv(c,x) {if (z_verbose>1 && (c)) fprintf x ;} #else # define Assert(cond,msg) # define Trace(x) # define Tracev(x) # define Tracevv(x) # define Tracec(c,x) # define Tracecv(c,x) #endif #ifndef Z_SOLO voidpf ZLIB_INTERNAL zcalloc(voidpf opaque, unsigned items, unsigned size); void ZLIB_INTERNAL zcfree(voidpf opaque, voidpf ptr); #endif #define ZALLOC(strm, items, size) \ (*((strm)->zalloc))((strm)->opaque, (items), (size)) #define ZFREE(strm, addr) (*((strm)->zfree))((strm)->opaque, (voidpf)(addr)) #define TRY_FREE(s, p) {if (p) ZFREE(s, p);} /* Reverse the bytes in a 32-bit value */ #define ZSWAP32(q) ((((q) >> 24) & 0xff) + (((q) >> 8) & 0xff00) + \ (((q) & 0xff00) << 8) + (((q) & 0xff) << 24)) #endif /* ZUTIL_H */
/* zlib.h -- interface of the 'zlib' general purpose compression library version 1.3.1, January 22nd, 2024 Copyright (C) 1995-2024 Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler This software is provided 'as-is', without any express or implied warranty. In no event will the authors be held liable for any damages arising from the use of this software. Permission is granted to anyone to use this software for any purpose, including commercial applications, and to alter it and redistribute it freely, subject to the following restrictions: 1. The origin of this software must not be misrepresented; you must not claim that you wrote the original software. If you use this software in a product, an acknowledgment in the product documentation would be appreciated but is not required. 2. Altered source versions must be plainly marked as such, and must not be misrepresented as being the original software. 3. This notice may not be removed or altered from any source distribution. Jean-loup Gailly Mark Adler jloup@gzip.org madler@alumni.caltech.edu The data format used by the zlib library is described by RFCs (Request for Comments) 1950 to 1952 in the files http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1950 (zlib format), rfc1951 (deflate format) and rfc1952 (gzip format). */ #ifndef ZLIB_H #define ZLIB_H #include "zconf.h" #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif #define ZLIB_VERSION "1.3.1" #define ZLIB_VERNUM 0x1310 #define ZLIB_VER_MAJOR 1 #define ZLIB_VER_MINOR 3 #define ZLIB_VER_REVISION 1 #define ZLIB_VER_SUBREVISION 0 /* The 'zlib' compression library provides in-memory compression and decompression functions, including integrity checks of the uncompressed data. This version of the library supports only one compression method (deflation) but other algorithms will be added later and will have the same stream interface. Compression can be done in a single step if the buffers are large enough, or can be done by repeated calls of the compression function. In the latter case, the application must provide more input and/or consume the output (providing more output space) before each call. The compressed data format used by default by the in-memory functions is the zlib format, which is a zlib wrapper documented in RFC 1950, wrapped around a deflate stream, which is itself documented in RFC 1951. The library also supports reading and writing files in gzip (.gz) format with an interface similar to that of stdio using the functions that start with "gz". The gzip format is different from the zlib format. gzip is a gzip wrapper, documented in RFC 1952, wrapped around a deflate stream. This library can optionally read and write gzip and raw deflate streams in memory as well. The zlib format was designed to be compact and fast for use in memory and on communications channels. The gzip format was designed for single- file compression on file systems, has a larger header than zlib to maintain directory information, and uses a different, slower check method than zlib. The library does not install any signal handler. The decoder checks the consistency of the compressed data, so the library should never crash even in the case of corrupted input. */ typedef voidpf (*alloc_func)(voidpf opaque, uInt items, uInt size); typedef void (*free_func)(voidpf opaque, voidpf address); struct internal_state; typedef struct z_stream_s { z_const Bytef *next_in; /* next input byte */ uInt avail_in; /* number of bytes available at next_in */ uLong total_in; /* total number of input bytes read so far */ Bytef *next_out; /* next output byte will go here */ uInt avail_out; /* remaining free space at next_out */ uLong total_out; /* total number of bytes output so far */ z_const char *msg; /* last error message, NULL if no error */ struct internal_state FAR *state; /* not visible by applications */ alloc_func zalloc; /* used to allocate the internal state */ free_func zfree; /* used to free the internal state */ voidpf opaque; /* private data object passed to zalloc and zfree */ int data_type; /* best guess about the data type: binary or text for deflate, or the decoding state for inflate */ uLong adler; /* Adler-32 or CRC-32 value of the uncompressed data */ uLong reserved; /* reserved for future use */ } z_stream; typedef z_stream FAR *z_streamp; /* gzip header information passed to and from zlib routines. See RFC 1952 for more details on the meanings of these fields. */ typedef struct gz_header_s { int text; /* true if compressed data believed to be text */ uLong time; /* modification time */ int xflags; /* extra flags (not used when writing a gzip file) */ int os; /* operating system */ Bytef *extra; /* pointer to extra field or Z_NULL if none */ uInt extra_len; /* extra field length (valid if extra != Z_NULL) */ uInt extra_max; /* space at extra (only when reading header) */ Bytef *name; /* pointer to zero-terminated file name or Z_NULL */ uInt name_max; /* space at name (only when reading header) */ Bytef *comment; /* pointer to zero-terminated comment or Z_NULL */ uInt comm_max; /* space at comment (only when reading header) */ int hcrc; /* true if there was or will be a header crc */ int done; /* true when done reading gzip header (not used when writing a gzip file) */ } gz_header; typedef gz_header FAR *gz_headerp; /* The application must update next_in and avail_in when avail_in has dropped to zero. It must update next_out and avail_out when avail_out has dropped to zero. The application must initialize zalloc, zfree and opaque before calling the init function. All other fields are set by the compression library and must not be updated by the application. The opaque value provided by the application will be passed as the first parameter for calls of zalloc and zfree. This can be useful for custom memory management. The compression library attaches no meaning to the opaque value. zalloc must return Z_NULL if there is not enough memory for the object. If zlib is used in a multi-threaded application, zalloc and zfree must be thread safe. In that case, zlib is thread-safe. When zalloc and zfree are Z_NULL on entry to the initialization function, they are set to internal routines that use the standard library functions malloc() and free(). On 16-bit systems, the functions zalloc and zfree must be able to allocate exactly 65536 bytes, but will not be required to allocate more than this if the symbol MAXSEG_64K is defined (see zconf.h). WARNING: On MSDOS, pointers returned by zalloc for objects of exactly 65536 bytes *must* have their offset normalized to zero. The default allocation function provided by this library ensures this (see zutil.c). To reduce memory requirements and avoid any allocation of 64K objects, at the expense of compression ratio, compile the library with -DMAX_WBITS=14 (see zconf.h). The fields total_in and total_out can be used for statistics or progress reports. After compression, total_in holds the total size of the uncompressed data and may be saved for use by the decompressor (particularly if the decompressor wants to decompress everything in a single step). */ /* constants */ #define Z_NO_FLUSH 0 #define Z_PARTIAL_FLUSH 1 #define Z_SYNC_FLUSH 2 #define Z_FULL_FLUSH 3 #define Z_FINISH 4 #define Z_BLOCK 5 #define Z_TREES 6 /* Allowed flush values; see deflate() and inflate() below for details */ #define Z_OK 0 #define Z_STREAM_END 1 #define Z_NEED_DICT 2 #define Z_ERRNO (-1) #define Z_STREAM_ERROR (-2) #define Z_DATA_ERROR (-3) #define Z_MEM_ERROR (-4) #define Z_BUF_ERROR (-5) #define Z_VERSION_ERROR (-6) /* Return codes for the compression/decompression functions. Negative values * are errors, positive values are used for special but normal events. */ #define Z_NO_COMPRESSION 0 #define Z_BEST_SPEED 1 #define Z_BEST_COMPRESSION 9 #define Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION (-1) /* compression levels */ #define Z_FILTERED 1 #define Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY 2 #define Z_RLE 3 #define Z_FIXED 4 #define Z_DEFAULT_STRATEGY 0 /* compression strategy; see deflateInit2() below for details */ #define Z_BINARY 0 #define Z_TEXT 1 #define Z_ASCII Z_TEXT /* for compatibility with 1.2.2 and earlier */ #define Z_UNKNOWN 2 /* Possible values of the data_type field for deflate() */ #define Z_DEFLATED 8 /* The deflate compression method (the only one supported in this version) */ #define Z_NULL 0 /* for initializing zalloc, zfree, opaque */ #define zlib_version zlibVersion() /* for compatibility with versions < 1.0.2 */ /* basic functions */ ZEXTERN const char * ZEXPORT zlibVersion(void); /* The application can compare zlibVersion and ZLIB_VERSION for consistency. If the first character differs, the library code actually used is not compatible with the zlib.h header file used by the application. This check is automatically made by deflateInit and inflateInit. */ /* ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateInit(z_streamp strm, int level); Initializes the internal stream state for compression. The fields zalloc, zfree and opaque must be initialized before by the caller. If zalloc and zfree are set to Z_NULL, deflateInit updates them to use default allocation functions. total_in, total_out, adler, and msg are initialized. The compression level must be Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION, or between 0 and 9: 1 gives best speed, 9 gives best compression, 0 gives no compression at all (the input data is simply copied a block at a time). Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION requests a default compromise between speed and compression (currently equivalent to level 6). deflateInit returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_STREAM_ERROR if level is not a valid compression level, or Z_VERSION_ERROR if the zlib library version (zlib_version) is incompatible with the version assumed by the caller (ZLIB_VERSION). msg is set to null if there is no error message. deflateInit does not perform any compression: this will be done by deflate(). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflate(z_streamp strm, int flush); /* deflate compresses as much data as possible, and stops when the input buffer becomes empty or the output buffer becomes full. It may introduce some output latency (reading input without producing any output) except when forced to flush. The detailed semantics are as follows. deflate performs one or both of the following actions: - Compress more input starting at next_in and update next_in and avail_in accordingly. If not all input can be processed (because there is not enough room in the output buffer), next_in and avail_in are updated and processing will resume at this point for the next call of deflate(). - Generate more output starting at next_out and update next_out and avail_out accordingly. This action is forced if the parameter flush is non zero. Forcing flush frequently degrades the compression ratio, so this parameter should be set only when necessary. Some output may be provided even if flush is zero. Before the call of deflate(), the application should ensure that at least one of the actions is possible, by providing more input and/or consuming more output, and updating avail_in or avail_out accordingly; avail_out should never be zero before the call. The application can consume the compressed output when it wants, for example when the output buffer is full (avail_out == 0), or after each call of deflate(). If deflate returns Z_OK and with zero avail_out, it must be called again after making room in the output buffer because there might be more output pending. See deflatePending(), which can be used if desired to determine whether or not there is more output in that case. Normally the parameter flush is set to Z_NO_FLUSH, which allows deflate to decide how much data to accumulate before producing output, in order to maximize compression. If the parameter flush is set to Z_SYNC_FLUSH, all pending output is flushed to the output buffer and the output is aligned on a byte boundary, so that the decompressor can get all input data available so far. (In particular avail_in is zero after the call if enough output space has been provided before the call.) Flushing may degrade compression for some compression algorithms and so it should be used only when necessary. This completes the current deflate block and follows it with an empty stored block that is three bits plus filler bits to the next byte, followed by four bytes (00 00 ff ff). If flush is set to Z_PARTIAL_FLUSH, all pending output is flushed to the output buffer, but the output is not aligned to a byte boundary. All of the input data so far will be available to the decompressor, as for Z_SYNC_FLUSH. This completes the current deflate block and follows it with an empty fixed codes block that is 10 bits long. This assures that enough bytes are output in order for the decompressor to finish the block before the empty fixed codes block. If flush is set to Z_BLOCK, a deflate block is completed and emitted, as for Z_SYNC_FLUSH, but the output is not aligned on a byte boundary, and up to seven bits of the current block are held to be written as the next byte after the next deflate block is completed. In this case, the decompressor may not be provided enough bits at this point in order to complete decompression of the data provided so far to the compressor. It may need to wait for the next block to be emitted. This is for advanced applications that need to control the emission of deflate blocks. If flush is set to Z_FULL_FLUSH, all output is flushed as with Z_SYNC_FLUSH, and the compression state is reset so that decompression can restart from this point if previous compressed data has been damaged or if random access is desired. Using Z_FULL_FLUSH too often can seriously degrade compression. If deflate returns with avail_out == 0, this function must be called again with the same value of the flush parameter and more output space (updated avail_out), until the flush is complete (deflate returns with non-zero avail_out). In the case of a Z_FULL_FLUSH or Z_SYNC_FLUSH, make sure that avail_out is greater than six when the flush marker begins, in order to avoid repeated flush markers upon calling deflate() again when avail_out == 0. If the parameter flush is set to Z_FINISH, pending input is processed, pending output is flushed and deflate returns with Z_STREAM_END if there was enough output space. If deflate returns with Z_OK or Z_BUF_ERROR, this function must be called again with Z_FINISH and more output space (updated avail_out) but no more input data, until it returns with Z_STREAM_END or an error. After deflate has returned Z_STREAM_END, the only possible operations on the stream are deflateReset or deflateEnd. Z_FINISH can be used in the first deflate call after deflateInit if all the compression is to be done in a single step. In order to complete in one call, avail_out must be at least the value returned by deflateBound (see below). Then deflate is guaranteed to return Z_STREAM_END. If not enough output space is provided, deflate will not return Z_STREAM_END, and it must be called again as described above. deflate() sets strm->adler to the Adler-32 checksum of all input read so far (that is, total_in bytes). If a gzip stream is being generated, then strm->adler will be the CRC-32 checksum of the input read so far. (See deflateInit2 below.) deflate() may update strm->data_type if it can make a good guess about the input data type (Z_BINARY or Z_TEXT). If in doubt, the data is considered binary. This field is only for information purposes and does not affect the compression algorithm in any manner. deflate() returns Z_OK if some progress has been made (more input processed or more output produced), Z_STREAM_END if all input has been consumed and all output has been produced (only when flush is set to Z_FINISH), Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream state was inconsistent (for example if next_in or next_out was Z_NULL or the state was inadvertently written over by the application), or Z_BUF_ERROR if no progress is possible (for example avail_in or avail_out was zero). Note that Z_BUF_ERROR is not fatal, and deflate() can be called again with more input and more output space to continue compressing. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateEnd(z_streamp strm); /* All dynamically allocated data structures for this stream are freed. This function discards any unprocessed input and does not flush any pending output. deflateEnd returns Z_OK if success, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream state was inconsistent, Z_DATA_ERROR if the stream was freed prematurely (some input or output was discarded). In the error case, msg may be set but then points to a static string (which must not be deallocated). */ /* ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateInit(z_streamp strm); Initializes the internal stream state for decompression. The fields next_in, avail_in, zalloc, zfree and opaque must be initialized before by the caller. In the current version of inflate, the provided input is not read or consumed. The allocation of a sliding window will be deferred to the first call of inflate (if the decompression does not complete on the first call). If zalloc and zfree are set to Z_NULL, inflateInit updates them to use default allocation functions. total_in, total_out, adler, and msg are initialized. inflateInit returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_VERSION_ERROR if the zlib library version is incompatible with the version assumed by the caller, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the parameters are invalid, such as a null pointer to the structure. msg is set to null if there is no error message. inflateInit does not perform any decompression. Actual decompression will be done by inflate(). So next_in, and avail_in, next_out, and avail_out are unused and unchanged. The current implementation of inflateInit() does not process any header information -- that is deferred until inflate() is called. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflate(z_streamp strm, int flush); /* inflate decompresses as much data as possible, and stops when the input buffer becomes empty or the output buffer becomes full. It may introduce some output latency (reading input without producing any output) except when forced to flush. The detailed semantics are as follows. inflate performs one or both of the following actions: - Decompress more input starting at next_in and update next_in and avail_in accordingly. If not all input can be processed (because there is not enough room in the output buffer), then next_in and avail_in are updated accordingly, and processing will resume at this point for the next call of inflate(). - Generate more output starting at next_out and update next_out and avail_out accordingly. inflate() provides as much output as possible, until there is no more input data or no more space in the output buffer (see below about the flush parameter). Before the call of inflate(), the application should ensure that at least one of the actions is possible, by providing more input and/or consuming more output, and updating the next_* and avail_* values accordingly. If the caller of inflate() does not provide both available input and available output space, it is possible that there will be no progress made. The application can consume the uncompressed output when it wants, for example when the output buffer is full (avail_out == 0), or after each call of inflate(). If inflate returns Z_OK and with zero avail_out, it must be called again after making room in the output buffer because there might be more output pending. The flush parameter of inflate() can be Z_NO_FLUSH, Z_SYNC_FLUSH, Z_FINISH, Z_BLOCK, or Z_TREES. Z_SYNC_FLUSH requests that inflate() flush as much output as possible to the output buffer. Z_BLOCK requests that inflate() stop if and when it gets to the next deflate block boundary. When decoding the zlib or gzip format, this will cause inflate() to return immediately after the header and before the first block. When doing a raw inflate, inflate() will go ahead and process the first block, and will return when it gets to the end of that block, or when it runs out of data. The Z_BLOCK option assists in appending to or combining deflate streams. To assist in this, on return inflate() always sets strm->data_type to the number of unused bits in the last byte taken from strm->next_in, plus 64 if inflate() is currently decoding the last block in the deflate stream, plus 128 if inflate() returned immediately after decoding an end-of-block code or decoding the complete header up to just before the first byte of the deflate stream. The end-of-block will not be indicated until all of the uncompressed data from that block has been written to strm->next_out. The number of unused bits may in general be greater than seven, except when bit 7 of data_type is set, in which case the number of unused bits will be less than eight. data_type is set as noted here every time inflate() returns for all flush options, and so can be used to determine the amount of currently consumed input in bits. The Z_TREES option behaves as Z_BLOCK does, but it also returns when the end of each deflate block header is reached, before any actual data in that block is decoded. This allows the caller to determine the length of the deflate block header for later use in random access within a deflate block. 256 is added to the value of strm->data_type when inflate() returns immediately after reaching the end of the deflate block header. inflate() should normally be called until it returns Z_STREAM_END or an error. However if all decompression is to be performed in a single step (a single call of inflate), the parameter flush should be set to Z_FINISH. In this case all pending input is processed and all pending output is flushed; avail_out must be large enough to hold all of the uncompressed data for the operation to complete. (The size of the uncompressed data may have been saved by the compressor for this purpose.) The use of Z_FINISH is not required to perform an inflation in one step. However it may be used to inform inflate that a faster approach can be used for the single inflate() call. Z_FINISH also informs inflate to not maintain a sliding window if the stream completes, which reduces inflate's memory footprint. If the stream does not complete, either because not all of the stream is provided or not enough output space is provided, then a sliding window will be allocated and inflate() can be called again to continue the operation as if Z_NO_FLUSH had been used. In this implementation, inflate() always flushes as much output as possible to the output buffer, and always uses the faster approach on the first call. So the effects of the flush parameter in this implementation are on the return value of inflate() as noted below, when inflate() returns early when Z_BLOCK or Z_TREES is used, and when inflate() avoids the allocation of memory for a sliding window when Z_FINISH is used. If a preset dictionary is needed after this call (see inflateSetDictionary below), inflate sets strm->adler to the Adler-32 checksum of the dictionary chosen by the compressor and returns Z_NEED_DICT; otherwise it sets strm->adler to the Adler-32 checksum of all output produced so far (that is, total_out bytes) and returns Z_OK, Z_STREAM_END or an error code as described below. At the end of the stream, inflate() checks that its computed Adler-32 checksum is equal to that saved by the compressor and returns Z_STREAM_END only if the checksum is correct. inflate() can decompress and check either zlib-wrapped or gzip-wrapped deflate data. The header type is detected automatically, if requested when initializing with inflateInit2(). Any information contained in the gzip header is not retained unless inflateGetHeader() is used. When processing gzip-wrapped deflate data, strm->adler32 is set to the CRC-32 of the output produced so far. The CRC-32 is checked against the gzip trailer, as is the uncompressed length, modulo 2^32. inflate() returns Z_OK if some progress has been made (more input processed or more output produced), Z_STREAM_END if the end of the compressed data has been reached and all uncompressed output has been produced, Z_NEED_DICT if a preset dictionary is needed at this point, Z_DATA_ERROR if the input data was corrupted (input stream not conforming to the zlib format or incorrect check value, in which case strm->msg points to a string with a more specific error), Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream structure was inconsistent (for example next_in or next_out was Z_NULL, or the state was inadvertently written over by the application), Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if no progress was possible or if there was not enough room in the output buffer when Z_FINISH is used. Note that Z_BUF_ERROR is not fatal, and inflate() can be called again with more input and more output space to continue decompressing. If Z_DATA_ERROR is returned, the application may then call inflateSync() to look for a good compression block if a partial recovery of the data is to be attempted. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateEnd(z_streamp strm); /* All dynamically allocated data structures for this stream are freed. This function discards any unprocessed input and does not flush any pending output. inflateEnd returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream state was inconsistent. */ /* Advanced functions */ /* The following functions are needed only in some special applications. */ /* ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateInit2(z_streamp strm, int level, int method, int windowBits, int memLevel, int strategy); This is another version of deflateInit with more compression options. The fields zalloc, zfree and opaque must be initialized before by the caller. The method parameter is the compression method. It must be Z_DEFLATED in this version of the library. The windowBits parameter is the base two logarithm of the window size (the size of the history buffer). It should be in the range 8..15 for this version of the library. Larger values of this parameter result in better compression at the expense of memory usage. The default value is 15 if deflateInit is used instead. For the current implementation of deflate(), a windowBits value of 8 (a window size of 256 bytes) is not supported. As a result, a request for 8 will result in 9 (a 512-byte window). In that case, providing 8 to inflateInit2() will result in an error when the zlib header with 9 is checked against the initialization of inflate(). The remedy is to not use 8 with deflateInit2() with this initialization, or at least in that case use 9 with inflateInit2(). windowBits can also be -8..-15 for raw deflate. In this case, -windowBits determines the window size. deflate() will then generate raw deflate data with no zlib header or trailer, and will not compute a check value. windowBits can also be greater than 15 for optional gzip encoding. Add 16 to windowBits to write a simple gzip header and trailer around the compressed data instead of a zlib wrapper. The gzip header will have no file name, no extra data, no comment, no modification time (set to zero), no header crc, and the operating system will be set to the appropriate value, if the operating system was determined at compile time. If a gzip stream is being written, strm->adler is a CRC-32 instead of an Adler-32. For raw deflate or gzip encoding, a request for a 256-byte window is rejected as invalid, since only the zlib header provides a means of transmitting the window size to the decompressor. The memLevel parameter specifies how much memory should be allocated for the internal compression state. memLevel=1 uses minimum memory but is slow and reduces compression ratio; memLevel=9 uses maximum memory for optimal speed. The default value is 8. See zconf.h for total memory usage as a function of windowBits and memLevel. The strategy parameter is used to tune the compression algorithm. Use the value Z_DEFAULT_STRATEGY for normal data, Z_FILTERED for data produced by a filter (or predictor), Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY to force Huffman encoding only (no string match), or Z_RLE to limit match distances to one (run-length encoding). Filtered data consists mostly of small values with a somewhat random distribution. In this case, the compression algorithm is tuned to compress them better. The effect of Z_FILTERED is to force more Huffman coding and less string matching; it is somewhat intermediate between Z_DEFAULT_STRATEGY and Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY. Z_RLE is designed to be almost as fast as Z_HUFFMAN_ONLY, but give better compression for PNG image data. The strategy parameter only affects the compression ratio but not the correctness of the compressed output even if it is not set appropriately. Z_FIXED prevents the use of dynamic Huffman codes, allowing for a simpler decoder for special applications. deflateInit2 returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_STREAM_ERROR if any parameter is invalid (such as an invalid method), or Z_VERSION_ERROR if the zlib library version (zlib_version) is incompatible with the version assumed by the caller (ZLIB_VERSION). msg is set to null if there is no error message. deflateInit2 does not perform any compression: this will be done by deflate(). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateSetDictionary(z_streamp strm, const Bytef *dictionary, uInt dictLength); /* Initializes the compression dictionary from the given byte sequence without producing any compressed output. When using the zlib format, this function must be called immediately after deflateInit, deflateInit2 or deflateReset, and before any call of deflate. When doing raw deflate, this function must be called either before any call of deflate, or immediately after the completion of a deflate block, i.e. after all input has been consumed and all output has been delivered when using any of the flush options Z_BLOCK, Z_PARTIAL_FLUSH, Z_SYNC_FLUSH, or Z_FULL_FLUSH. The compressor and decompressor must use exactly the same dictionary (see inflateSetDictionary). The dictionary should consist of strings (byte sequences) that are likely to be encountered later in the data to be compressed, with the most commonly used strings preferably put towards the end of the dictionary. Using a dictionary is most useful when the data to be compressed is short and can be predicted with good accuracy; the data can then be compressed better than with the default empty dictionary. Depending on the size of the compression data structures selected by deflateInit or deflateInit2, a part of the dictionary may in effect be discarded, for example if the dictionary is larger than the window size provided in deflateInit or deflateInit2. Thus the strings most likely to be useful should be put at the end of the dictionary, not at the front. In addition, the current implementation of deflate will use at most the window size minus 262 bytes of the provided dictionary. Upon return of this function, strm->adler is set to the Adler-32 value of the dictionary; the decompressor may later use this value to determine which dictionary has been used by the compressor. (The Adler-32 value applies to the whole dictionary even if only a subset of the dictionary is actually used by the compressor.) If a raw deflate was requested, then the Adler-32 value is not computed and strm->adler is not set. deflateSetDictionary returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if a parameter is invalid (e.g. dictionary being Z_NULL) or the stream state is inconsistent (for example if deflate has already been called for this stream or if not at a block boundary for raw deflate). deflateSetDictionary does not perform any compression: this will be done by deflate(). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateGetDictionary(z_streamp strm, Bytef *dictionary, uInt *dictLength); /* Returns the sliding dictionary being maintained by deflate. dictLength is set to the number of bytes in the dictionary, and that many bytes are copied to dictionary. dictionary must have enough space, where 32768 bytes is always enough. If deflateGetDictionary() is called with dictionary equal to Z_NULL, then only the dictionary length is returned, and nothing is copied. Similarly, if dictLength is Z_NULL, then it is not set. deflateGetDictionary() may return a length less than the window size, even when more than the window size in input has been provided. It may return up to 258 bytes less in that case, due to how zlib's implementation of deflate manages the sliding window and lookahead for matches, where matches can be up to 258 bytes long. If the application needs the last window-size bytes of input, then that would need to be saved by the application outside of zlib. deflateGetDictionary returns Z_OK on success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream state is inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateCopy(z_streamp dest, z_streamp source); /* Sets the destination stream as a complete copy of the source stream. This function can be useful when several compression strategies will be tried, for example when there are several ways of pre-processing the input data with a filter. The streams that will be discarded should then be freed by calling deflateEnd. Note that deflateCopy duplicates the internal compression state which can be quite large, so this strategy is slow and can consume lots of memory. deflateCopy returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent (such as zalloc being Z_NULL). msg is left unchanged in both source and destination. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateReset(z_streamp strm); /* This function is equivalent to deflateEnd followed by deflateInit, but does not free and reallocate the internal compression state. The stream will leave the compression level and any other attributes that may have been set unchanged. total_in, total_out, adler, and msg are initialized. deflateReset returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent (such as zalloc or state being Z_NULL). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateParams(z_streamp strm, int level, int strategy); /* Dynamically update the compression level and compression strategy. The interpretation of level and strategy is as in deflateInit2(). This can be used to switch between compression and straight copy of the input data, or to switch to a different kind of input data requiring a different strategy. If the compression approach (which is a function of the level) or the strategy is changed, and if there have been any deflate() calls since the state was initialized or reset, then the input available so far is compressed with the old level and strategy using deflate(strm, Z_BLOCK). There are three approaches for the compression levels 0, 1..3, and 4..9 respectively. The new level and strategy will take effect at the next call of deflate(). If a deflate(strm, Z_BLOCK) is performed by deflateParams(), and it does not have enough output space to complete, then the parameter change will not take effect. In this case, deflateParams() can be called again with the same parameters and more output space to try again. In order to assure a change in the parameters on the first try, the deflate stream should be flushed using deflate() with Z_BLOCK or other flush request until strm.avail_out is not zero, before calling deflateParams(). Then no more input data should be provided before the deflateParams() call. If this is done, the old level and strategy will be applied to the data compressed before deflateParams(), and the new level and strategy will be applied to the data compressed after deflateParams(). deflateParams returns Z_OK on success, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent or if a parameter was invalid, or Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough output space to complete the compression of the available input data before a change in the strategy or approach. Note that in the case of a Z_BUF_ERROR, the parameters are not changed. A return value of Z_BUF_ERROR is not fatal, in which case deflateParams() can be retried with more output space. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateTune(z_streamp strm, int good_length, int max_lazy, int nice_length, int max_chain); /* Fine tune deflate's internal compression parameters. This should only be used by someone who understands the algorithm used by zlib's deflate for searching for the best matching string, and even then only by the most fanatic optimizer trying to squeeze out the last compressed bit for their specific input data. Read the deflate.c source code for the meaning of the max_lazy, good_length, nice_length, and max_chain parameters. deflateTune() can be called after deflateInit() or deflateInit2(), and returns Z_OK on success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR for an invalid deflate stream. */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT deflateBound(z_streamp strm, uLong sourceLen); /* deflateBound() returns an upper bound on the compressed size after deflation of sourceLen bytes. It must be called after deflateInit() or deflateInit2(), and after deflateSetHeader(), if used. This would be used to allocate an output buffer for deflation in a single pass, and so would be called before deflate(). If that first deflate() call is provided the sourceLen input bytes, an output buffer allocated to the size returned by deflateBound(), and the flush value Z_FINISH, then deflate() is guaranteed to return Z_STREAM_END. Note that it is possible for the compressed size to be larger than the value returned by deflateBound() if flush options other than Z_FINISH or Z_NO_FLUSH are used. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflatePending(z_streamp strm, unsigned *pending, int *bits); /* deflatePending() returns the number of bytes and bits of output that have been generated, but not yet provided in the available output. The bytes not provided would be due to the available output space having being consumed. The number of bits of output not provided are between 0 and 7, where they await more bits to join them in order to fill out a full byte. If pending or bits are Z_NULL, then those values are not set. deflatePending returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflatePrime(z_streamp strm, int bits, int value); /* deflatePrime() inserts bits in the deflate output stream. The intent is that this function is used to start off the deflate output with the bits leftover from a previous deflate stream when appending to it. As such, this function can only be used for raw deflate, and must be used before the first deflate() call after a deflateInit2() or deflateReset(). bits must be less than or equal to 16, and that many of the least significant bits of value will be inserted in the output. deflatePrime returns Z_OK if success, Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough room in the internal buffer to insert the bits, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateSetHeader(z_streamp strm, gz_headerp head); /* deflateSetHeader() provides gzip header information for when a gzip stream is requested by deflateInit2(). deflateSetHeader() may be called after deflateInit2() or deflateReset() and before the first call of deflate(). The text, time, os, extra field, name, and comment information in the provided gz_header structure are written to the gzip header (xflag is ignored -- the extra flags are set according to the compression level). The caller must assure that, if not Z_NULL, name and comment are terminated with a zero byte, and that if extra is not Z_NULL, that extra_len bytes are available there. If hcrc is true, a gzip header crc is included. Note that the current versions of the command-line version of gzip (up through version 1.3.x) do not support header crc's, and will report that it is a "multi-part gzip file" and give up. If deflateSetHeader is not used, the default gzip header has text false, the time set to zero, and os set to the current operating system, with no extra, name, or comment fields. The gzip header is returned to the default state by deflateReset(). deflateSetHeader returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent. */ /* ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateInit2(z_streamp strm, int windowBits); This is another version of inflateInit with an extra parameter. The fields next_in, avail_in, zalloc, zfree and opaque must be initialized before by the caller. The windowBits parameter is the base two logarithm of the maximum window size (the size of the history buffer). It should be in the range 8..15 for this version of the library. The default value is 15 if inflateInit is used instead. windowBits must be greater than or equal to the windowBits value provided to deflateInit2() while compressing, or it must be equal to 15 if deflateInit2() was not used. If a compressed stream with a larger window size is given as input, inflate() will return with the error code Z_DATA_ERROR instead of trying to allocate a larger window. windowBits can also be zero to request that inflate use the window size in the zlib header of the compressed stream. windowBits can also be -8..-15 for raw inflate. In this case, -windowBits determines the window size. inflate() will then process raw deflate data, not looking for a zlib or gzip header, not generating a check value, and not looking for any check values for comparison at the end of the stream. This is for use with other formats that use the deflate compressed data format such as zip. Those formats provide their own check values. If a custom format is developed using the raw deflate format for compressed data, it is recommended that a check value such as an Adler-32 or a CRC-32 be applied to the uncompressed data as is done in the zlib, gzip, and zip formats. For most applications, the zlib format should be used as is. Note that comments above on the use in deflateInit2() applies to the magnitude of windowBits. windowBits can also be greater than 15 for optional gzip decoding. Add 32 to windowBits to enable zlib and gzip decoding with automatic header detection, or add 16 to decode only the gzip format (the zlib format will return a Z_DATA_ERROR). If a gzip stream is being decoded, strm->adler is a CRC-32 instead of an Adler-32. Unlike the gunzip utility and gzread() (see below), inflate() will *not* automatically decode concatenated gzip members. inflate() will return Z_STREAM_END at the end of the gzip member. The state would need to be reset to continue decoding a subsequent gzip member. This *must* be done if there is more data after a gzip member, in order for the decompression to be compliant with the gzip standard (RFC 1952). inflateInit2 returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_VERSION_ERROR if the zlib library version is incompatible with the version assumed by the caller, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the parameters are invalid, such as a null pointer to the structure. msg is set to null if there is no error message. inflateInit2 does not perform any decompression apart from possibly reading the zlib header if present: actual decompression will be done by inflate(). (So next_in and avail_in may be modified, but next_out and avail_out are unused and unchanged.) The current implementation of inflateInit2() does not process any header information -- that is deferred until inflate() is called. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateSetDictionary(z_streamp strm, const Bytef *dictionary, uInt dictLength); /* Initializes the decompression dictionary from the given uncompressed byte sequence. This function must be called immediately after a call of inflate, if that call returned Z_NEED_DICT. The dictionary chosen by the compressor can be determined from the Adler-32 value returned by that call of inflate. The compressor and decompressor must use exactly the same dictionary (see deflateSetDictionary). For raw inflate, this function can be called at any time to set the dictionary. If the provided dictionary is smaller than the window and there is already data in the window, then the provided dictionary will amend what's there. The application must insure that the dictionary that was used for compression is provided. inflateSetDictionary returns Z_OK if success, Z_STREAM_ERROR if a parameter is invalid (e.g. dictionary being Z_NULL) or the stream state is inconsistent, Z_DATA_ERROR if the given dictionary doesn't match the expected one (incorrect Adler-32 value). inflateSetDictionary does not perform any decompression: this will be done by subsequent calls of inflate(). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateGetDictionary(z_streamp strm, Bytef *dictionary, uInt *dictLength); /* Returns the sliding dictionary being maintained by inflate. dictLength is set to the number of bytes in the dictionary, and that many bytes are copied to dictionary. dictionary must have enough space, where 32768 bytes is always enough. If inflateGetDictionary() is called with dictionary equal to Z_NULL, then only the dictionary length is returned, and nothing is copied. Similarly, if dictLength is Z_NULL, then it is not set. inflateGetDictionary returns Z_OK on success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream state is inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateSync(z_streamp strm); /* Skips invalid compressed data until a possible full flush point (see above for the description of deflate with Z_FULL_FLUSH) can be found, or until all available input is skipped. No output is provided. inflateSync searches for a 00 00 FF FF pattern in the compressed data. All full flush points have this pattern, but not all occurrences of this pattern are full flush points. inflateSync returns Z_OK if a possible full flush point has been found, Z_BUF_ERROR if no more input was provided, Z_DATA_ERROR if no flush point has been found, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream structure was inconsistent. In the success case, the application may save the current value of total_in which indicates where valid compressed data was found. In the error case, the application may repeatedly call inflateSync, providing more input each time, until success or end of the input data. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateCopy(z_streamp dest, z_streamp source); /* Sets the destination stream as a complete copy of the source stream. This function can be useful when randomly accessing a large stream. The first pass through the stream can periodically record the inflate state, allowing restarting inflate at those points when randomly accessing the stream. inflateCopy returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent (such as zalloc being Z_NULL). msg is left unchanged in both source and destination. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateReset(z_streamp strm); /* This function is equivalent to inflateEnd followed by inflateInit, but does not free and reallocate the internal decompression state. The stream will keep attributes that may have been set by inflateInit2. total_in, total_out, adler, and msg are initialized. inflateReset returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent (such as zalloc or state being Z_NULL). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateReset2(z_streamp strm, int windowBits); /* This function is the same as inflateReset, but it also permits changing the wrap and window size requests. The windowBits parameter is interpreted the same as it is for inflateInit2. If the window size is changed, then the memory allocated for the window is freed, and the window will be reallocated by inflate() if needed. inflateReset2 returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent (such as zalloc or state being Z_NULL), or if the windowBits parameter is invalid. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflatePrime(z_streamp strm, int bits, int value); /* This function inserts bits in the inflate input stream. The intent is that this function is used to start inflating at a bit position in the middle of a byte. The provided bits will be used before any bytes are used from next_in. This function should only be used with raw inflate, and should be used before the first inflate() call after inflateInit2() or inflateReset(). bits must be less than or equal to 16, and that many of the least significant bits of value will be inserted in the input. If bits is negative, then the input stream bit buffer is emptied. Then inflatePrime() can be called again to put bits in the buffer. This is used to clear out bits leftover after feeding inflate a block description prior to feeding inflate codes. inflatePrime returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN long ZEXPORT inflateMark(z_streamp strm); /* This function returns two values, one in the lower 16 bits of the return value, and the other in the remaining upper bits, obtained by shifting the return value down 16 bits. If the upper value is -1 and the lower value is zero, then inflate() is currently decoding information outside of a block. If the upper value is -1 and the lower value is non-zero, then inflate is in the middle of a stored block, with the lower value equaling the number of bytes from the input remaining to copy. If the upper value is not -1, then it is the number of bits back from the current bit position in the input of the code (literal or length/distance pair) currently being processed. In that case the lower value is the number of bytes already emitted for that code. A code is being processed if inflate is waiting for more input to complete decoding of the code, or if it has completed decoding but is waiting for more output space to write the literal or match data. inflateMark() is used to mark locations in the input data for random access, which may be at bit positions, and to note those cases where the output of a code may span boundaries of random access blocks. The current location in the input stream can be determined from avail_in and data_type as noted in the description for the Z_BLOCK flush parameter for inflate. inflateMark returns the value noted above, or -65536 if the provided source stream state was inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateGetHeader(z_streamp strm, gz_headerp head); /* inflateGetHeader() requests that gzip header information be stored in the provided gz_header structure. inflateGetHeader() may be called after inflateInit2() or inflateReset(), and before the first call of inflate(). As inflate() processes the gzip stream, head->done is zero until the header is completed, at which time head->done is set to one. If a zlib stream is being decoded, then head->done is set to -1 to indicate that there will be no gzip header information forthcoming. Note that Z_BLOCK or Z_TREES can be used to force inflate() to return immediately after header processing is complete and before any actual data is decompressed. The text, time, xflags, and os fields are filled in with the gzip header contents. hcrc is set to true if there is a header CRC. (The header CRC was valid if done is set to one.) If extra is not Z_NULL, then extra_max contains the maximum number of bytes to write to extra. Once done is true, extra_len contains the actual extra field length, and extra contains the extra field, or that field truncated if extra_max is less than extra_len. If name is not Z_NULL, then up to name_max characters are written there, terminated with a zero unless the length is greater than name_max. If comment is not Z_NULL, then up to comm_max characters are written there, terminated with a zero unless the length is greater than comm_max. When any of extra, name, or comment are not Z_NULL and the respective field is not present in the header, then that field is set to Z_NULL to signal its absence. This allows the use of deflateSetHeader() with the returned structure to duplicate the header. However if those fields are set to allocated memory, then the application will need to save those pointers elsewhere so that they can be eventually freed. If inflateGetHeader is not used, then the header information is simply discarded. The header is always checked for validity, including the header CRC if present. inflateReset() will reset the process to discard the header information. The application would need to call inflateGetHeader() again to retrieve the header from the next gzip stream. inflateGetHeader returns Z_OK if success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the source stream state was inconsistent. */ /* ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateBackInit(z_streamp strm, int windowBits, unsigned char FAR *window); Initialize the internal stream state for decompression using inflateBack() calls. The fields zalloc, zfree and opaque in strm must be initialized before the call. If zalloc and zfree are Z_NULL, then the default library- derived memory allocation routines are used. windowBits is the base two logarithm of the window size, in the range 8..15. window is a caller supplied buffer of that size. Except for special applications where it is assured that deflate was used with small window sizes, windowBits must be 15 and a 32K byte window must be supplied to be able to decompress general deflate streams. See inflateBack() for the usage of these routines. inflateBackInit will return Z_OK on success, Z_STREAM_ERROR if any of the parameters are invalid, Z_MEM_ERROR if the internal state could not be allocated, or Z_VERSION_ERROR if the version of the library does not match the version of the header file. */ typedef unsigned (*in_func)(void FAR *, z_const unsigned char FAR * FAR *); typedef int (*out_func)(void FAR *, unsigned char FAR *, unsigned); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateBack(z_streamp strm, in_func in, void FAR *in_desc, out_func out, void FAR *out_desc); /* inflateBack() does a raw inflate with a single call using a call-back interface for input and output. This is potentially more efficient than inflate() for file i/o applications, in that it avoids copying between the output and the sliding window by simply making the window itself the output buffer. inflate() can be faster on modern CPUs when used with large buffers. inflateBack() trusts the application to not change the output buffer passed by the output function, at least until inflateBack() returns. inflateBackInit() must be called first to allocate the internal state and to initialize the state with the user-provided window buffer. inflateBack() may then be used multiple times to inflate a complete, raw deflate stream with each call. inflateBackEnd() is then called to free the allocated state. A raw deflate stream is one with no zlib or gzip header or trailer. This routine would normally be used in a utility that reads zip or gzip files and writes out uncompressed files. The utility would decode the header and process the trailer on its own, hence this routine expects only the raw deflate stream to decompress. This is different from the default behavior of inflate(), which expects a zlib header and trailer around the deflate stream. inflateBack() uses two subroutines supplied by the caller that are then called by inflateBack() for input and output. inflateBack() calls those routines until it reads a complete deflate stream and writes out all of the uncompressed data, or until it encounters an error. The function's parameters and return types are defined above in the in_func and out_func typedefs. inflateBack() will call in(in_desc, &buf) which should return the number of bytes of provided input, and a pointer to that input in buf. If there is no input available, in() must return zero -- buf is ignored in that case -- and inflateBack() will return a buffer error. inflateBack() will call out(out_desc, buf, len) to write the uncompressed data buf[0..len-1]. out() should return zero on success, or non-zero on failure. If out() returns non-zero, inflateBack() will return with an error. Neither in() nor out() are permitted to change the contents of the window provided to inflateBackInit(), which is also the buffer that out() uses to write from. The length written by out() will be at most the window size. Any non-zero amount of input may be provided by in(). For convenience, inflateBack() can be provided input on the first call by setting strm->next_in and strm->avail_in. If that input is exhausted, then in() will be called. Therefore strm->next_in must be initialized before calling inflateBack(). If strm->next_in is Z_NULL, then in() will be called immediately for input. If strm->next_in is not Z_NULL, then strm->avail_in must also be initialized, and then if strm->avail_in is not zero, input will initially be taken from strm->next_in[0 .. strm->avail_in - 1]. The in_desc and out_desc parameters of inflateBack() is passed as the first parameter of in() and out() respectively when they are called. These descriptors can be optionally used to pass any information that the caller- supplied in() and out() functions need to do their job. On return, inflateBack() will set strm->next_in and strm->avail_in to pass back any unused input that was provided by the last in() call. The return values of inflateBack() can be Z_STREAM_END on success, Z_BUF_ERROR if in() or out() returned an error, Z_DATA_ERROR if there was a format error in the deflate stream (in which case strm->msg is set to indicate the nature of the error), or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream was not properly initialized. In the case of Z_BUF_ERROR, an input or output error can be distinguished using strm->next_in which will be Z_NULL only if in() returned an error. If strm->next_in is not Z_NULL, then the Z_BUF_ERROR was due to out() returning non-zero. (in() will always be called before out(), so strm->next_in is assured to be defined if out() returns non-zero.) Note that inflateBack() cannot return Z_OK. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateBackEnd(z_streamp strm); /* All memory allocated by inflateBackInit() is freed. inflateBackEnd() returns Z_OK on success, or Z_STREAM_ERROR if the stream state was inconsistent. */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT zlibCompileFlags(void); /* Return flags indicating compile-time options. Type sizes, two bits each, 00 = 16 bits, 01 = 32, 10 = 64, 11 = other: 1.0: size of uInt 3.2: size of uLong 5.4: size of voidpf (pointer) 7.6: size of z_off_t Compiler, assembler, and debug options: 8: ZLIB_DEBUG 9: ASMV or ASMINF -- use ASM code 10: ZLIB_WINAPI -- exported functions use the WINAPI calling convention 11: 0 (reserved) One-time table building (smaller code, but not thread-safe if true): 12: BUILDFIXED -- build static block decoding tables when needed 13: DYNAMIC_CRC_TABLE -- build CRC calculation tables when needed 14,15: 0 (reserved) Library content (indicates missing functionality): 16: NO_GZCOMPRESS -- gz* functions cannot compress (to avoid linking deflate code when not needed) 17: NO_GZIP -- deflate can't write gzip streams, and inflate can't detect and decode gzip streams (to avoid linking crc code) 18-19: 0 (reserved) Operation variations (changes in library functionality): 20: PKZIP_BUG_WORKAROUND -- slightly more permissive inflate 21: FASTEST -- deflate algorithm with only one, lowest compression level 22,23: 0 (reserved) The sprintf variant used by gzprintf (zero is best): 24: 0 = vs*, 1 = s* -- 1 means limited to 20 arguments after the format 25: 0 = *nprintf, 1 = *printf -- 1 means gzprintf() not secure! 26: 0 = returns value, 1 = void -- 1 means inferred string length returned Remainder: 27-31: 0 (reserved) */ #ifndef Z_SOLO /* utility functions */ /* The following utility functions are implemented on top of the basic stream-oriented functions. To simplify the interface, some default options are assumed (compression level and memory usage, standard memory allocation functions). The source code of these utility functions can be modified if you need special options. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT compress(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen); /* Compresses the source buffer into the destination buffer. sourceLen is the byte length of the source buffer. Upon entry, destLen is the total size of the destination buffer, which must be at least the value returned by compressBound(sourceLen). Upon exit, destLen is the actual size of the compressed data. compress() is equivalent to compress2() with a level parameter of Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION. compress returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough room in the output buffer. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT compress2(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen, int level); /* Compresses the source buffer into the destination buffer. The level parameter has the same meaning as in deflateInit. sourceLen is the byte length of the source buffer. Upon entry, destLen is the total size of the destination buffer, which must be at least the value returned by compressBound(sourceLen). Upon exit, destLen is the actual size of the compressed data. compress2 returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough room in the output buffer, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the level parameter is invalid. */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT compressBound(uLong sourceLen); /* compressBound() returns an upper bound on the compressed size after compress() or compress2() on sourceLen bytes. It would be used before a compress() or compress2() call to allocate the destination buffer. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT uncompress(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen); /* Decompresses the source buffer into the destination buffer. sourceLen is the byte length of the source buffer. Upon entry, destLen is the total size of the destination buffer, which must be large enough to hold the entire uncompressed data. (The size of the uncompressed data must have been saved previously by the compressor and transmitted to the decompressor by some mechanism outside the scope of this compression library.) Upon exit, destLen is the actual size of the uncompressed data. uncompress returns Z_OK if success, Z_MEM_ERROR if there was not enough memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if there was not enough room in the output buffer, or Z_DATA_ERROR if the input data was corrupted or incomplete. In the case where there is not enough room, uncompress() will fill the output buffer with the uncompressed data up to that point. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT uncompress2(Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong *sourceLen); /* Same as uncompress, except that sourceLen is a pointer, where the length of the source is *sourceLen. On return, *sourceLen is the number of source bytes consumed. */ /* gzip file access functions */ /* This library supports reading and writing files in gzip (.gz) format with an interface similar to that of stdio, using the functions that start with "gz". The gzip format is different from the zlib format. gzip is a gzip wrapper, documented in RFC 1952, wrapped around a deflate stream. */ typedef struct gzFile_s *gzFile; /* semi-opaque gzip file descriptor */ /* ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzopen(const char *path, const char *mode); Open the gzip (.gz) file at path for reading and decompressing, or compressing and writing. The mode parameter is as in fopen ("rb" or "wb") but can also include a compression level ("wb9") or a strategy: 'f' for filtered data as in "wb6f", 'h' for Huffman-only compression as in "wb1h", 'R' for run-length encoding as in "wb1R", or 'F' for fixed code compression as in "wb9F". (See the description of deflateInit2 for more information about the strategy parameter.) 'T' will request transparent writing or appending with no compression and not using the gzip format. "a" can be used instead of "w" to request that the gzip stream that will be written be appended to the file. "+" will result in an error, since reading and writing to the same gzip file is not supported. The addition of "x" when writing will create the file exclusively, which fails if the file already exists. On systems that support it, the addition of "e" when reading or writing will set the flag to close the file on an execve() call. These functions, as well as gzip, will read and decode a sequence of gzip streams in a file. The append function of gzopen() can be used to create such a file. (Also see gzflush() for another way to do this.) When appending, gzopen does not test whether the file begins with a gzip stream, nor does it look for the end of the gzip streams to begin appending. gzopen will simply append a gzip stream to the existing file. gzopen can be used to read a file which is not in gzip format; in this case gzread will directly read from the file without decompression. When reading, this will be detected automatically by looking for the magic two- byte gzip header. gzopen returns NULL if the file could not be opened, if there was insufficient memory to allocate the gzFile state, or if an invalid mode was specified (an 'r', 'w', or 'a' was not provided, or '+' was provided). errno can be checked to determine if the reason gzopen failed was that the file could not be opened. */ ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzdopen(int fd, const char *mode); /* Associate a gzFile with the file descriptor fd. File descriptors are obtained from calls like open, dup, creat, pipe or fileno (if the file has been previously opened with fopen). The mode parameter is as in gzopen. The next call of gzclose on the returned gzFile will also close the file descriptor fd, just like fclose(fdopen(fd, mode)) closes the file descriptor fd. If you want to keep fd open, use fd = dup(fd_keep); gz = gzdopen(fd, mode);. The duplicated descriptor should be saved to avoid a leak, since gzdopen does not close fd if it fails. If you are using fileno() to get the file descriptor from a FILE *, then you will have to use dup() to avoid double-close()ing the file descriptor. Both gzclose() and fclose() will close the associated file descriptor, so they need to have different file descriptors. gzdopen returns NULL if there was insufficient memory to allocate the gzFile state, if an invalid mode was specified (an 'r', 'w', or 'a' was not provided, or '+' was provided), or if fd is -1. The file descriptor is not used until the next gz* read, write, seek, or close operation, so gzdopen will not detect if fd is invalid (unless fd is -1). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzbuffer(gzFile file, unsigned size); /* Set the internal buffer size used by this library's functions for file to size. The default buffer size is 8192 bytes. This function must be called after gzopen() or gzdopen(), and before any other calls that read or write the file. The buffer memory allocation is always deferred to the first read or write. Three times that size in buffer space is allocated. A larger buffer size of, for example, 64K or 128K bytes will noticeably increase the speed of decompression (reading). The new buffer size also affects the maximum length for gzprintf(). gzbuffer() returns 0 on success, or -1 on failure, such as being called too late. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzsetparams(gzFile file, int level, int strategy); /* Dynamically update the compression level and strategy for file. See the description of deflateInit2 for the meaning of these parameters. Previously provided data is flushed before applying the parameter changes. gzsetparams returns Z_OK if success, Z_STREAM_ERROR if the file was not opened for writing, Z_ERRNO if there is an error writing the flushed data, or Z_MEM_ERROR if there is a memory allocation error. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzread(gzFile file, voidp buf, unsigned len); /* Read and decompress up to len uncompressed bytes from file into buf. If the input file is not in gzip format, gzread copies the given number of bytes into the buffer directly from the file. After reaching the end of a gzip stream in the input, gzread will continue to read, looking for another gzip stream. Any number of gzip streams may be concatenated in the input file, and will all be decompressed by gzread(). If something other than a gzip stream is encountered after a gzip stream, that remaining trailing garbage is ignored (and no error is returned). gzread can be used to read a gzip file that is being concurrently written. Upon reaching the end of the input, gzread will return with the available data. If the error code returned by gzerror is Z_OK or Z_BUF_ERROR, then gzclearerr can be used to clear the end of file indicator in order to permit gzread to be tried again. Z_OK indicates that a gzip stream was completed on the last gzread. Z_BUF_ERROR indicates that the input file ended in the middle of a gzip stream. Note that gzread does not return -1 in the event of an incomplete gzip stream. This error is deferred until gzclose(), which will return Z_BUF_ERROR if the last gzread ended in the middle of a gzip stream. Alternatively, gzerror can be used before gzclose to detect this case. gzread returns the number of uncompressed bytes actually read, less than len for end of file, or -1 for error. If len is too large to fit in an int, then nothing is read, -1 is returned, and the error state is set to Z_STREAM_ERROR. */ ZEXTERN z_size_t ZEXPORT gzfread(voidp buf, z_size_t size, z_size_t nitems, gzFile file); /* Read and decompress up to nitems items of size size from file into buf, otherwise operating as gzread() does. This duplicates the interface of stdio's fread(), with size_t request and return types. If the library defines size_t, then z_size_t is identical to size_t. If not, then z_size_t is an unsigned integer type that can contain a pointer. gzfread() returns the number of full items read of size size, or zero if the end of the file was reached and a full item could not be read, or if there was an error. gzerror() must be consulted if zero is returned in order to determine if there was an error. If the multiplication of size and nitems overflows, i.e. the product does not fit in a z_size_t, then nothing is read, zero is returned, and the error state is set to Z_STREAM_ERROR. In the event that the end of file is reached and only a partial item is available at the end, i.e. the remaining uncompressed data length is not a multiple of size, then the final partial item is nevertheless read into buf and the end-of-file flag is set. The length of the partial item read is not provided, but could be inferred from the result of gztell(). This behavior is the same as the behavior of fread() implementations in common libraries, but it prevents the direct use of gzfread() to read a concurrently written file, resetting and retrying on end-of-file, when size is not 1. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzwrite(gzFile file, voidpc buf, unsigned len); /* Compress and write the len uncompressed bytes at buf to file. gzwrite returns the number of uncompressed bytes written or 0 in case of error. */ ZEXTERN z_size_t ZEXPORT gzfwrite(voidpc buf, z_size_t size, z_size_t nitems, gzFile file); /* Compress and write nitems items of size size from buf to file, duplicating the interface of stdio's fwrite(), with size_t request and return types. If the library defines size_t, then z_size_t is identical to size_t. If not, then z_size_t is an unsigned integer type that can contain a pointer. gzfwrite() returns the number of full items written of size size, or zero if there was an error. If the multiplication of size and nitems overflows, i.e. the product does not fit in a z_size_t, then nothing is written, zero is returned, and the error state is set to Z_STREAM_ERROR. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORTVA gzprintf(gzFile file, const char *format, ...); /* Convert, format, compress, and write the arguments (...) to file under control of the string format, as in fprintf. gzprintf returns the number of uncompressed bytes actually written, or a negative zlib error code in case of error. The number of uncompressed bytes written is limited to 8191, or one less than the buffer size given to gzbuffer(). The caller should assure that this limit is not exceeded. If it is exceeded, then gzprintf() will return an error (0) with nothing written. In this case, there may also be a buffer overflow with unpredictable consequences, which is possible only if zlib was compiled with the insecure functions sprintf() or vsprintf(), because the secure snprintf() or vsnprintf() functions were not available. This can be determined using zlibCompileFlags(). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzputs(gzFile file, const char *s); /* Compress and write the given null-terminated string s to file, excluding the terminating null character. gzputs returns the number of characters written, or -1 in case of error. */ ZEXTERN char * ZEXPORT gzgets(gzFile file, char *buf, int len); /* Read and decompress bytes from file into buf, until len-1 characters are read, or until a newline character is read and transferred to buf, or an end-of-file condition is encountered. If any characters are read or if len is one, the string is terminated with a null character. If no characters are read due to an end-of-file or len is less than one, then the buffer is left untouched. gzgets returns buf which is a null-terminated string, or it returns NULL for end-of-file or in case of error. If there was an error, the contents at buf are indeterminate. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzputc(gzFile file, int c); /* Compress and write c, converted to an unsigned char, into file. gzputc returns the value that was written, or -1 in case of error. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzgetc(gzFile file); /* Read and decompress one byte from file. gzgetc returns this byte or -1 in case of end of file or error. This is implemented as a macro for speed. As such, it does not do all of the checking the other functions do. I.e. it does not check to see if file is NULL, nor whether the structure file points to has been clobbered or not. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzungetc(int c, gzFile file); /* Push c back onto the stream for file to be read as the first character on the next read. At least one character of push-back is always allowed. gzungetc() returns the character pushed, or -1 on failure. gzungetc() will fail if c is -1, and may fail if a character has been pushed but not read yet. If gzungetc is used immediately after gzopen or gzdopen, at least the output buffer size of pushed characters is allowed. (See gzbuffer above.) The pushed character will be discarded if the stream is repositioned with gzseek() or gzrewind(). */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzflush(gzFile file, int flush); /* Flush all pending output to file. The parameter flush is as in the deflate() function. The return value is the zlib error number (see function gzerror below). gzflush is only permitted when writing. If the flush parameter is Z_FINISH, the remaining data is written and the gzip stream is completed in the output. If gzwrite() is called again, a new gzip stream will be started in the output. gzread() is able to read such concatenated gzip streams. gzflush should be called only when strictly necessary because it will degrade compression if called too often. */ /* ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gzseek(gzFile file, z_off_t offset, int whence); Set the starting position to offset relative to whence for the next gzread or gzwrite on file. The offset represents a number of bytes in the uncompressed data stream. The whence parameter is defined as in lseek(2); the value SEEK_END is not supported. If the file is opened for reading, this function is emulated but can be extremely slow. If the file is opened for writing, only forward seeks are supported; gzseek then compresses a sequence of zeroes up to the new starting position. gzseek returns the resulting offset location as measured in bytes from the beginning of the uncompressed stream, or -1 in case of error, in particular if the file is opened for writing and the new starting position would be before the current position. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzrewind(gzFile file); /* Rewind file. This function is supported only for reading. gzrewind(file) is equivalent to (int)gzseek(file, 0L, SEEK_SET). */ /* ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gztell(gzFile file); Return the starting position for the next gzread or gzwrite on file. This position represents a number of bytes in the uncompressed data stream, and is zero when starting, even if appending or reading a gzip stream from the middle of a file using gzdopen(). gztell(file) is equivalent to gzseek(file, 0L, SEEK_CUR) */ /* ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gzoffset(gzFile file); Return the current compressed (actual) read or write offset of file. This offset includes the count of bytes that precede the gzip stream, for example when appending or when using gzdopen() for reading. When reading, the offset does not include as yet unused buffered input. This information can be used for a progress indicator. On error, gzoffset() returns -1. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzeof(gzFile file); /* Return true (1) if the end-of-file indicator for file has been set while reading, false (0) otherwise. Note that the end-of-file indicator is set only if the read tried to go past the end of the input, but came up short. Therefore, just like feof(), gzeof() may return false even if there is no more data to read, in the event that the last read request was for the exact number of bytes remaining in the input file. This will happen if the input file size is an exact multiple of the buffer size. If gzeof() returns true, then the read functions will return no more data, unless the end-of-file indicator is reset by gzclearerr() and the input file has grown since the previous end of file was detected. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzdirect(gzFile file); /* Return true (1) if file is being copied directly while reading, or false (0) if file is a gzip stream being decompressed. If the input file is empty, gzdirect() will return true, since the input does not contain a gzip stream. If gzdirect() is used immediately after gzopen() or gzdopen() it will cause buffers to be allocated to allow reading the file to determine if it is a gzip file. Therefore if gzbuffer() is used, it should be called before gzdirect(). When writing, gzdirect() returns true (1) if transparent writing was requested ("wT" for the gzopen() mode), or false (0) otherwise. (Note: gzdirect() is not needed when writing. Transparent writing must be explicitly requested, so the application already knows the answer. When linking statically, using gzdirect() will include all of the zlib code for gzip file reading and decompression, which may not be desired.) */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzclose(gzFile file); /* Flush all pending output for file, if necessary, close file and deallocate the (de)compression state. Note that once file is closed, you cannot call gzerror with file, since its structures have been deallocated. gzclose must not be called more than once on the same file, just as free must not be called more than once on the same allocation. gzclose will return Z_STREAM_ERROR if file is not valid, Z_ERRNO on a file operation error, Z_MEM_ERROR if out of memory, Z_BUF_ERROR if the last read ended in the middle of a gzip stream, or Z_OK on success. */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzclose_r(gzFile file); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzclose_w(gzFile file); /* Same as gzclose(), but gzclose_r() is only for use when reading, and gzclose_w() is only for use when writing or appending. The advantage to using these instead of gzclose() is that they avoid linking in zlib compression or decompression code that is not used when only reading or only writing respectively. If gzclose() is used, then both compression and decompression code will be included the application when linking to a static zlib library. */ ZEXTERN const char * ZEXPORT gzerror(gzFile file, int *errnum); /* Return the error message for the last error which occurred on file. errnum is set to zlib error number. If an error occurred in the file system and not in the compression library, errnum is set to Z_ERRNO and the application may consult errno to get the exact error code. The application must not modify the returned string. Future calls to this function may invalidate the previously returned string. If file is closed, then the string previously returned by gzerror will no longer be available. gzerror() should be used to distinguish errors from end-of-file for those functions above that do not distinguish those cases in their return values. */ ZEXTERN void ZEXPORT gzclearerr(gzFile file); /* Clear the error and end-of-file flags for file. This is analogous to the clearerr() function in stdio. This is useful for continuing to read a gzip file that is being written concurrently. */ #endif /* !Z_SOLO */ /* checksum functions */ /* These functions are not related to compression but are exported anyway because they might be useful in applications using the compression library. */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32(uLong adler, const Bytef *buf, uInt len); /* Update a running Adler-32 checksum with the bytes buf[0..len-1] and return the updated checksum. An Adler-32 value is in the range of a 32-bit unsigned integer. If buf is Z_NULL, this function returns the required initial value for the checksum. An Adler-32 checksum is almost as reliable as a CRC-32 but can be computed much faster. Usage example: uLong adler = adler32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); while (read_buffer(buffer, length) != EOF) { adler = adler32(adler, buffer, length); } if (adler != original_adler) error(); */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_z(uLong adler, const Bytef *buf, z_size_t len); /* Same as adler32(), but with a size_t length. */ /* ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine(uLong adler1, uLong adler2, z_off_t len2); Combine two Adler-32 checksums into one. For two sequences of bytes, seq1 and seq2 with lengths len1 and len2, Adler-32 checksums were calculated for each, adler1 and adler2. adler32_combine() returns the Adler-32 checksum of seq1 and seq2 concatenated, requiring only adler1, adler2, and len2. Note that the z_off_t type (like off_t) is a signed integer. If len2 is negative, the result has no meaning or utility. */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32(uLong crc, const Bytef *buf, uInt len); /* Update a running CRC-32 with the bytes buf[0..len-1] and return the updated CRC-32. A CRC-32 value is in the range of a 32-bit unsigned integer. If buf is Z_NULL, this function returns the required initial value for the crc. Pre- and post-conditioning (one's complement) is performed within this function so it shouldn't be done by the application. Usage example: uLong crc = crc32(0L, Z_NULL, 0); while (read_buffer(buffer, length) != EOF) { crc = crc32(crc, buffer, length); } if (crc != original_crc) error(); */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_z(uLong crc, const Bytef *buf, z_size_t len); /* Same as crc32(), but with a size_t length. */ /* ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine(uLong crc1, uLong crc2, z_off_t len2); Combine two CRC-32 check values into one. For two sequences of bytes, seq1 and seq2 with lengths len1 and len2, CRC-32 check values were calculated for each, crc1 and crc2. crc32_combine() returns the CRC-32 check value of seq1 and seq2 concatenated, requiring only crc1, crc2, and len2. len2 must be non-negative. */ /* ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen(z_off_t len2); Return the operator corresponding to length len2, to be used with crc32_combine_op(). len2 must be non-negative. */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_op(uLong crc1, uLong crc2, uLong op); /* Give the same result as crc32_combine(), using op in place of len2. op is is generated from len2 by crc32_combine_gen(). This will be faster than crc32_combine() if the generated op is used more than once. */ /* various hacks, don't look :) */ /* deflateInit and inflateInit are macros to allow checking the zlib version * and the compiler's view of z_stream: */ ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateInit_(z_streamp strm, int level, const char *version, int stream_size); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateInit_(z_streamp strm, const char *version, int stream_size); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateInit2_(z_streamp strm, int level, int method, int windowBits, int memLevel, int strategy, const char *version, int stream_size); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateInit2_(z_streamp strm, int windowBits, const char *version, int stream_size); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateBackInit_(z_streamp strm, int windowBits, unsigned char FAR *window, const char *version, int stream_size); #ifdef Z_PREFIX_SET # define z_deflateInit(strm, level) \ deflateInit_((strm), (level), ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define z_inflateInit(strm) \ inflateInit_((strm), ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define z_deflateInit2(strm, level, method, windowBits, memLevel, strategy) \ deflateInit2_((strm),(level),(method),(windowBits),(memLevel),\ (strategy), ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define z_inflateInit2(strm, windowBits) \ inflateInit2_((strm), (windowBits), ZLIB_VERSION, \ (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define z_inflateBackInit(strm, windowBits, window) \ inflateBackInit_((strm), (windowBits), (window), \ ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) #else # define deflateInit(strm, level) \ deflateInit_((strm), (level), ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define inflateInit(strm) \ inflateInit_((strm), ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define deflateInit2(strm, level, method, windowBits, memLevel, strategy) \ deflateInit2_((strm),(level),(method),(windowBits),(memLevel),\ (strategy), ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define inflateInit2(strm, windowBits) \ inflateInit2_((strm), (windowBits), ZLIB_VERSION, \ (int)sizeof(z_stream)) # define inflateBackInit(strm, windowBits, window) \ inflateBackInit_((strm), (windowBits), (window), \ ZLIB_VERSION, (int)sizeof(z_stream)) #endif #ifndef Z_SOLO /* gzgetc() macro and its supporting function and exposed data structure. Note * that the real internal state is much larger than the exposed structure. * This abbreviated structure exposes just enough for the gzgetc() macro. The * user should not mess with these exposed elements, since their names or * behavior could change in the future, perhaps even capriciously. They can * only be used by the gzgetc() macro. You have been warned. */ struct gzFile_s { unsigned have; unsigned char *next; z_off64_t pos; }; ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT gzgetc_(gzFile file); /* backward compatibility */ #ifdef Z_PREFIX_SET # undef z_gzgetc # define z_gzgetc(g) \ ((g)->have ? ((g)->have--, (g)->pos++, *((g)->next)++) : (gzgetc)(g)) #else # define gzgetc(g) \ ((g)->have ? ((g)->have--, (g)->pos++, *((g)->next)++) : (gzgetc)(g)) #endif /* provide 64-bit offset functions if _LARGEFILE64_SOURCE defined, and/or * change the regular functions to 64 bits if _FILE_OFFSET_BITS is 64 (if * both are true, the application gets the *64 functions, and the regular * functions are changed to 64 bits) -- in case these are set on systems * without large file support, _LFS64_LARGEFILE must also be true */ #ifdef Z_LARGE64 ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzopen64(const char *, const char *); ZEXTERN z_off64_t ZEXPORT gzseek64(gzFile, z_off64_t, int); ZEXTERN z_off64_t ZEXPORT gztell64(gzFile); ZEXTERN z_off64_t ZEXPORT gzoffset64(gzFile); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine64(uLong, uLong, z_off64_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine64(uLong, uLong, z_off64_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen64(z_off64_t); #endif #if !defined(ZLIB_INTERNAL) && defined(Z_WANT64) # ifdef Z_PREFIX_SET # define z_gzopen z_gzopen64 # define z_gzseek z_gzseek64 # define z_gztell z_gztell64 # define z_gzoffset z_gzoffset64 # define z_adler32_combine z_adler32_combine64 # define z_crc32_combine z_crc32_combine64 # define z_crc32_combine_gen z_crc32_combine_gen64 # else # define gzopen gzopen64 # define gzseek gzseek64 # define gztell gztell64 # define gzoffset gzoffset64 # define adler32_combine adler32_combine64 # define crc32_combine crc32_combine64 # define crc32_combine_gen crc32_combine_gen64 # endif # ifndef Z_LARGE64 ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzopen64(const char *, const char *); ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gzseek64(gzFile, z_off_t, int); ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gztell64(gzFile); ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gzoffset64(gzFile); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine64(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine64(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen64(z_off_t); # endif #else ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzopen(const char *, const char *); ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gzseek(gzFile, z_off_t, int); ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gztell(gzFile); ZEXTERN z_off_t ZEXPORT gzoffset(gzFile); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen(z_off_t); #endif #else /* Z_SOLO */ ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT adler32_combine(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine(uLong, uLong, z_off_t); ZEXTERN uLong ZEXPORT crc32_combine_gen(z_off_t); #endif /* !Z_SOLO */ /* undocumented functions */ ZEXTERN const char * ZEXPORT zError(int); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateSyncPoint(z_streamp); ZEXTERN const z_crc_t FAR * ZEXPORT get_crc_table(void); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateUndermine(z_streamp, int); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateValidate(z_streamp, int); ZEXTERN unsigned long ZEXPORT inflateCodesUsed(z_streamp); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT inflateResetKeep(z_streamp); ZEXTERN int ZEXPORT deflateResetKeep(z_streamp); #if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(Z_SOLO) ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzopen_w(const wchar_t *path, const char *mode); #endif #if defined(STDC) || defined(Z_HAVE_STDARG_H) # ifndef Z_SOLO ZEXTERN int ZEXPORTVA gzvprintf(gzFile file, const char *format, va_list va); # endif #endif #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif /* ZLIB_H */
/* inffixed.h -- table for decoding fixed codes * Generated automatically by makefixed(). */ /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications. It is part of the implementation of this library and is subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h. */ static const code lenfix[512] = { {96,7,0},{0,8,80},{0,8,16},{20,8,115},{18,7,31},{0,8,112},{0,8,48}, {0,9,192},{16,7,10},{0,8,96},{0,8,32},{0,9,160},{0,8,0},{0,8,128}, {0,8,64},{0,9,224},{16,7,6},{0,8,88},{0,8,24},{0,9,144},{19,7,59}, {0,8,120},{0,8,56},{0,9,208},{17,7,17},{0,8,104},{0,8,40},{0,9,176}, {0,8,8},{0,8,136},{0,8,72},{0,9,240},{16,7,4},{0,8,84},{0,8,20}, {21,8,227},{19,7,43},{0,8,116},{0,8,52},{0,9,200},{17,7,13},{0,8,100}, {0,8,36},{0,9,168},{0,8,4},{0,8,132},{0,8,68},{0,9,232},{16,7,8}, {0,8,92},{0,8,28},{0,9,152},{20,7,83},{0,8,124},{0,8,60},{0,9,216}, {18,7,23},{0,8,108},{0,8,44},{0,9,184},{0,8,12},{0,8,140},{0,8,76}, {0,9,248},{16,7,3},{0,8,82},{0,8,18},{21,8,163},{19,7,35},{0,8,114}, {0,8,50},{0,9,196},{17,7,11},{0,8,98},{0,8,34},{0,9,164},{0,8,2}, {0,8,130},{0,8,66},{0,9,228},{16,7,7},{0,8,90},{0,8,26},{0,9,148}, {20,7,67},{0,8,122},{0,8,58},{0,9,212},{18,7,19},{0,8,106},{0,8,42}, {0,9,180},{0,8,10},{0,8,138},{0,8,74},{0,9,244},{16,7,5},{0,8,86}, {0,8,22},{64,8,0},{19,7,51},{0,8,118},{0,8,54},{0,9,204},{17,7,15}, {0,8,102},{0,8,38},{0,9,172},{0,8,6},{0,8,134},{0,8,70},{0,9,236}, {16,7,9},{0,8,94},{0,8,30},{0,9,156},{20,7,99},{0,8,126},{0,8,62}, {0,9,220},{18,7,27},{0,8,110},{0,8,46},{0,9,188},{0,8,14},{0,8,142}, {0,8,78},{0,9,252},{96,7,0},{0,8,81},{0,8,17},{21,8,131},{18,7,31}, {0,8,113},{0,8,49},{0,9,194},{16,7,10},{0,8,97},{0,8,33},{0,9,162}, {0,8,1},{0,8,129},{0,8,65},{0,9,226},{16,7,6},{0,8,89},{0,8,25}, {0,9,146},{19,7,59},{0,8,121},{0,8,57},{0,9,210},{17,7,17},{0,8,105}, {0,8,41},{0,9,178},{0,8,9},{0,8,137},{0,8,73},{0,9,242},{16,7,4}, {0,8,85},{0,8,21},{16,8,258},{19,7,43},{0,8,117},{0,8,53},{0,9,202}, {17,7,13},{0,8,101},{0,8,37},{0,9,170},{0,8,5},{0,8,133},{0,8,69}, {0,9,234},{16,7,8},{0,8,93},{0,8,29},{0,9,154},{20,7,83},{0,8,125}, {0,8,61},{0,9,218},{18,7,23},{0,8,109},{0,8,45},{0,9,186},{0,8,13}, {0,8,141},{0,8,77},{0,9,250},{16,7,3},{0,8,83},{0,8,19},{21,8,195}, {19,7,35},{0,8,115},{0,8,51},{0,9,198},{17,7,11},{0,8,99},{0,8,35}, {0,9,166},{0,8,3},{0,8,131},{0,8,67},{0,9,230},{16,7,7},{0,8,91}, {0,8,27},{0,9,150},{20,7,67},{0,8,123},{0,8,59},{0,9,214},{18,7,19}, {0,8,107},{0,8,43},{0,9,182},{0,8,11},{0,8,139},{0,8,75},{0,9,246}, {16,7,5},{0,8,87},{0,8,23},{64,8,0},{19,7,51},{0,8,119},{0,8,55}, {0,9,206},{17,7,15},{0,8,103},{0,8,39},{0,9,174},{0,8,7},{0,8,135}, {0,8,71},{0,9,238},{16,7,9},{0,8,95},{0,8,31},{0,9,158},{20,7,99}, {0,8,127},{0,8,63},{0,9,222},{18,7,27},{0,8,111},{0,8,47},{0,9,190}, {0,8,15},{0,8,143},{0,8,79},{0,9,254},{96,7,0},{0,8,80},{0,8,16}, {20,8,115},{18,7,31},{0,8,112},{0,8,48},{0,9,193},{16,7,10},{0,8,96}, {0,8,32},{0,9,161},{0,8,0},{0,8,128},{0,8,64},{0,9,225},{16,7,6}, {0,8,88},{0,8,24},{0,9,145},{19,7,59},{0,8,120},{0,8,56},{0,9,209}, {17,7,17},{0,8,104},{0,8,40},{0,9,177},{0,8,8},{0,8,136},{0,8,72}, {0,9,241},{16,7,4},{0,8,84},{0,8,20},{21,8,227},{19,7,43},{0,8,116}, {0,8,52},{0,9,201},{17,7,13},{0,8,100},{0,8,36},{0,9,169},{0,8,4}, {0,8,132},{0,8,68},{0,9,233},{16,7,8},{0,8,92},{0,8,28},{0,9,153}, {20,7,83},{0,8,124},{0,8,60},{0,9,217},{18,7,23},{0,8,108},{0,8,44}, {0,9,185},{0,8,12},{0,8,140},{0,8,76},{0,9,249},{16,7,3},{0,8,82}, {0,8,18},{21,8,163},{19,7,35},{0,8,114},{0,8,50},{0,9,197},{17,7,11}, {0,8,98},{0,8,34},{0,9,165},{0,8,2},{0,8,130},{0,8,66},{0,9,229}, {16,7,7},{0,8,90},{0,8,26},{0,9,149},{20,7,67},{0,8,122},{0,8,58}, {0,9,213},{18,7,19},{0,8,106},{0,8,42},{0,9,181},{0,8,10},{0,8,138}, {0,8,74},{0,9,245},{16,7,5},{0,8,86},{0,8,22},{64,8,0},{19,7,51}, {0,8,118},{0,8,54},{0,9,205},{17,7,15},{0,8,102},{0,8,38},{0,9,173}, {0,8,6},{0,8,134},{0,8,70},{0,9,237},{16,7,9},{0,8,94},{0,8,30}, {0,9,157},{20,7,99},{0,8,126},{0,8,62},{0,9,221},{18,7,27},{0,8,110}, {0,8,46},{0,9,189},{0,8,14},{0,8,142},{0,8,78},{0,9,253},{96,7,0}, {0,8,81},{0,8,17},{21,8,131},{18,7,31},{0,8,113},{0,8,49},{0,9,195}, {16,7,10},{0,8,97},{0,8,33},{0,9,163},{0,8,1},{0,8,129},{0,8,65}, {0,9,227},{16,7,6},{0,8,89},{0,8,25},{0,9,147},{19,7,59},{0,8,121}, {0,8,57},{0,9,211},{17,7,17},{0,8,105},{0,8,41},{0,9,179},{0,8,9}, {0,8,137},{0,8,73},{0,9,243},{16,7,4},{0,8,85},{0,8,21},{16,8,258}, {19,7,43},{0,8,117},{0,8,53},{0,9,203},{17,7,13},{0,8,101},{0,8,37}, {0,9,171},{0,8,5},{0,8,133},{0,8,69},{0,9,235},{16,7,8},{0,8,93}, {0,8,29},{0,9,155},{20,7,83},{0,8,125},{0,8,61},{0,9,219},{18,7,23}, {0,8,109},{0,8,45},{0,9,187},{0,8,13},{0,8,141},{0,8,77},{0,9,251}, {16,7,3},{0,8,83},{0,8,19},{21,8,195},{19,7,35},{0,8,115},{0,8,51}, {0,9,199},{17,7,11},{0,8,99},{0,8,35},{0,9,167},{0,8,3},{0,8,131}, {0,8,67},{0,9,231},{16,7,7},{0,8,91},{0,8,27},{0,9,151},{20,7,67}, {0,8,123},{0,8,59},{0,9,215},{18,7,19},{0,8,107},{0,8,43},{0,9,183}, {0,8,11},{0,8,139},{0,8,75},{0,9,247},{16,7,5},{0,8,87},{0,8,23}, {64,8,0},{19,7,51},{0,8,119},{0,8,55},{0,9,207},{17,7,15},{0,8,103}, {0,8,39},{0,9,175},{0,8,7},{0,8,135},{0,8,71},{0,9,239},{16,7,9}, {0,8,95},{0,8,31},{0,9,159},{20,7,99},{0,8,127},{0,8,63},{0,9,223}, {18,7,27},{0,8,111},{0,8,47},{0,9,191},{0,8,15},{0,8,143},{0,8,79}, {0,9,255} }; static const code distfix[32] = { {16,5,1},{23,5,257},{19,5,17},{27,5,4097},{17,5,5},{25,5,1025}, {21,5,65},{29,5,16385},{16,5,3},{24,5,513},{20,5,33},{28,5,8193}, {18,5,9},{26,5,2049},{22,5,129},{64,5,0},{16,5,2},{23,5,385}, {19,5,25},{27,5,6145},{17,5,7},{25,5,1537},{21,5,97},{29,5,24577}, {16,5,4},{24,5,769},{20,5,49},{28,5,12289},{18,5,13},{26,5,3073}, {22,5,193},{64,5,0} };
/* deflate.h -- internal compression state * Copyright (C) 1995-2024 Jean-loup Gailly * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications. It is part of the implementation of the compression library and is subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h. */ /* @(#) $Id$ */ #ifndef DEFLATE_H #define DEFLATE_H #include "zutil.h" /* define NO_GZIP when compiling if you want to disable gzip header and trailer creation by deflate(). NO_GZIP would be used to avoid linking in the crc code when it is not needed. For shared libraries, gzip encoding should be left enabled. */ #ifndef NO_GZIP # define GZIP #endif /* define LIT_MEM to slightly increase the speed of deflate (order 1% to 2%) at the cost of a larger memory footprint */ /* #define LIT_MEM */ /* =========================================================================== * Internal compression state. */ #define LENGTH_CODES 29 /* number of length codes, not counting the special END_BLOCK code */ #define LITERALS 256 /* number of literal bytes 0..255 */ #define L_CODES (LITERALS+1+LENGTH_CODES) /* number of Literal or Length codes, including the END_BLOCK code */ #define D_CODES 30 /* number of distance codes */ #define BL_CODES 19 /* number of codes used to transfer the bit lengths */ #define HEAP_SIZE (2*L_CODES+1) /* maximum heap size */ #define MAX_BITS 15 /* All codes must not exceed MAX_BITS bits */ #define Buf_size 16 /* size of bit buffer in bi_buf */ #define INIT_STATE 42 /* zlib header -> BUSY_STATE */ #ifdef GZIP # define GZIP_STATE 57 /* gzip header -> BUSY_STATE | EXTRA_STATE */ #endif #define EXTRA_STATE 69 /* gzip extra block -> NAME_STATE */ #define NAME_STATE 73 /* gzip file name -> COMMENT_STATE */ #define COMMENT_STATE 91 /* gzip comment -> HCRC_STATE */ #define HCRC_STATE 103 /* gzip header CRC -> BUSY_STATE */ #define BUSY_STATE 113 /* deflate -> FINISH_STATE */ #define FINISH_STATE 666 /* stream complete */ /* Stream status */ /* Data structure describing a single value and its code string. */ typedef struct ct_data_s { union { ush freq; /* frequency count */ ush code; /* bit string */ } fc; union { ush dad; /* father node in Huffman tree */ ush len; /* length of bit string */ } dl; } FAR ct_data; #define Freq fc.freq #define Code fc.code #define Dad dl.dad #define Len dl.len typedef struct static_tree_desc_s static_tree_desc; typedef struct tree_desc_s { ct_data *dyn_tree; /* the dynamic tree */ int max_code; /* largest code with non zero frequency */ const static_tree_desc *stat_desc; /* the corresponding static tree */ } FAR tree_desc; typedef ush Pos; typedef Pos FAR Posf; typedef unsigned IPos; /* A Pos is an index in the character window. We use short instead of int to * save space in the various tables. IPos is used only for parameter passing. */ typedef struct internal_state { z_streamp strm; /* pointer back to this zlib stream */ int status; /* as the name implies */ Bytef *pending_buf; /* output still pending */ ulg pending_buf_size; /* size of pending_buf */ Bytef *pending_out; /* next pending byte to output to the stream */ ulg pending; /* nb of bytes in the pending buffer */ int wrap; /* bit 0 true for zlib, bit 1 true for gzip */ gz_headerp gzhead; /* gzip header information to write */ ulg gzindex; /* where in extra, name, or comment */ Byte method; /* can only be DEFLATED */ int last_flush; /* value of flush param for previous deflate call */ /* used by deflate.c: */ uInt w_size; /* LZ77 window size (32K by default) */ uInt w_bits; /* log2(w_size) (8..16) */ uInt w_mask; /* w_size - 1 */ Bytef *window; /* Sliding window. Input bytes are read into the second half of the window, * and move to the first half later to keep a dictionary of at least wSize * bytes. With this organization, matches are limited to a distance of * wSize-MAX_MATCH bytes, but this ensures that IO is always * performed with a length multiple of the block size. Also, it limits * the window size to 64K, which is quite useful on MSDOS. * To do: use the user input buffer as sliding window. */ ulg window_size; /* Actual size of window: 2*wSize, except when the user input buffer * is directly used as sliding window. */ Posf *prev; /* Link to older string with same hash index. To limit the size of this * array to 64K, this link is maintained only for the last 32K strings. * An index in this array is thus a window index modulo 32K. */ Posf *head; /* Heads of the hash chains or NIL. */ uInt ins_h; /* hash index of string to be inserted */ uInt hash_size; /* number of elements in hash table */ uInt hash_bits; /* log2(hash_size) */ uInt hash_mask; /* hash_size-1 */ uInt hash_shift; /* Number of bits by which ins_h must be shifted at each input * step. It must be such that after MIN_MATCH steps, the oldest * byte no longer takes part in the hash key, that is: * hash_shift * MIN_MATCH >= hash_bits */ long block_start; /* Window position at the beginning of the current output block. Gets * negative when the window is moved backwards. */ uInt match_length; /* length of best match */ IPos prev_match; /* previous match */ int match_available; /* set if previous match exists */ uInt strstart; /* start of string to insert */ uInt match_start; /* start of matching string */ uInt lookahead; /* number of valid bytes ahead in window */ uInt prev_length; /* Length of the best match at previous step. Matches not greater than this * are discarded. This is used in the lazy match evaluation. */ uInt max_chain_length; /* To speed up deflation, hash chains are never searched beyond this * length. A higher limit improves compression ratio but degrades the * speed. */ uInt max_lazy_match; /* Attempt to find a better match only when the current match is strictly * smaller than this value. This mechanism is used only for compression * levels >= 4. */ # define max_insert_length max_lazy_match /* Insert new strings in the hash table only if the match length is not * greater than this length. This saves time but degrades compression. * max_insert_length is used only for compression levels <= 3. */ int level; /* compression level (1..9) */ int strategy; /* favor or force Huffman coding*/ uInt good_match; /* Use a faster search when the previous match is longer than this */ int nice_match; /* Stop searching when current match exceeds this */ /* used by trees.c: */ /* Didn't use ct_data typedef below to suppress compiler warning */ struct ct_data_s dyn_ltree[HEAP_SIZE]; /* literal and length tree */ struct ct_data_s dyn_dtree[2*D_CODES+1]; /* distance tree */ struct ct_data_s bl_tree[2*BL_CODES+1]; /* Huffman tree for bit lengths */ struct tree_desc_s l_desc; /* desc. for literal tree */ struct tree_desc_s d_desc; /* desc. for distance tree */ struct tree_desc_s bl_desc; /* desc. for bit length tree */ ush bl_count[MAX_BITS+1]; /* number of codes at each bit length for an optimal tree */ int heap[2*L_CODES+1]; /* heap used to build the Huffman trees */ int heap_len; /* number of elements in the heap */ int heap_max; /* element of largest frequency */ /* The sons of heap[n] are heap[2*n] and heap[2*n+1]. heap[0] is not used. * The same heap array is used to build all trees. */ uch depth[2*L_CODES+1]; /* Depth of each subtree used as tie breaker for trees of equal frequency */ #ifdef LIT_MEM # define LIT_BUFS 5 ushf *d_buf; /* buffer for distances */ uchf *l_buf; /* buffer for literals/lengths */ #else # define LIT_BUFS 4 uchf *sym_buf; /* buffer for distances and literals/lengths */ #endif uInt lit_bufsize; /* Size of match buffer for literals/lengths. There are 4 reasons for * limiting lit_bufsize to 64K: * - frequencies can be kept in 16 bit counters * - if compression is not successful for the first block, all input * data is still in the window so we can still emit a stored block even * when input comes from standard input. (This can also be done for * all blocks if lit_bufsize is not greater than 32K.) * - if compression is not successful for a file smaller than 64K, we can * even emit a stored file instead of a stored block (saving 5 bytes). * This is applicable only for zip (not gzip or zlib). * - creating new Huffman trees less frequently may not provide fast * adaptation to changes in the input data statistics. (Take for * example a binary file with poorly compressible code followed by * a highly compressible string table.) Smaller buffer sizes give * fast adaptation but have of course the overhead of transmitting * trees more frequently. * - I can't count above 4 */ uInt sym_next; /* running index in symbol buffer */ uInt sym_end; /* symbol table full when sym_next reaches this */ ulg opt_len; /* bit length of current block with optimal trees */ ulg static_len; /* bit length of current block with static trees */ uInt matches; /* number of string matches in current block */ uInt insert; /* bytes at end of window left to insert */ #ifdef ZLIB_DEBUG ulg compressed_len; /* total bit length of compressed file mod 2^32 */ ulg bits_sent; /* bit length of compressed data sent mod 2^32 */ #endif ush bi_buf; /* Output buffer. bits are inserted starting at the bottom (least * significant bits). */ int bi_valid; /* Number of valid bits in bi_buf. All bits above the last valid bit * are always zero. */ ulg high_water; /* High water mark offset in window for initialized bytes -- bytes above * this are set to zero in order to avoid memory check warnings when * longest match routines access bytes past the input. This is then * updated to the new high water mark. */ } FAR deflate_state; /* Output a byte on the stream. * IN assertion: there is enough room in pending_buf. */ #define put_byte(s, c) {s->pending_buf[s->pending++] = (Bytef)(c);} #define MIN_LOOKAHEAD (MAX_MATCH+MIN_MATCH+1) /* Minimum amount of lookahead, except at the end of the input file. * See deflate.c for comments about the MIN_MATCH+1. */ #define MAX_DIST(s) ((s)->w_size-MIN_LOOKAHEAD) /* In order to simplify the code, particularly on 16 bit machines, match * distances are limited to MAX_DIST instead of WSIZE. */ #define WIN_INIT MAX_MATCH /* Number of bytes after end of data in window to initialize in order to avoid memory checker errors from longest match routines */ /* in trees.c */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_init(deflate_state *s); int ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_tally(deflate_state *s, unsigned dist, unsigned lc); void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_flush_block(deflate_state *s, charf *buf, ulg stored_len, int last); void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_flush_bits(deflate_state *s); void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_align(deflate_state *s); void ZLIB_INTERNAL _tr_stored_block(deflate_state *s, charf *buf, ulg stored_len, int last); #define d_code(dist) \ ((dist) < 256 ? _dist_code[dist] : _dist_code[256+((dist)>>7)]) /* Mapping from a distance to a distance code. dist is the distance - 1 and * must not have side effects. _dist_code[256] and _dist_code[257] are never * used. */ #ifndef ZLIB_DEBUG /* Inline versions of _tr_tally for speed: */ #if defined(GEN_TREES_H) || !defined(STDC) extern uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _length_code[]; extern uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _dist_code[]; #else extern const uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _length_code[]; extern const uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _dist_code[]; #endif #ifdef LIT_MEM # define _tr_tally_lit(s, c, flush) \ { uch cc = (c); \ s->d_buf[s->sym_next] = 0; \ s->l_buf[s->sym_next++] = cc; \ s->dyn_ltree[cc].Freq++; \ flush = (s->sym_next == s->sym_end); \ } # define _tr_tally_dist(s, distance, length, flush) \ { uch len = (uch)(length); \ ush dist = (ush)(distance); \ s->d_buf[s->sym_next] = dist; \ s->l_buf[s->sym_next++] = len; \ dist--; \ s->dyn_ltree[_length_code[len]+LITERALS+1].Freq++; \ s->dyn_dtree[d_code(dist)].Freq++; \ flush = (s->sym_next == s->sym_end); \ } #else # define _tr_tally_lit(s, c, flush) \ { uch cc = (c); \ s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = 0; \ s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = 0; \ s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = cc; \ s->dyn_ltree[cc].Freq++; \ flush = (s->sym_next == s->sym_end); \ } # define _tr_tally_dist(s, distance, length, flush) \ { uch len = (uch)(length); \ ush dist = (ush)(distance); \ s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = (uch)dist; \ s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = (uch)(dist >> 8); \ s->sym_buf[s->sym_next++] = len; \ dist--; \ s->dyn_ltree[_length_code[len]+LITERALS+1].Freq++; \ s->dyn_dtree[d_code(dist)].Freq++; \ flush = (s->sym_next == s->sym_end); \ } #endif #else # define _tr_tally_lit(s, c, flush) flush = _tr_tally(s, 0, c) # define _tr_tally_dist(s, distance, length, flush) \ flush = _tr_tally(s, distance, length) #endif #endif /* DEFLATE_H */
/* header created automatically with -DGEN_TREES_H */
local const ct_data static_ltree[L_CODES+2] = {
{{ 12},{ 8}}, {{140},{ 8}}, {{ 76},{ 8}}, {{204},{ 8}}, {{ 44},{ 8}},
{{172},{ 8}}, {{108},{ 8}}, {{236},{ 8}}, {{ 28},{ 8}}, {{156},{ 8}},
{{ 92},{ 8}}, {{220},{ 8}}, {{ 60},{ 8}}, {{188},{ 8}}, {{124},{ 8}},
{{252},{ 8}}, {{ 2},{ 8}}, {{130},{ 8}}, {{ 66},{ 8}}, {{194},{ 8}},
{{ 34},{ 8}}, {{162},{ 8}}, {{ 98},{ 8}}, {{226},{ 8}}, {{ 18},{ 8}},
{{146},{ 8}}, {{ 82},{ 8}}, {{210},{ 8}}, {{ 50},{ 8}}, {{178},{ 8}},
{{114},{ 8}}, {{242},{ 8}}, {{ 10},{ 8}}, {{138},{ 8}}, {{ 74},{ 8}},
{{202},{ 8}}, {{ 42},{ 8}}, {{170},{ 8}}, {{106},{ 8}}, {{234},{ 8}},
{{ 26},{ 8}}, {{154},{ 8}}, {{ 90},{ 8}}, {{218},{ 8}}, {{ 58},{ 8}},
{{186},{ 8}}, {{122},{ 8}}, {{250},{ 8}}, {{ 6},{ 8}}, {{134},{ 8}},
{{ 70},{ 8}}, {{198},{ 8}}, {{ 38},{ 8}}, {{166},{ 8}}, {{102},{ 8}},
{{230},{ 8}}, {{ 22},{ 8}}, {{150},{ 8}}, {{ 86},{ 8}}, {{214},{ 8}},
{{ 54},{ 8}}, {{182},{ 8}}, {{118},{ 8}}, {{246},{ 8}}, {{ 14},{ 8}},
{{142},{ 8}}, {{ 78},{ 8}}, {{206},{ 8}}, {{ 46},{ 8}}, {{174},{ 8}},
{{110},{ 8}}, {{238},{ 8}}, {{ 30},{ 8}}, {{158},{ 8}}, {{ 94},{ 8}},
{{222},{ 8}}, {{ 62},{ 8}}, {{190},{ 8}}, {{126},{ 8}}, {{254},{ 8}},
{{ 1},{ 8}}, {{129},{ 8}}, {{ 65},{ 8}}, {{193},{ 8}}, {{ 33},{ 8}},
{{161},{ 8}}, {{ 97},{ 8}}, {{225},{ 8}}, {{ 17},{ 8}}, {{145},{ 8}},
{{ 81},{ 8}}, {{209},{ 8}}, {{ 49},{ 8}}, {{177},{ 8}}, {{113},{ 8}},
{{241},{ 8}}, {{ 9},{ 8}}, {{137},{ 8}}, {{ 73},{ 8}}, {{201},{ 8}},
{{ 41},{ 8}}, {{169},{ 8}}, {{105},{ 8}}, {{233},{ 8}}, {{ 25},{ 8}},
{{153},{ 8}}, {{ 89},{ 8}}, {{217},{ 8}}, {{ 57},{ 8}}, {{185},{ 8}},
{{121},{ 8}}, {{249},{ 8}}, {{ 5},{ 8}}, {{133},{ 8}}, {{ 69},{ 8}},
{{197},{ 8}}, {{ 37},{ 8}}, {{165},{ 8}}, {{101},{ 8}}, {{229},{ 8}},
{{ 21},{ 8}}, {{149},{ 8}}, {{ 85},{ 8}}, {{213},{ 8}}, {{ 53},{ 8}},
{{181},{ 8}}, {{117},{ 8}}, {{245},{ 8}}, {{ 13},{ 8}}, {{141},{ 8}},
{{ 77},{ 8}}, {{205},{ 8}}, {{ 45},{ 8}}, {{173},{ 8}}, {{109},{ 8}},
{{237},{ 8}}, {{ 29},{ 8}}, {{157},{ 8}}, {{ 93},{ 8}}, {{221},{ 8}},
{{ 61},{ 8}}, {{189},{ 8}}, {{125},{ 8}}, {{253},{ 8}}, {{ 19},{ 9}},
{{275},{ 9}}, {{147},{ 9}}, {{403},{ 9}}, {{ 83},{ 9}}, {{339},{ 9}},
{{211},{ 9}}, {{467},{ 9}}, {{ 51},{ 9}}, {{307},{ 9}}, {{179},{ 9}},
{{435},{ 9}}, {{115},{ 9}}, {{371},{ 9}}, {{243},{ 9}}, {{499},{ 9}},
{{ 11},{ 9}}, {{267},{ 9}}, {{139},{ 9}}, {{395},{ 9}}, {{ 75},{ 9}},
{{331},{ 9}}, {{203},{ 9}}, {{459},{ 9}}, {{ 43},{ 9}}, {{299},{ 9}},
{{171},{ 9}}, {{427},{ 9}}, {{107},{ 9}}, {{363},{ 9}}, {{235},{ 9}},
{{491},{ 9}}, {{ 27},{ 9}}, {{283},{ 9}}, {{155},{ 9}}, {{411},{ 9}},
{{ 91},{ 9}}, {{347},{ 9}}, {{219},{ 9}}, {{475},{ 9}}, {{ 59},{ 9}},
{{315},{ 9}}, {{187},{ 9}}, {{443},{ 9}}, {{123},{ 9}}, {{379},{ 9}},
{{251},{ 9}}, {{507},{ 9}}, {{ 7},{ 9}}, {{263},{ 9}}, {{135},{ 9}},
{{391},{ 9}}, {{ 71},{ 9}}, {{327},{ 9}}, {{199},{ 9}}, {{455},{ 9}},
{{ 39},{ 9}}, {{295},{ 9}}, {{167},{ 9}}, {{423},{ 9}}, {{103},{ 9}},
{{359},{ 9}}, {{231},{ 9}}, {{487},{ 9}}, {{ 23},{ 9}}, {{279},{ 9}},
{{151},{ 9}}, {{407},{ 9}}, {{ 87},{ 9}}, {{343},{ 9}}, {{215},{ 9}},
{{471},{ 9}}, {{ 55},{ 9}}, {{311},{ 9}}, {{183},{ 9}}, {{439},{ 9}},
{{119},{ 9}}, {{375},{ 9}}, {{247},{ 9}}, {{503},{ 9}}, {{ 15},{ 9}},
{{271},{ 9}}, {{143},{ 9}}, {{399},{ 9}}, {{ 79},{ 9}}, {{335},{ 9}},
{{207},{ 9}}, {{463},{ 9}}, {{ 47},{ 9}}, {{303},{ 9}}, {{175},{ 9}},
{{431},{ 9}}, {{111},{ 9}}, {{367},{ 9}}, {{239},{ 9}}, {{495},{ 9}},
{{ 31},{ 9}}, {{287},{ 9}}, {{159},{ 9}}, {{415},{ 9}}, {{ 95},{ 9}},
{{351},{ 9}}, {{223},{ 9}}, {{479},{ 9}}, {{ 63},{ 9}}, {{319},{ 9}},
{{191},{ 9}}, {{447},{ 9}}, {{127},{ 9}}, {{383},{ 9}}, {{255},{ 9}},
{{511},{ 9}}, {{ 0},{ 7}}, {{ 64},{ 7}}, {{ 32},{ 7}}, {{ 96},{ 7}},
{{ 16},{ 7}}, {{ 80},{ 7}}, {{ 48},{ 7}}, {{112},{ 7}}, {{ 8},{ 7}},
{{ 72},{ 7}}, {{ 40},{ 7}}, {{104},{ 7}}, {{ 24},{ 7}}, {{ 88},{ 7}},
{{ 56},{ 7}}, {{120},{ 7}}, {{ 4},{ 7}}, {{ 68},{ 7}}, {{ 36},{ 7}},
{{100},{ 7}}, {{ 20},{ 7}}, {{ 84},{ 7}}, {{ 52},{ 7}}, {{116},{ 7}},
{{ 3},{ 8}}, {{131},{ 8}}, {{ 67},{ 8}}, {{195},{ 8}}, {{ 35},{ 8}},
{{163},{ 8}}, {{ 99},{ 8}}, {{227},{ 8}}
};
local const ct_data static_dtree[D_CODES] = {
{{ 0},{ 5}}, {{16},{ 5}}, {{ 8},{ 5}}, {{24},{ 5}}, {{ 4},{ 5}},
{{20},{ 5}}, {{12},{ 5}}, {{28},{ 5}}, {{ 2},{ 5}}, {{18},{ 5}},
{{10},{ 5}}, {{26},{ 5}}, {{ 6},{ 5}}, {{22},{ 5}}, {{14},{ 5}},
{{30},{ 5}}, {{ 1},{ 5}}, {{17},{ 5}}, {{ 9},{ 5}}, {{25},{ 5}},
{{ 5},{ 5}}, {{21},{ 5}}, {{13},{ 5}}, {{29},{ 5}}, {{ 3},{ 5}},
{{19},{ 5}}, {{11},{ 5}}, {{27},{ 5}}, {{ 7},{ 5}}, {{23},{ 5}}
};
const uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _dist_code[DIST_CODE_LEN] = {
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8,
8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,
10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11,
11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12,
12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 13, 13, 13, 13,
13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13,
13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14,
14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14,
14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14,
14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 14, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15,
15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15,
15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15,
15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 0, 0, 16, 17,
18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 20, 20, 21, 21, 21, 21, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22,
23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24,
24, 24, 24, 24, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25,
26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26,
26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27,
27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27,
27, 27, 27, 27, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28,
28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28,
28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28,
28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 28, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29,
29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29,
29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29,
29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29, 29
};
const uch ZLIB_INTERNAL _length_code[MAX_MATCH-MIN_MATCH+1]= {
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 9, 9, 10, 10, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12,
13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 14, 14, 15, 15, 15, 15, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16,
17, 17, 17, 17, 17, 17, 17, 17, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 19,
19, 19, 19, 19, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20,
21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 22, 22, 22, 22,
22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23,
23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24,
24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24,
25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25,
25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26,
26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26, 26,
26, 26, 26, 26, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27,
27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 28
};
local const int base_length[LENGTH_CODES] = {
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 40, 48, 56,
64, 80, 96, 112, 128, 160, 192, 224, 0
};
local const int base_dist[D_CODES] = {
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24,
32, 48, 64, 96, 128, 192, 256, 384, 512, 768,
1024, 1536, 2048, 3072, 4096, 6144, 8192, 12288, 16384, 24576
};
/* inftrees.h -- header to use inftrees.c * Copyright (C) 1995-2005, 2010 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications. It is part of the implementation of the compression library and is subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h. */ /* Structure for decoding tables. Each entry provides either the information needed to do the operation requested by the code that indexed that table entry, or it provides a pointer to another table that indexes more bits of the code. op indicates whether the entry is a pointer to another table, a literal, a length or distance, an end-of-block, or an invalid code. For a table pointer, the low four bits of op is the number of index bits of that table. For a length or distance, the low four bits of op is the number of extra bits to get after the code. bits is the number of bits in this code or part of the code to drop off of the bit buffer. val is the actual byte to output in the case of a literal, the base length or distance, or the offset from the current table to the next table. Each entry is four bytes. */ typedef struct { unsigned char op; /* operation, extra bits, table bits */ unsigned char bits; /* bits in this part of the code */ unsigned short val; /* offset in table or code value */ } code; /* op values as set by inflate_table(): 00000000 - literal 0000tttt - table link, tttt != 0 is the number of table index bits 0001eeee - length or distance, eeee is the number of extra bits 01100000 - end of block 01000000 - invalid code */ /* Maximum size of the dynamic table. The maximum number of code structures is 1444, which is the sum of 852 for literal/length codes and 592 for distance codes. These values were found by exhaustive searches using the program examples/enough.c found in the zlib distribution. The arguments to that program are the number of symbols, the initial root table size, and the maximum bit length of a code. "enough 286 9 15" for literal/length codes returns 852, and "enough 30 6 15" for distance codes returns 592. The initial root table size (9 or 6) is found in the fifth argument of the inflate_table() calls in inflate.c and infback.c. If the root table size is changed, then these maximum sizes would be need to be recalculated and updated. */ #define ENOUGH_LENS 852 #define ENOUGH_DISTS 592 #define ENOUGH (ENOUGH_LENS+ENOUGH_DISTS) /* Type of code to build for inflate_table() */ typedef enum { CODES, LENS, DISTS } codetype; int ZLIB_INTERNAL inflate_table(codetype type, unsigned short FAR *lens, unsigned codes, code FAR * FAR *table, unsigned FAR *bits, unsigned short FAR *work);
/* inflate.h -- internal inflate state definition * Copyright (C) 1995-2019 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications. It is part of the implementation of the compression library and is subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h. */ /* define NO_GZIP when compiling if you want to disable gzip header and trailer decoding by inflate(). NO_GZIP would be used to avoid linking in the crc code when it is not needed. For shared libraries, gzip decoding should be left enabled. */ #ifndef NO_GZIP # define GUNZIP #endif /* Possible inflate modes between inflate() calls */ typedef enum { HEAD = 16180, /* i: waiting for magic header */ FLAGS, /* i: waiting for method and flags (gzip) */ TIME, /* i: waiting for modification time (gzip) */ OS, /* i: waiting for extra flags and operating system (gzip) */ EXLEN, /* i: waiting for extra length (gzip) */ EXTRA, /* i: waiting for extra bytes (gzip) */ NAME, /* i: waiting for end of file name (gzip) */ COMMENT, /* i: waiting for end of comment (gzip) */ HCRC, /* i: waiting for header crc (gzip) */ DICTID, /* i: waiting for dictionary check value */ DICT, /* waiting for inflateSetDictionary() call */ TYPE, /* i: waiting for type bits, including last-flag bit */ TYPEDO, /* i: same, but skip check to exit inflate on new block */ STORED, /* i: waiting for stored size (length and complement) */ COPY_, /* i/o: same as COPY below, but only first time in */ COPY, /* i/o: waiting for input or output to copy stored block */ TABLE, /* i: waiting for dynamic block table lengths */ LENLENS, /* i: waiting for code length code lengths */ CODELENS, /* i: waiting for length/lit and distance code lengths */ LEN_, /* i: same as LEN below, but only first time in */ LEN, /* i: waiting for length/lit/eob code */ LENEXT, /* i: waiting for length extra bits */ DIST, /* i: waiting for distance code */ DISTEXT, /* i: waiting for distance extra bits */ MATCH, /* o: waiting for output space to copy string */ LIT, /* o: waiting for output space to write literal */ CHECK, /* i: waiting for 32-bit check value */ LENGTH, /* i: waiting for 32-bit length (gzip) */ DONE, /* finished check, done -- remain here until reset */ BAD, /* got a data error -- remain here until reset */ MEM, /* got an inflate() memory error -- remain here until reset */ SYNC /* looking for synchronization bytes to restart inflate() */ } inflate_mode; /* State transitions between above modes - (most modes can go to BAD or MEM on error -- not shown for clarity) Process header: HEAD -> (gzip) or (zlib) or (raw) (gzip) -> FLAGS -> TIME -> OS -> EXLEN -> EXTRA -> NAME -> COMMENT -> HCRC -> TYPE (zlib) -> DICTID or TYPE DICTID -> DICT -> TYPE (raw) -> TYPEDO Read deflate blocks: TYPE -> TYPEDO -> STORED or TABLE or LEN_ or CHECK STORED -> COPY_ -> COPY -> TYPE TABLE -> LENLENS -> CODELENS -> LEN_ LEN_ -> LEN Read deflate codes in fixed or dynamic block: LEN -> LENEXT or LIT or TYPE LENEXT -> DIST -> DISTEXT -> MATCH -> LEN LIT -> LEN Process trailer: CHECK -> LENGTH -> DONE */ /* State maintained between inflate() calls -- approximately 7K bytes, not including the allocated sliding window, which is up to 32K bytes. */ struct inflate_state { z_streamp strm; /* pointer back to this zlib stream */ inflate_mode mode; /* current inflate mode */ int last; /* true if processing last block */ int wrap; /* bit 0 true for zlib, bit 1 true for gzip, bit 2 true to validate check value */ int havedict; /* true if dictionary provided */ int flags; /* gzip header method and flags, 0 if zlib, or -1 if raw or no header yet */ unsigned dmax; /* zlib header max distance (INFLATE_STRICT) */ unsigned long check; /* protected copy of check value */ unsigned long total; /* protected copy of output count */ gz_headerp head; /* where to save gzip header information */ /* sliding window */ unsigned wbits; /* log base 2 of requested window size */ unsigned wsize; /* window size or zero if not using window */ unsigned whave; /* valid bytes in the window */ unsigned wnext; /* window write index */ unsigned char FAR *window; /* allocated sliding window, if needed */ /* bit accumulator */ unsigned long hold; /* input bit accumulator */ unsigned bits; /* number of bits in "in" */ /* for string and stored block copying */ unsigned length; /* literal or length of data to copy */ unsigned offset; /* distance back to copy string from */ /* for table and code decoding */ unsigned extra; /* extra bits needed */ /* fixed and dynamic code tables */ code const FAR *lencode; /* starting table for length/literal codes */ code const FAR *distcode; /* starting table for distance codes */ unsigned lenbits; /* index bits for lencode */ unsigned distbits; /* index bits for distcode */ /* dynamic table building */ unsigned ncode; /* number of code length code lengths */ unsigned nlen; /* number of length code lengths */ unsigned ndist; /* number of distance code lengths */ unsigned have; /* number of code lengths in lens[] */ code FAR *next; /* next available space in codes[] */ unsigned short lens[320]; /* temporary storage for code lengths */ unsigned short work[288]; /* work area for code table building */ code codes[ENOUGH]; /* space for code tables */ int sane; /* if false, allow invalid distance too far */ int back; /* bits back of last unprocessed length/lit */ unsigned was; /* initial length of match */ };
/* inffast.h -- header to use inffast.c * Copyright (C) 1995-2003, 2010 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ /* WARNING: this file should *not* be used by applications. It is part of the implementation of the compression library and is subject to change. Applications should only use zlib.h. */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL inflate_fast(z_streamp strm, unsigned start);
/* gzguts.h -- zlib internal header definitions for gz* operations * Copyright (C) 2004-2024 Mark Adler * For conditions of distribution and use, see copyright notice in zlib.h */ #ifdef _LARGEFILE64_SOURCE # ifndef _LARGEFILE_SOURCE # define _LARGEFILE_SOURCE 1 # endif # undef _FILE_OFFSET_BITS # undef _TIME_BITS #endif #ifdef HAVE_HIDDEN # define ZLIB_INTERNAL __attribute__((visibility ("hidden"))) #else # define ZLIB_INTERNAL #endif #include <stdio.h> #include "zlib.h" #ifdef STDC # include <string.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <limits.h> #endif #ifndef _POSIX_SOURCE # define _POSIX_SOURCE #endif #include <fcntl.h> #ifdef _WIN32 # include <stddef.h> #endif #if defined(__TURBOC__) || defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(_WIN32) # include <io.h> #endif #if defined(_WIN32) # define WIDECHAR #endif #ifdef WINAPI_FAMILY # define open _open # define read _read # define write _write # define close _close #endif #ifdef NO_DEFLATE /* for compatibility with old definition */ # define NO_GZCOMPRESS #endif #if defined(STDC99) || (defined(__TURBOC__) && __TURBOC__ >= 0x550) # ifndef HAVE_VSNPRINTF # define HAVE_VSNPRINTF # endif #endif #if defined(__CYGWIN__) # ifndef HAVE_VSNPRINTF # define HAVE_VSNPRINTF # endif #endif #if defined(MSDOS) && defined(__BORLANDC__) && (BORLANDC > 0x410) # ifndef HAVE_VSNPRINTF # define HAVE_VSNPRINTF # endif #endif #ifndef HAVE_VSNPRINTF # ifdef MSDOS /* vsnprintf may exist on some MS-DOS compilers (DJGPP?), but for now we just assume it doesn't. */ # define NO_vsnprintf # endif # ifdef __TURBOC__ # define NO_vsnprintf # endif # ifdef WIN32 /* In Win32, vsnprintf is available as the "non-ANSI" _vsnprintf. */ # if !defined(vsnprintf) && !defined(NO_vsnprintf) # if !defined(_MSC_VER) || ( defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER < 1500 ) # define vsnprintf _vsnprintf # endif # endif # endif # ifdef __SASC # define NO_vsnprintf # endif # ifdef VMS # define NO_vsnprintf # endif # ifdef __OS400__ # define NO_vsnprintf # endif # ifdef __MVS__ # define NO_vsnprintf # endif #endif /* unlike snprintf (which is required in C99), _snprintf does not guarantee null termination of the result -- however this is only used in gzlib.c where the result is assured to fit in the space provided */ #if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER < 1900 # define snprintf _snprintf #endif #ifndef local # define local static #endif /* since "static" is used to mean two completely different things in C, we define "local" for the non-static meaning of "static", for readability (compile with -Dlocal if your debugger can't find static symbols) */ /* gz* functions always use library allocation functions */ #ifndef STDC extern voidp malloc(uInt size); extern void free(voidpf ptr); #endif /* get errno and strerror definition */ #if defined UNDER_CE # include <windows.h> # define zstrerror() gz_strwinerror((DWORD)GetLastError()) #else # ifndef NO_STRERROR # include <errno.h> # define zstrerror() strerror(errno) # else # define zstrerror() "stdio error (consult errno)" # endif #endif /* provide prototypes for these when building zlib without LFS */ #if !defined(_LARGEFILE64_SOURCE) || _LFS64_LARGEFILE-0 == 0 ZEXTERN gzFile ZEXPORT gzopen64(const char *, const char *); ZEXTERN z_off64_t ZEXPORT gzseek64(gzFile, z_off64_t, int); ZEXTERN z_off64_t ZEXPORT gztell64(gzFile); ZEXTERN z_off64_t ZEXPORT gzoffset64(gzFile); #endif /* default memLevel */ #if MAX_MEM_LEVEL >= 8 # define DEF_MEM_LEVEL 8 #else # define DEF_MEM_LEVEL MAX_MEM_LEVEL #endif /* default i/o buffer size -- double this for output when reading (this and twice this must be able to fit in an unsigned type) */ #define GZBUFSIZE 8192 /* gzip modes, also provide a little integrity check on the passed structure */ #define GZ_NONE 0 #define GZ_READ 7247 #define GZ_WRITE 31153 #define GZ_APPEND 1 /* mode set to GZ_WRITE after the file is opened */ /* values for gz_state how */ #define LOOK 0 /* look for a gzip header */ #define COPY 1 /* copy input directly */ #define GZIP 2 /* decompress a gzip stream */ /* internal gzip file state data structure */ typedef struct { /* exposed contents for gzgetc() macro */ struct gzFile_s x; /* "x" for exposed */ /* x.have: number of bytes available at x.next */ /* x.next: next output data to deliver or write */ /* x.pos: current position in uncompressed data */ /* used for both reading and writing */ int mode; /* see gzip modes above */ int fd; /* file descriptor */ char *path; /* path or fd for error messages */ unsigned size; /* buffer size, zero if not allocated yet */ unsigned want; /* requested buffer size, default is GZBUFSIZE */ unsigned char *in; /* input buffer (double-sized when writing) */ unsigned char *out; /* output buffer (double-sized when reading) */ int direct; /* 0 if processing gzip, 1 if transparent */ /* just for reading */ int how; /* 0: get header, 1: copy, 2: decompress */ z_off64_t start; /* where the gzip data started, for rewinding */ int eof; /* true if end of input file reached */ int past; /* true if read requested past end */ /* just for writing */ int level; /* compression level */ int strategy; /* compression strategy */ int reset; /* true if a reset is pending after a Z_FINISH */ /* seek request */ z_off64_t skip; /* amount to skip (already rewound if backwards) */ int seek; /* true if seek request pending */ /* error information */ int err; /* error code */ char *msg; /* error message */ /* zlib inflate or deflate stream */ z_stream strm; /* stream structure in-place (not a pointer) */ } gz_state; typedef gz_state FAR *gz_statep; /* shared functions */ void ZLIB_INTERNAL gz_error(gz_statep, int, const char *); #if defined UNDER_CE char ZLIB_INTERNAL *gz_strwinerror(DWORD error); #endif /* GT_OFF(x), where x is an unsigned value, is true if x > maximum z_off64_t value -- needed when comparing unsigned to z_off64_t, which is signed (possible z_off64_t types off_t, off64_t, and long are all signed) */ unsigned ZLIB_INTERNAL gz_intmax(void); #define GT_OFF(x) (sizeof(int) == sizeof(z_off64_t) && (x) > gz_intmax())
reframe.parms cover.parms reframe.c mapcover.c munchparms.c munchparms.h rescale.c memory.h quadinterp.h spng.c spng.h tinyreadjpg.c nanojpeg.c readjpg.h schrift.c schrift.h adler32.c compress.c crc32.c deflate.c infback.c inffast.c inflate.c inftrees.c trees.c uncompr.c zutil.c zutil.h zlib.h deflate.h inftrees.h inflate.h inffast.h gzguts.h inffixed.h trees.h